“You go to the field.” U.S. Borlaug Fellows in Global Food Security
When asked how you become a successful wheat breeder, Dr. Norman E. Borlaug replied, “Well, you go to the field. You go to the field again, and then you go to the field. When the wheat plants start to talk to you, you know you have made it.” The Nobel Peace Prize, the Congressional Gold Medal, and the Presidential Medal of Freedom were awarded to Dr. Borlaug for saving the lives of over one billion through his efforts. Borlaug’s legacy continues today through the U.S. Borlaug Fellows in Global Food Security Program at the Center for Global Food Security, Purdue University, providing graduate students the opportunity to “go to the field” and become successful scientists in their own right.
Funded by USAID, the Borlaug Fellowship provides graduate students the opportunity to collaborate with agricultural scientists in developing nations. The program fosters connections between scientists internationally, while furthering research and developing community around important agricultural themes, such as production, natural resource conservation, and development. With a focus on interdisciplinary and cross-cultural experiences, students benefit from the ability to practice their science on the ground in an international setting, preparing them to become important members of the global scientific community. Doctoral candidates Ariel N. Rivers of Pennsylvania State University and Sean M. Thompson of Texas A&M University were given the opportunity to “go to the field” during the 2013 field season in partnership with CIMMYT.
Of the dual-title program, Entomology and International Agriculture and Development at Pennsylvania State University, Rivers (pictured above) is mid-way through her six-month tenure at CIMMYT’s El Batán station. By studying the three practices of conservation agriculture —crop rotation, minimal soil disturbance, and retention of crop residues on the soil surface— Rivers hopes to better understand which of these practices augment beneficial insect communities and how. In high enough numbers, beneficial insects can contribute to pest control, nutrient cycling, and soil aeration, all of which are essential to agricultural production in low-input developing country agriculture.
Thompson (pictured right), of the Department of Soil and Crop Sciences at Texas A&M University, is working with Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) to non-destructively assess wheat root biomass. This technology could allow for rapid, non-destructive assessment of populations and selection for traits undetectable by traditional methods. The primary objective of this research is to define the capability of GPR to phenotype below ground crop biomass, in the context of higher yield and quality stability in wheat during drought stress. GPR is one of the many field-based high-throughput phenotyping technologies being tested in CIMMYT’s Wheat Physiology program.
Both Rivers and Thompson plan to collaborate internationally after they complete their doctoral studies. “We have benefitted from the opportunity to practice that skill at CIMMYT,” they both agree. “Thanks to the example set by Borlaug, we are better prepared to take our science ‘to the field’.” Further information about the research or the U.S. Borlaug Fellowship in Global Food Security can be obtained by contacting the Purdue Center for Global Food Security.
 The third Dialogue on Ethiopian Agricultural Development: Agricultural Research for National Development in the Face of Climate Change and Food Security was held during 4-5 July 2013 at the Haramaya University of Agriculture, Haramaya Harar. The Dialogue aimed to provide a platform for discussion on agricultural research for development and transformation of the sector for food security in Ethiopia.
The third Dialogue on Ethiopian Agricultural Development: Agricultural Research for National Development in the Face of Climate Change and Food Security was held during 4-5 July 2013 at the Haramaya University of Agriculture, Haramaya Harar. The Dialogue aimed to provide a platform for discussion on agricultural research for development and transformation of the sector for food security in Ethiopia. “All the maize for my home consumption comes from my aflasafe™-treated field,” says farmer Alhaji Al-Hassan from Nigeria’s Kaduna State. “When I take my maize to the market, buyers rush for it because the quality looks better. The grains look clean.”
“All the maize for my home consumption comes from my aflasafe™-treated field,” says farmer Alhaji Al-Hassan from Nigeria’s Kaduna State. “When I take my maize to the market, buyers rush for it because the quality looks better. The grains look clean.” Kenya has experienced tremendous improvements in maize productivity, rising from 1,530,000 metric tons in 2002 to 3,420,000 in 2011. However, postharvest losses of up to 40% of the harvested grain pose great challenges to attaining food security, as about 80% of Kenyans live in rural areas and derive their livelihoods mostly from agricultural activities. With maize being the main staple crop and agriculture the cornerstone of Kenya’s economy accounting for 27% of GDP and producing over 75% of industrial raw materials, postharvest losses also pose a challenge to the economic development of the country. To address these issues, CIMMYT and the Kenya Agricultural Research Institute (
Kenya has experienced tremendous improvements in maize productivity, rising from 1,530,000 metric tons in 2002 to 3,420,000 in 2011. However, postharvest losses of up to 40% of the harvested grain pose great challenges to attaining food security, as about 80% of Kenyans live in rural areas and derive their livelihoods mostly from agricultural activities. With maize being the main staple crop and agriculture the cornerstone of Kenya’s economy accounting for 27% of GDP and producing over 75% of industrial raw materials, postharvest losses also pose a challenge to the economic development of the country. To address these issues, CIMMYT and the Kenya Agricultural Research Institute (
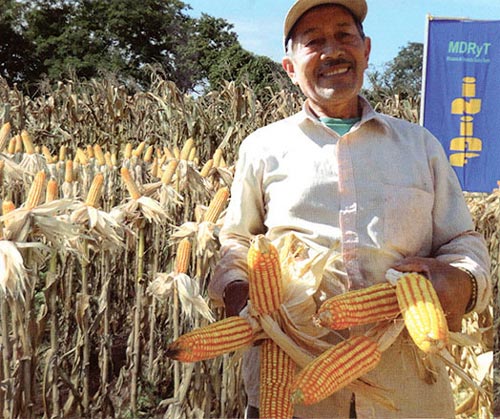 Bolivia’s National Institute for Agricultural, Livestock and Forestry Innovation (
Bolivia’s National Institute for Agricultural, Livestock and Forestry Innovation (

 The Nutrient Expert™ decision support tools for maize and wheat in India were officially launched for public use on 20 June 2013 at the National Agricultural Science Centre Complex in New Delhi during a meeting jointly organized by the International Plant Nutrition Institute (
The Nutrient Expert™ decision support tools for maize and wheat in India were officially launched for public use on 20 June 2013 at the National Agricultural Science Centre Complex in New Delhi during a meeting jointly organized by the International Plant Nutrition Institute (
 The Government of Nepal and the Nepal Agricultural Research Council (
The Government of Nepal and the Nepal Agricultural Research Council ( Since obtaining official accreditation in 2007, CIMMYT’s Seed Health Lab (SHL) must undergo a yearly audit to detect any deviation ISO/ IEC 17025 (General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories). To fulfill this requirement, on 17-18 June 2013, the Mexican Accreditation Entity reviewed the SHL’s quality system and seed testing protocols, and also inspected its new facilities in the Bioscience Building. It applied international standards on the general requirements for testing and calibration laboratories and found zero non-conformities at the SHL.
Since obtaining official accreditation in 2007, CIMMYT’s Seed Health Lab (SHL) must undergo a yearly audit to detect any deviation ISO/ IEC 17025 (General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories). To fulfill this requirement, on 17-18 June 2013, the Mexican Accreditation Entity reviewed the SHL’s quality system and seed testing protocols, and also inspected its new facilities in the Bioscience Building. It applied international standards on the general requirements for testing and calibration laboratories and found zero non-conformities at the SHL.
 Although many of us know that cereals such as maize contain starch, very few of us are aware of its usefulness and numerous applications. Luis Arturo Bello from the National Polytechnic Institute (
Although many of us know that cereals such as maize contain starch, very few of us are aware of its usefulness and numerous applications. Luis Arturo Bello from the National Polytechnic Institute (
 “Reducing post-harvest losses is key to increasing availability of food as it is not only important to increase domestic food production but also to protect what is produced by minimizing losses,” stated Zechariah Luhanga, Permanent Secretary, Provincial Administration at the Office of the President, Eastern Province, at the Provincial Stakeholders Workshop on Effective Grain Storage for Sustainable Livelihoods of African Farmers Project (EGSP-II) held in Chipata, Zambia, on 29 May 2013. “We as the key stakeholders and participants in the agricultural sector can enhance food security and improve incomes of resource poor farmers and artisans by promoting improved storage technologies such as metal silos and hermetic bags in Zambia.”
“Reducing post-harvest losses is key to increasing availability of food as it is not only important to increase domestic food production but also to protect what is produced by minimizing losses,” stated Zechariah Luhanga, Permanent Secretary, Provincial Administration at the Office of the President, Eastern Province, at the Provincial Stakeholders Workshop on Effective Grain Storage for Sustainable Livelihoods of African Farmers Project (EGSP-II) held in Chipata, Zambia, on 29 May 2013. “We as the key stakeholders and participants in the agricultural sector can enhance food security and improve incomes of resource poor farmers and artisans by promoting improved storage technologies such as metal silos and hermetic bags in Zambia.” After a year of exchanges, planning, and construction, CIMMYT and
After a year of exchanges, planning, and construction, CIMMYT and