A catastrophe avoided
There are decades when nothing happens and weeks when decades happen. So goes the old saw. In the social sciences, these “weeks” are often referred to as critical junctures. They are moments when the old rules of the game — the long-established ways of doings things — go out the window and new patterns begin to emerge. The breadbasket states of northwestern India seem to be having one of those weeks.
After years of research and advocacy that appeared to be making little headway, researchers at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) are seeing a sudden and dramatic increase in the adoption of some of the technologies and techniques they have long argued are necessary in this region, including direct-seeding of rice, crop diversification and the adoption of Happy Seeder technology.
A case of unintended consequences
In March 2020 the Indian government decreed a national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 crisis. This triggered the largest internal migration since partition, as millions of migrant workers and day laborers scrambled to return to their home villages. Estimates suggest that up to 1 million workers left the northwestern states of Haryana and Punjab alone.
Agriculture in the region is dominated by the labor- and input-intensive production of rice and wheat in rotation. This system is the most productive per hectare in India, but it is also extremely sensitive to external shocks. The success of both the rice and wheat crop depend on the timely transplantation of rice in mid-June.
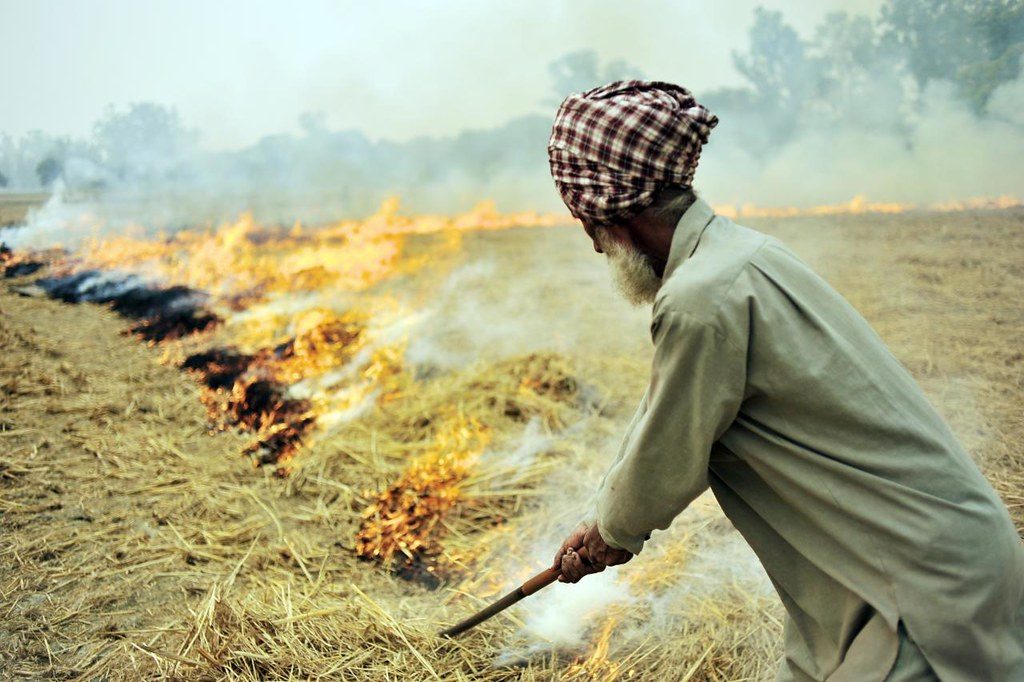
As the results of a recently published study demonstrate, delays in this schedule can have devastating downstream effects not only on rice and wheat yields, but on regional air quality too. Models of the worst-case delay scenario predicted a total economic loss of nearly $1.5 billion. Moreover, they predicted that, if no action were taken, up to 80% of rice residue would be burned later in the autumn, when cooler conditions contribute to seasonally poor air quality.
Such an exacerbation of the region’s air pollution would be dire under normal conditions. During a global pandemic of a primarily respiratory illness, it could be devastating.
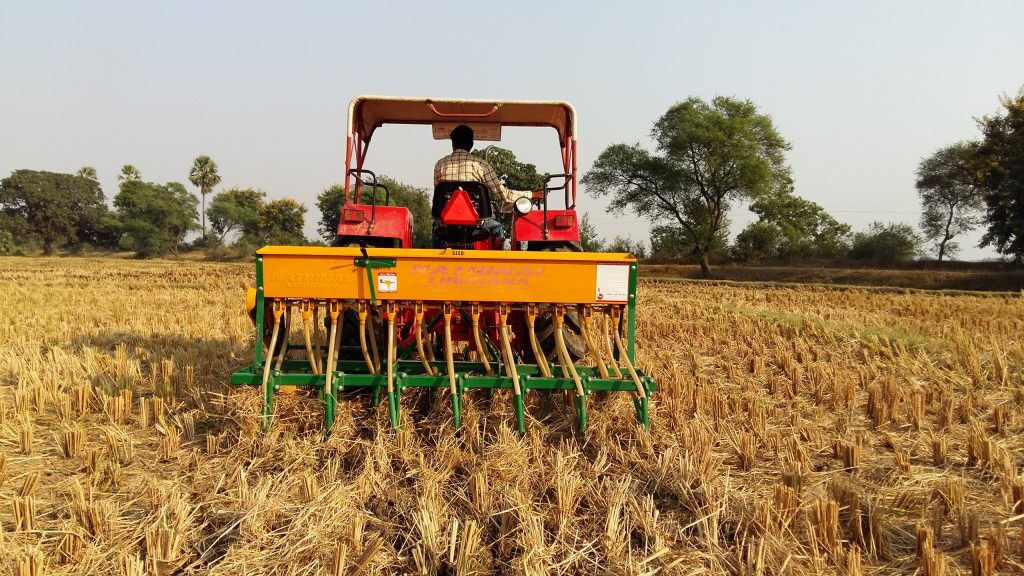
Fortunately, solutions and technologies that CIMMYT researchers had been studying for decades, along with ICAR, Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) and other national partners, promised to help ward off the worst effects of the crisis. The adoption of direct-seeding technology could help reduce the labor-intensiveness of rice production, crop diversification could minimize the economic impacts of the crisis, and the use of Happy Seeder technology could alleviate the practice of residue burning.

Decades of work pay off
The study, co-authored by researchers at CIMMYT, ICAR and the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), relied on a sophisticated ex ante model of four different rice-transplanting delay scenarios. It is published in the November 2020 issue of Agricultural Systems.
However, given the time-sensitivity and high-stakes of the issue, the lead researchers did not wait for the articles publication to press their case. Earlier this year they circulated their initial findings and recommendations to policymakers via their national partners. Notably, after receiving a one-pager summarizing these, the Chief Minister of Punjab released a video address echoing their points.
“Policymakers realized the need for these kinds of solutions,” says Balwinder Singh, a CIMMYT scientist and lead author of the paper. They then moved quickly to incentivize their adoption through various mechanisms, such as subsidizing direct-seeding drills and ensuring the timely availability of machines and other inputs.
This year, 500,000 hectares were converted to direct seeding, explains M.L. Jat, a principal scientist at CIMMYT. This represents 34% more area converted in 2020 alone than in the previous 10 years. Additionally, 330,000 hectares were converted to other crops, principally cotton, maize and legumes.
Singh and Jat have been carrying out a multi-year survey to assess farmer willingness to adopt Happy Seeder technology and have documented a drastic increase in farmer interest in the technology during 2020. For Jat, this highlights the power of partnerships. “If you don’t include your partners from the beginning, they will not own what you say,” he argues.
Such changes are to be celebrated not only as an important response to the current labor shortage, but also as key to ensuring the long-term sustainability of agricultural production in the region, having important implications for the stewardship of water resources, air pollution and soil health.
“Policies encouraging farming practices that save resources and protect the environment will improve long-term productivity and sustainability of the nation,” says S. K. Chaudhari, deputy director general for Natural Resource Management at ICAR.

Warding off catastrophe
Although the agricultural cycle is not yet over, and early data are still partial, Singh and Jat estimate that thanks to the dramatic adoption of alternative agricultural practices this year, their worst-case estimates have been avoided. Given the rapid response from both policymakers and farmers, the real-world effects of the COVID-19 labor crisis are likely closer to the mid-range severity scenarios of their analysis. Indeed, early estimates predict no rice yield losses and minor-to-no wheat yield losses over baseline. For the researchers, the relief is palpable and the lessons couldn’t be clearer.
“These technologies were there for decades, but they were never appreciated because everything was normal,” says Jat. “This clearly indicates a need for investment in the technology and the research. You may encounter a problem at any time, but you cannot generate the technology overnight.”













 With global agriculture in stasis and under threat from climate change, Latin America’s role to address these challenges through innovation and partnerships is crucial. This was the main takeaway from a 2020
With global agriculture in stasis and under threat from climate change, Latin America’s role to address these challenges through innovation and partnerships is crucial. This was the main takeaway from a 2020 







 The World Food Prize Foundation is honoring the work of Rattan Lal, who dedicated his life to study the effect of soil health in food production and climate change mitigation. On October 15 he will receive the 2020 World Food Prize, considered the “Nobel Prize” of agriculture.
The World Food Prize Foundation is honoring the work of Rattan Lal, who dedicated his life to study the effect of soil health in food production and climate change mitigation. On October 15 he will receive the 2020 World Food Prize, considered the “Nobel Prize” of agriculture.




