Reflections on resilience
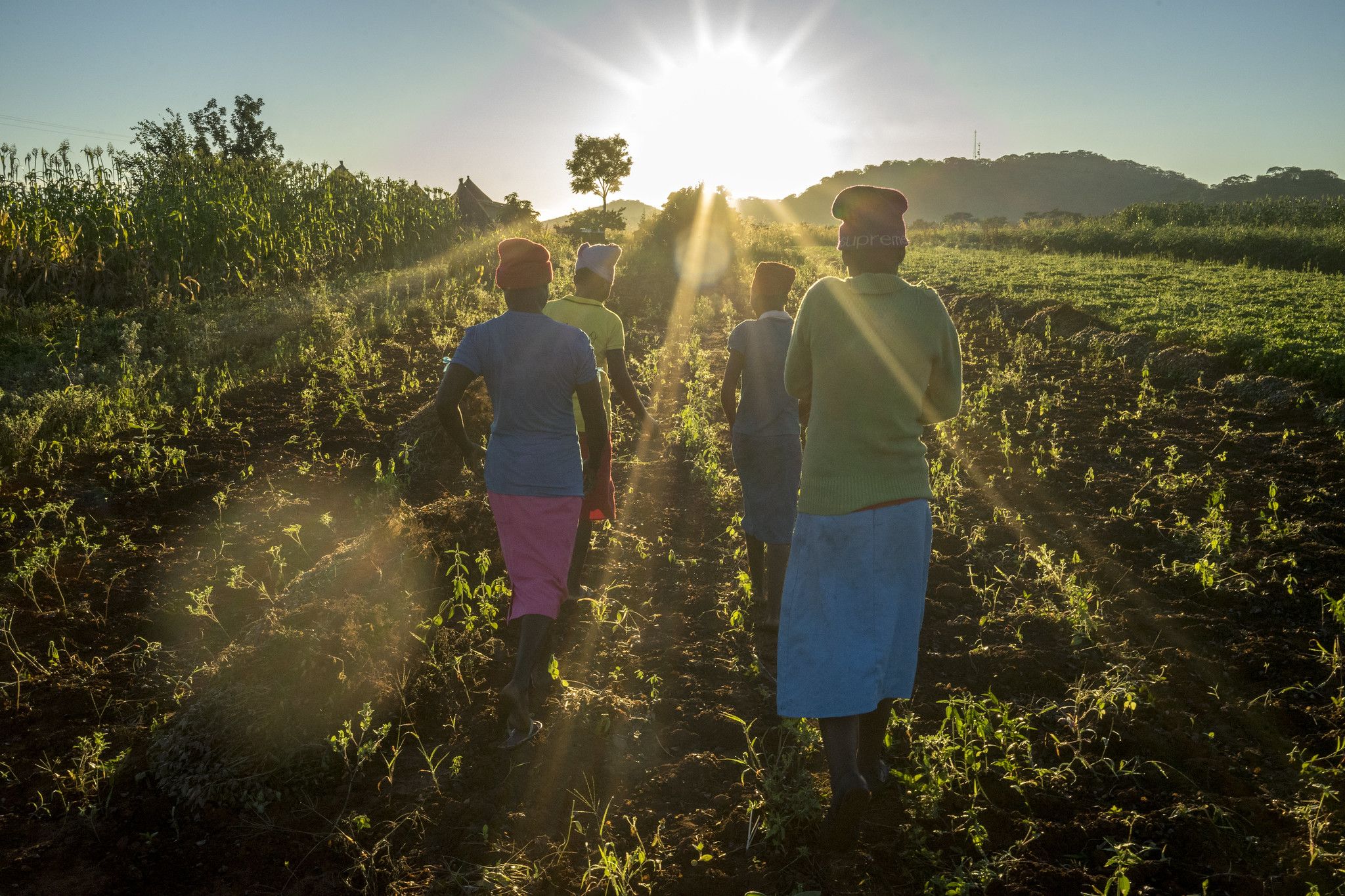
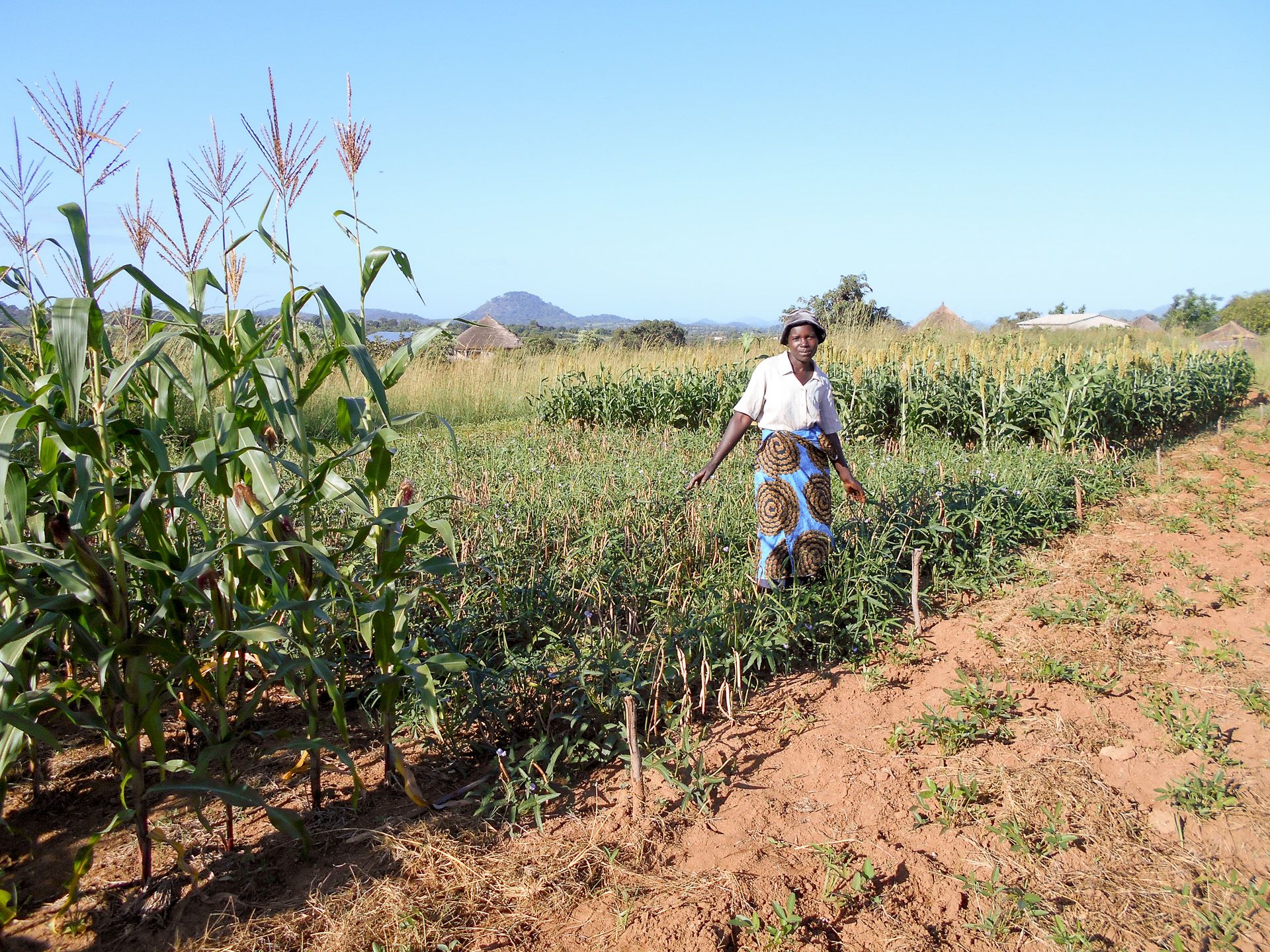
Approaching Ward 6 in Mwenezi, southern Zimbabwe, tracts of empty fields around homesteads on either side of the road signal the end of harvesting for the 2019/20 farming season. Farmers have stored away maize fodder on tree branches or inside the family compounds.
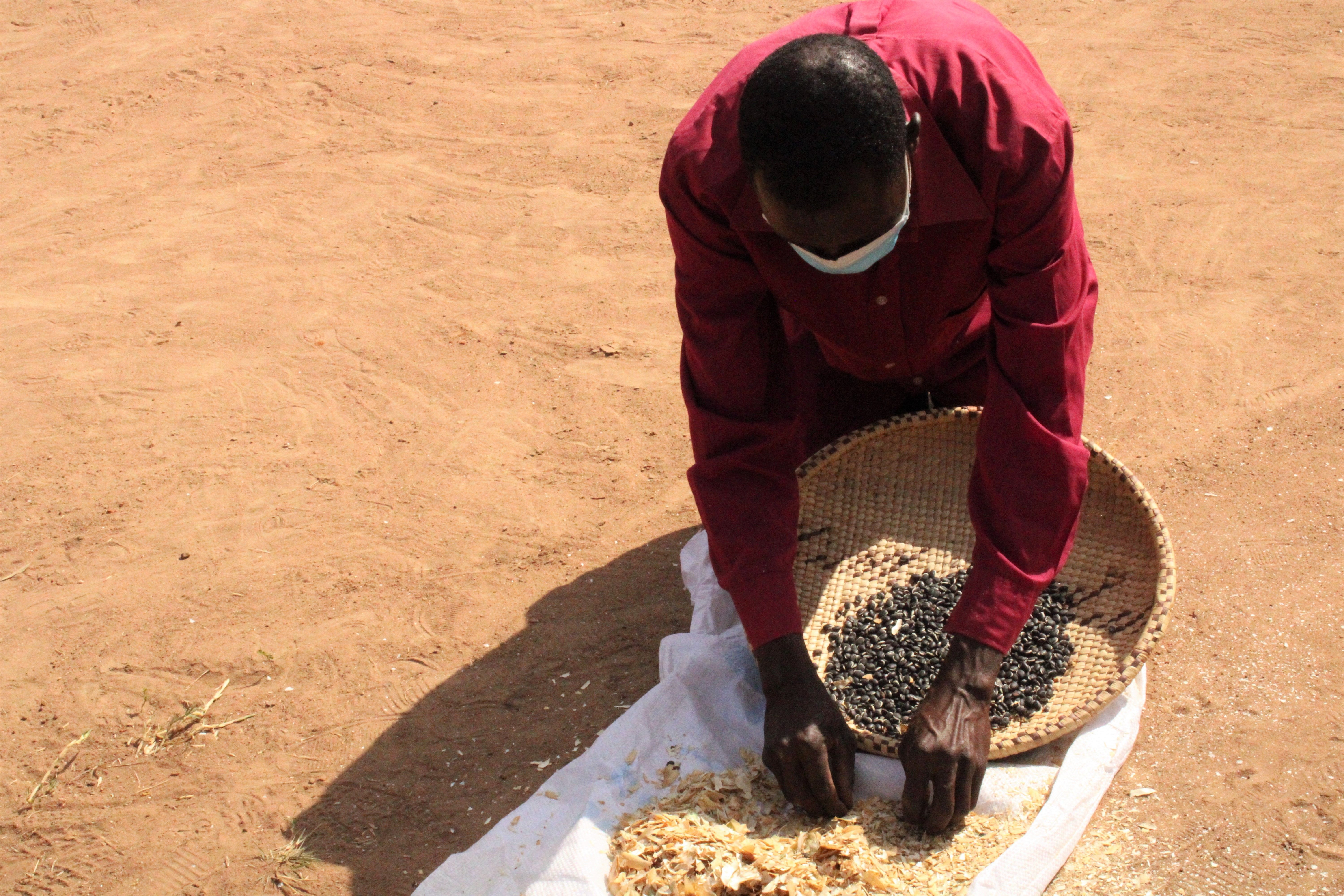
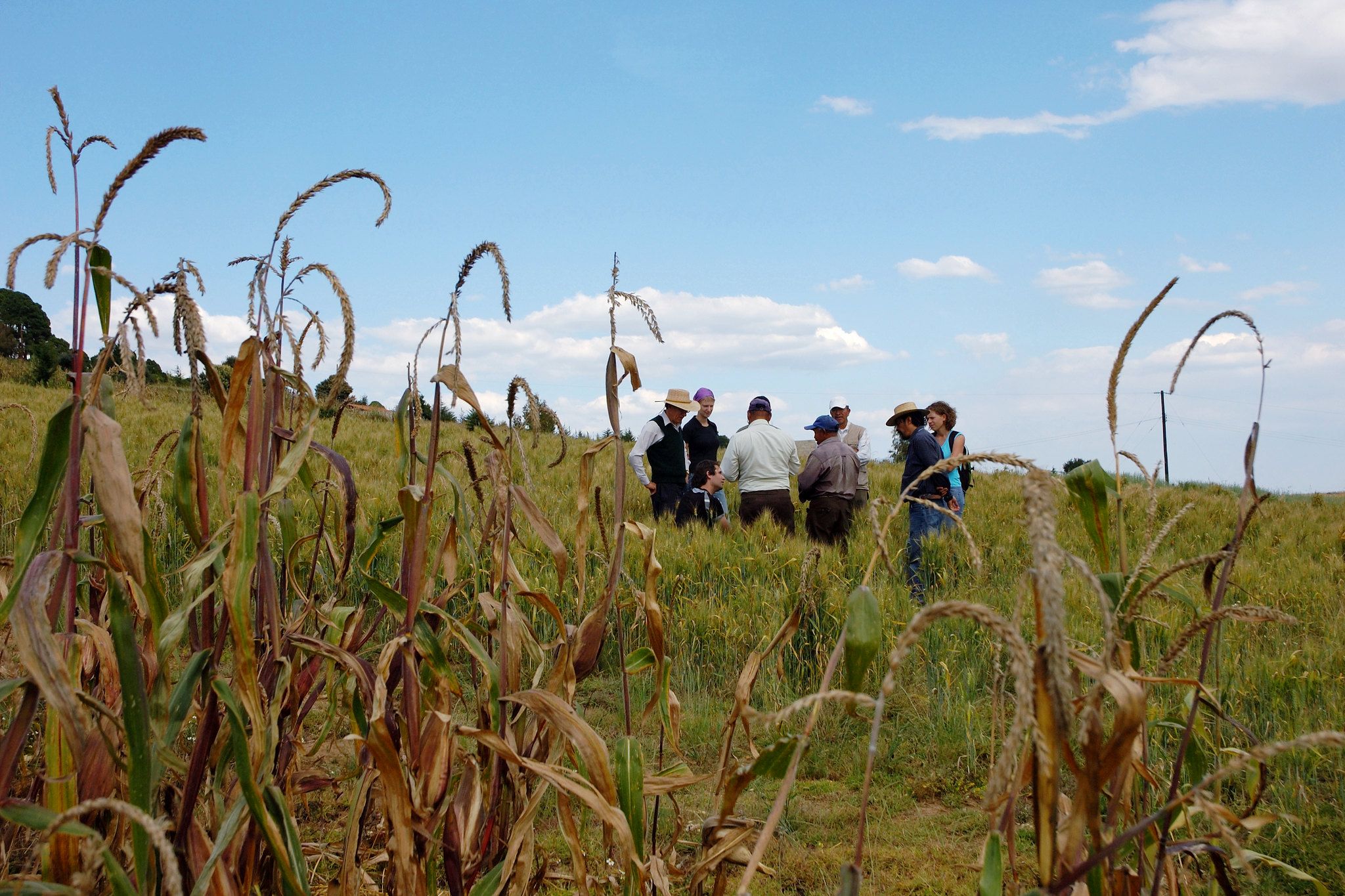
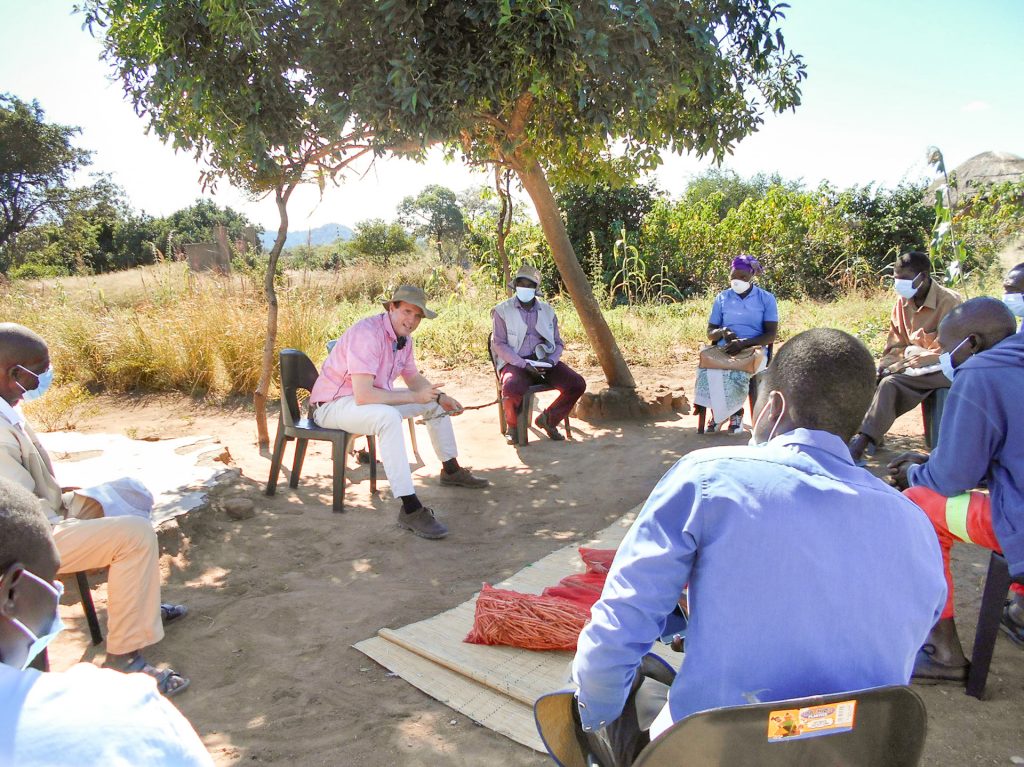
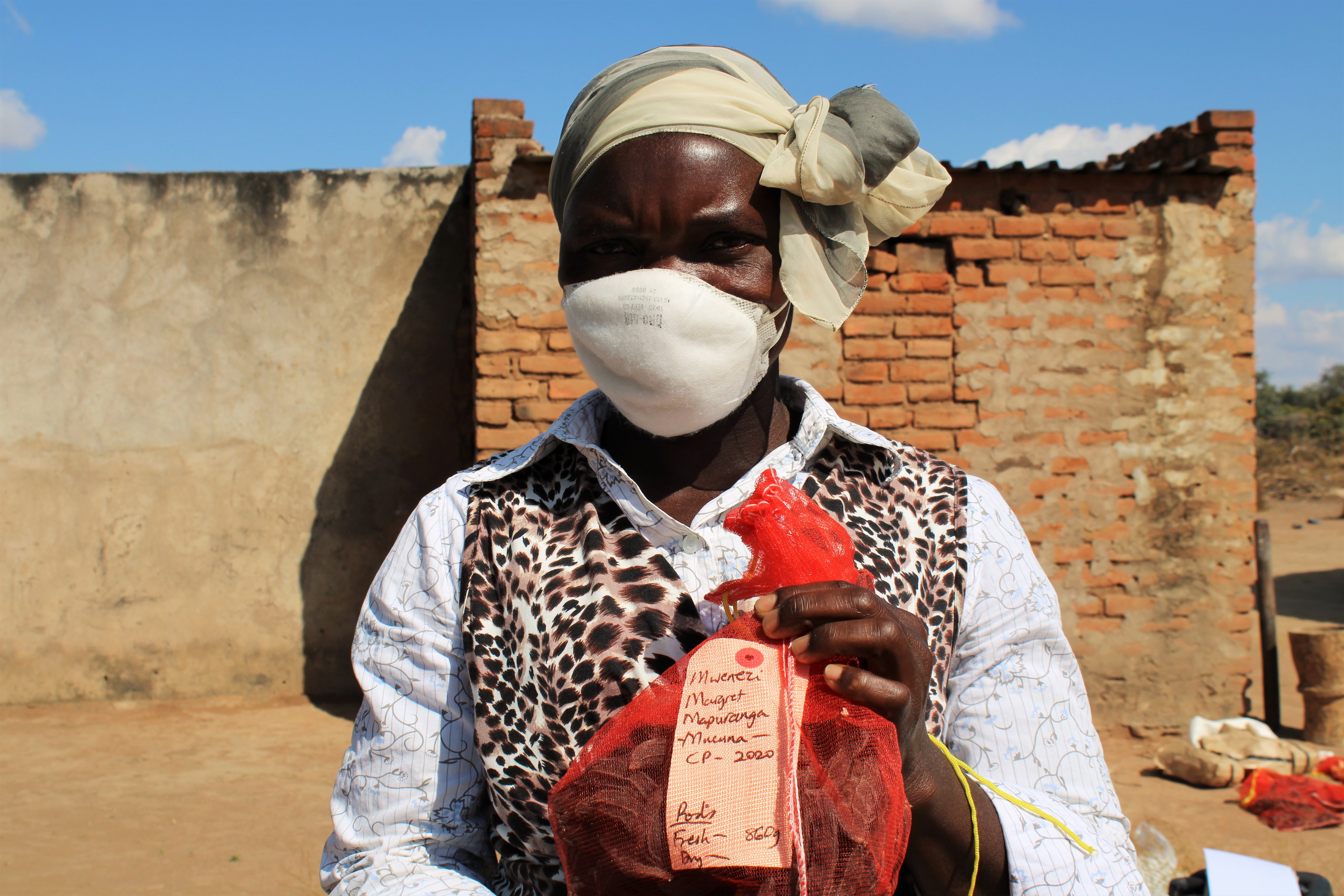
At one of the homesteads in the village of Chikwalakwala A, ten farmers are gathered while agricultural extension officers weigh grain and legume samples. They are participating in mother trials from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), using improved farming practices and drought-resilient seed varieties. This is one of the eight villages in Ward 6 where CIMMYT has established demonstration sites, as part of the Zambuko Livelihoods Initiative, supported by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
“Most of us here were born and raised in this ward, helping our parents with farming activities and continuing with farming when we finally had our own families,” farmer Tevera Romichi explains. However, the dry spells, high temperatures and erratic rainfall have become increasingly disturbing for him in recent years. “It became difficult to determine when we would receive enough rain to plant our crops without risking long dry spells,” he says.
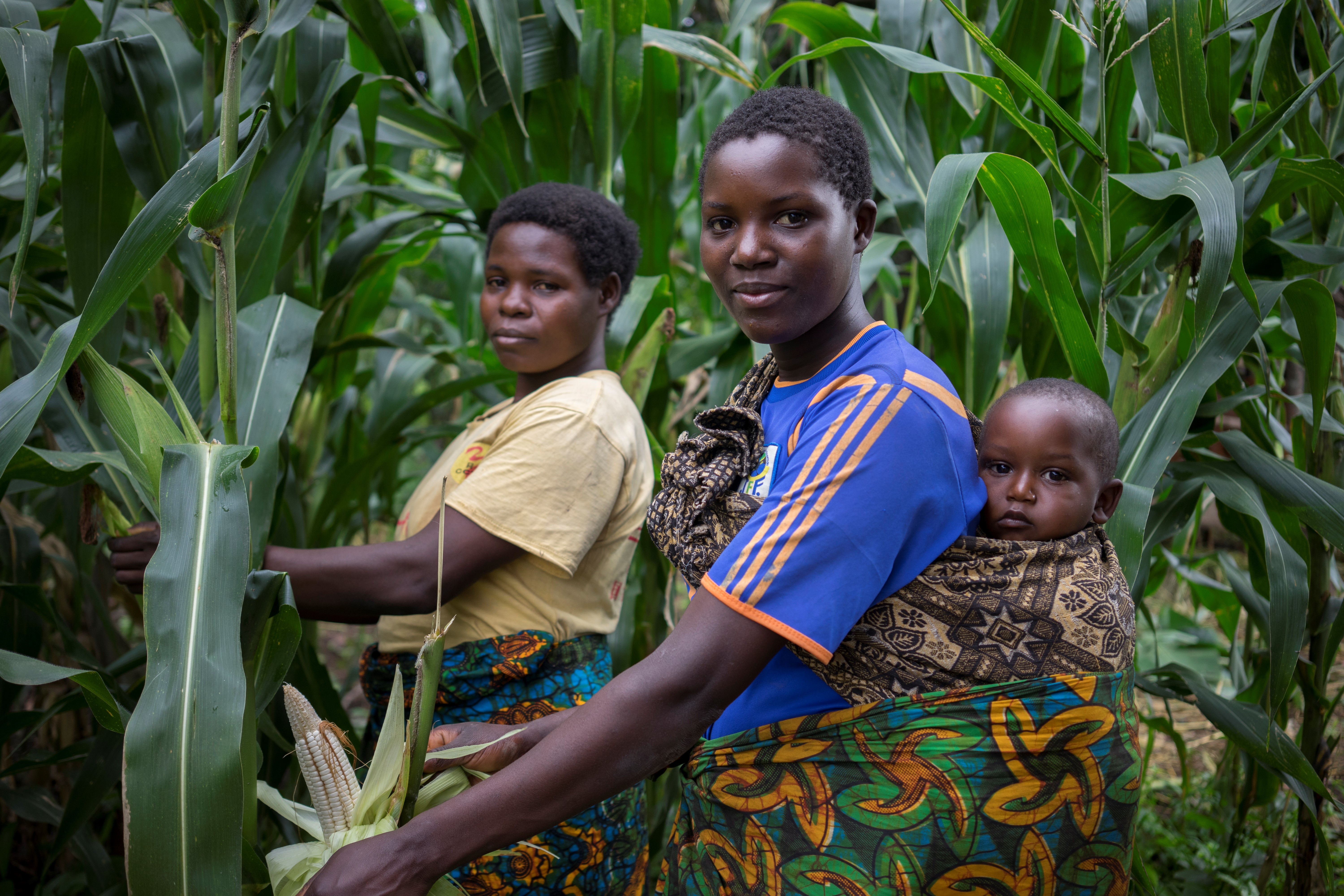
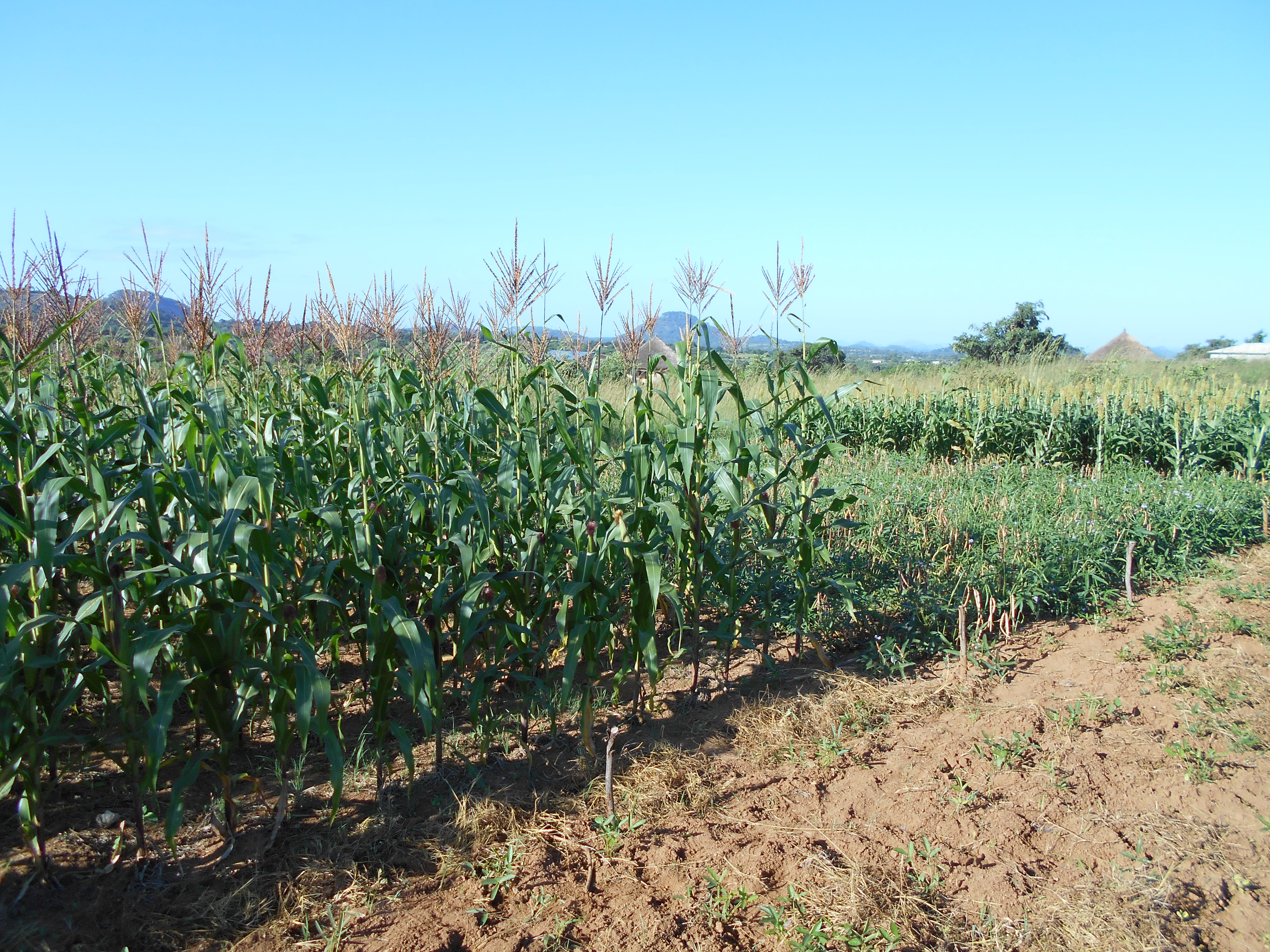
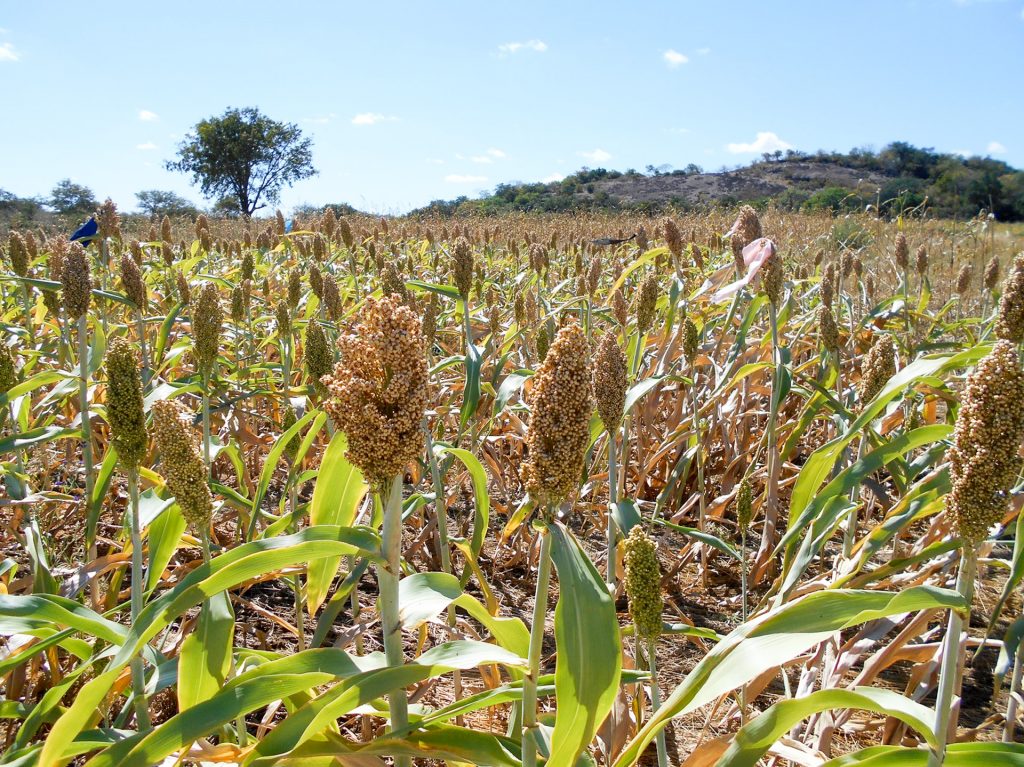
The onset of rains in Mwenezi has shifted over the years, from late September to the end of October or early November. With most families in the district depending on agriculture for their livelihoods, the adverse change in climatic conditions has compromised food security. These farmers grow crops such as millet, sorghum and groundnut.
Clemence Hlungwane, another farmer participating in mother trials, further explains how traditional practices of repeated tillage with ox-drawn ploughs weakened the soil structure, exposing it to soil erosion and loss of fertility. “These soils have been overused without any thought of how to replenish all the nutrients that were found in the soil in past years,” he says. The result for families like Hlungwane’s were poor germination, susceptibility to pests and diseases and poor yields.

Being smart in the field
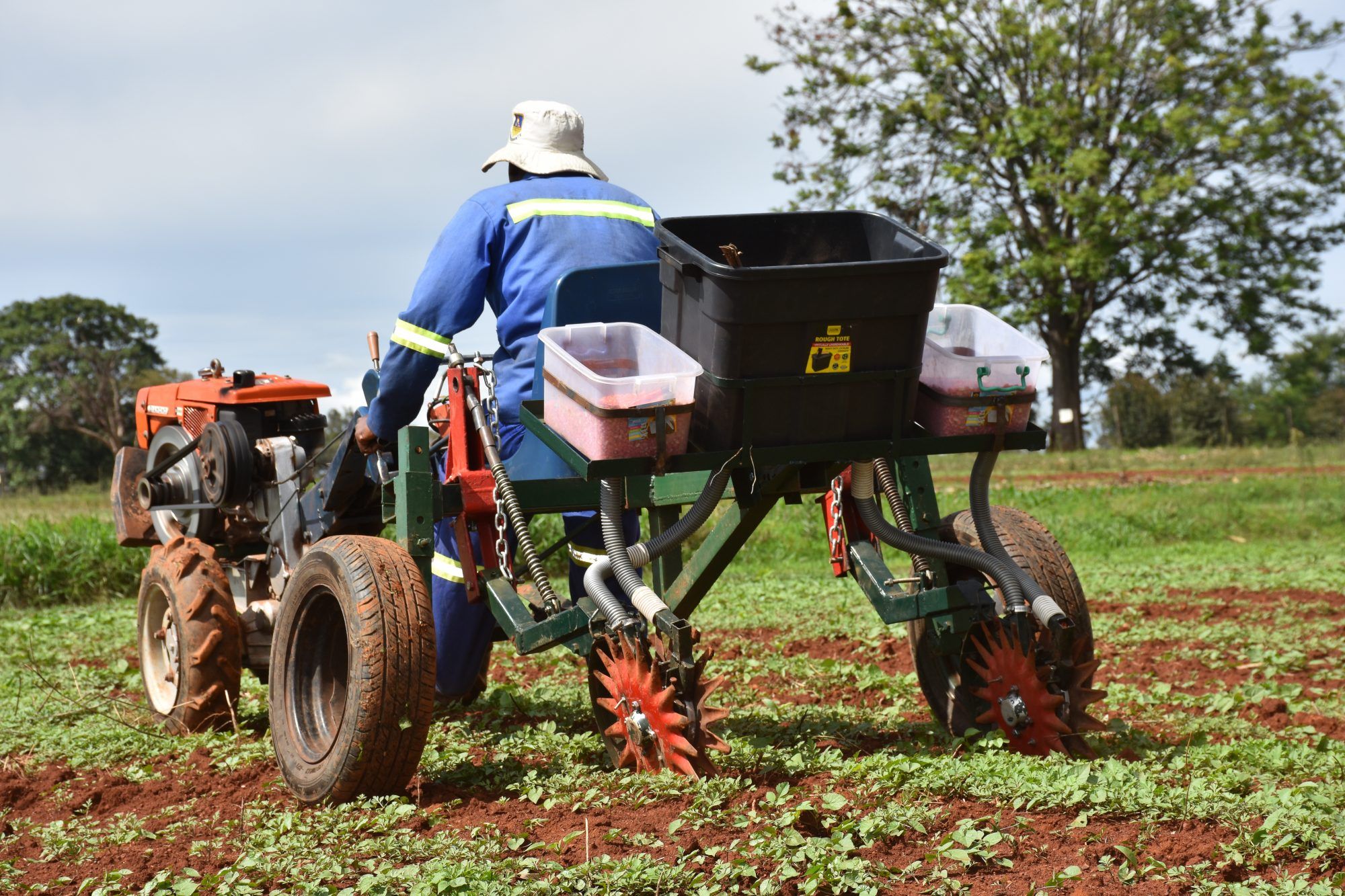
The introduction of climate-smart technologies by CIMMYT provided a channel through which mother-trial farmers in Ward 6 could explore alternative farming practices in a sustainable way while adapting to climate-induced risks. The principles of conservation agriculture, which encourage the preservation of soil moisture and nutrients, underpinned the technologies introduced by CIMMYT.
Initially, mother trial farmers expressed mixed feelings when the CIMMYT team and the Agricultural Extension and Technical Services (AGRITEX) officials took them through the process of establishing the demonstration plots. “It seemed like a lot of work,” Charleton Midzi recalls. “There was a lot of measuring, pegging and marking the demonstration plots but we soon realized that this would be important when planting the small grains and legumes.”
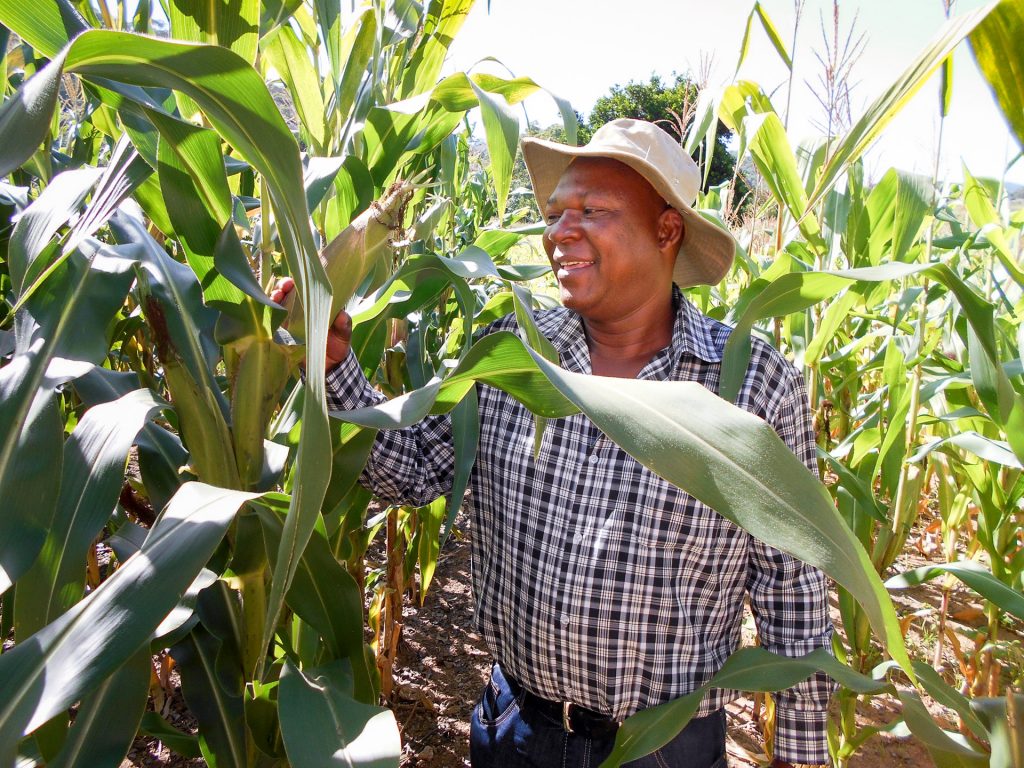
“At the same time, I was curious to see how ploughing with a ripper would help the soil and crops along with the practice of mulching,” Midzi says. “Where mulch was applied, the moisture was well preserved, and the crops looked much healthier and vibrant than in portions without mulch.” Another important lesson was understanding the importance of record keeping for planting dates, harvesting dates and rainfall records to inform the next season. In addition, good agronomy practices such as spacing, correct application of nutrients and use of pesticides contributed to the successful production at the demonstration plots.
“We no longer waste inputs,” says Caleb Matandare, a farmer in the village of Chikwalakwala C. “Being smart in the field means applying the correct amount of fertilizer using the measuring cups provided and keeping a record of the suitable amount for the crop.”
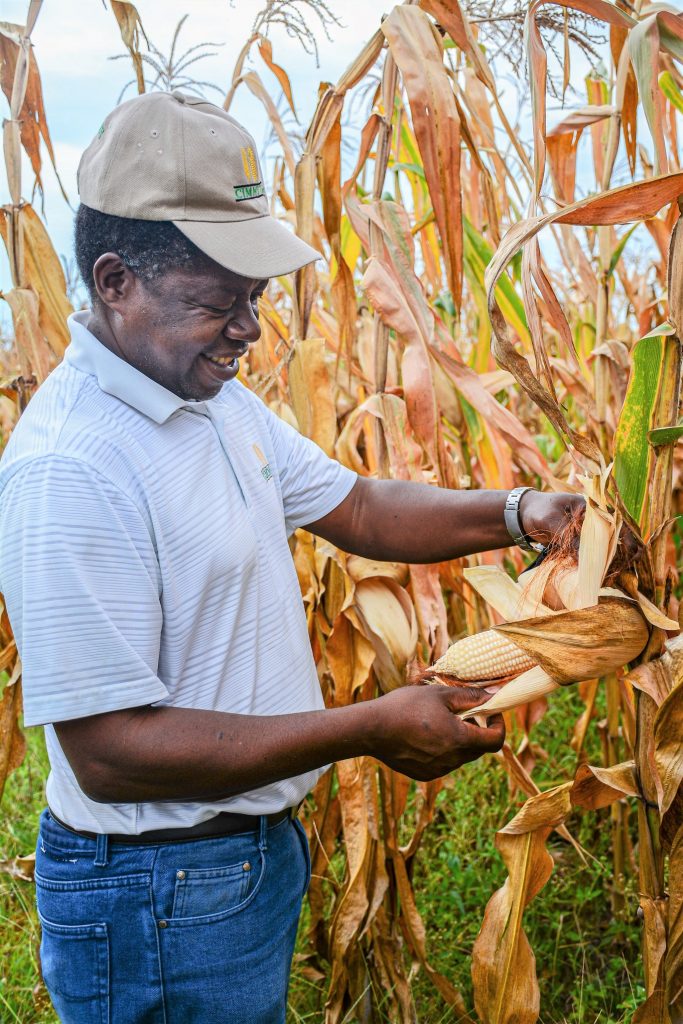
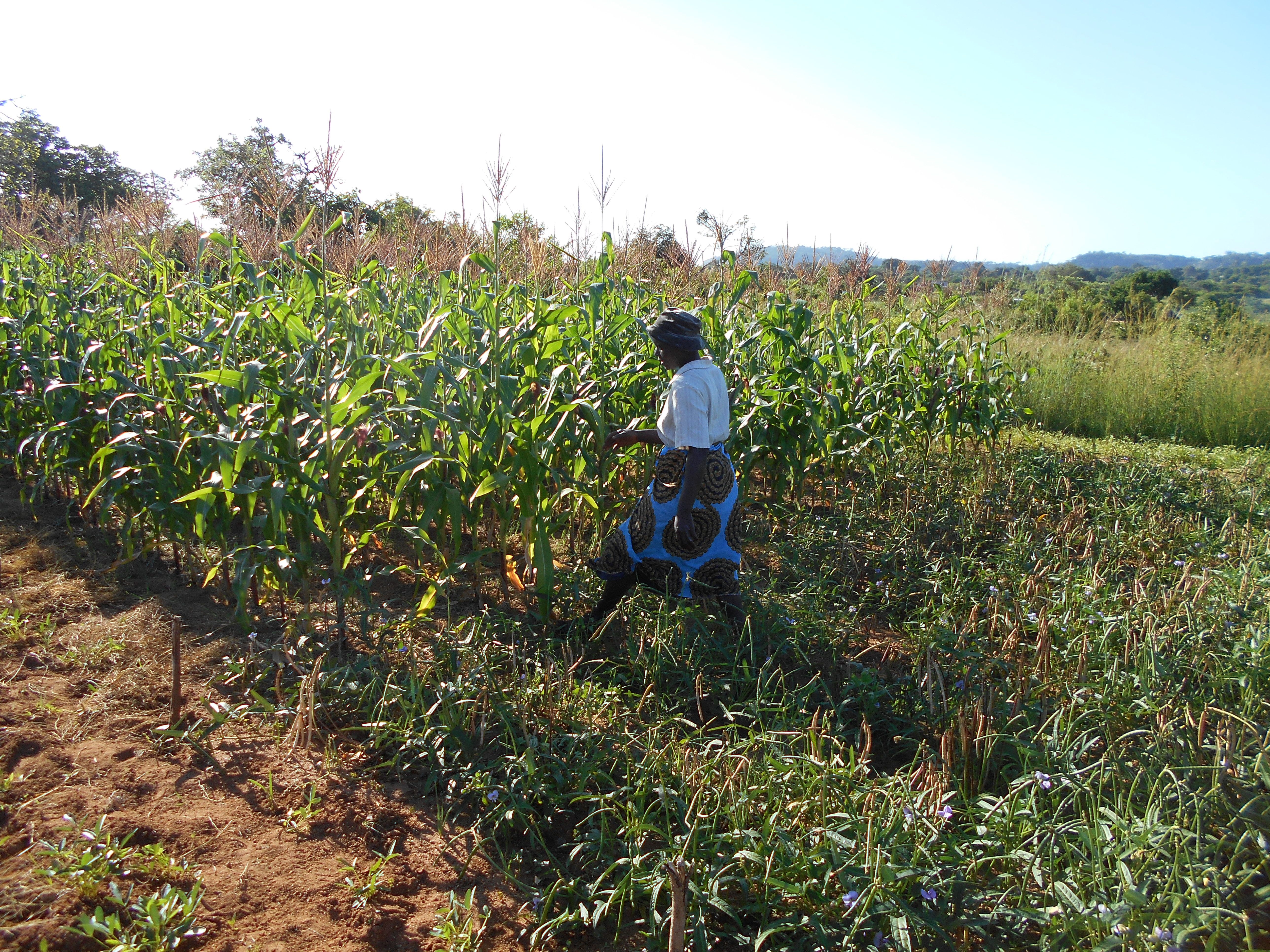
By the end of the season, the mother farmers observed the evident difference in the higher quality of the millet and sorghum planted on the conservation agriculture plots, compared to the conventional plots. From the yields of sorghum, millet and cowpeas, Matandare’s family of 13 are guaranteed enough diverse and nutritious food, particularly in the “lean season,” the period between harvests.

Baby-trial farmers eager to learn
Since the establishment of the mother trials in Ward 6, several farmers witnessing the advantages of producing under conservation agriculture and using drought-resilient varieties are keen to adopt the improved technologies.
Margaret Mapuranga shares how her neighbor inquired about the legume crops. “I explained to her how lablab, velvet bean and cowpeas fix nitrogen in the soil, which will be useful for the grain crops in the next season. She would like to try out the same in her own field in the coming season.” Mapuranga is confident that she can promote these sustainable practices with farmers selected for the baby trials in her village.
The coming 2020/21 season looks promising as more farmers in Ward 6 adopt the improved technologies. Mother-trial farmers are eager to expand conservation agriculture practices to other portions of their land as a safeguard against climate risks. For them, the ability to share the climate-smart technologies promoted by CIMMYT is an empowering process that will transform agriculture in the ward and beyond.