Roots of resilience: my journey as a Conservation Agriculture champion
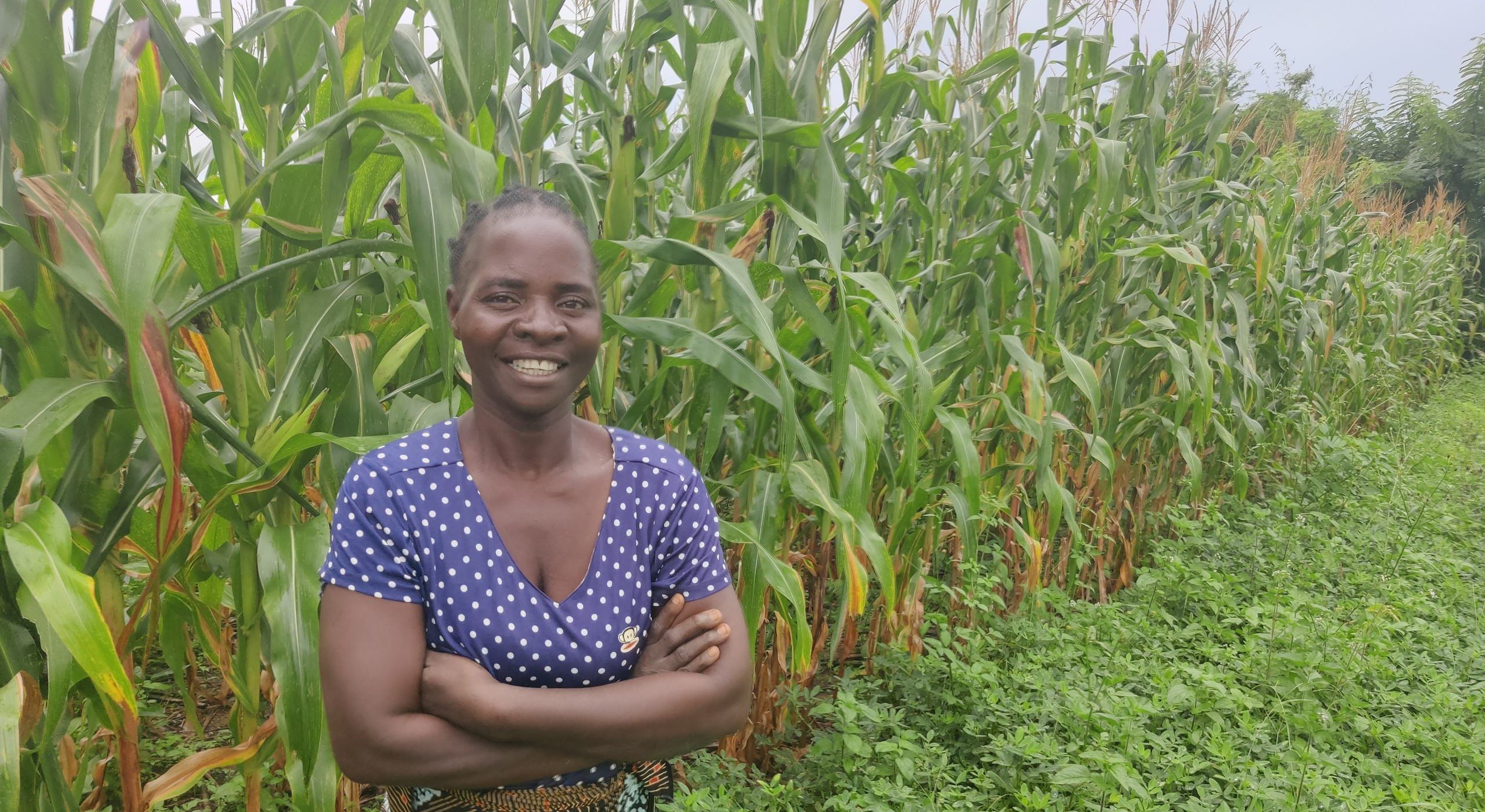
I am Grace Malaicha, a proud native of the Zidyana Extension Planning Areas in Central Malawi, where my journey with Conservation Agriculture (CA) began. In 2005, I observed neighboring farmers practicing CA techniques on their land. Intrigued and inspired, I decided to embark on this path myself, joining the CA program initiated by CIMMYT and Total LandCare in 2006. I started practicing it on my demonstration plot and observed that yields were getting higher from the second year onwards.
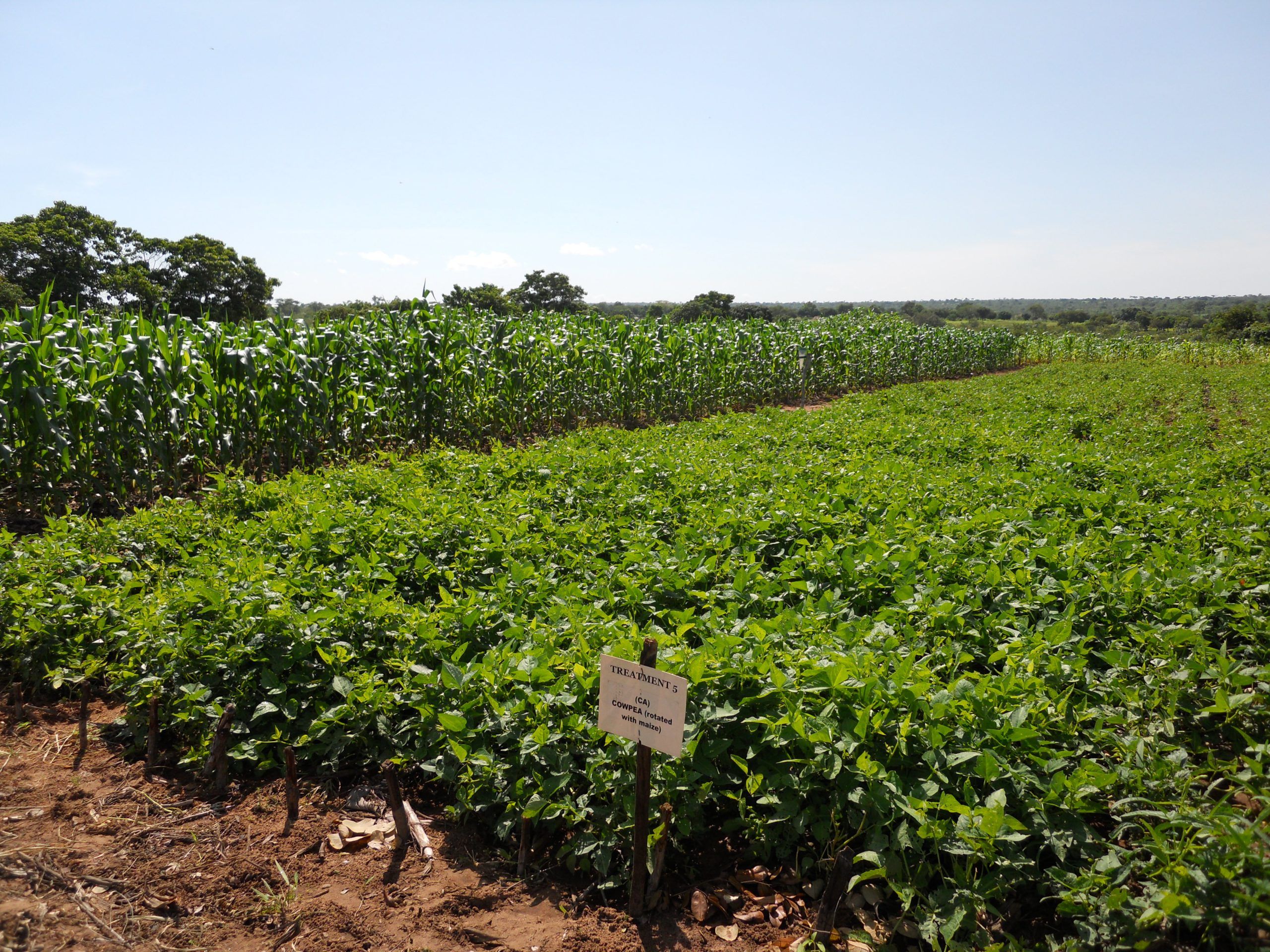
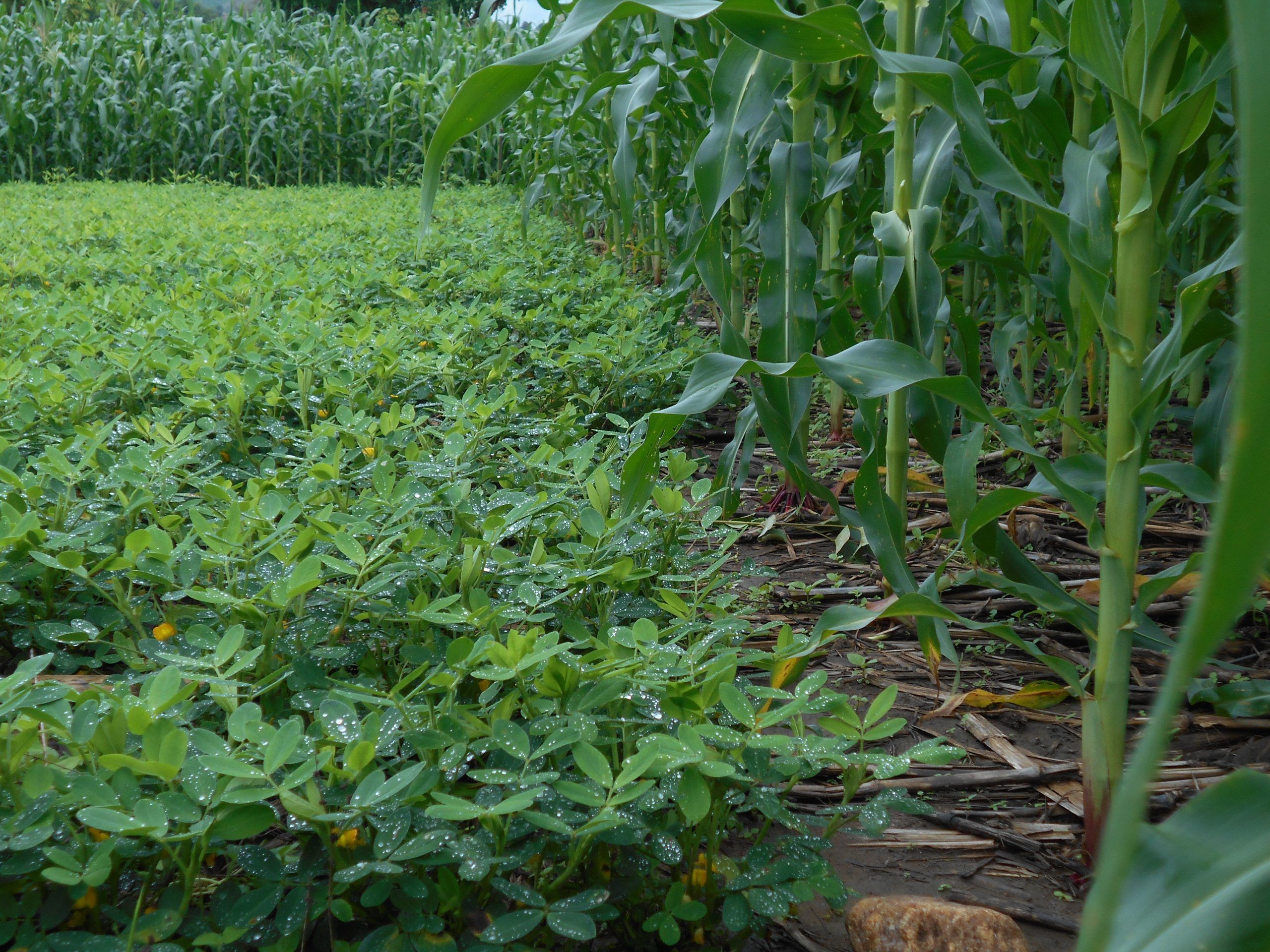
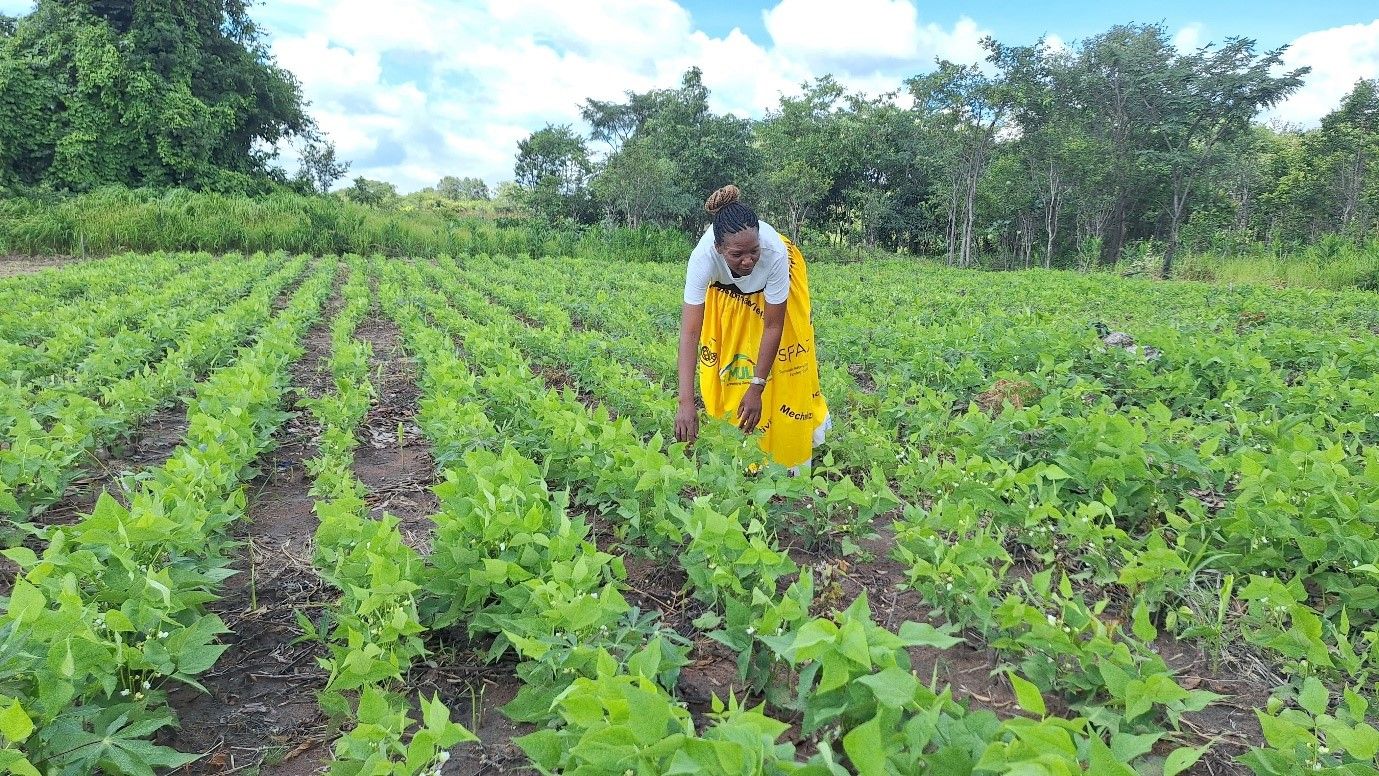
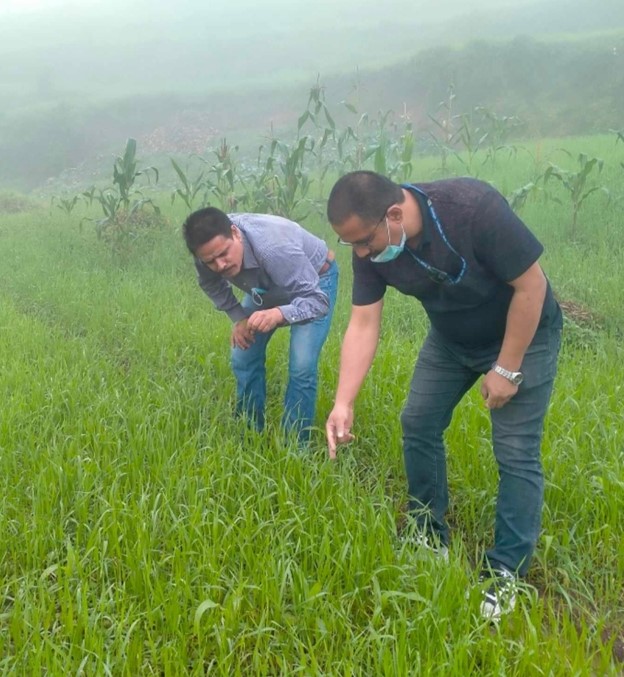
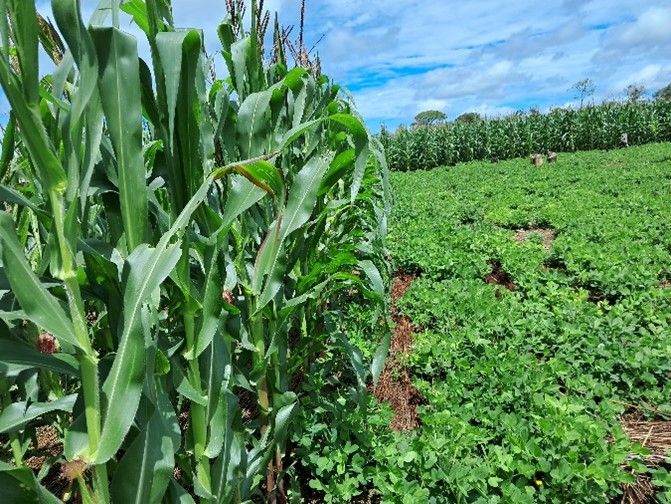
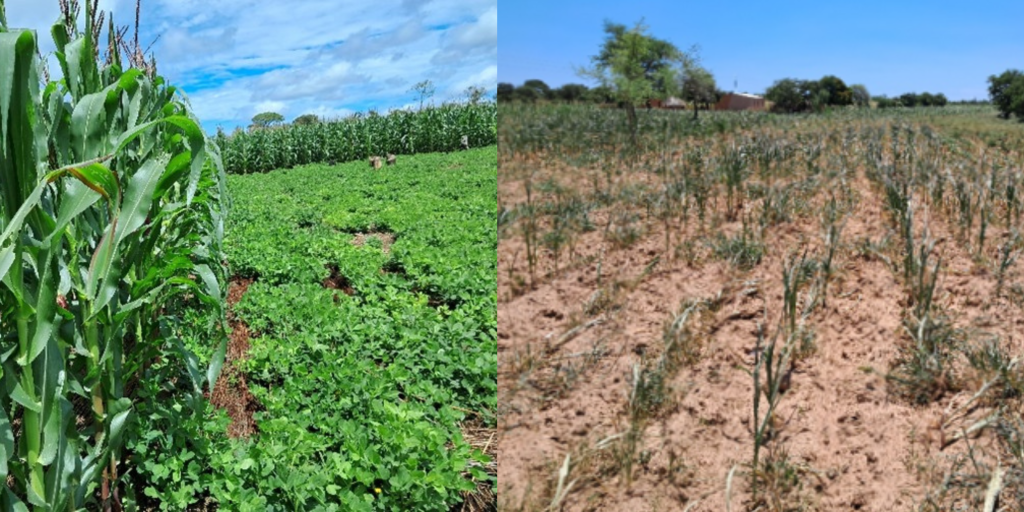
My dedication to CA has changed not only myself but also influenced other members of my farming community. As a mother trial host farmer under the CGIAR Initiative: Diversification for resilient agribusiness ecosystems in East and Southern Africa today, I have been implementing different treatments, which include maize doubled-up legume system and improved drought-tolerant maize varieties planted under CA on flat land and comparing it to the traditional ridge tillage system that involves substantial soil movement.
But what does CA mean to me? It is more than just a set of principles that I apply like minimum soil disturbance, mulching, and crop rotation. CA reduces drudgery, secures yields, and maintains productivity in times of climate change. CA has changed my approach to farming, transforming my once conventional maize monocrop into a diverse maize-legume system. By intercropping with two crops, I have spread the risk of unanticipated crop failure, while incorporating groundnut, cowpeas, and pigeon pea into the mix, which are more drought tolerant. I increased the land area under CA and tried it on many other crops including different legumes as rotation or intercrops, birds-eye chili, vegetables, and cassava.
Over the years, I have witnessed firsthand the harsh realities of a changing climate in central Malawi, from intense heat to prolonged droughts and erratic rainfall patterns. This year, 2024, has even been worse due to the prolonged dry spells between January and February, and the erratic rainfall during this time. Despite these challenges, our CA plots have continued to thrive, showcasing the resilience and adaptability of climate-smart farming practices.
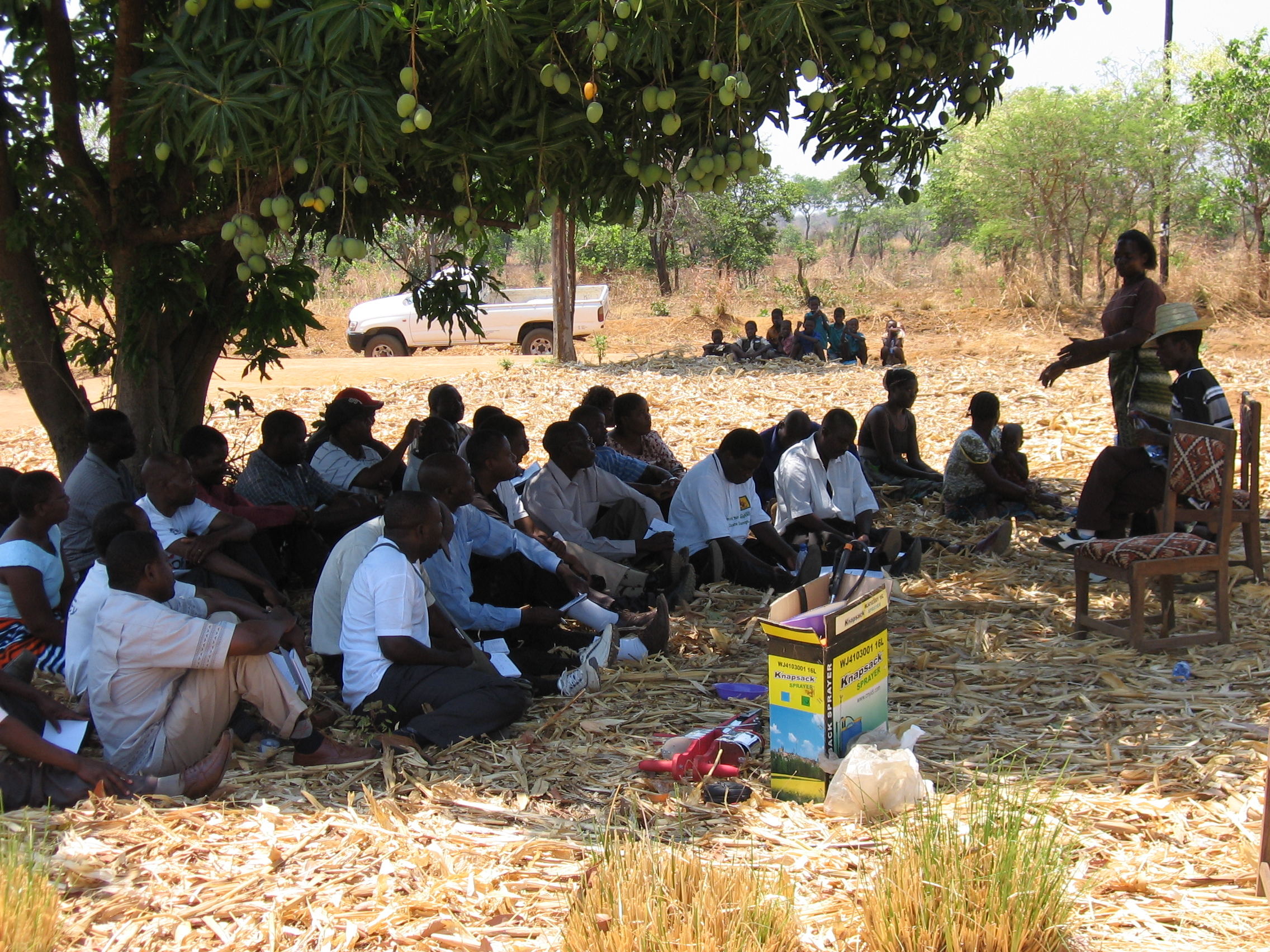

Recognizing the power of knowledge sharing and from the encouragement by CIMMYT and Total LandCare, I started to train fellow farmers, both locally and across borders. At first, I worked with women groups around my homestead and trained about 100 female farmers on the principles of CA. I was fortunate to be given the opportunity to train other farmers in other districts of Malawi. Since 2008, I have also trained farmers in eastern Zambia and from Mozambique where all farmers speak my language Chichewa. Farmers believe other farmers more and are now realizing the benefits of implementing CA in their own fields.
I enrolled to be a local trainer in CA within my community in 2016. My passion for teaching and catalyzing change has led to the adoption of CA by numerous farmers. I embrace my commitment to ongoing learning through carefully implementing these CA trials and playing an active role during awareness meetings.
My life had changed so much. I was speaking on the radio and television. In 2012, the Minister of Agriculture visited my plot, and I was asked to speak in front of a Parliamentary Committee about my experiences as a smallholder woman farmer in Malawi. I spoke about what women can do in agriculture and what changes I made on my land. From representing my country at high level meetings, each step has shaped me into a resilient and empowered woman.
However, my journey has not been without obstacles, including hardships in my personal relationship. In 2012, I made the decision to join my husband in South Africa where I took up menial jobs to earn a living, abandoning my plot back home. But my true passion lay in farming, and I decided to make the bold decision to come back home, leaving my husband and continue with farming. Through perseverance and determination, I have overcome these challenges, and I am now much stronger.
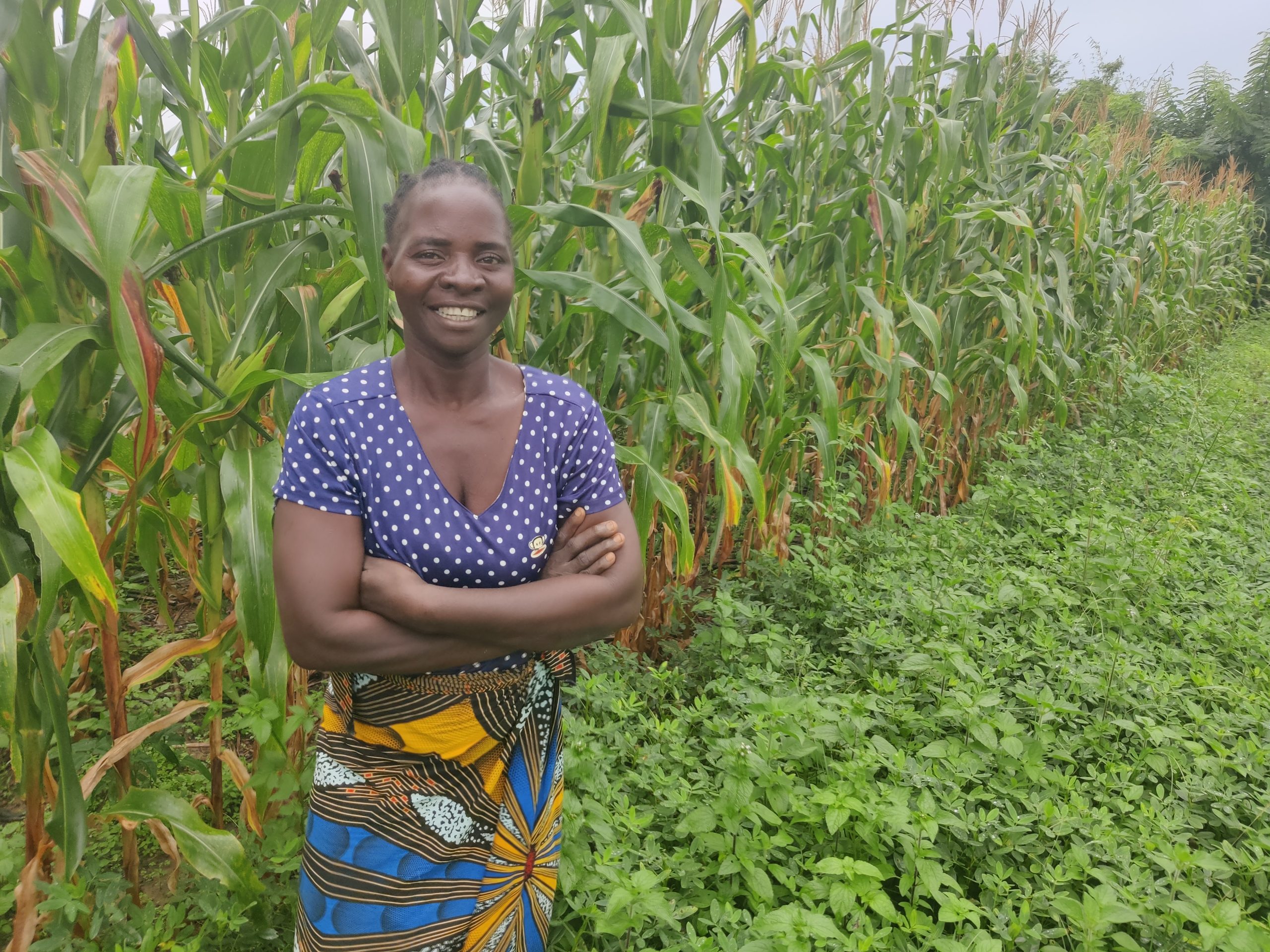

Today, I stand with pride in front of my CA plot, not only sustaining my family but also sending all my children to school. I now converted all my land to conservation agriculture, 3ha are under maize and 2ha under groundnuts. Beyond farming, I have investments in housing, claiming rentals in the nearby town of Salima to sustain my financial income and expand in farming.
I will continue on this path as I learned so much over the years and believe that CA may be the only climate-smart agriculture response in reach of smallholder farmers that everybody can apply, and I will continue to support others as a champion of CA.