Promising CIMMYT maize inbreds and pre-commercial hybrids identified against maize lethal necrosis (MLN)
 The maize lethal necrosis (MLN) disease first appeared in Kenya’s Rift Valley in 2011 and quickly spread to other parts of Kenya, as well as to Uganda and Tanzania. Caused by a synergistic interplay of maize chlorotic mottle virus (MCMV) and any of the cereal viruses in the family, Potyviridae, such as Sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV), Maize dwarf mosaic virus (MDMV), or Wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV), MLN can cause total crop loss if not controlled effectively.
The maize lethal necrosis (MLN) disease first appeared in Kenya’s Rift Valley in 2011 and quickly spread to other parts of Kenya, as well as to Uganda and Tanzania. Caused by a synergistic interplay of maize chlorotic mottle virus (MCMV) and any of the cereal viruses in the family, Potyviridae, such as Sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV), Maize dwarf mosaic virus (MDMV), or Wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV), MLN can cause total crop loss if not controlled effectively.
A regional workshop on MLN and the control strategies was organized by CIMMYT and KARI during February 12-14, 2013 in Nairobi, which was attended by some 70 scientists, seed company breeders and managers, and representatives of ministries of agriculture and regulatory authorities in Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, and the USA. The Workshop led to identification of important action points steps for effectively controlling the disease.
CIMMYT scientists have been working closely with virology experts from USDA-ARS and Kenya Agricultural Research Institute (KARI) to develop suitable protocols for testing the responses of maize germplasm against MLN, and to identify promising inbred lines and hybrids with resistance to MLN. During the 2012-2013 crop season, the CIMMYT-KARI team undertook extensive screening of inbred lines, pre-commercial and commercial hybrids in Naivasha and Narok in Kenya, under high natural disease pressure and artificial inoculation, respectively.
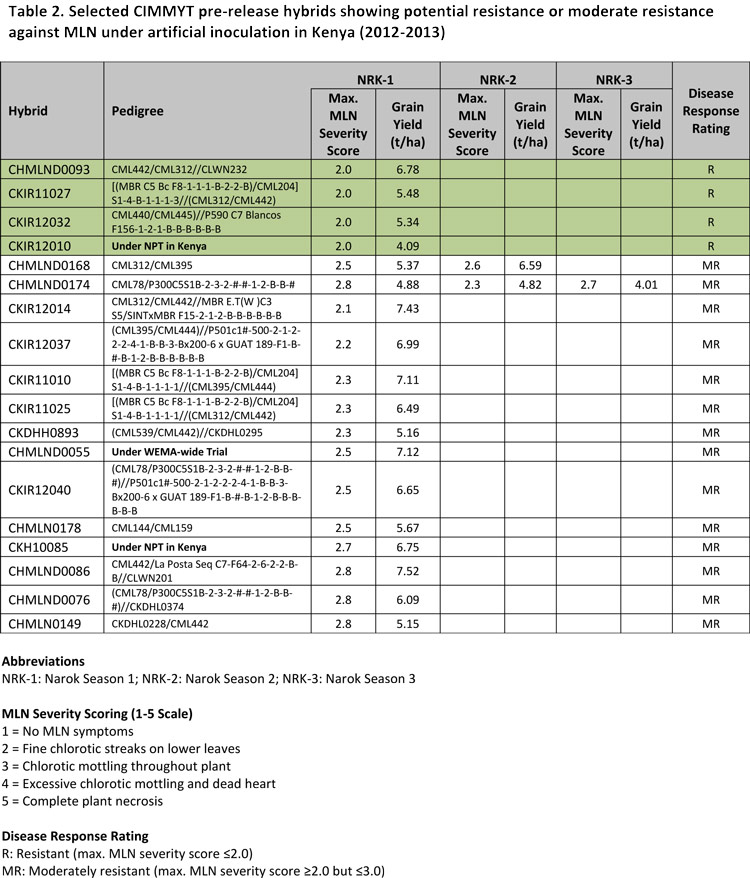
A trial featuring 119 commercial maize varieties (released in Kenya) under artificial inoculation during 2012-2013 revealed that as many as 117 varieties were susceptible to MLN. Another set of trials including 335 elite inbred lines, 366 pre-commercial hybrids and 7 commercial hybrids (as checks) under MLN artificial inoculation in Narok, and another set of trials comprising 350 elite inbred lines and 135 pre-commercial hybrids under natural disease pressure in Naivasha, led to identification of some promising CIMMYT inbred lines as well as pre-commercial hybrids showing resistance or moderate resistance. These results offer considerable hope to combat, through breeding efforts, the deadly MLN disease that has severely affected maize harvests and discouraged farmers from growing maize in eastern Africa.

Notes on trial results
The details of the promising CIMMYT elite inbred lines and pre-commercial hybrids against MLN are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. The results presented in Table 1 are based on evaluation of CIMMYT inbred lines in four independent trials, two under artificial inoculation (Narok) and two under natural disease pressure (Naivasha) during 2012-2013. In each trial, entries were replicated (minimum two), and MLN severity scores (on a 1-5 scale basis) were recorded three or more times during the crop cycle, from the vegetative to the reproductive stage. The highest average MLN severity score (max. MLN score), recorded at any stage during the trial, is presented as representative of a given entry.

The data must be critically assessed and cautiously used by stakeholders and partners. More weight should be given to data from artificially inoculated trials, since trials under natural disease pressure are more liable to ‘disease escapes’ and identification of false positives. Caution must be exercised when using specific lines identified as potentially resistant (R) or moderately resistant (MR), especially when classification is based on data from only one trial (even under artificial inoculation). Please note that in such cases, the responses of the lines need to be validated by CIMMYT through further trials.
CIMMYT is working closely with both public and private sector partners to significantly expand the MLN evaluation network capacity in eastern Africa, and will continue the intensive efforts to identify/develop and deliver new sources of resistance to MLN.
For further information on:
MLN research-for-development efforts undertaken by CIMMYT, please contact: Dr BM Prasanna, Director, Global Maize Program, CIMMYT, Nairobi, Kenya; Email: b.m.prasanna@cgiar.org.
Availability of seed material of the promising lines and pre-commercial hybrids, please contact: Dr Mosisa Regasa (m.regasa@cgiar.org) if your institution is based in eastern Africa, or Dr James Gethi (j.gethi@cgiar.org) if your institution is based in southern Africa or outside eastern and southern Africa.
Additional resources
UPDATE: Promising CIMMYT maize inbreds and pre-commercial hybrids identified against maize lethal necrosis (MLN) in eastern Africa
Maize lethal necrosis (MLN) disease in Kenya and Tanzania: Facts and actions (Download )
KARI-CIMMYT maize lethal necrosis (MLN) screeing facility (1.43 MB)
Maize lethal necrosis: Scientists and key stakeholders discuss strategies as the battle continues
Videos
 MLN: A farmer’s plea MLN: A farmer’s plea |
 Maize lethal necrosis disease: A new challenge Maize lethal necrosis disease: A new challengefor maize scientists in eastern Africa |
Media coverage
Deadly maize disease resurfaces in N. Rift. Business Daily, 31 May 2013.
Fresh viral maize disease worries farmers. Daily Nation, 31 May 2013.
Alert out in Coast over maize disease. Daily Nation, 31 May 2013.
 Download table in pdf format
Download table in pdf format Agricultural extension service staff members in Zambia have been challenged to be the first adopters of metal silos to help promote the technology for effective grain storage. “I implore you, extension workers, to be the first adopters and users of the metal silo technology. As citizens that live side by side with farmers, go and be the first to practice what you will be preaching. You must lead by example,” stated Bert Mushala, the Permanent Secretary, Provincial Administration, Office of the President, Eastern Province, in a speech read on his behalf by his assistant Beenzu Chichuka at the official opening of the Improved Postharvest Management Training Workshop for Extension and Media Personnel held during 27- 28 May 2013 in Chipata, Zambia. “Farmers learn by seeing. Therefore, before they start using the metal silos, they want to see the chief executives, the business executives, extension workers, journalists, and other opinion leaders in the forefront, zealously storing maize in the metal silos,” he added.
Agricultural extension service staff members in Zambia have been challenged to be the first adopters of metal silos to help promote the technology for effective grain storage. “I implore you, extension workers, to be the first adopters and users of the metal silo technology. As citizens that live side by side with farmers, go and be the first to practice what you will be preaching. You must lead by example,” stated Bert Mushala, the Permanent Secretary, Provincial Administration, Office of the President, Eastern Province, in a speech read on his behalf by his assistant Beenzu Chichuka at the official opening of the Improved Postharvest Management Training Workshop for Extension and Media Personnel held during 27- 28 May 2013 in Chipata, Zambia. “Farmers learn by seeing. Therefore, before they start using the metal silos, they want to see the chief executives, the business executives, extension workers, journalists, and other opinion leaders in the forefront, zealously storing maize in the metal silos,” he added.


 Breeding of durable resistance to stripe rust —the greatest biotic threat to wheat production in the largest wheat producer and consumer in the world, China— was the major theme of a workshop jointly organized by the CIMMYT-Sichuan office and the Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SAAS) at the SAAS Plant Breeding Institute in Chengdu, Sichuan province, China, on 18 May 2013. The workshop aimed to promote the adoption of second-generation parents and slow-rusting breeding strategies in spring wheat-producing areas of China and to facilitate collaborative breeding strategies between SAAS and its sister organizations in neighboring provinces. The workshop consisted of a seminar and a discussion session on germplasm and breeding strategies led by Gary Rosewarne (CIMMYT Global Wheat Program senior scientist) and Bob McIntosh (Emeritus Professor at the
Breeding of durable resistance to stripe rust —the greatest biotic threat to wheat production in the largest wheat producer and consumer in the world, China— was the major theme of a workshop jointly organized by the CIMMYT-Sichuan office and the Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SAAS) at the SAAS Plant Breeding Institute in Chengdu, Sichuan province, China, on 18 May 2013. The workshop aimed to promote the adoption of second-generation parents and slow-rusting breeding strategies in spring wheat-producing areas of China and to facilitate collaborative breeding strategies between SAAS and its sister organizations in neighboring provinces. The workshop consisted of a seminar and a discussion session on germplasm and breeding strategies led by Gary Rosewarne (CIMMYT Global Wheat Program senior scientist) and Bob McIntosh (Emeritus Professor at the 



 The Nutritious Maize for Ethiopia (NuME) aims to develop and promote quality protein maize (QPM) in the major maize growing areas of Ethiopia, including the highlands and the dry lands, to improve nutritional status of children. The project has a strong gender component, ensuring women’s full participation in all activities and equal share of benefits, which was discussed during a Gender Analysis and Strategy workshop at the
The Nutritious Maize for Ethiopia (NuME) aims to develop and promote quality protein maize (QPM) in the major maize growing areas of Ethiopia, including the highlands and the dry lands, to improve nutritional status of children. The project has a strong gender component, ensuring women’s full participation in all activities and equal share of benefits, which was discussed during a Gender Analysis and Strategy workshop at the  On 26-27 April 2013, the
On 26-27 April 2013, the  The project has generally been considered very successful. “We now know which mycotoxins are important in the region and we have the products to potentially minimize the risk,” commented Mahuku. “What we need is to widely test and disseminate the products so that they reach as many farmers as possible. With a little infusion of resources, the dedication demonstrated by this group, and support from policy makers, I have no doubt that we will get there.”
The project has generally been considered very successful. “We now know which mycotoxins are important in the region and we have the products to potentially minimize the risk,” commented Mahuku. “What we need is to widely test and disseminate the products so that they reach as many farmers as possible. With a little infusion of resources, the dedication demonstrated by this group, and support from policy makers, I have no doubt that we will get there.” “I am so excited to be here,” said Dr. Evangelina Villegas as she received her Outstanding Alumni Award from the Department of Grain Science and Industry at the Kansas State University (
“I am so excited to be here,” said Dr. Evangelina Villegas as she received her Outstanding Alumni Award from the Department of Grain Science and Industry at the Kansas State University ( The Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS)
The Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) The field day was followed by a feedback session and a technical seminar on the maize lethal necrosis (MLN) disease that has emerged recently in East Africa. During the seminar presented by Magorokosho and MacRobert, principal director of the Department of Agriculture Research Services Danisile Hikwa expressed her appreciation to CIMMYT for its efforts to develop MLN resistant varieties.
The field day was followed by a feedback session and a technical seminar on the maize lethal necrosis (MLN) disease that has emerged recently in East Africa. During the seminar presented by Magorokosho and MacRobert, principal director of the Department of Agriculture Research Services Danisile Hikwa expressed her appreciation to CIMMYT for its efforts to develop MLN resistant varieties. As traditional storage methods are proving less efficient, especially when faced with pests, a team of scientists from CIMMYT and the Kenya Agricultural Research Institute researched the effectiveness of hermetic systems in controlling maize storage pests in Kenya. To identify the most effective system, CIMMYT’s Hugo De Groote, Simon C. Kimenju, Fred Kanampiu, Tadele Tefera, and Jon Hellin, and KARI’s Paddy Likhayo, tested metal silos and super grain bags at three sites in Kenya and concluded that it is technically feasible to control storage insects without insecticides in Africa by using hermetic storage. However, several unanswered questions remain:
As traditional storage methods are proving less efficient, especially when faced with pests, a team of scientists from CIMMYT and the Kenya Agricultural Research Institute researched the effectiveness of hermetic systems in controlling maize storage pests in Kenya. To identify the most effective system, CIMMYT’s Hugo De Groote, Simon C. Kimenju, Fred Kanampiu, Tadele Tefera, and Jon Hellin, and KARI’s Paddy Likhayo, tested metal silos and super grain bags at three sites in Kenya and concluded that it is technically feasible to control storage insects without insecticides in Africa by using hermetic storage. However, several unanswered questions remain: On 12 April 2013, CIMMYT director general Thomas Lumpkin and José Ortega Cabello, chairman of the Campo de Tejada cooperative in Spain, signed a five-year extension of a collaborative agreement between Agrovegetal S.A. and CIMMYT dating back to 1998. The objective of the agreement is to develop improved durum wheat, bread wheat, and triticale varieties.
On 12 April 2013, CIMMYT director general Thomas Lumpkin and José Ortega Cabello, chairman of the Campo de Tejada cooperative in Spain, signed a five-year extension of a collaborative agreement between Agrovegetal S.A. and CIMMYT dating back to 1998. The objective of the agreement is to develop improved durum wheat, bread wheat, and triticale varieties. On daily basis, we interact with farmers, extension workers, researchers, seed companies, government officials, and many others. Our work would not be possible without these actors, many of whom focus on bringing new products, new processes, new policies, and new forms of organization into economic use. In their attempts to bring about change in agriculture, these multiple stakeholders are all part of what may be seen as agricultural innovation systems (AIS). However, CIMMYT’s engagement with AIS and its role within innovation platforms was not discussed more closely until recently. To review CIMMYT’s role and current approach to the AIS framework, summarize what has been done, and touch upon future plans,
On daily basis, we interact with farmers, extension workers, researchers, seed companies, government officials, and many others. Our work would not be possible without these actors, many of whom focus on bringing new products, new processes, new policies, and new forms of organization into economic use. In their attempts to bring about change in agriculture, these multiple stakeholders are all part of what may be seen as agricultural innovation systems (AIS). However, CIMMYT’s engagement with AIS and its role within innovation platforms was not discussed more closely until recently. To review CIMMYT’s role and current approach to the AIS framework, summarize what has been done, and touch upon future plans, 