Out of the classroom and into the field
When farmers in rural Kasungu, Malawi, are asked to list some of the challenges they face, much of what they say is to be expected. Crop pests, climate change, low soil fertility, and lack of improved seed and purchasing power — these are faced by smallholders across districts and the country as a whole.
But there is one surprising response. “Sometimes it’s difficult to get feedback from research centers on what does and doesn’t work,” says Maxwell Phiri.
Capacity building and knowledge transfer are key elements of agricultural development work, but there is often a gap between research, outreach and extension to farmers. New techniques and crop varieties tested at experimental stations can take a while to reach rural communities, who want solutions to the challenges they are facing in real time.
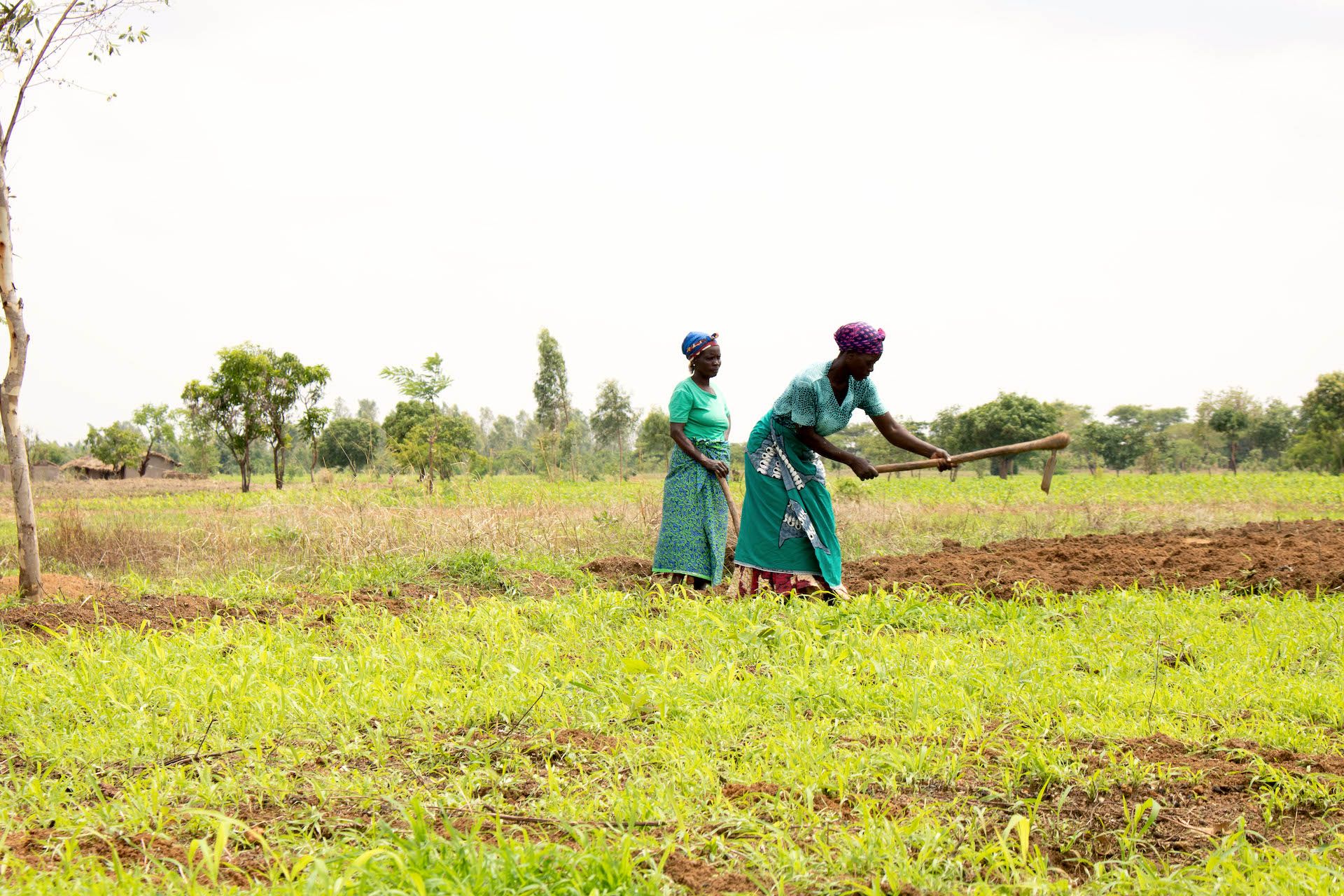
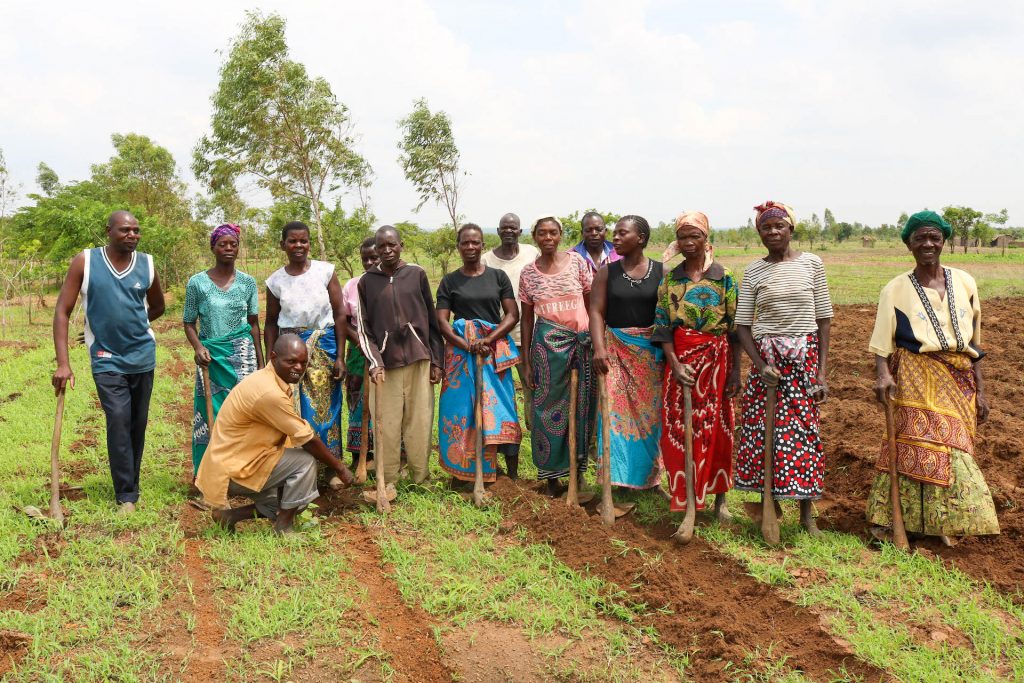
“But now it’s easier for us because the research is being done here.” Phiri points to the farmer field school in Msambafumu, a few hectares of communal land where 23 smallholders from the surrounding area meet regularly to learn about new technologies and farming techniques.
At the school they have been able to learn first-hand about improved and new agricultural practices and technologies. Following an introduction to climate-smart agriculture practices, they have moved on to agroforestry, learning about the benefits of intercropping drought-tolerant maize with pigeon peas and fruit trees. “We’ve even started practicing climate-smart agriculture in our own fields and planting agroforestry trees,” says Ntendeleza Mwale, a member of the field school in Msambafumu and chair of a network of 17 schools in the district. “Now everybody is growing fruit trees at home.”

Back to school
A farmer field school is a group of 25-30 farmers, led by a master trainer, who come together to solve common challenges faced in their local area, such as soil degradation or poor water availability. Since 2014, the Government of Malawi has been using this innovative approach to help farmers learn about and improve their production systems through the KULIMA project. With support from a CGIAR consortium led by the International Potato Center (CIP), 15 schools have been established across the districts of Kasungu, Mulanje and Mzuzu, including master training hubs and outreach centers run by NGOs.
The overall objective is to increase agricultural productivity and diversification by upscaling climate-smart technologies,” explains Mathinda Sopo, a monitoring and evaluation specialist and project manager at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT). “Master trainer candidates are selected in each district and then invited to sit down with researchers and identify their core production challenges. The plans are then developed collaboratively and based on agroecological zone.”
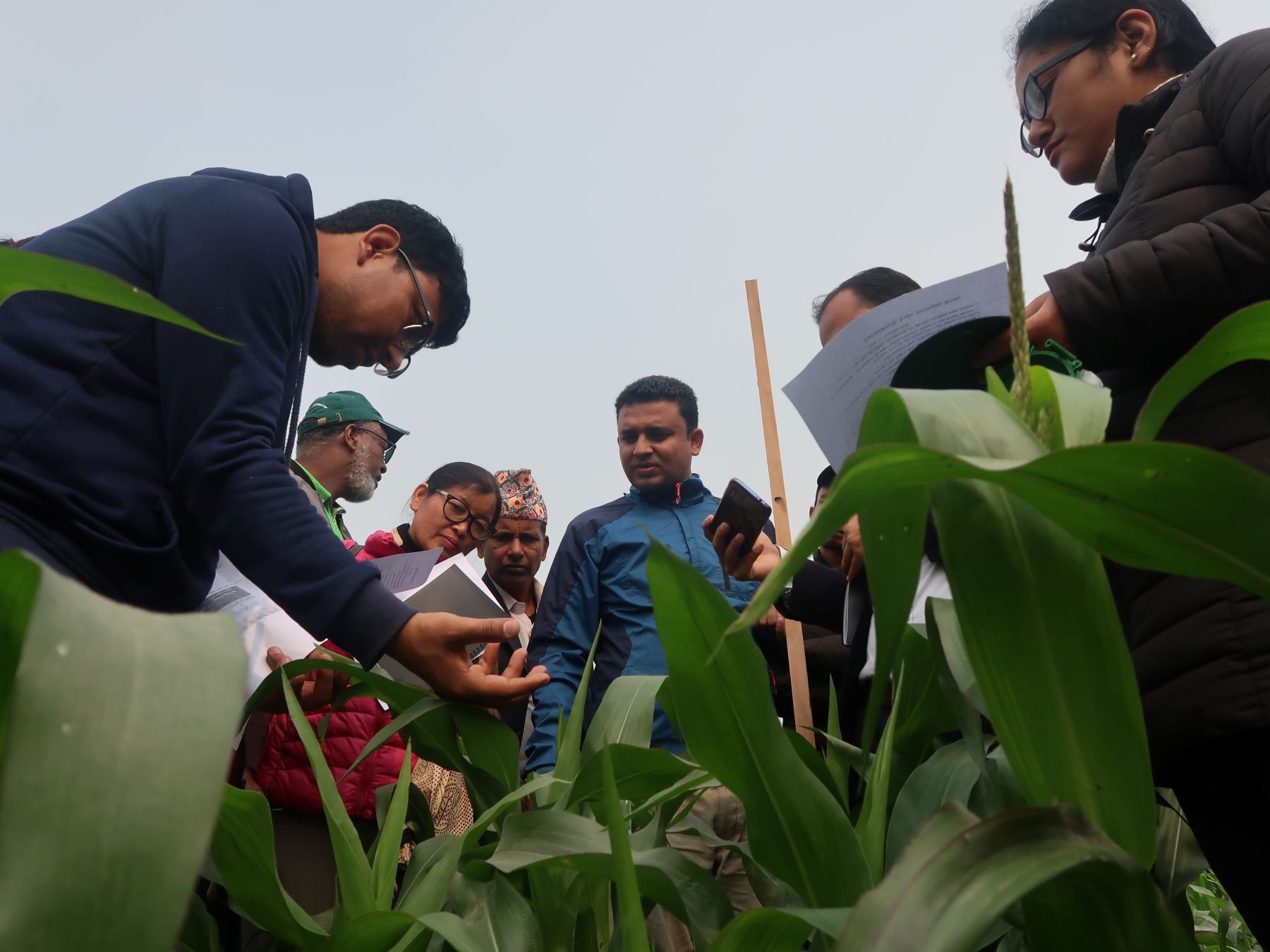
In February 2020, a new cohort of trainees arrived at the Lisasadizi Regional Training Center in Kasungu, where the Ministry of Agriculture coordinates trainings on four key topics — soil health, climate change, pests and diseases and nutrition — in collaboration with the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the CGIAR consortium, supported by the German development agency GIZ.
The 13-week residential course is mostly practical but does include some classroom-based study and a community outreach component. Guided by a facilitator — usually a researcher or extension worker — participants are encouraged to learn from their experiences as they conduct experiments in their own fields, make observations and evaluate results throughout the cropping season. Outside of the core curriculum, they are free to investigate additional topics of their own choice.
After completing the course, master trainers move back to their respective areas to help train facilitators, who are ultimately responsible for running the field schools with support from NGO extension staff.
“The CGIAR centers bring in technologies they want to promote like improved crop varieties, but there are ongoing evaluations throughout the process to respond to newly emerging challenges such as fall armyworm,” says Sopo. “There’s also a review at the end of each season to discuss lessons learned and knowledge gaps.”
CIMMYT, for example, is focusing on promoting drought-tolerant, quality protein maize (QPM), and provitamin A maize, as well as climate-smart agriculture practices. At Msambafumu, the group have been comparing five improved maize varieties with local ones. “So far we’ve seen that the new varieties have bigger yields and cob sizes,” says Mwale. “Varieties like Chitedze 2 QPM and MH43A are also early maturing and are more nutritious.”
Learning by doing
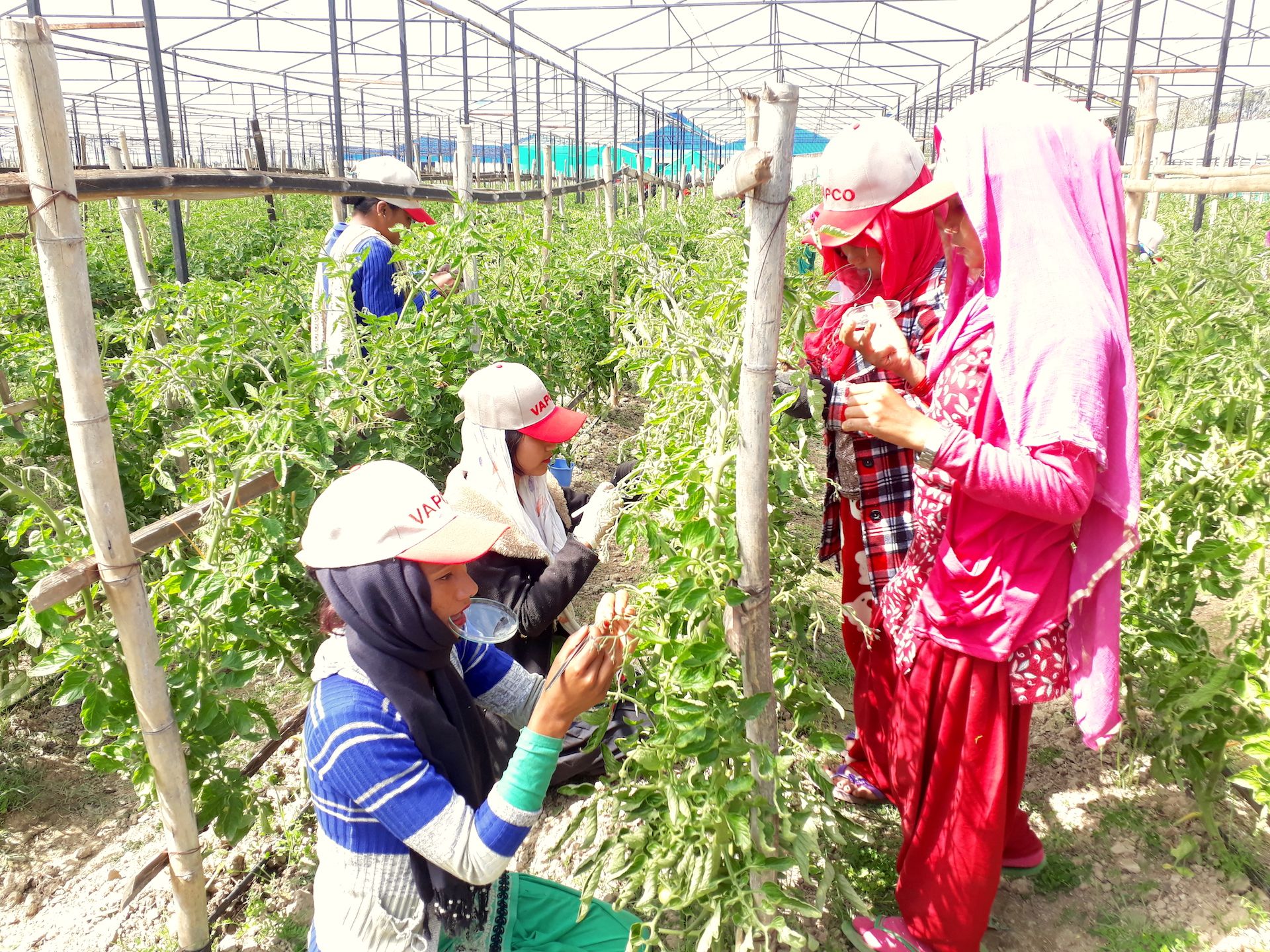
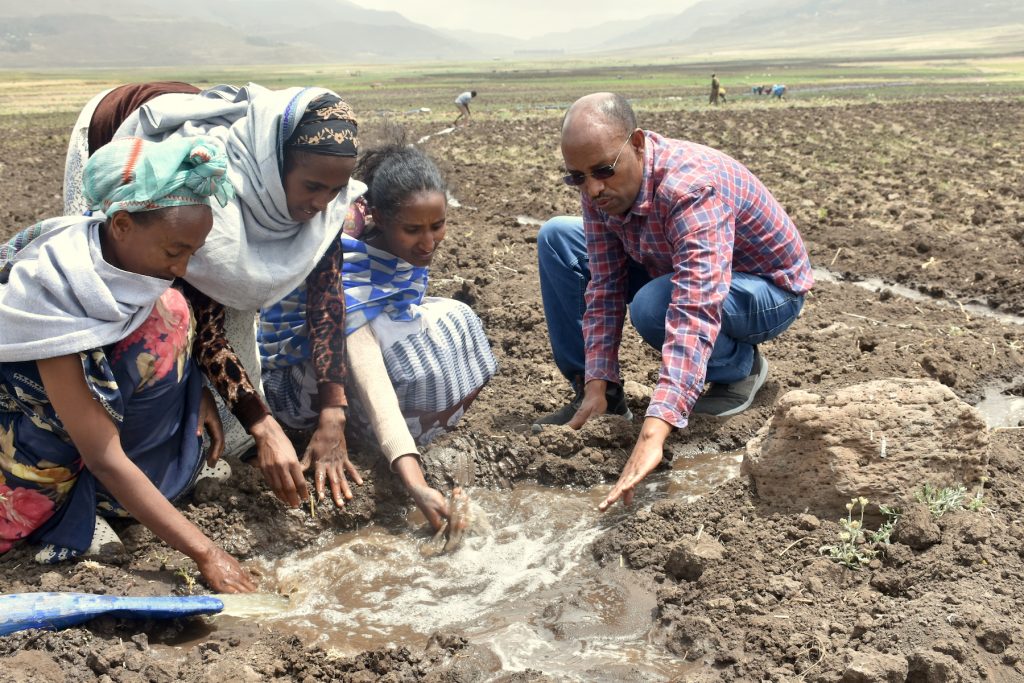
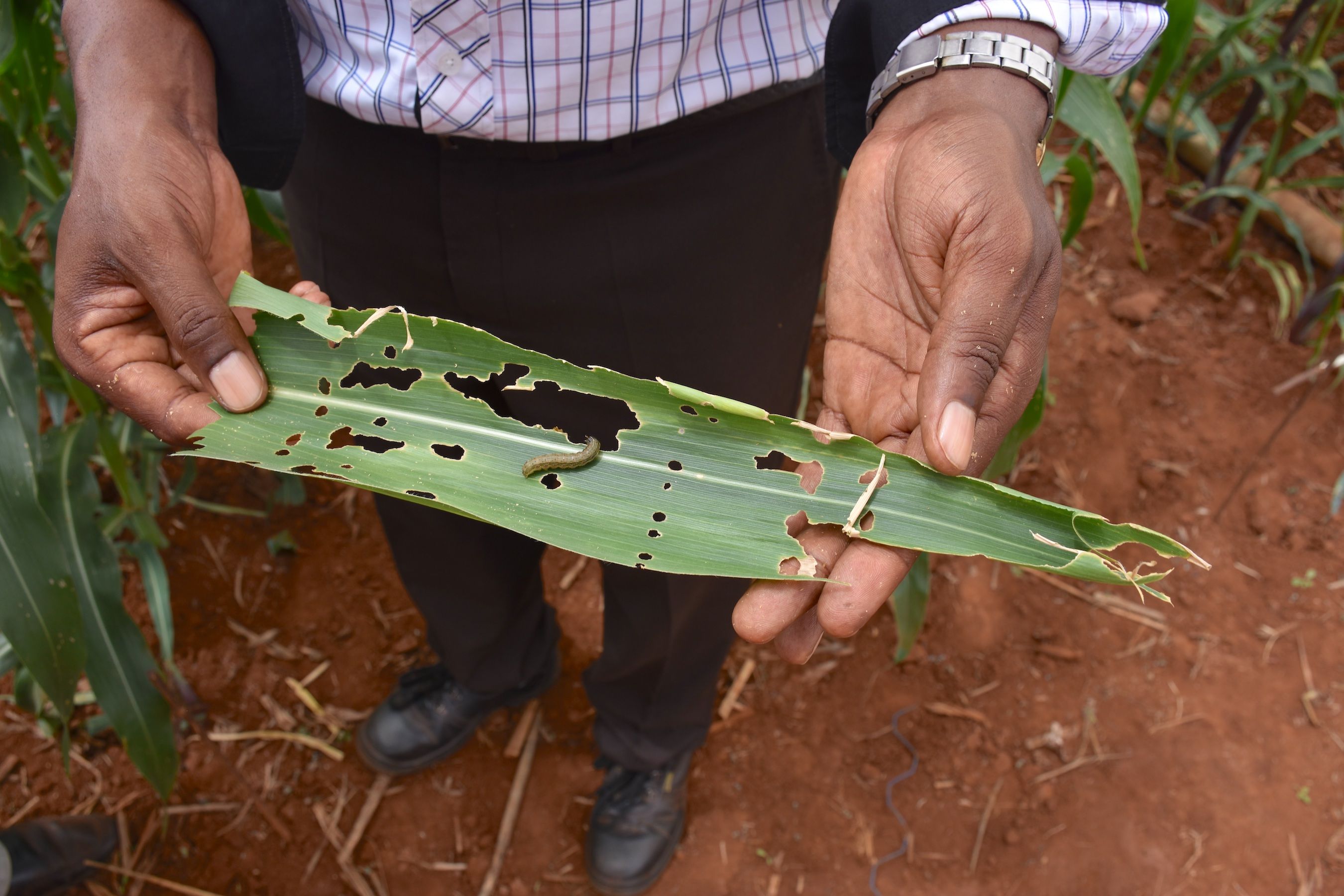
A few kilometers down the road, in Galika village, members of the Tiyese field school have been learning how to control a variety of pests and diseases. So far, they have been taught about different pesticides and the benefits of using inoculant on soya beans and ground nuts to improve soil fertility, and how to identify and mitigate disease in susceptible potato varieties. They have also been learning how to apply Aflasafe while crops are still in the field to reduce aflatoxins in maize and groundnuts.
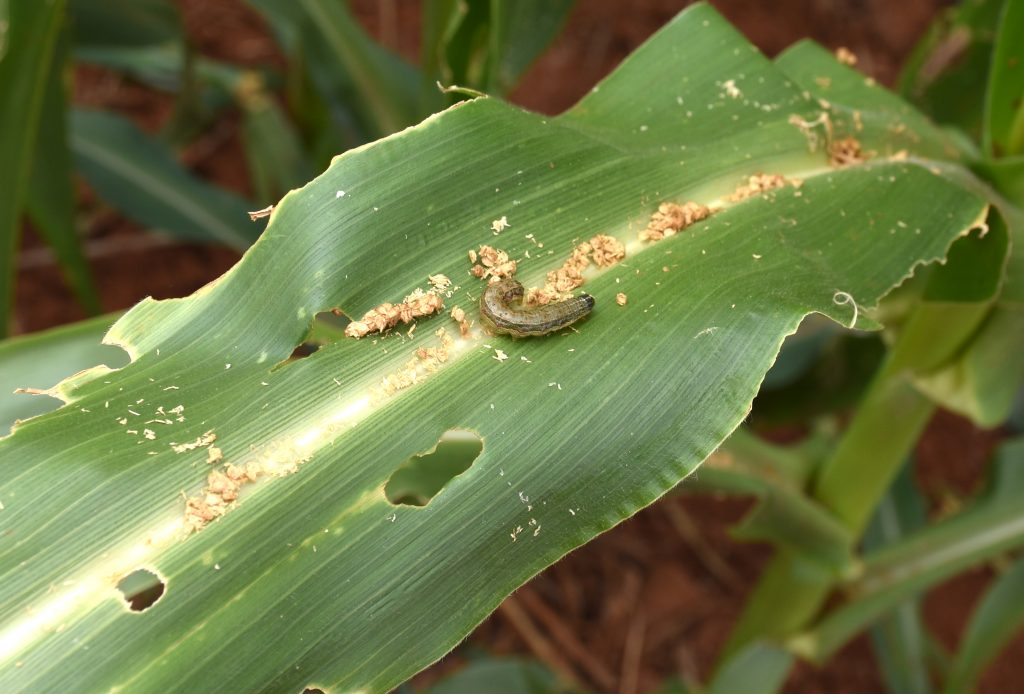
But the most pressing challenge is fall armyworm, says Matolino Zimba, a member of the Tiyese field school. “We’ve been trying new methods for controlling it,” he explains. “Last year we planted mucuna beans in our banana orchard as a cover crop. Later we soaked mucuna leaves in water and poured the solution on the infested maize and noticed that the worms were dying.”
Zimba is satisfied with the learning methods at the field school. “This approach is better for us because we get to see the process, rather than just receiving an explanation.”
Emily Kaponda agrees. She first joined the group after noticing that participating farmers were getting higher yields by using new planting methods. “The school has a smaller plot of land than I do, but their bundles of maize were much larger,” she explains.
Since joining the field school, she has learned how to increase her yields, how to conserve moisture in the soil using zero-tillage farming and the importance of diversifying her family’s diets. “We’re learning how we can use cassava or sweet potato as a starch, instead of only using maize.”
Zimba and Kaponda are both excited to be trying out QPM and provitamin A maize varieties, as well as new varieties of cassava, orange-fleshed sweet potato, improved groundnuts, biofortified beans and bananas. Much like their peers at Msambafumu, they had not known that many of these could be grown in the area, and the group has already started planning to multiply planting materials to use in their own fields next year.
“These groups are really inspirational,” says Sopo. “Most members are already practicing things they’ve learned at their school and are getting positive results.”
Sopo is already seeing success stories from schools established one year ago, but collaboration will need to be sustained to ensure lasting progress. A new research initiative, Development-Smart Innovations through Research in Agriculture (DeSIRA), will help to maintain the positive feedback loop by investigating emerging issues raised during on-farm experiments. “We can take farmer observations from the study plots to DeSIRA for further research, and the outputs from that will complement KULIMA.”