This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that Sudanese families are beginning to starve — and while emergency food aid is needed, so is investment in longer-term food production.
This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that Sudanese families are beginning to starve — and while emergency food aid is needed, so is investment in longer-term food production.
Political, economic, and social upheaval in the country has displaced over 8 million people and left nearly 25 million people in need of urgent food assistance, including more than 14 million children. The anniversary saw major donors mark the day with more than $2 billion in new aid pledges.
While these pledges are important, the international community also needs to rethink some of its aid strategies. Emergency food assistance for those at immediate risk of starvation is understandably a high priority now, but restoring food production within the country is just as important — otherwise donors risk racing from crisis to crisis and always falling short. It is time to break away from an aid-dependency model and invest directly in farmers.
In fact, challenges to Sudan’s agriculture were likely a contributing factor to the current conflict. The livelihoods of most people in Sudan depend on the agri-food sector, which has been under pressure in recent years. Economic stagnation, weather shocks, land conflicts, high inflation, and health crises made 9.8 million Sudanese severely food-insecure by 2021.
Sudan’s already low-yielding cropping system has been hit by global tightening in fertilizer supplies. The livestock sector represents 60% of Sudan’s agricultural GDP, and has been suffering from diminished rangelands, water shortages, flood events, and lack of animal health services.
Sudan is not alone, and it’s important that the donor community understand how. Eight out of 10 of the world’s worst food crises are driven by war, persecution, and conflict, in places such as Sudan, Yemen, the Palestinian territories, Myanmar, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. The confluence of conflict, state fragility, climate change, and poverty is already overwhelming the international community’s ability to respond to escalating humanitarian needs. The international community has to put more emphasis on anticipatory action, because reaction is just not going to be enough anymore.
The need to get ahead of the growing scale of humanitarian disasters has provoked new thinking and partnerships among research, development, and humanitarian organizations, such as ours.
We are investing in better risk assessment, preparation for future food crises, and accelerated learning about how climate change is affecting agricultural productivity and production. The significant resources and expertise of the international research-for-development community can make humanitarian responses in fragile and conflict-affected states more effective and optimal.
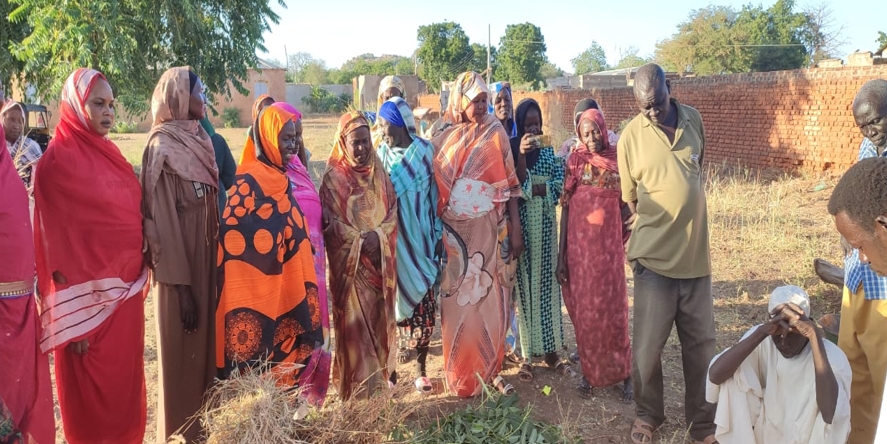
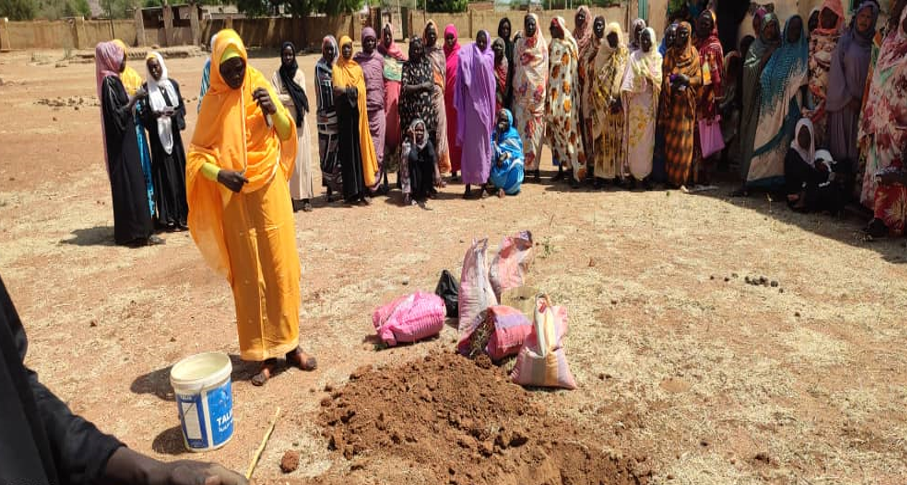
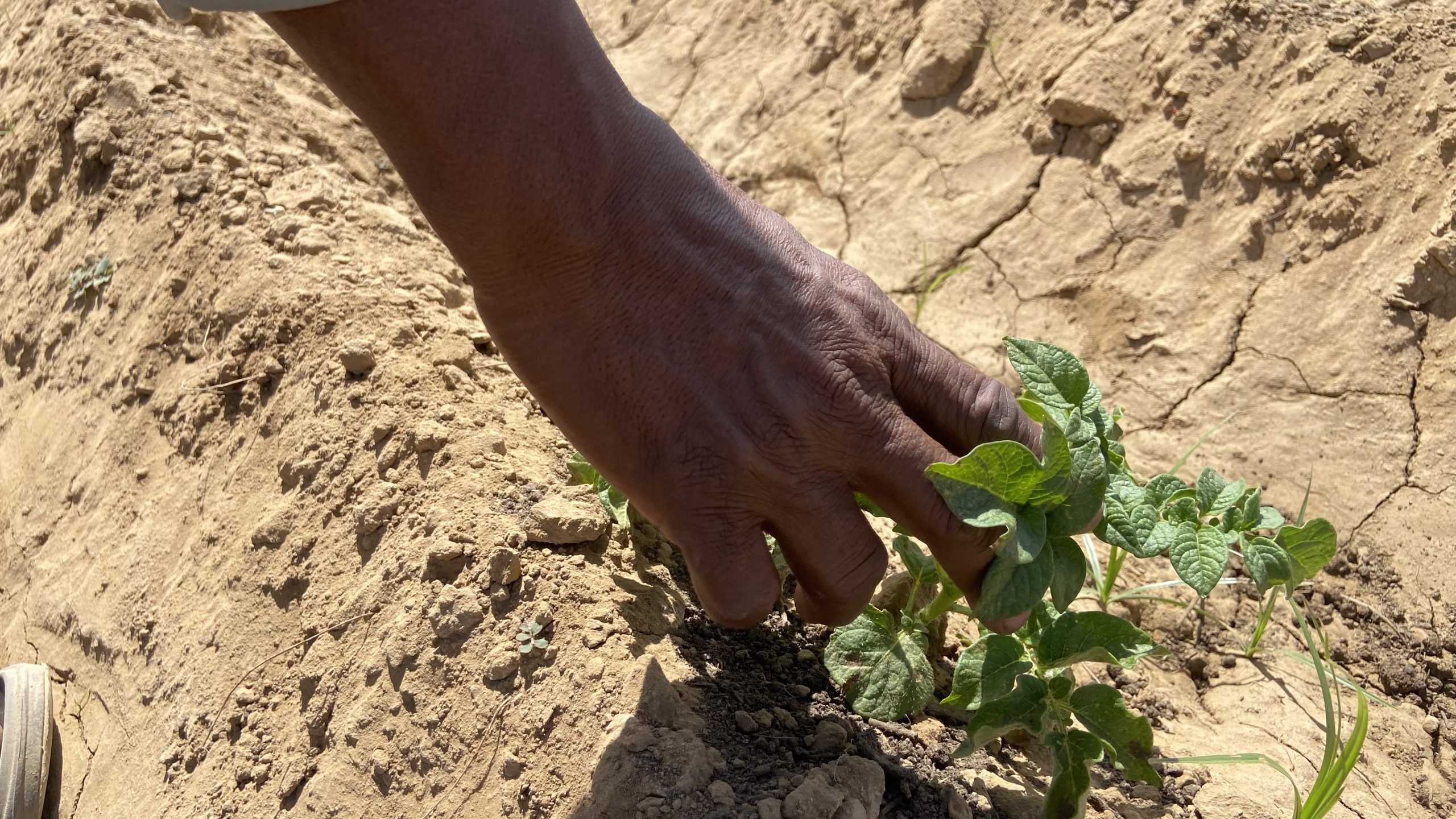
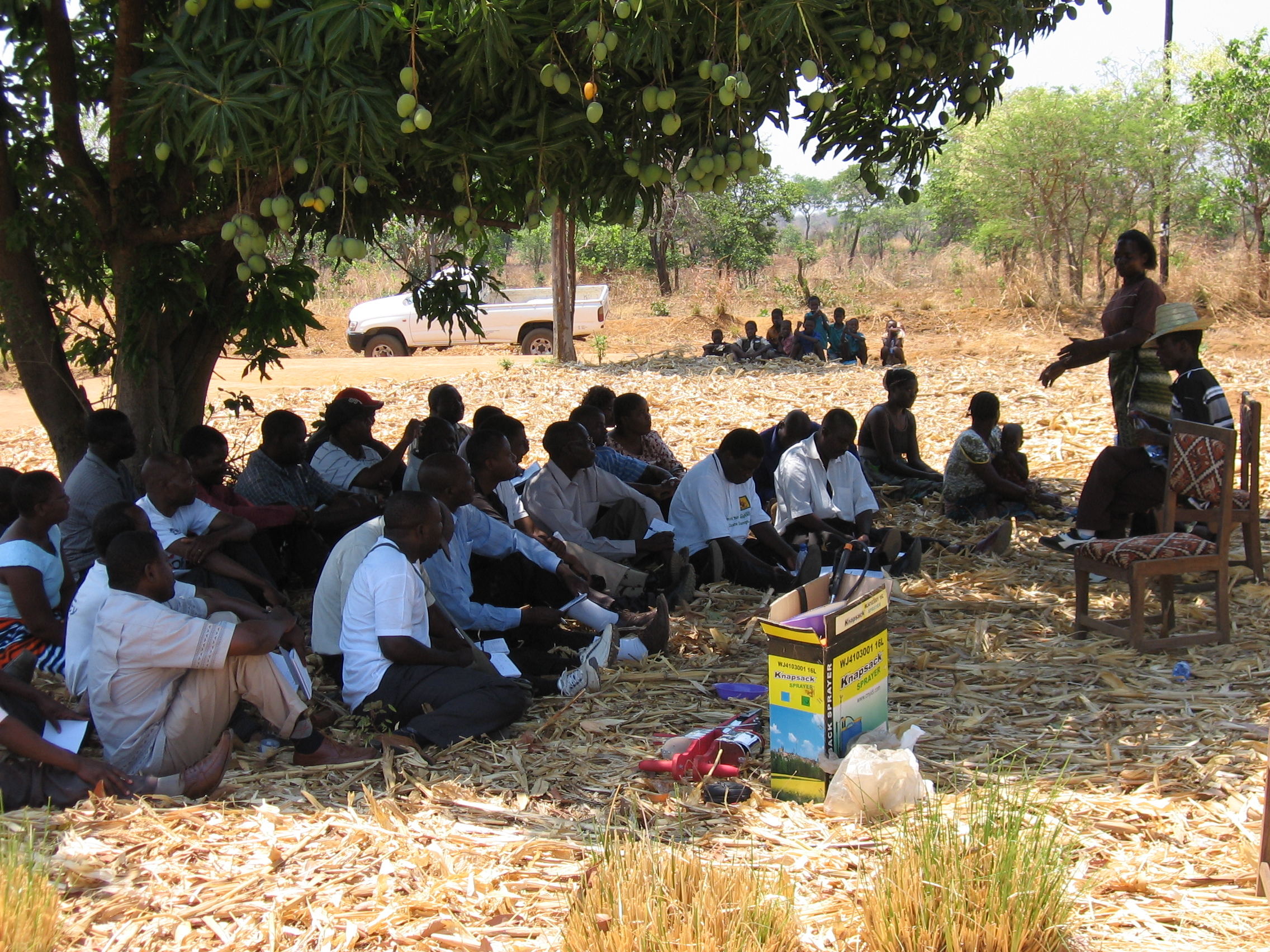
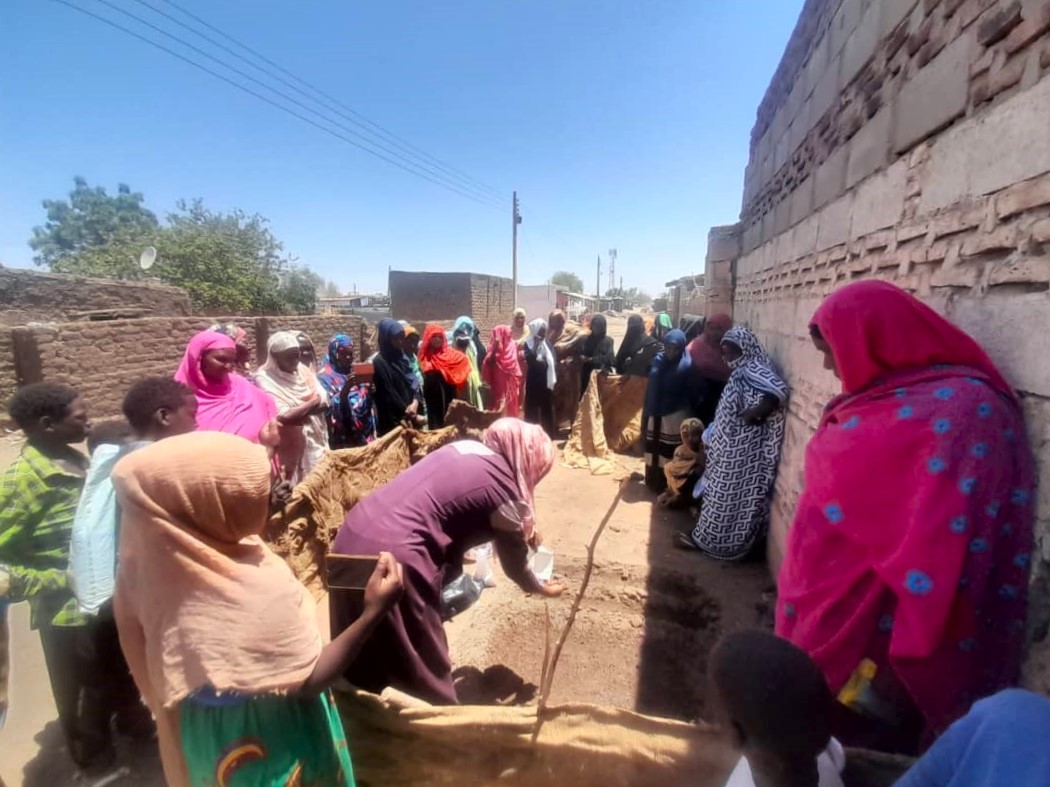
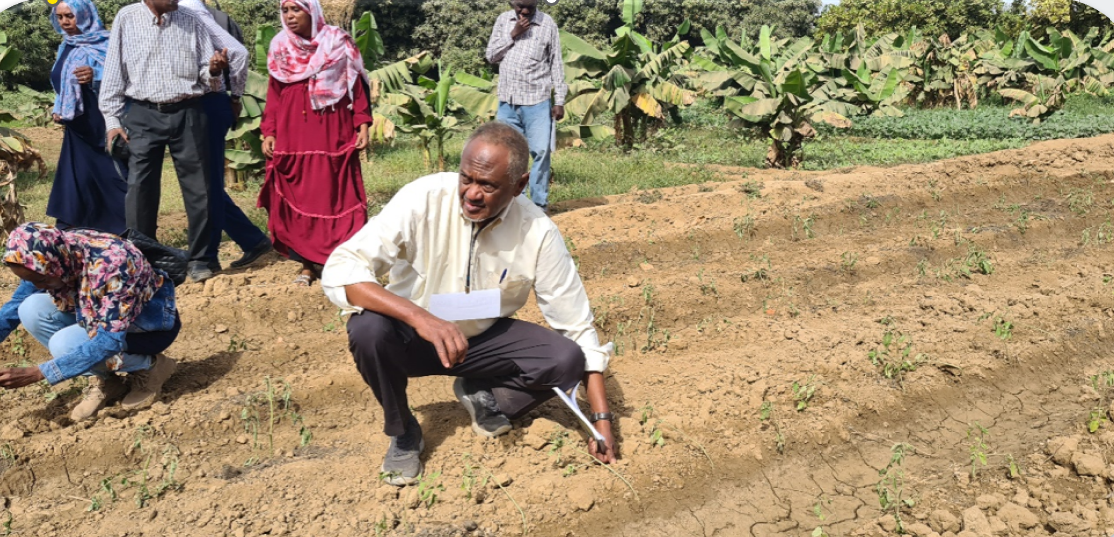
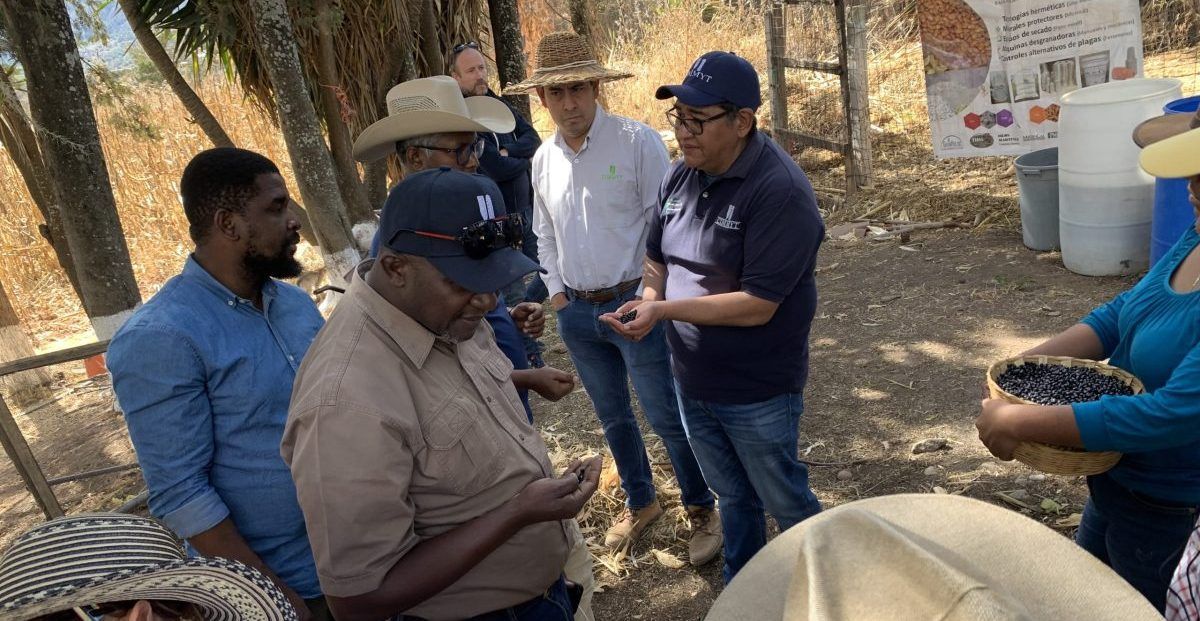
Sudan will hopefully show how this kind of intervention can work. Our organizations are part of an international effort to partner with Sudan’s farmers to improve livelihoods in the country. We had started operating across six Sudanese states just before the outbreak of the current conflict, training farmers on how to manage their crops, livestock, and natural resources, and supporting them to access drought-tolerant seeds, with a specific focus on last-mile delivery to women and youth. When the civil war started last year, we quickly pivoted to supporting farmers in safer locations and focusing on the needs of internally displaced people in new areas.
Make no mistake: Implementing these interventions in the current conditions is a heavy lift. Roadblocks, skyrocketing fuel costs, denied travel permits, and breakdowns in telephone service all impede communication with farmers and the delivery of seeds, tools, and training. The threat of emergent violence is driving displacement and staff turnover.
Nonetheless, our coalition has continued to operate. Local partners, including cooperatives, microfinance institutions, and private sector players have shown themselves to be especially effective as the conflict has escalated. These cooperatives, strengthened by farmer training, enable farmers to improve their production and incomes by pooling their resources.
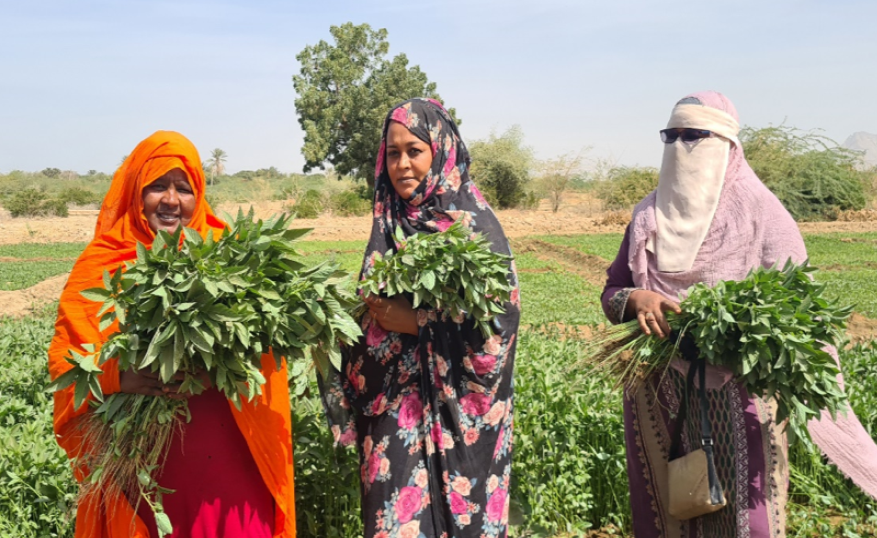
For example, the 72-member Al Etihad women-led farmer cooperative in South Kordofan has initiated multiple enterprises, guided by a structured business plan that steers them toward a more empowered role in local food value chains.
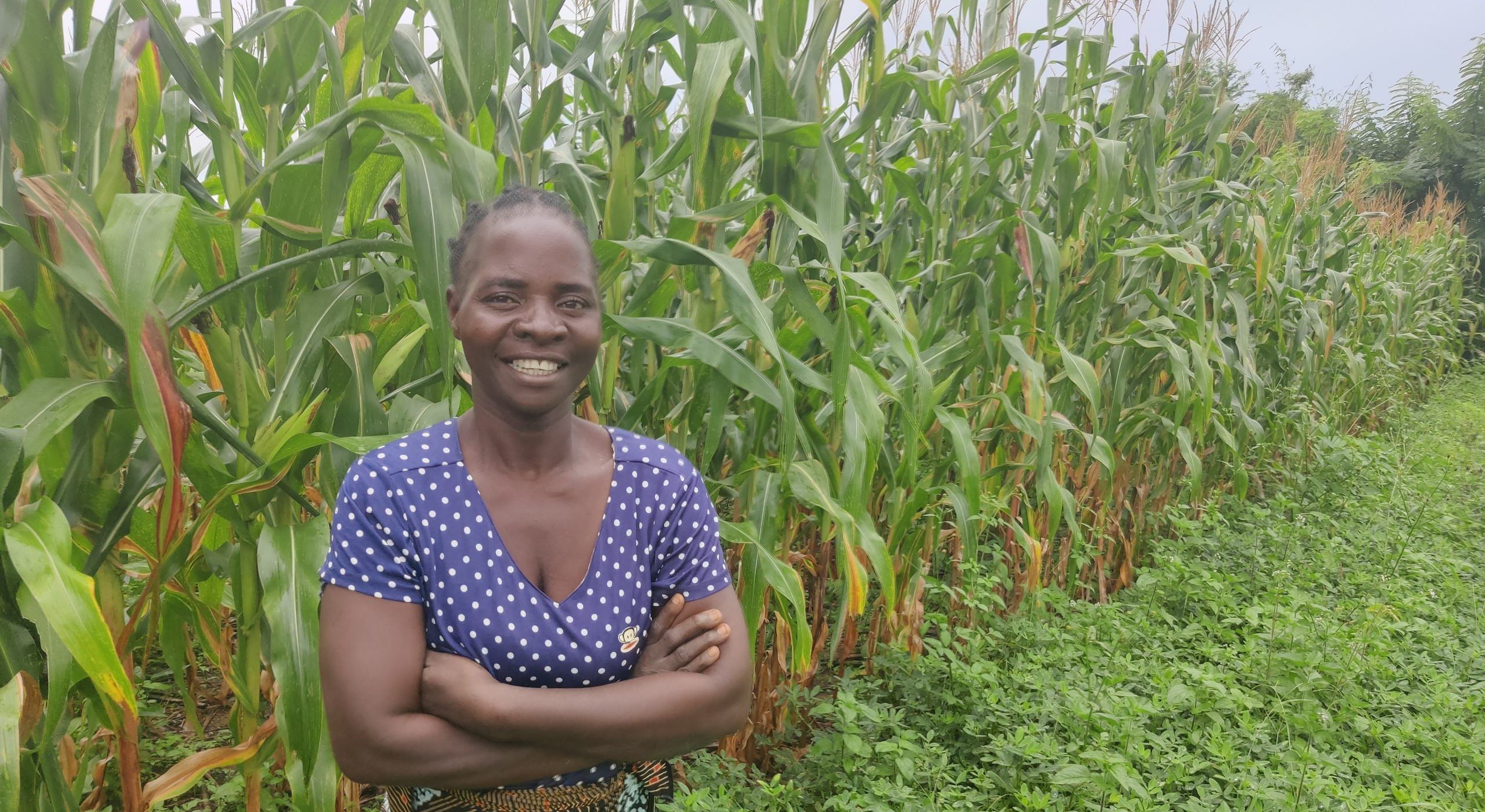
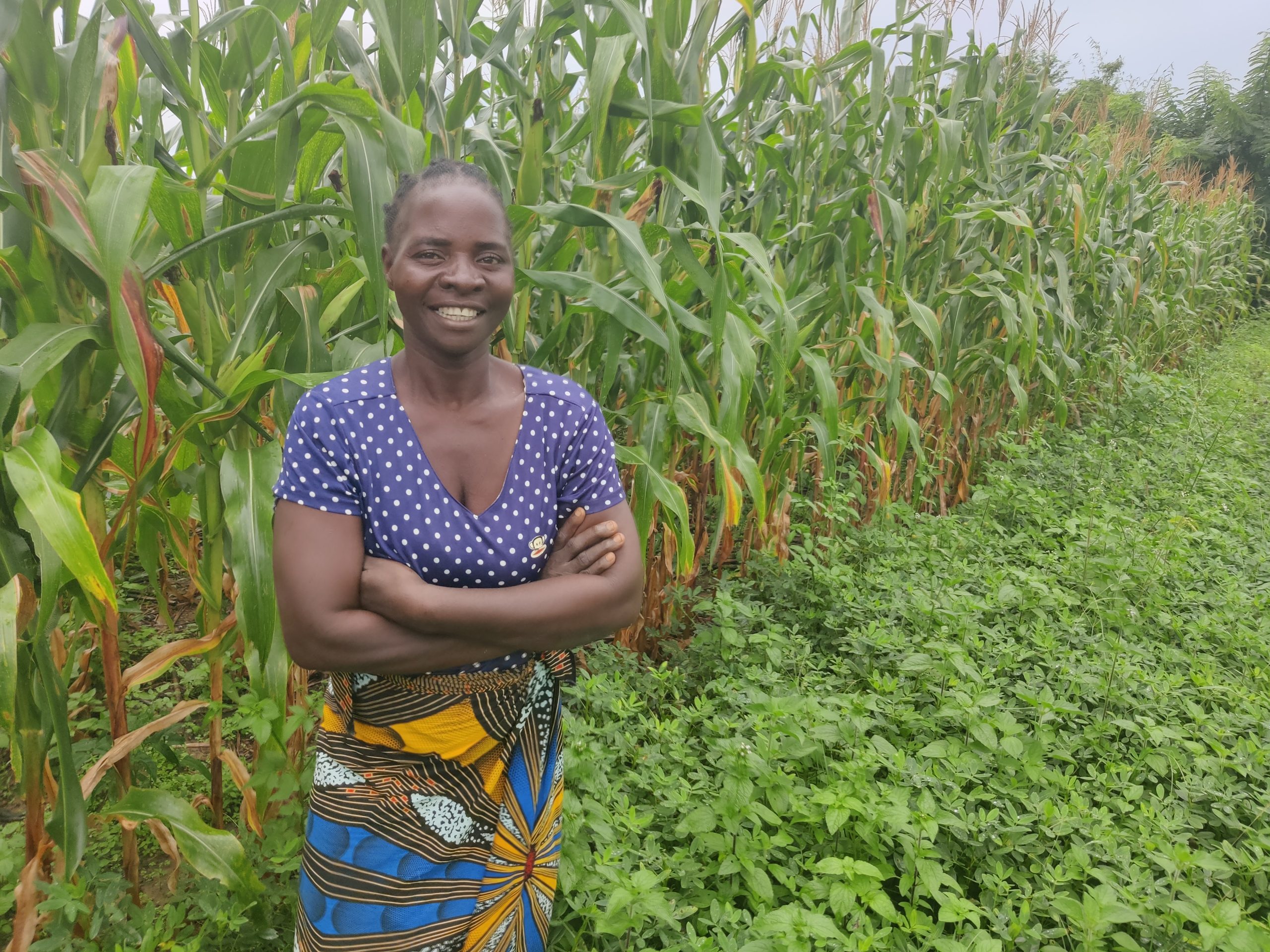
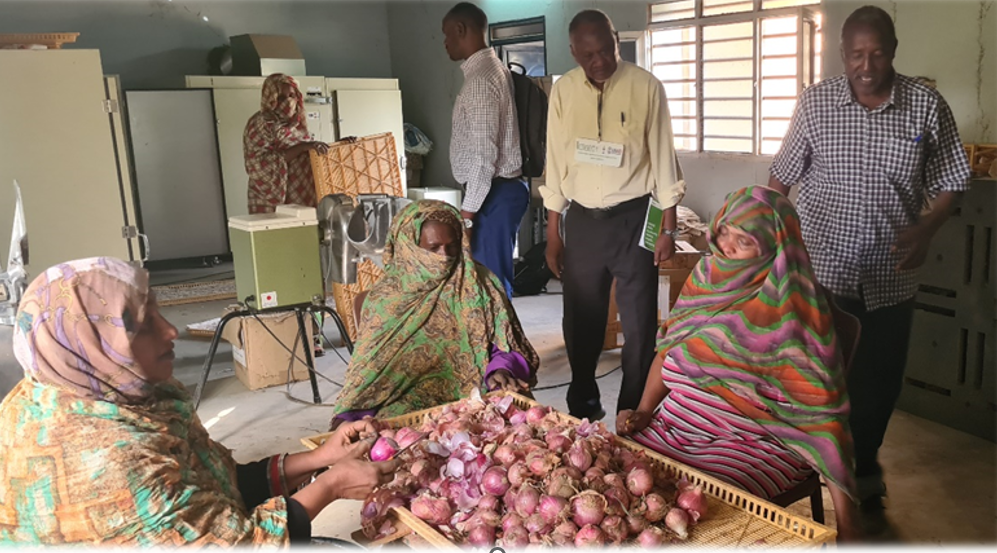
Through the program, last-mile seed retailers have helped nearly 6,000 farmers access agronomic advisories and seeds at a subsidized price. This has empowered farmers like Fatna Mohammed, a 48-year-old widow and mother of three, to build a better livelihood from her small-scale groundnut and vegetable production. She reports that an increased harvest of 18 sacks of groundnut, up from five sacks, enabled her to invest in her farm and better feed her family.
This unique last-mile delivery network, carefully tailored to local realities and drivers, is helping Sudanese communities to survive the current crisis and it can be activated for the rebuilding period — which cannot come soon enough.
Sudan, as with many war-affected nations, is caught in a doom loop of insecurity: Any restoration of political stability requires economic activity, but any economic activity requires political stability. Both depend on physical security, which is hard to achieve without political stability and economic activity.
While a cessation of violence and the restoration of civil order is ultimately up to the parties to the conflict, a direct, international investment in farmers is a way to potentially break the cycle, simultaneously addressing the growing hunger crisis and helping build the preconditions for peace.
Read the original piece on Devex













 This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that
This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that