Precision planters boost maize yields in Pakistan
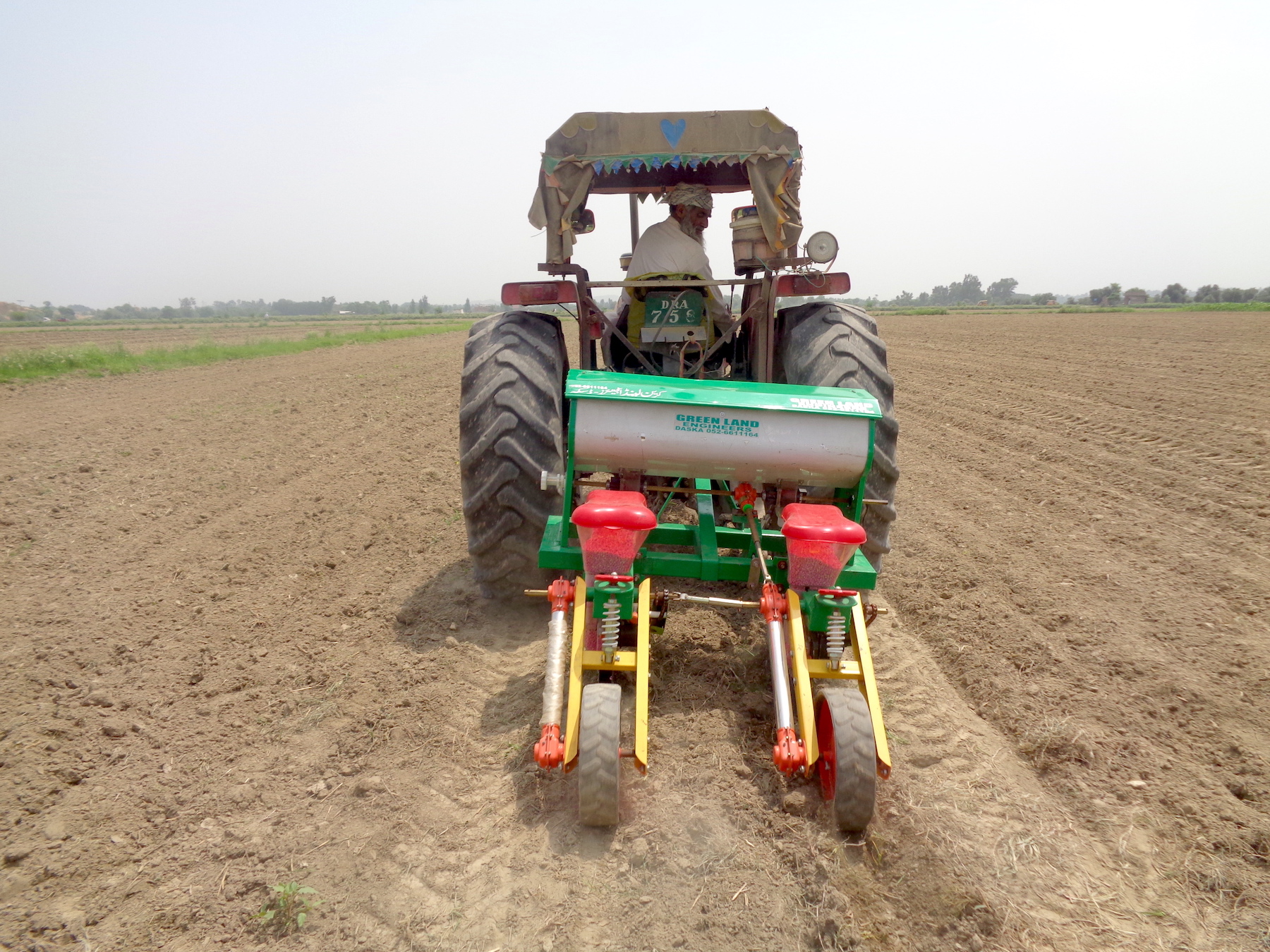

In the northwestern province of Pakistan, near the Afghan border, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) is helping connect farmers with precision planters to support higher maize yields and incomes. Maize is one of the most important cereals in Pakistan, but in the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa yields are significantly lower than the national average. The majority of maize farmers in this province have less than five acres of land and limited access to resources, including high-quality maize seed and mechanization.
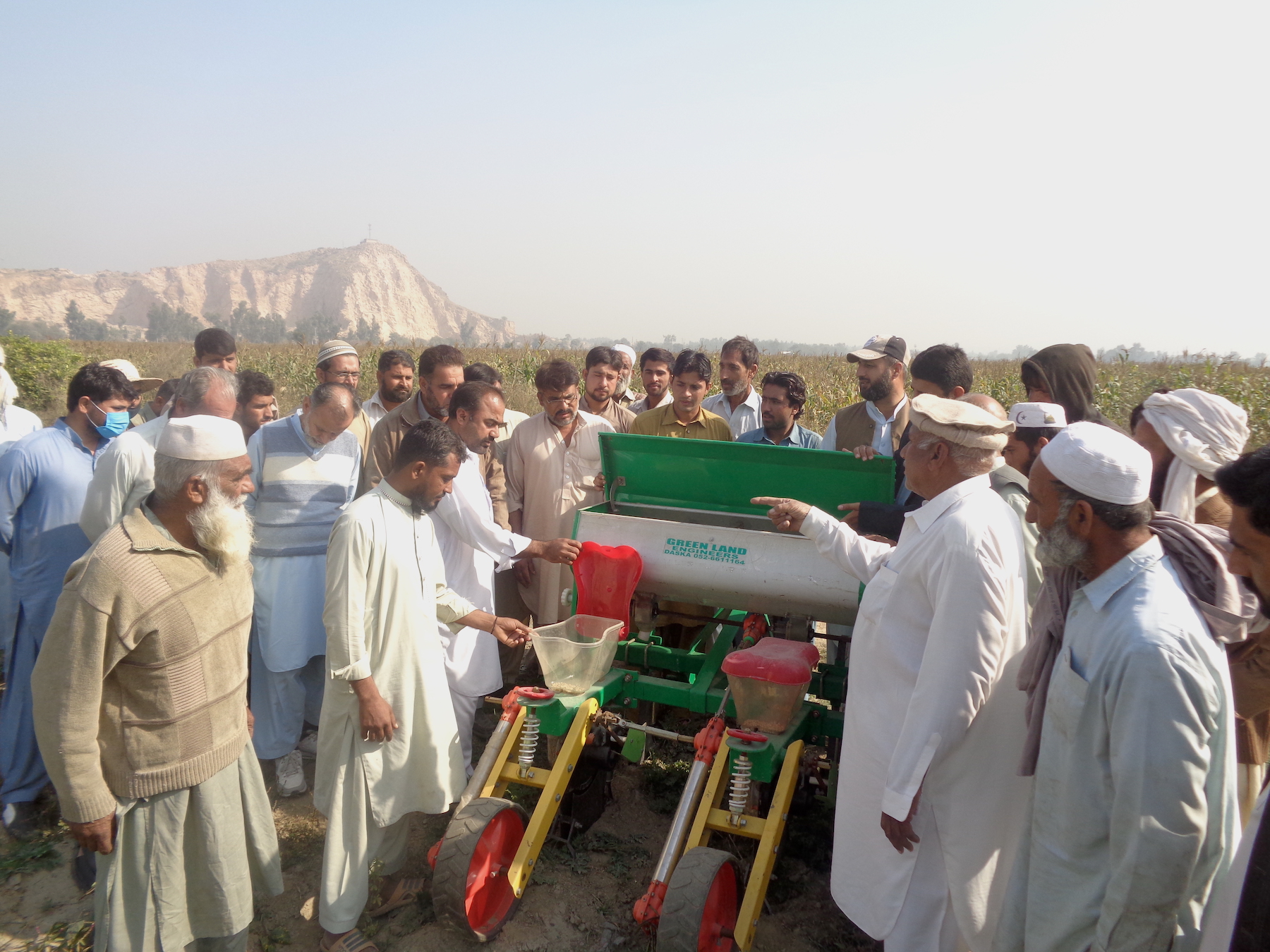
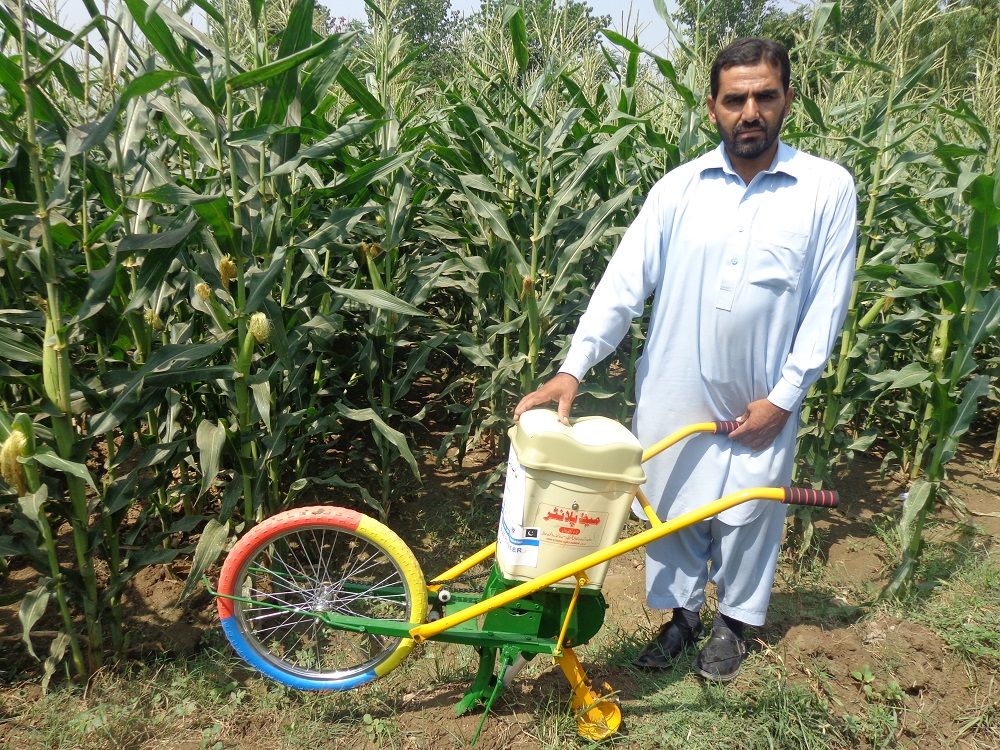
Under the Agricultural Innovation Program (AIP) for Pakistan, CIMMYT introduced push row planters in 2016 to help farmers to get a uniform crop stand and save labor costs and time as compared to traditional planting practices. CIMMYT has since then partnered with Greenland Engineering to import tractor-operated precision maize planters. These precision planters allow farmers to plant two rows of maize in one pass and evenly distribute both seeds and fertilizer.
“Optimum planting density in combination with nutrient supply is key to getting the maximum maize yield,” says Muhammad Asim, a senior researcher with the Cereal Crops Research Institute (CCRI). “The precision planter helps farmers achieve this while also getting a uniform crop stand and uniform cobs.”
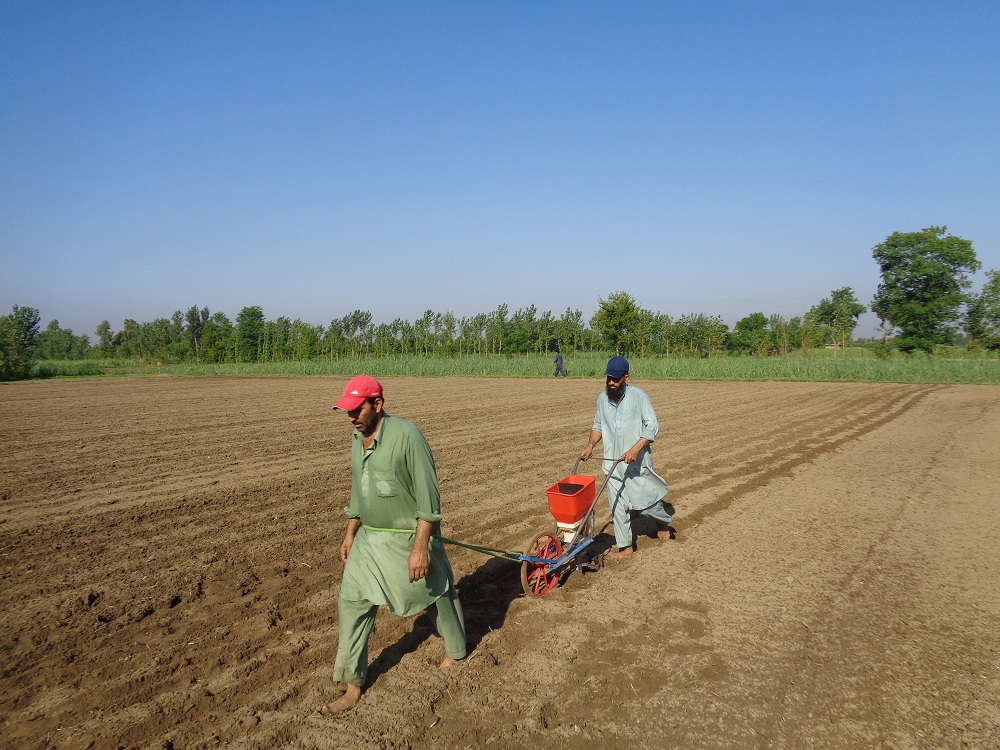

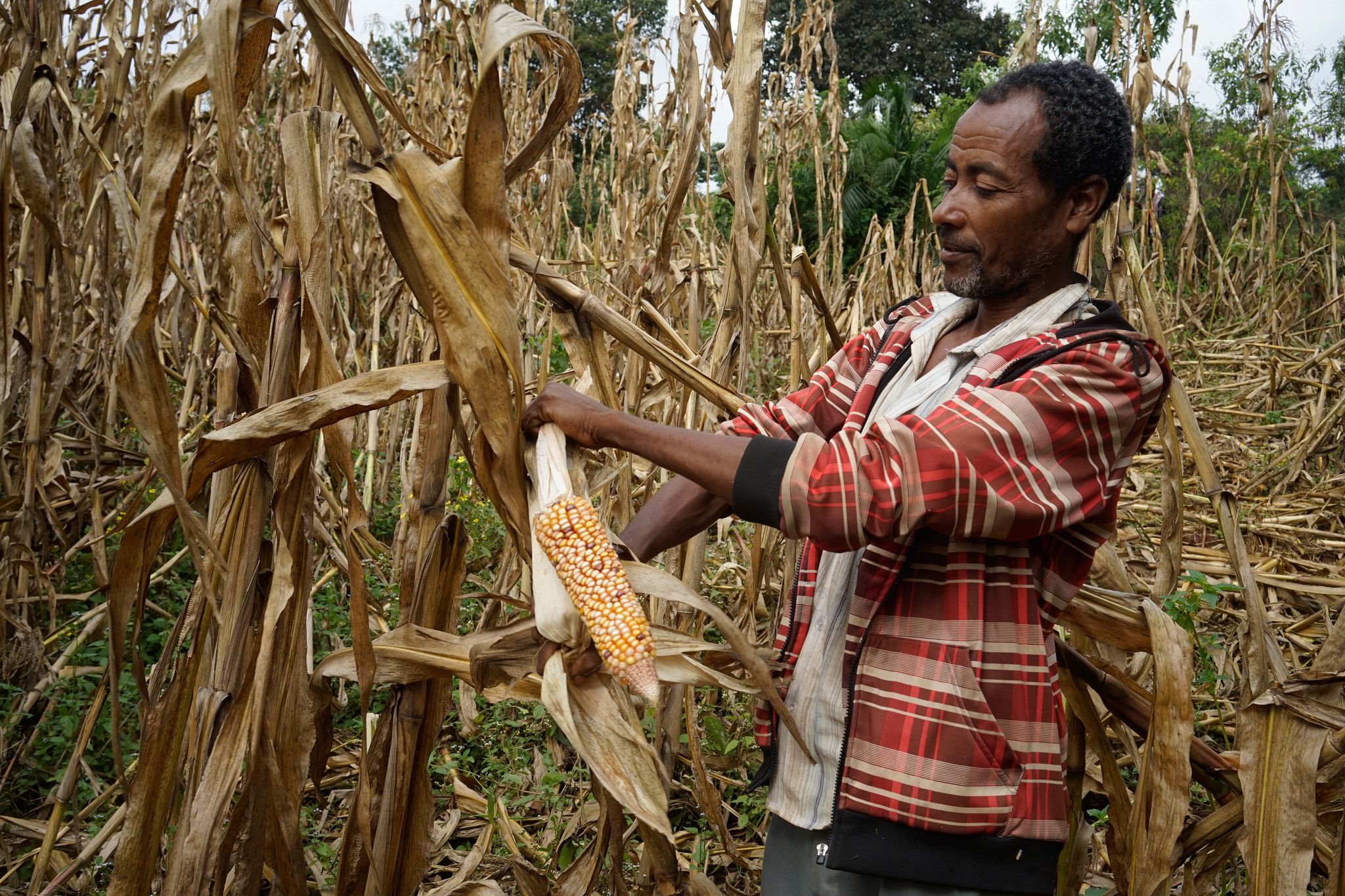
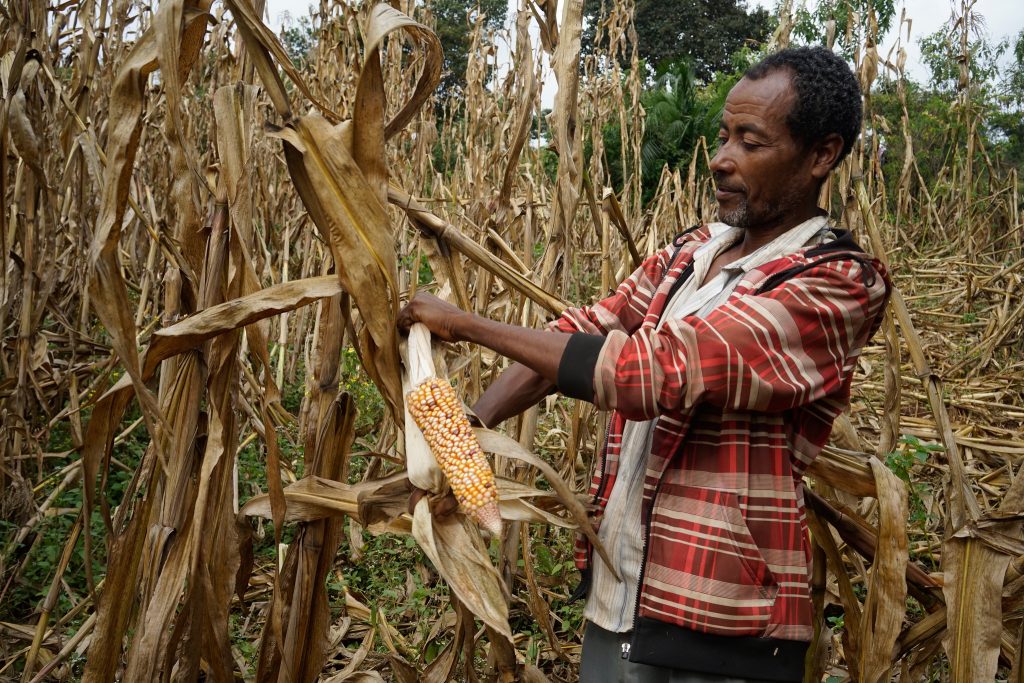
Jalees Ahmed, a smallholder maize farmer from the Nowshera district, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, received a push row planter through CIMMYT’s AIP program. He used to hire six laborers to plant one acre of maize, but with the push row planter, Jalees only needs to hire one laborer and benefits from a more uniform crop.
Raham Dil, another farmer in the Mardan district, recently purchased a push row planter for his farm which he also rents to fellow farmers in the area.
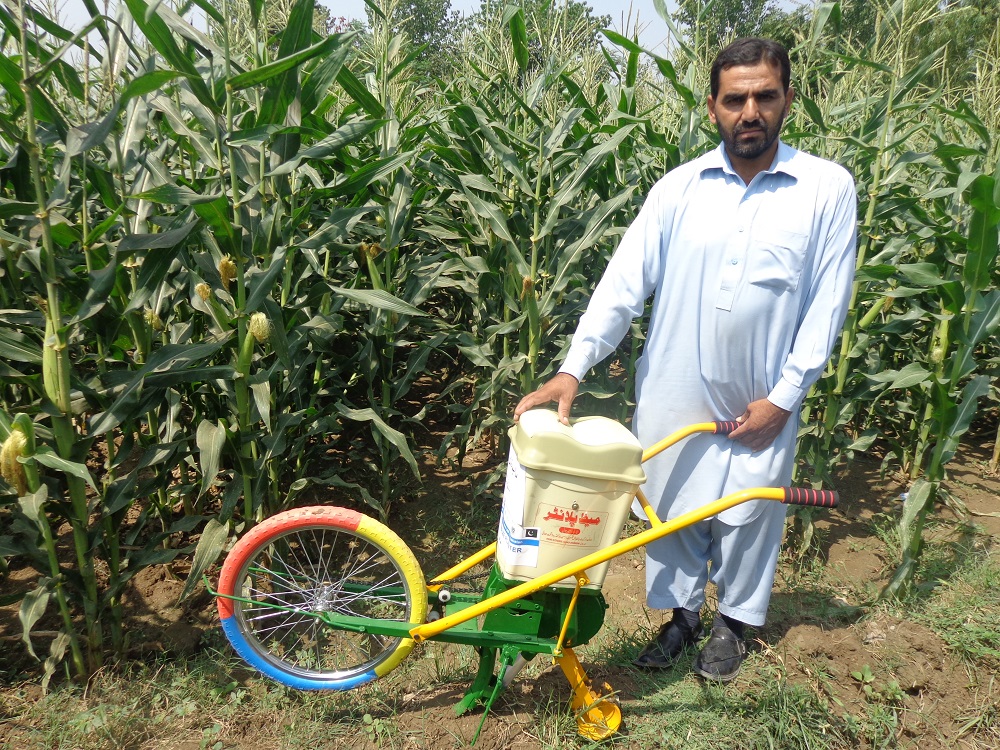

Both Ahmed and Dil say these planters have made it easier to support their families financially. Interest in precision planters continues to grow.
Last fall, more than 80 farmers attended a field day in the Nowshera district where CIMMYT researchers demonstrated how to use the precision planter to sow maize. CIMMYT’s country representative for Pakistan, Imtiaz Muhammad, highlighted the importance of mechanized maize planting for farmers and CIMMYT’s commitment to improve maize-based system productivity in less developed regions of the country.

The Agricultural Innovation Program for Pakistan is led by CIMMYT and funded by USAID. This project seeks to increase productivity and incomes by testing and promoting modern practices for agriculture’s major sub-sectors in the country.


















 A new report by more than 30 world-leading experts in health and environmental sustainability offers a roadmap for a global food system that provides a healthy, sustainable diet for the world’s 10 billion people by 2050.
A new report by more than 30 world-leading experts in health and environmental sustainability offers a roadmap for a global food system that provides a healthy, sustainable diet for the world’s 10 billion people by 2050.