Women leaders in science: reaching out to break through
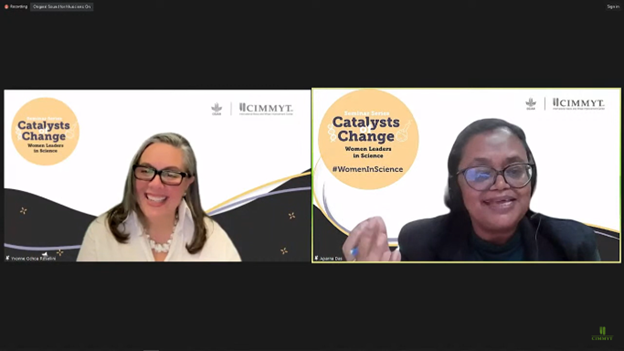
 On August 15, 2023, CIMMYT organized the third series of the Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science virtual seminar for a conversation on advancing women’s leadership in science, showcasing a wealth of power-packed insights and success stories.
On August 15, 2023, CIMMYT organized the third series of the Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science virtual seminar for a conversation on advancing women’s leadership in science, showcasing a wealth of power-packed insights and success stories.
Featuring Catherine Bertini, an accomplished leader in international organization reform and a powerful advocate for women and girls, the TED talk meets fireside chat style seminar began with a pre-recorded message from Catherine highlighting how women as catalysts of change can play an essential role in breaking through gender barriers in leadership roles. “Each of us must define for ourselves what’s important to us. We should assume opportunities to lead and to improve. We need to reach out, look forward and say, I’m going to make a difference. We can all be a catalyst for change,” stated Catherine, the 2003 World Food Prize laureate.
CIMMYT Director General Bram Govaerts highlighted the importance of recognizing the immeasurable contributions of women leaders in science. “We want more women leaders in organizations like CIMMYT. Through the recently launched CIMMYT 2030 Strategy, we are taking one step further in ensuring that gender equality isn’t just a concept but a reality, he reiterated. “The CIMMYT 2030 Strategy leverages a systems approach to overcome barriers to achieving gender equity by providing more opportunities to hear and learn from current women leaders in all capacities,” explained Govaerts.
“Girls can do anything,” Catherine set the scene for her presentation, showcasing personal stories based on her remarkable career and leadership journey. She detailed her distinguished career of improving the efficiency and operations of organizations serving poor and hungry people around the world. Sharing behind-the-scenes insights and actionable takeaways, Catherine wanted participants to walk away remembering, “here are some of the things that I have learned that I’d like to share with you today: engage in meaningful networking opportunities; be intentional about the impacts you want to create; understand your own tolerance level; be grounded in your principles, and champion inclusive leadership by mentoring others.”
Natalia Palacios, a member of the Woman in Science group at CIMMYT, interviewed Catherine. “Catherine’s contributions have been instrumental in enhancing food security, nutrition, and gender equality. Her advocacy has shed light on the crucial roles that women play in food production, family nutrition and community resilience—areas that are aligned with CIMMYT’s mission,” said Natalia. Responding to Natalia’s question on proud moments, Catherine talked about the Trust Fund she created with her World Food Prize to support programs that increased opportunities for girls and women to attend school. “I created the Catherine Bertini Trust Fund for Girls’ Education. There are some wonderful stories of support we’ve given. I learned that nobody should underestimate their potential to be a role model,” she added.
Catherine also addressed questions from session participants on how to build inclusive organizations through a learning culture; tips to help employees adapt to new technology in the age of artificial intelligence (AI); and approaches to manage culture change: how to find the balance and address tensions and trade-offs.
The third session ended with closing remarks from Bram who expressed his gratitude to Catherine for participating in the Catalysts of Change Seminar Series, highlighting her incredible leadership journey and unwavering passion in accelerating the advancement of women in leadership. “This was such an inspiring conversation. There are two take home messages for me: let us appreciate the contributions of those who came before us; and we need more dialogue and to listen to each other much more,” he concluded, underscoring CIMMYT’s commitment to changing the leadership equation through greater representation of women leaders at CIMMYT and CGIAR.
To learn more about Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science, click here to watch the seminar video or visit our website.









 In July 2023, CIMMYT launched a new seminar series on women’s leadership — Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science. Pitched as a ‘TED Talk meets fireside chat’, the series shines a spotlight on successful women who are leaders in their fields, providing a platform for them to share insights from their lives and careers. Taking into consideration the fact that leadership can take make many different forms, the talks will highlight women who are leaders in all sorts of disciplines and capacities.
In July 2023, CIMMYT launched a new seminar series on women’s leadership — Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science. Pitched as a ‘TED Talk meets fireside chat’, the series shines a spotlight on successful women who are leaders in their fields, providing a platform for them to share insights from their lives and careers. Taking into consideration the fact that leadership can take make many different forms, the talks will highlight women who are leaders in all sorts of disciplines and capacities.





 The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) hosted the first seminar of Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science, on July 4, 2023. This exciting seminar series, which supports women’s empowerment, features inspiring women leaders who share their expertise and perspectives on today’s women leadership styles, extending insights into their own leadership journey, and shedding light on the extraordinary impact of women leadership transforming today’s leadership through their critical roles as catalysts of change.
The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) hosted the first seminar of Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science, on July 4, 2023. This exciting seminar series, which supports women’s empowerment, features inspiring women leaders who share their expertise and perspectives on today’s women leadership styles, extending insights into their own leadership journey, and shedding light on the extraordinary impact of women leadership transforming today’s leadership through their critical roles as catalysts of change.