2022 Excellence in International Service Award

Scientist Pablo D Olivera Firpo has been awarded the Excellence in International Service Award by Advancing the Science of Plant Pathology (APS) for outstanding contributions to plant pathology by APS members for countries other than their own.
Firpo was born in Montevideo, Uruguay, where he received a BSc degree as an agronomy engineer in 1997 from the University of the Republic, College of Agronomy. His PhD degree in 2008 was from the Department of Plant Pathology at the University of Minnesota (UMN). He began his career as a postdoctoral research associate with the Department of Plant Pathology and the USDA-ARS Cereal Disease Lab, and then became a research assistant professor in the Department of Plant Pathology at UMN in 2017.
Firpo has been a vital member in the global cereal rust pathology community and contributed substantially to the fight against Ug99 and other virulent wheat stem rust races that have re-emerged around the world and pose serious threats to food security. Firpo’s contributions are not only within the realm of research of great impact, but also include training 79 scientists and facilitating the establishment of a world-class research group in Ethiopia. He has worked to improve international germplasm screening in Ethiopia. As a postdoctoral research associate, Firpo’s first assignment was to search for new sources of resistance to Ug99 in durum wheat, used for pasta, and related tetraploid wheat lines. That project took him to Ethiopia, where an international Ug99-screening nursery for durum wheat was established at Debre Zeit Research Center. He worked closely with researchers from the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR) and the International Maize and Wheat Research Center (CIMMYT) to improve the methodologies for screening and to provide hands-on training to researchers managing the international screening nursery. During a period of 10 years (from 2009 to 2019), he traveled to Ethiopia 21 times to evaluate stem rust reactions of US and international durum wheat germplasm and completed the screening of the entire durum collection (more than 8,000 accessions) from the USDA National Small Grains Collection.
Firpo’s research on sources and genetics of stem rust resistance led to discoveries of valuable genetic resistance in durum and other relatives of wheat. These sources of resistance have provided the needed diversity to ensure the development and sustainability of durable stem rust resistance.
With frequent epidemics and severe yield losses caused by stem rust in eastern Africa, establishing a functional rust pathology laboratory to support international screening, as well as to monitor and detect new virulences in the pathogen population, became a high priority for the international wheat research community. Utilizing the onground opportunities in Ethiopia, Firpo and his colleagues at the CDL and UMN enthusiastically participated in building up the rust pathology lab at the Ambo Plant Protection Center of EIAR. Firpo traveled to Ambo 11 times to provide hands-on training to staff and to develop cereal rust protocols to suit local conditions. He worked closely with colleagues at CDL, EIAR, and CIMMYT to secure and upgrade facilities, equipment and supplies to a standard that ensures reliable rust work will be carried out. As a result, the rust pathology lab at the Ambo Center became the only laboratory in eastern Africa, and one of a handful in the world, that can conduct high-quality race analysis of wheat stem rust samples and provide vital and necessary support for breeding global wheat varieties for rust resistance. Currently, the laboratory is playing a critical role in the global surveillance of the stem rust pathogen and supports wheat breeding efforts led by EIAR, CIMMYT, and the USDA.
Firpo has been passionate in supporting capacity building of human resources in Ethiopia and elsewhere. He has been eager to share his knowledge whenever he encounters an opportunity to do so. In addition to the direct training of the staff at the Ambo Center, Firpo accepted invitations to provide training lectures and hands-on field- and greenhouse-based workshops on rust pathology at three research centers in Ethiopia. He prepared training materials, delivered a total of 12 lectures and 10 practical sessions in three Ethiopia national workshops in 2014, 2015, and 2017. These workshops enhanced human resource development and technical capacity in Ethiopia in cereal rust pathology; participants included a total of 64 junior scientists and technical staff from nationwide research centers. Beyond Ethiopia, he was responsible for developing and implementing a six-week training program in cereal rust prevention and control for international scientists. This training program, under the aegis of the Stakman-Borlaug Center for Sustainable Plant Health in the Department of Plant Pathology, University of Minnesota, provided an experiential learning opportunity for international scientists interested in acquiring knowledge and practical skills in all facets of working with cereal rusts. The program trained 15 rust pathologists and wheat scientists from Ethiopia, Kenya, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Georgia, and Kyrgyzstan, ranging from promising young scientists selected by the USDA as Borlaug Fellows to principal and senior scientists in their respective countries. Many of these trainees have become vital partners in the global surveillance network for cereal rusts.
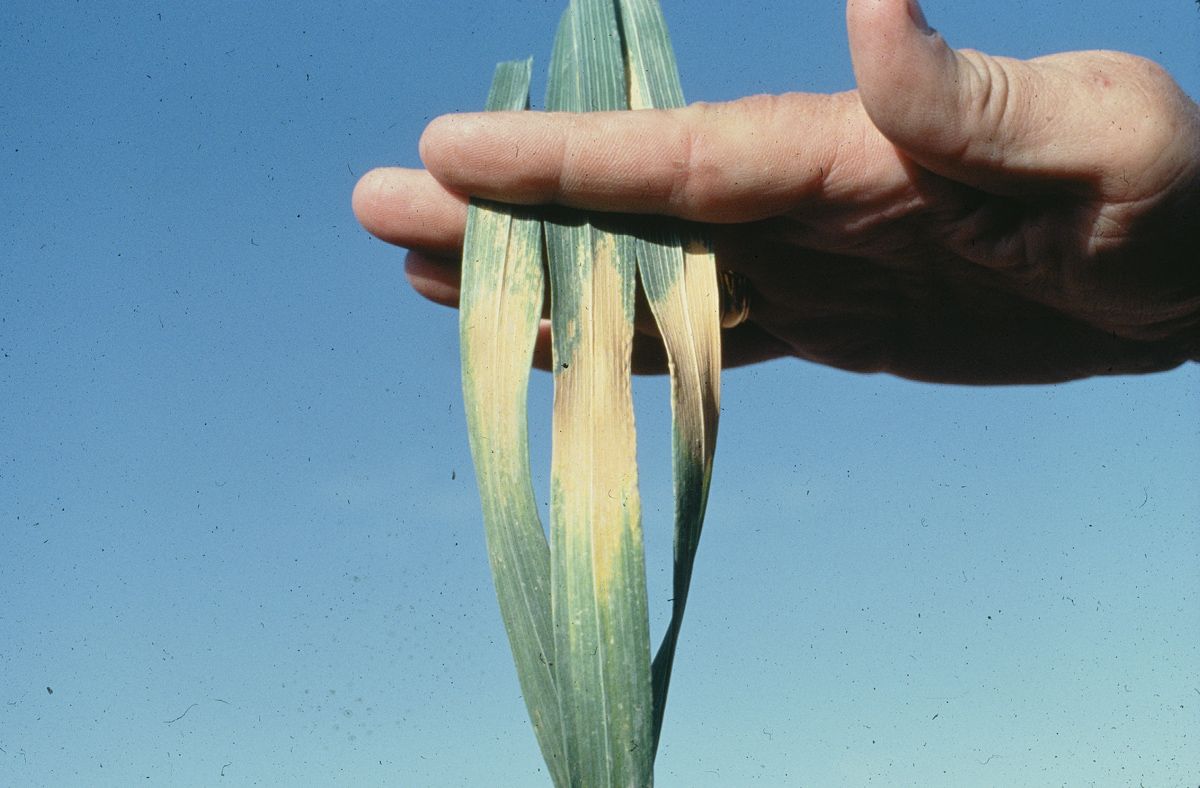
Working in collaboration with CDL and international scientists, Firpo has been closely involved in global surveillance of the stem rust pathogen, spurred by monitoring the movements of, and detecting, new variants in the Ug99 race group. Since 2009, he and the team at the CDL have analyzed 2,500 stem rust samples from 22 countries, described over 35 new races, and identified significant virulence combinations that overcome stem rust resistance genes widely deployed in global wheat varieties. Among the most significant discoveries were the identification of active sexual populations of the stem rust pathogen in Kazakhstan, Georgia, Germany, and Spain that have unprecedented virulence and genetic diversities. More than 320 new virulent types (or races) were identified from these sexual populations. Evolution in these populations will present continued challenges to wheat breeding. Research in race analysis has provided valuable pathogen isolates that are used to evaluate breeding germplasm to select for resistant wheat varieties and to identify novel sources of stem rust resistance.