Q&A: A decade of improved and climate-smart maize through collaborative research and innovation
The food security and livelihoods of smallholder farming families in sub-Saharan Africa depend on maize production. The region accounts for up to two-thirds of global maize production, but is facing challenges related to extreme weather events, climate-induced stresses, pests and diseases, and deteriorating soil quality. These require swift interventions and innovations to safeguard maize yields and quality.
In this Q&A, we reflect on the results and impact of the long-term collaborative work on drought-tolerant maize innovations spearheaded by two CGIAR Research Centers: the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA). This innovative work has changed guises over the years, from the early work of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) and Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa Seed Scaling (DTMASS) projects through later iterations such as Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) and the newest project, Accelerating Genetic Gains in Maize and Wheat (AGG).
In this Q&A, three leaders of this collaborative research reflect on the challenges their work has faced, the innovations and impact it has generated for smallholder farmers, and possible directions for future research. They are: B.M Prasanna, director of CIMMYT’s Global Maize Program and of the CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE); Abebe Menkir, a maize breeder and maize improvement lead at IITA; and Cosmos Magorokosho, project lead for AGG-Maize at CIMMYT.
Briefly describe the challenges confronting small-scale farmers prior to the introduction of drought-tolerant maize and how CIMMYT and IITA responded to these challenges?
B.M.P.: Maize is grown on over 38 million hectares in sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for 40% of cereal production in the region and providing at least 30% of the population’s total calorie intake. The crop is predominantly grown under rainfed conditions by resource-constrained smallholder farmers who often face erratic rainfall, poor soil fertility, increasing incidence of climatic extremes — especially drought and heat — and the threat of devastating diseases and insect pests.
Around 40% of maize-growing areas in sub-Saharan Africa face occasional drought stress with a yield loss of 10–25%. An additional 25% of the maize crop suffers frequent drought, with yield losses of up to 50%. Climate change is further exacerbating the situation, with devastating effects on the food security and livelihoods of the millions of smallholder farmers and their families who depend on maize in sub-Saharan Africa. Therefore, the improved maize varieties with drought tolerance, disease resistance and other farmer-preferred traits developed and deployed by CIMMYT and IITA over the last ten years in partnership with an array of national partners and seed companies across sub-Saharan Africa are critical in effectively tackling this major challenge.
A.M.: Consumption of maize as food varies considerably across sub-Saharan Africa, exceeding 100 kg per capita per year in many countries in southern Africa. In years when rainfall is adequate, virtually all maize consumed for food is grown in sub-Saharan Africa, with a minimal dependence on imported grain. Maize production, however, is highly variable from year to year due to the occurrence of drought and the dependence of national maize yields on seasonal rainfall. One consequence has been widespread famine occurring every five to ten years in sub-Saharan Africa, accompanied by large volumes of imported maize grain as food aid or direct imports.
This places a significant strain on resources of the World Food Programme and on national foreign exchange. It also disincentivizes local food production and may not prevent or address cyclical famine. It also leaves countries ill-equipped to address famine conditions in the period between the onset of the crisis and the arrival of food aid. Investment in local production, which would strengthen the resilience and self-sufficiency in food production of smallholder farming families, is a far better option to mitigate food shortages than relying on food aid and grain imports.
C.M.: Smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa face innumerable natural and socioeconomic constraints. CIMMYT, in partnership with IITA and national agricultural research system partners, responded by developing and catalyzing the commercialization of new maize varieties that produce reasonable maize yields under unpredictable rainfall-dependent growing season.
Over the life of the partnership, more than 300 new climate-adaptive maize varieties were developed and released in more than 20 countries across sub-Saharan Africa where maize is a major staple food crop. Certified seed of over 100 stress-tolerant improved maize varieties have been produced by seed company partners, reaching more than 110,000 tons in 2019. The seeds of these drought-tolerant maize varieties have benefited more than 8 million households and were estimated to be grown on more than 5 million hectares in eastern, southern and west Africa in 2020.

In what ways did the drought-tolerant maize innovation transform small-scale farmers’ ability to respond to climate-induced risks? Are there any additional impacts on small scale farmers in addition to climate adaptation?
B.M.P.: The elite drought-tolerant maize varieties can not only provide increased yield in drought-stressed crop seasons, they also offer much needed yield stability. This means better performance than non-drought-tolerant varieties in both good years and bad years to a smallholder farmer.
Drought-tolerant maize varieties developed by CIMMYT and IITA demonstrate at least 25-30% grain yield advantage over non-drought-tolerant maize varieties in sub-Saharan Africa under drought stress at flowering. This translates into at least a 1 ton per hectare enhanced grain yield on average, as well as reduced downside risk in terms of lost income, food insecurity and other risks associated with crop yield variability. In addition to climate adaptation, smallholder farmers benefit from these varieties due to improved resistance to major diseases like maize lethal necrosis and parasitic weeds like Striga. We have also developed drought-tolerant maize varieties with enhanced protein quality — such as Quality Protein Maize or QPM — and provitamin A, which improve nutritional outcomes.
We must also note that drought risk in sub-Saharan Africa has multiple and far-reaching consequences. It reduces incentives for smallholder farmers to intensify maize-based systems and for commercial seed companies to invest and evolve due to a limited seed market.
Drought-tolerant maize is, therefore, a game changer as it reduces the downside risk for both farmers and seed companies and increases demand for improved maize seed, thus strengthening the commercial seed market in sub-Saharan Africa. Extensive public-private partnerships around drought-tolerant maize varieties supported the nascent seed sector in sub-Saharan Africa and has enabled maize-based seed companies to significantly grow over the last decade. Seed companies in turn are investing in marketing drought-tolerant maize varieties and taking the products to scale.
A.M.: The DTMA and STMA projects were jointly implemented by CIMMYT and IITA in partnership with diverse national and private sector partners in major maize producing countries in eastern, southern and western Africa to develop and deploy multiple stress-tolerant and productive maize varieties to help farmers adapt to recurrent droughts and other stresses including climate change.
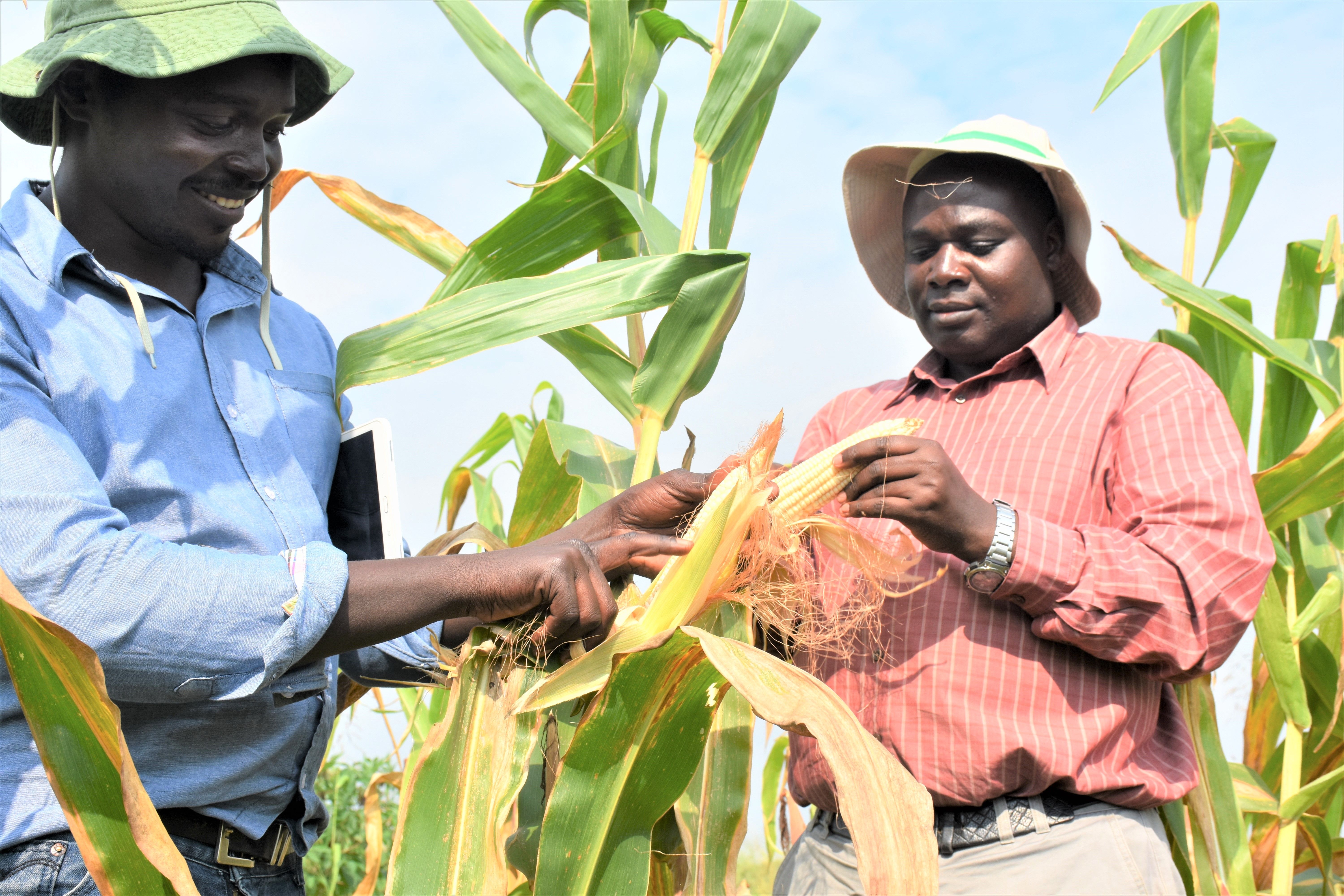
These projects catalyzed the release and commercialization of numerous stress-resilient new maize varieties in target countries across Africa. Increasing the resilience of farming systems means that smallholder farmers need guaranteed access to good quality stress resilient maize seeds. To this end, the two projects worked with public and private sector partners to produce large quantities of certified seeds with a continual supply of breeder seeds from CIMMYT and IITA. The availability of considerable amount of certified seeds of resilient maize varieties has enabled partners to reach farmers producing maize under stressful conditions, thus contributing to the mitigation of food shortages that affect poor people the most in both rural and urban areas.
C.M.: The drought-tolerant maize innovation stabilized maize production under drought stress conditions in sub-Saharan Africa countries. Recent study results showed that households that grew drought-tolerant maize varieties had at least half a ton more maize harvest than the households that did not grow the drought-tolerant maize varieties, thus curbing food insecurity while simultaneously increasing farmers’ economic benefits. Besides the benefit from drought-tolerant innovation, the new maize varieties developed through the partnership also stabilized farmers’ yields under major diseases, Striga infestation, and poor soil fertility prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa.
How is the project addressing emerging challenges in breeding for drought-tolerant maize and what opportunities are available to address these challenges in the future?

B.M.P.: A strong pipeline of elite, multiple-stress-tolerant maize varieties — combining other relevant adaptive and farmer-preferred traits — has been built in sub-Saharan Africa through a strong germplasm base, partnerships with national research partners and small- and medium-sized seed companies, an extensive phenotyping and multi-location testing network, and engagement with farming communities through regional on-farm trials for the identification of relevant farmer-preferred products.
CGIAR maize breeding in sub-Saharan Africa continues to evolve in order to more effectively and efficiently create value for the farmers we serve. We are now intensively working on several areas: (a) increasing genetic gains (both on-station and on-farm) through maize breeding in the stress-prone environments of sub-Saharan Africa by optimizing our breeding pipelines and effectively integrating novel tools, technologies and strategies (e.g., doubled haploids, genomics-assisted breeding, high-throughput and precise phenotyping, improved breeding data management system, etc.); (b) targeted replacement of old or obsolete maize varieties in sub-Saharan Africa with climate-adaptive and new varieties; (c) developing next-generation climate-adaptive maize varieties with traits such as native genetic resistance to fall armyworm, and introgressed nutritional quality traits (e.g., provitamin A, high Zinc) to make a positive impact on the nutritional well-being of consumers; and (d) further strengthening the breeding capacity of national partners and small and medium-sized seed companies in sub-Saharan Africa for a sustainable way forward.
A.M.: The DTMA and STMA projects established effective product pipelines integrating cutting-edge phenotyping and molecular tools to develop stress-resilient maize varieties that are also resistant or tolerant to MLN disease and fall armyworm. These new varieties are awaiting release and commercialization. Increased investment in strengthening public and private sector partnerships is needed to speed up the uptake and commercialization of new multiple stress-resilient maize varieties that can replace the old ones in farmers’ fields and help achieve higher yield gains.
Farmers’ access to new multiple-stress-tolerant maize varieties will have a significant impact on productivity at the farm level. This will largely be due to new varieties’ improved response to fertilizer and favorable growing environments as well as their resilience to stressful production conditions. Studies show that the adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties increased maize productivity, reduced exposure to farming risk among adopters and led to a decline in poverty among adopters. The availability of enough grain from highly productive and stress-resilient maize varieties can be the cheapest source of food and release land to expand the cultivation of other crops to facilitate increased access to diversified and healthy diets.
C.M.: The project is tackling emerging challenges posed by new diseases and pests by building upon the successful genetic base of drought-tolerant maize. This is being done by breeding new varieties that add tolerance to the emerging disease and pest challenges onto the existing drought-tolerant maize backgrounds. Successes have already been registered in breeding new varieties that have high levels of resistance to MLN disease and the fall armyworm pest.
Opportunities are also available to address new challenges including: pre-emptively breeding for threats to maize production challenges that exist in other regions of the world before these threats reach sub-Saharan Africa; enhancing the capacity of national partners to build strong breeding programs that can address new threats once they emerge in sub-Saharan Africa; and sharing knowledge and novel high-value breeding materials across different geographies to immediately address new threats once they emerge.
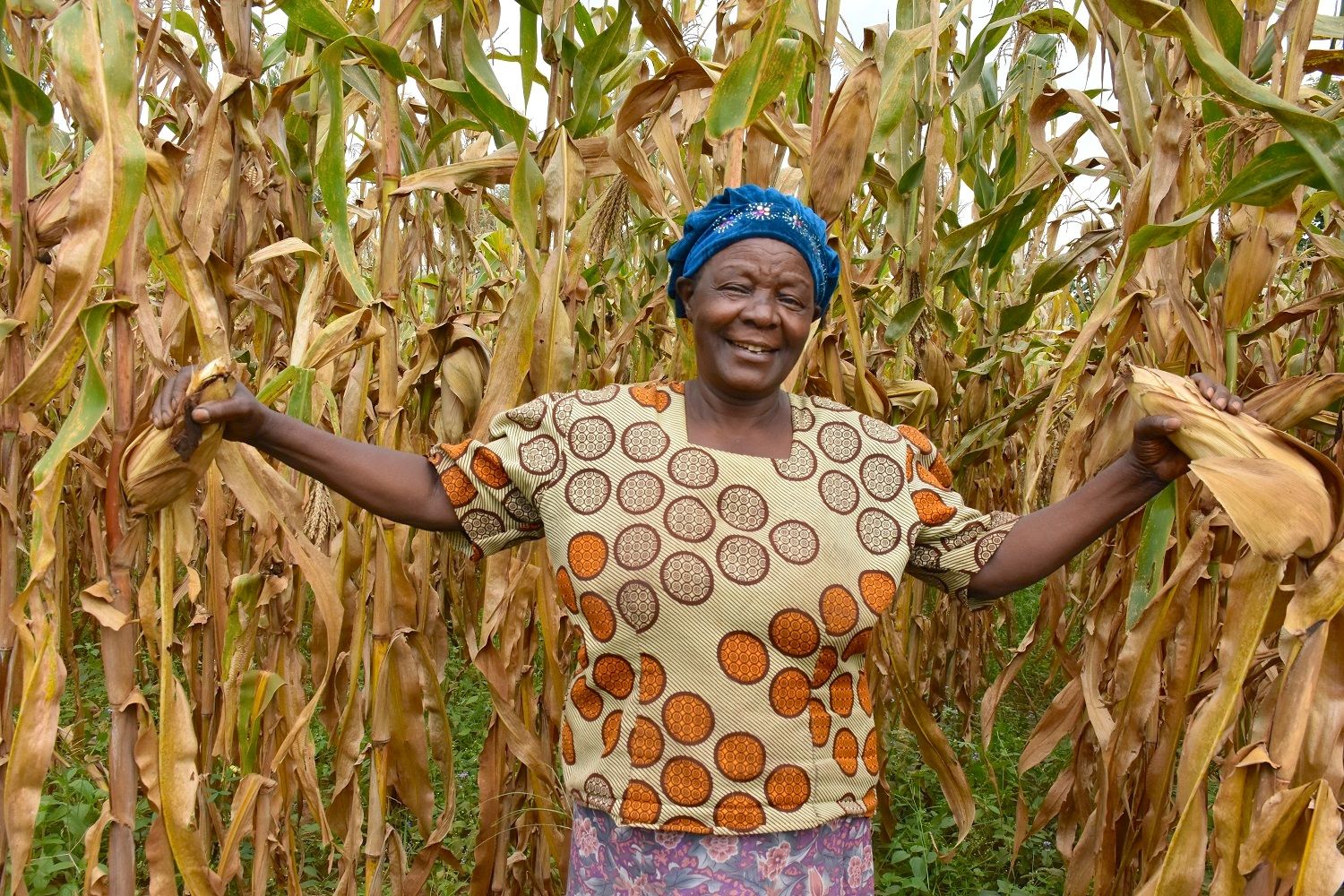
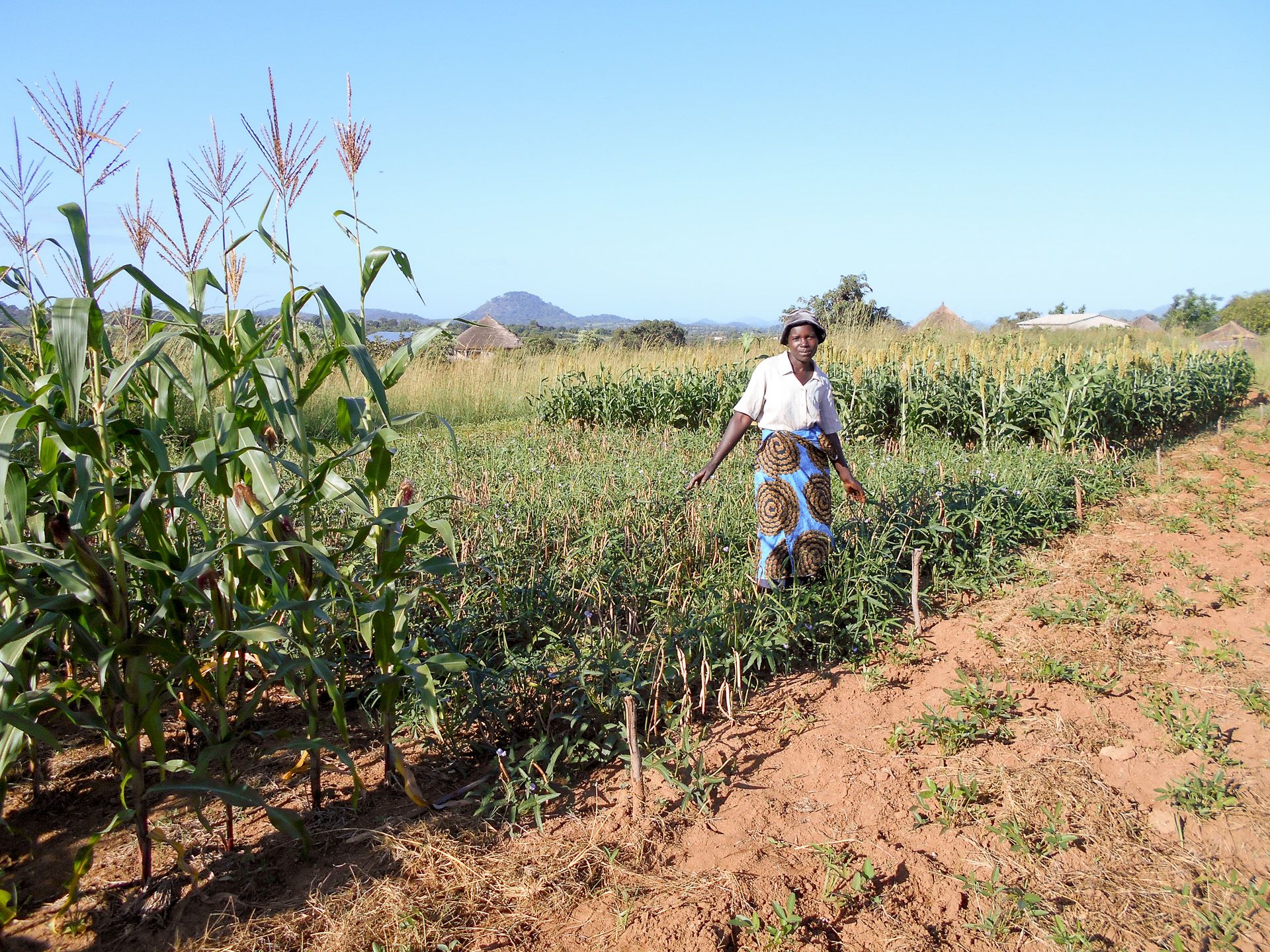
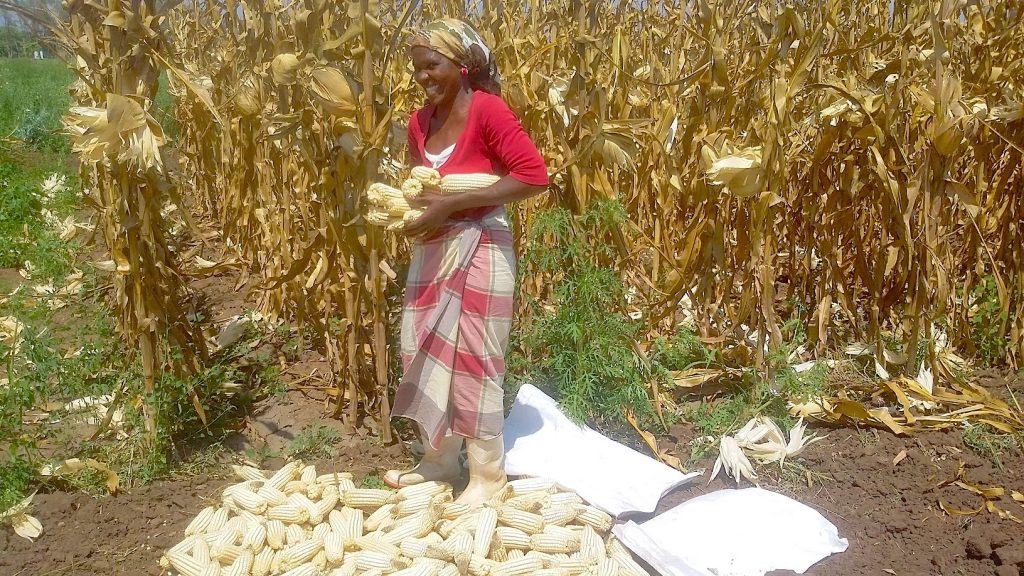
Cover photo: Alice Nasiyimu stands in front of a drought-tolerant maize plot at her family farm in Bungoma County, in western Kenya. (Photo: Joshua Masinde/CIMMYT)