Digital revolution can transform agri-food systems
A digital transformation is changing the face of international research for development and agri-food systems worldwide. This was the key takeaway from the 4th annual CGIAR Big Data in Agriculture Convention held virtually last month.
“In many countries, farmers are using data to learn about market trends and weather predictions,” said Martin Kropff, director general of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), in a video address to convention participants. “But many still do not have access to everything that big data offers, and that is where CIMMYT and partners come in.”
As a member of CGIAR, CIMMYT is committed to ensuring that farmers around the world get access to data-driven solutions and information, while at the same time ensuring that the data generated by farmers, researchers and others is used ethically.
According to CGIAR experts and partner organizations, there are four key areas with the potential to transform agriculture in the next 10 years: data, artificial intelligence (AI), digital services and sector intelligence.
Key interventions will involve enabling open data and responsible data use, developing responsible AI, enabling and validating bundled digital services for food systems, and building trust in technology and big data — many of which CIMMYT has been working on already.
Harnessing data and data analytics
Led by CIMMYT, the CGIAR Excellence in Breeding (EiB) team have been developing the Enterprise Breeding System (EBS) — a single data management software solution for global breeding programs. The software aims to provide a solution to manage data across the entire breeding data workflow — from experiment creation to analytics — all in a single user-friendly dashboard.
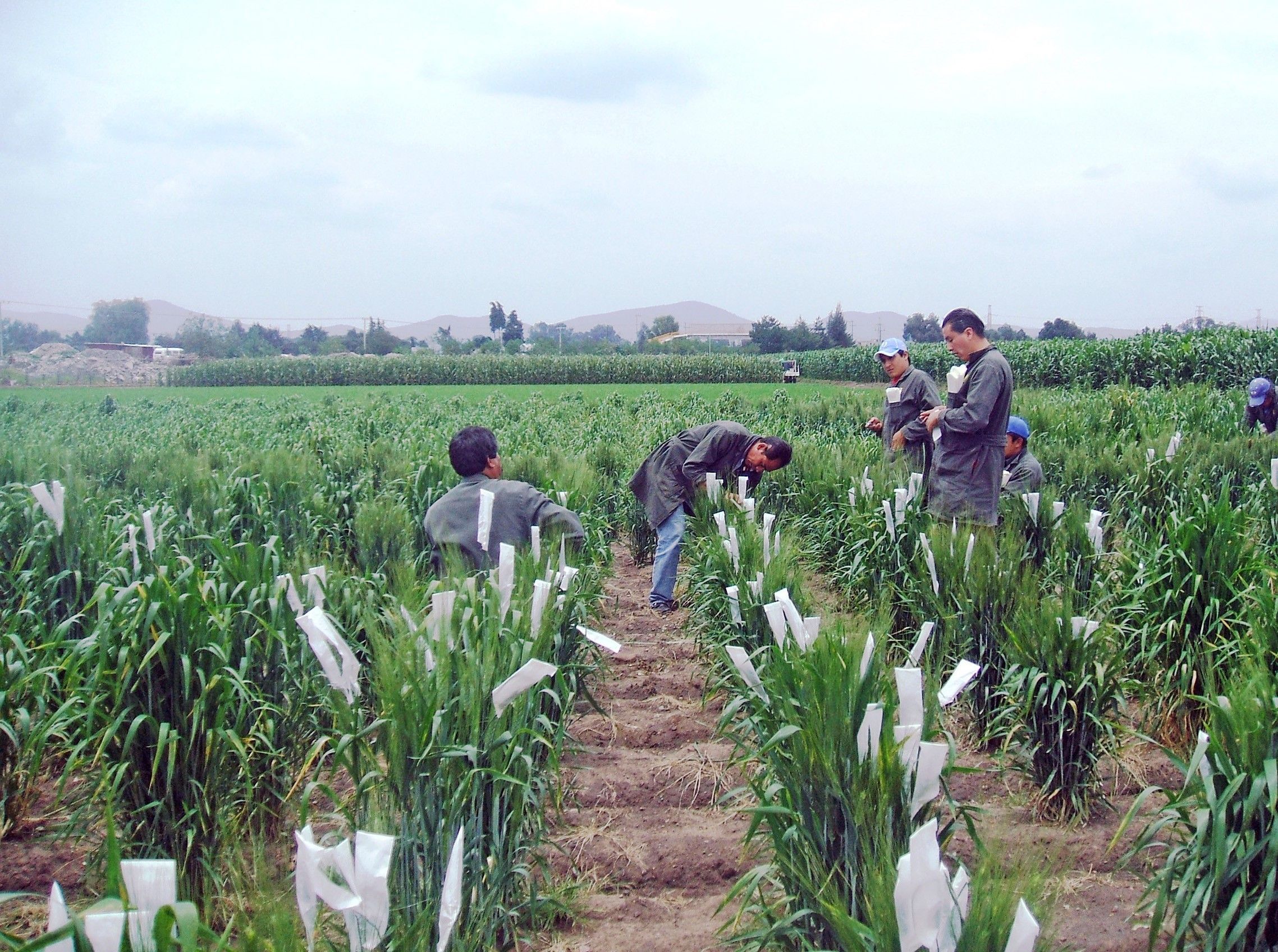
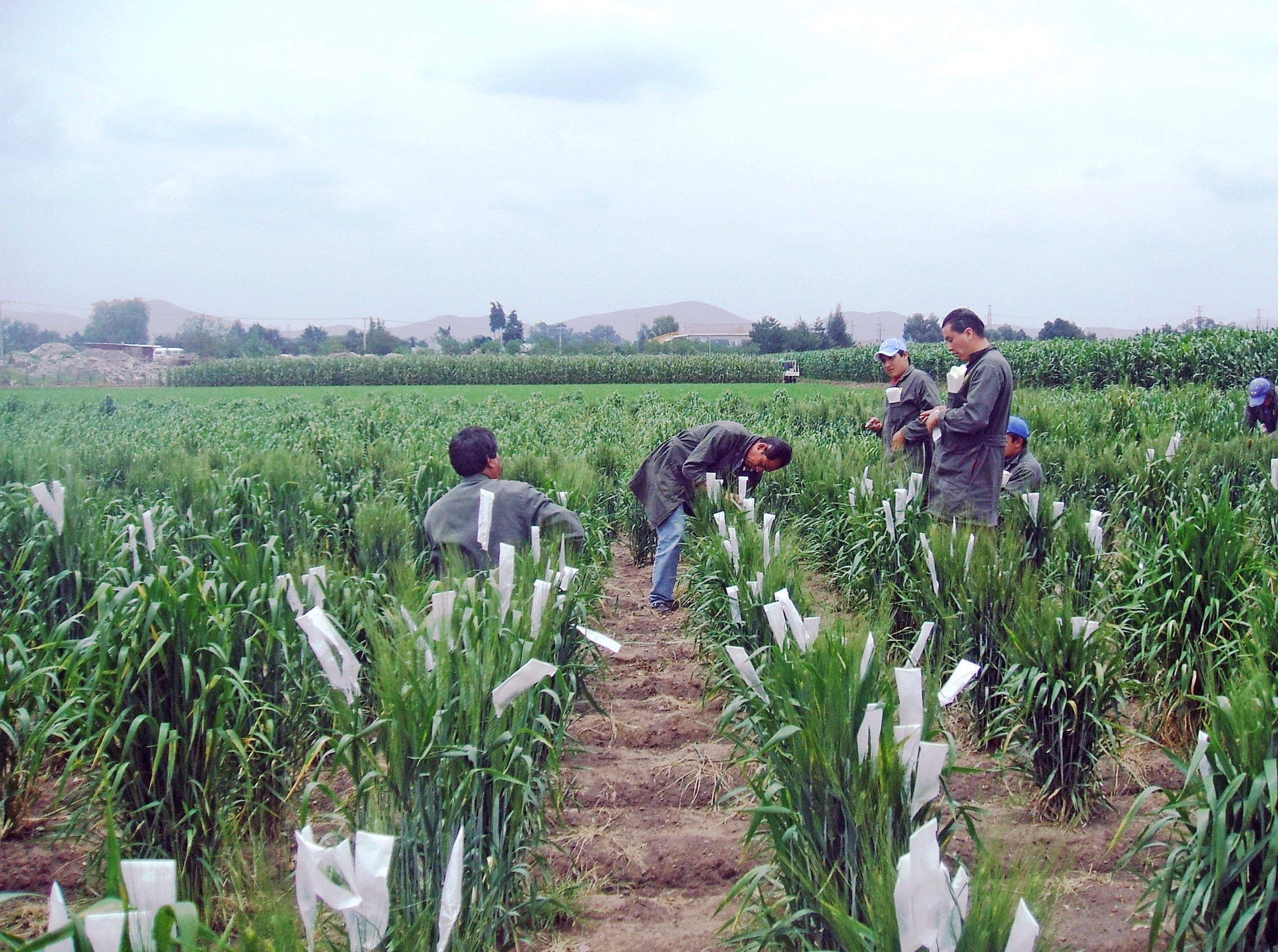
CIMMYT and partners have also made significant breakthroughs in crop modelling to better understand crop performance and yield gaps, optimize planting dates and irrigation systems, and improve predictions of pest outbreaks. The Community of Practice (CoP) on Crop Modeling, a CGIAR initiative led by CIMMYT Crop Physiologist Matthew Reynolds, aims to foster collaboration and improve the collection of open access, easy-to-use data available for crop modelling.
The CIMMYT-led Community of Practice (CoP) on Socio-Economic Data continues to work at the forefront of making messy socio-economic data interoperable to address urgent and pressing global development issues in agri-food systems. Data interoperability, one of the foundational components of the FAIR data standards supported by CGIAR, addresses the ability of systems and services that create, exchange and consume data to have clear, shared expectations for its content, context and meaning. In the wake of COVID-19, the world witnessed the need for better data interoperability to understand what is happening in global food systems, and the CoP actively supports that process.
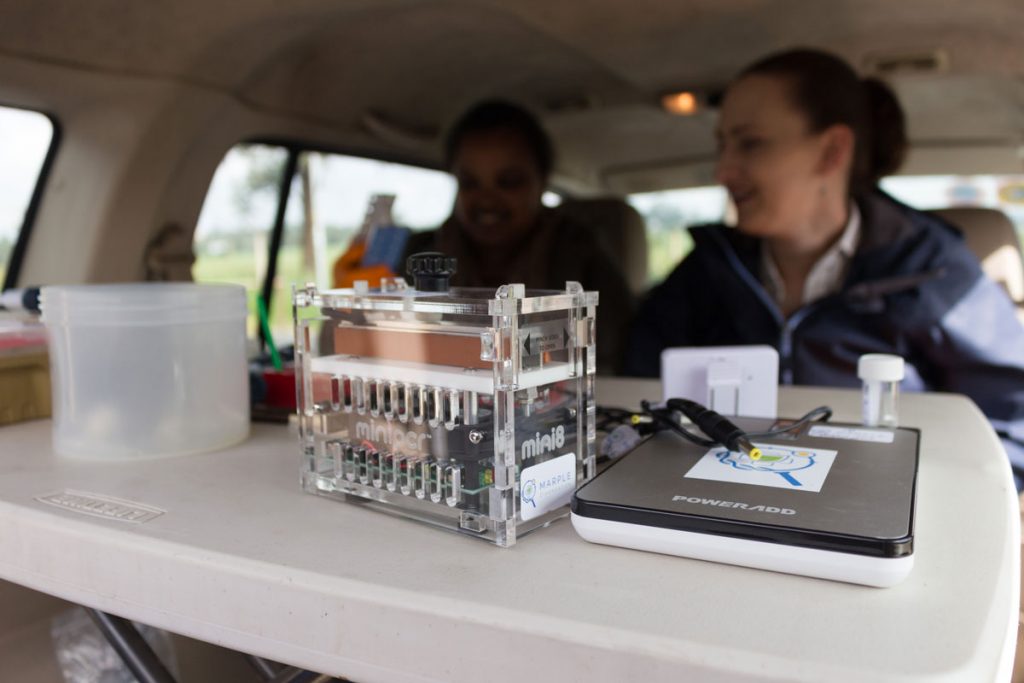

Improving data use and supporting digital transformation
In Ethiopia, the MARPLE (Mobile And Real-time PLant disEase) diagnostic kit — developed by CIMMYT, the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR) and the John Innes Centre (JIC) — has helped researchers, local governments and farmers to rapidly detect diseases like wheat rust in the field. The suitcase-sized kit cuts down the time it takes to detect this disease from months to just 48 hours.
In collaboration with research and meteorological organizations including Wageningen University and the European Space Agency (ESA), CIMMYT researchers have also been developing practical applications for satellite-sourced weather data. Crop scientists have been using this data to analyze maize and wheat cropping systems on a larger scale and create more precise crop models to predict the tolerance of crop varieties to stresses like drought and heatwaves. The aim is to share the climate and weather data available on an open access, user-friendly database.
Through the AgriFoodTrust platform — a new testing and learning platform for digital trust and transparency technologies – CIMMYT researchers have been experimenting with technologies like blockchain to tackle issues such as food safety, traceability, sustainability, and adulterated and counterfeit fertilizers and seeds. Findings will be used to build capacity on all aspects of the technologies and their application to ensure this they are inclusive and usable.
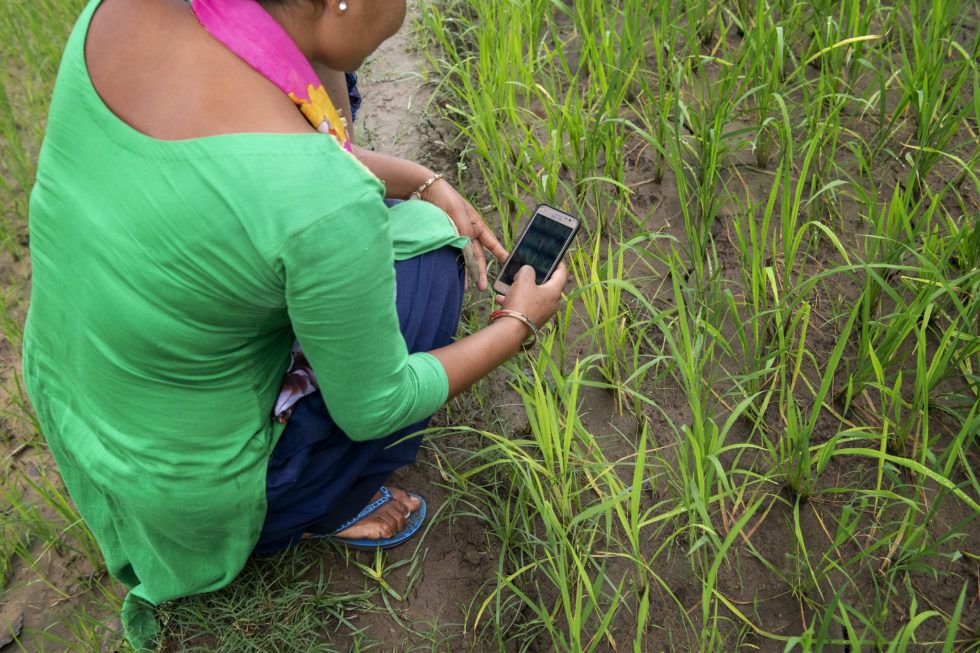
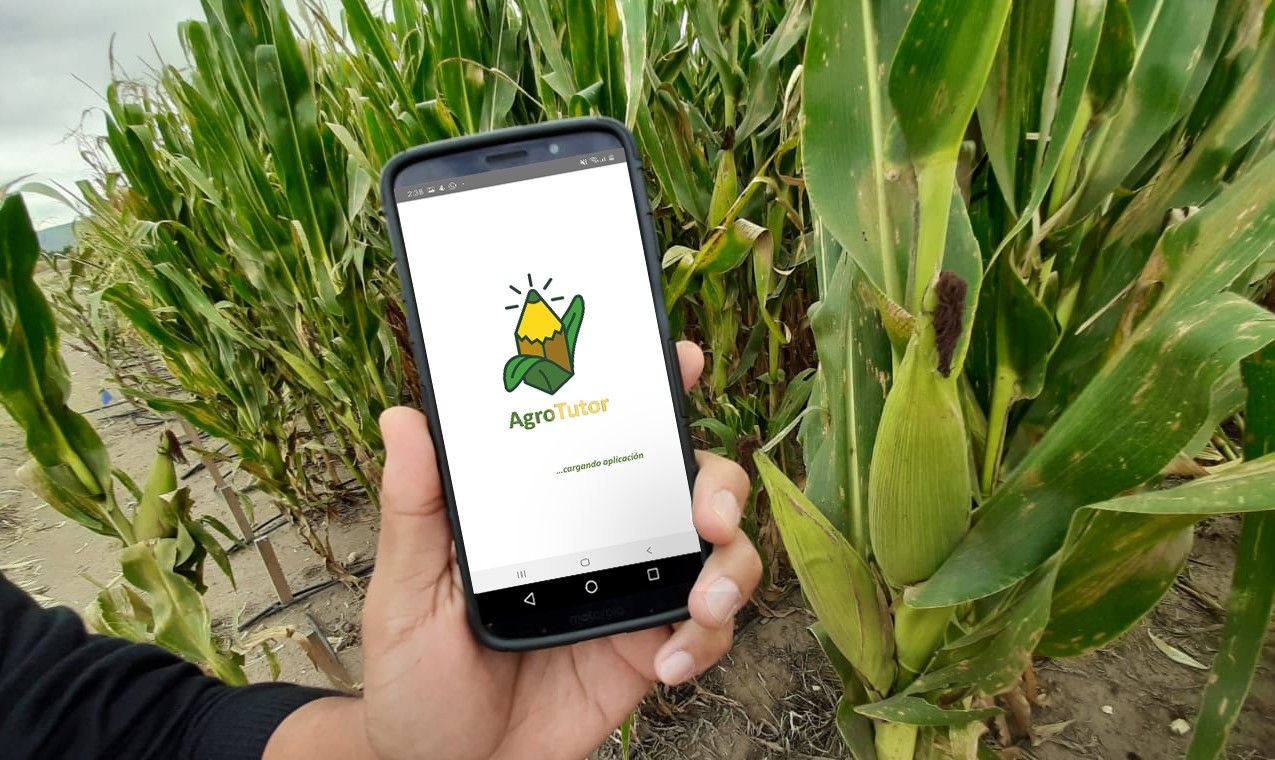
In Mexico, CIMMYT and partners have developed an application which offers tailored recommendations to help individual farmers deal with crop production challenges sustainably. The AgroTutor app offers farmers free information on historic yield potential, local benchmarks, recommended agricultural practices, commodity price forecasting and more.
Stepping up to the challenge
As the world becomes increasingly digital, harnessing the full potential of digital technologies is a huge area of opportunity for the agricultural research for development community, but one that is currently lacking clear leadership. As a global organization already working on global problems, it’s time for the CGIAR network to step up to the challenge. Carrying a legacy of agronomic research, agricultural extension, and research into adoption of technologies and innovations, CGIAR has an opportunity to become a leader in the digital transformation of agriculture.
Currently, the CGIAR System is coming together as One CGIAR. This transformation process is a dynamic reformulation of CGIAR’s partnerships, knowledge, assets, and global presence, aiming for greater integration and impact in the face of the interdependent challenges facing today’s world.
“One CGIAR’s role in supporting digitalization is both to improve research driven by data and data analytics, but also to foster the digitalization of agriculture in low and lower-middle income countries,” said CIMMYT Economist Gideon Kruseman at a session on Exploring CGIAR Digital Strategy at last month’s Big Data convention.
“One CGIAR — with its neutral stance and its focus on global public goods — can act as an honest broker between different stakeholders in the digital ecosystem.”
Cover photo: A researcher demonstrates the use of the AgroTutor app on a mobile phone in Mexico. (Photo: Francisco Alarcón/CIMMYT)















 With global agriculture in stasis and under threat from climate change, Latin America’s role to address these challenges through innovation and partnerships is crucial. This was the main takeaway from a 2020
With global agriculture in stasis and under threat from climate change, Latin America’s role to address these challenges through innovation and partnerships is crucial. This was the main takeaway from a 2020