Scientists ship 2 tons of wheat seed samples around the world

EL BATAN, Mexico (CIMMYT) — Wheat farmers can boost yields and protect crops from pests and disease by using improved seed varieties, but in the developing world more than 80 percent of farmers use poor quality varieties, losing potential earnings and putting food security at risk, according to research.
Farmers often sell and trade wheat seed among themselves without having much knowledge about the size of the yield they can expect and how a particular variety fares with regard to climate, soil type or disease resistance.
Scientists at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) are continuously developing improved varieties and each year seed samples — known as International Wheat Nurseries — are sent out to government and university research institutions and national agricultural research systems around the world.
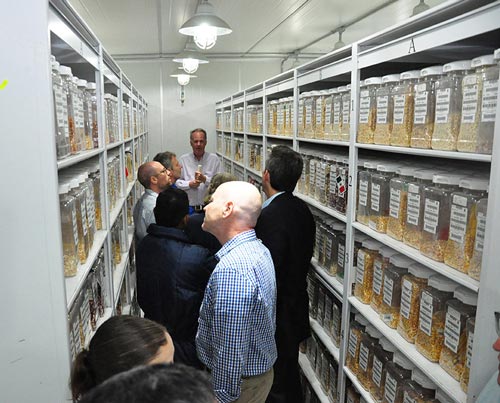
“Wheat plays a vital role in food security,” said Tom Payne, head of CIMMYT’s Wheat Germplasm Bank, which stores almost 145,000 wheat varieties collected over the past 60 years. “We’ve been sending out wheat samples each year since 1974, so if you do the math that’s 367 tons over the years.”
In October, 1,720 kilograms (3,790 pounds) of experimental seeds were shipped to India, one of 75 current recipient countries.
Overall, the 2014 international shipment of seeds delivered in 351,990 sample envelopes weighed 9,230 kilograms. Recent recipient countries included Algeria, Pakistan, Turkey, Ukraine and Sudan.
SORTING SEEDS
Over the past 24 years, Efren Rodriguez, head of CIMMYT’s Seed Distribution Unit has overseen the five-month process of preparing, packaging and shipping of wheat seed samples.
“This year the seed requests we received filled 94 boxes,” Rodriguez said. “Seeds are requested at the end of summer prior to planting season. Each box is filled with envelopes of wheat seed and weighs up to 10 kilograms (22 pounds).”
Seeds arrive at CIMMYT’s headquarters near Mexico City in June in bags weighing from 10 to 35 kilograms from CIMMYT’s research station in Mexicali in northeastern Mexico accompanied with paperwork naming the varieties for inclusion in the shipment.
The seed is sorted according to instructions from the wheat breeders, cleaned with chlorine, rinsed in an industrial restaurant-style dishwasher, doused in protective fungicide, dried, placed in small envelopes by machine, then boxed.
“Research institutions plant the seeds, which have different characteristics designed to solve particular problems – for example, they may be heat, drought- or disease-resistant – and then recommend varieties for general release and sale to farmers,” Rodriguez said, explaining that the seeds tested and selected by the international research programs are incorporated into national wheat breeding or growing programs.
CIMMYT also distributes wheat nurseries as part of a partnership with Turkey and the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
Globally, wheat provides 20 percent of the world’s daily protein and calories.