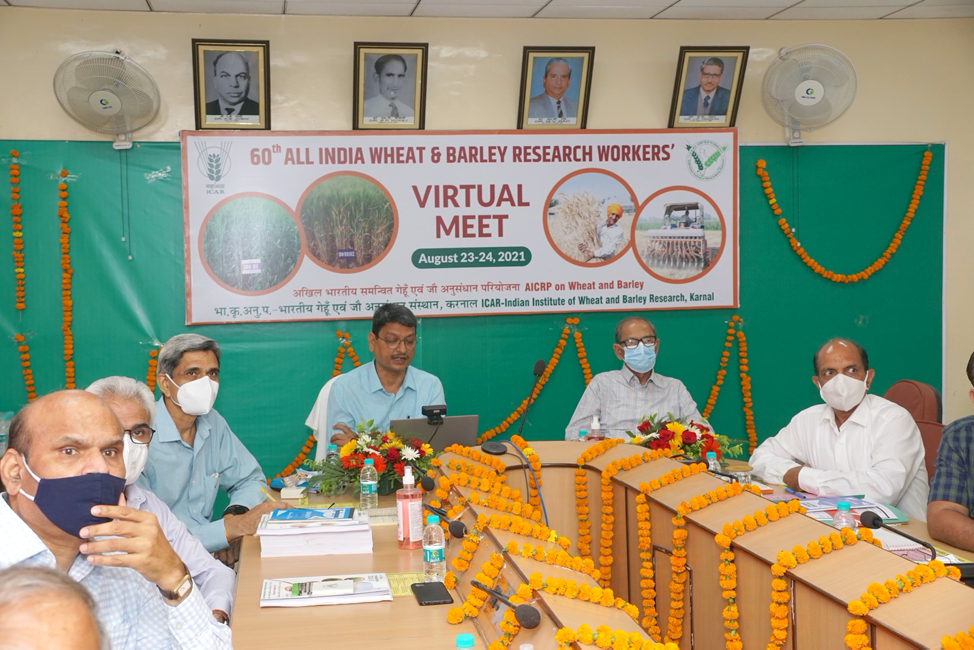
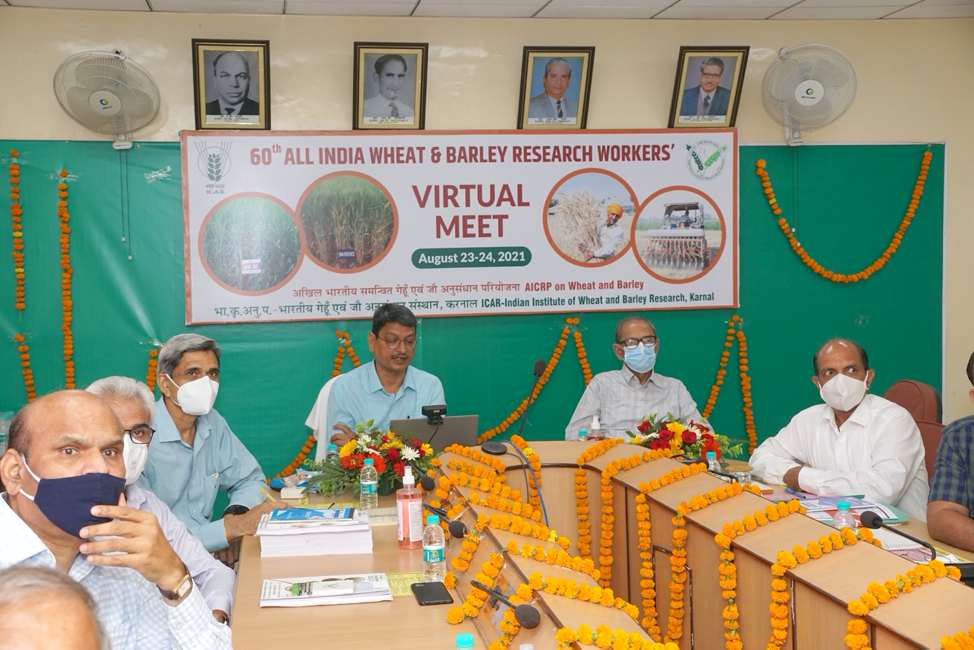
CIMMYT scientists join 60th All India Wheat and Barley Research Workers’ Meet

The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center’s (CIMMYT) legacy of work with the Indian Centre for Agricultural Research (ICAR) has once again produced more successful collaborations this year. This solid partnership resulted in the release of new varieties poised to bring new, superior yielding, disease-resistant, high-quality wheat varieties suitable for different production environments to Indian farms.
The National Variety Release Committee announced the release of nine new varieties at the 60th All India Wheat and Barley Research Workers’ Virtual Meet on August 23–24, 2021, hosted by the Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research (IIWBR) of ICAR. Of the nine new varieties identified, five were selected by national partners from CIMMYT international trials and nurseries.
At the event, ICAR-IIWBR director Gyanendra Pratap (GP) Singh highlighted the impressive growth trajectory of India’s wheat production, estimated at 109.52 million tons of wheat harvested in 2021, a figure which was 86.53 million tons in 2015 and less than 60 million tons in 1991. Singh highlighted that this success is dependent upon the deployment of superior wheat varieties, bridging yield and information gaps, strengthened seed value chain, supportive government policies and, of course, farmer support to adopt new varieties and technologies.
The CIMMYT-derived varieties announced at the meeting include DBW296, DBW327, DBW332, HUW296 and JKW261. A few days earlier, variety PBW869 was released by the Punjab Agricultural University for growing in Punjab State under conservation agriculture practices.
“An innovative and powerful feature of ICAR-CIMMYT collaboration has been the introduction of long-term (10-month) rotational involvement of Indian young scientists in CIMMYTs breeding program at Mexico as well as in wheat blast screening in Bolivia,” said Arun Joshi, CIMMYT Regional Representative for Asia and Managing Director, Borlaug Institute for South Asia (BISA). “In this way, the breeding program of CIMMYT is an excellent example of joint breeding program with national institutions.”
Beyond expectations
In addition to these important new wheat varieties, some CIMMYT-derived wheat varieties that were released in recent years have now been deemed suitable for regions beyond their initial region of cultivation, showing wide adaptation and yield stability.
Wheat variety DBW222, released in 2020 for the northwestern plain zone, has now been deemed suitable for cultivation in the northeastern plain zone. Similarly, DBW187, which was initially released for the northeastern plain zone, and then for northwestern plain zone as well for early sowing, is now also extended for sowing in the central zone, together representing 25 million hectares of the 31 million hectares of wheat grown in India.
“Farmers prefer these types of varieties that give them flexibility during sowing time, and have high, stable yields, and disease resistance,” GP Singh said at the meeting.
A major achievement discussed at this year’s event was that three of the new varieties — DBW187, DBW303 and DBW222 — achieved record-high demand in Breeders Seed Indent, with first, second and seventh ranks, respectively. This is a reflection and indirect measure of popularity and demand for a variety. IIWBR’s innovative strategy to implement pre-release seed multiplication and create demand for seeds from new varieties has led to a faster turnover of improved varieties.
According to Ravi Singh, Distinguished Scientist and Head of Global Wheat Improvement at CIMMYT, the collaborators are “further expanding our partnership through the support from the Accelerating Genetic Gains in Maize and Wheat (AGG) and zinc-mainstreaming projects, to expand testing of larger sets of elite lines in targeted populations of environments of the four South Asian countries where various IIBWR-affiliated institutions shall expand testing in the 2021–22 crop season.” CIMMYT looks forward to continuing ongoing and new collaborations with the ICAR-IIWBR programs to deliver even faster genetic gain for yield and grain zinc levels in new varieties, he explained.
Speaking during the meeting Alison Bentley, Director of CIMMYT’s Global Wheat Program, highlighted the collaborative efforts underway as part of the AGG project to accelerate breeding progress. “Innovations and discoveries in breeding approaches are being rapidly made — with further investment needed — to quickly and equitably accumulate and deploy them to farmers,” she said.