Potential for independent performance information to shape farmers’ seed choice for hybrid maize: Insights from Kenya
Maize production in Kenya is a critical component of the country’s agriculture and food security. However, climate change poses a serious threat to its production. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect maize growth, reduce yields, and increase the incidence of pests and diseases.
Prolonged droughts and unpredictable rainfall can lead to crop failures, while extreme weather events can damage crops and infrastructure. As the climate continues to change, it is essential for Kenyan farmers to adopt resilient agricultural practices and more adapted seed products to safeguard maize production and ensure food security for the population.
For decades, seed companies as well as governments and donors have invested in maize hybrid breeding. Dozens of new hybrids have been made available to seed companies throughout East Africa for multiplication and distribution. These hybrids are designed and tested to outperform older hybrids in terms of yield under rainfed conditions, to include tolerance to drought and pests.
However, the potential impact of these investments has been hampered by the slow turnover of hybrids among farmers. Research has shown that, despite the availability of newer, higher-performing varieties, farmers tend to purchase older, less productive hybrids. The ‘turnover problem’ in Kenya has been described by CIMMYT researchers in a recent publication.[1]
One of the constraints responsible for the low turnover of varieties is a lack of information among farmers on the performance of the newer products. Despite advancements in the development of new seeds and the retail infrastructure to reach farmers, neither the public nor the private sector is generating and disseminating information on the performance of different maize seed products across various agroecologies. Farmers therefore have choice overload but lack objective information on relative seed performance required to make informed seed choices across seasons and growing conditions.
CIMMYT conducted a field experiment to shed light on the potential influence of seed-product performance information on farmers’ seed choices. The study involved aggregating and packaging farmer reported yield data for some seed products and presenting this to randomly selected farmers at the point of sale to assess whether the new information would influence their choice of products. The study was conducted in Kirinyaga and Embu counties where, like many parts of Kenya, farmers have access to a diverse range of maize seed products from seed companies which promise benefits like higher yields and improved resilience but lack objective information on their performance which could support their choices, including when to switch and to what.
[1] https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0030727019900520

The experiment
The study was conducted in March 2024, at the onset of the long rain season. The research team collaborated with 36 local agro-dealers in five towns and surveyed over one thousand farmers. Farmers were intercepted as they approached the agro-dealer outlets and briefed about the study. Upon consent, they were informed on the benefits of trying something new (experimenting with varieties) and were offered a voucher for one free bag of maize seed to encourage them to try a seed product new to them. They then were randomly assigned to two experimental groups: treatment and comparison. Participants in the treatment group were shown a chart containing product-specific yield data on maize hybrids grown in their counties (see the chart below). The chart contained farmer-reported yields from the previous year’s long rain season aggregated at two levels: county average yield and the average yield of the top 25% of farmers who realized the highest yields. The latter demonstrated the actual potential of a seed product. They were asked that, if they wished, they could choose the voucher product for experimentation from the list but they were not required to. Participants in the comparison group were offered placebo information that would not affect their seed choice: they were given some fun facts about Kenya and agriculture in Kenya. We assess the effect of the information on the choice of the bag of seed they were buying with the voucher to experiment with.
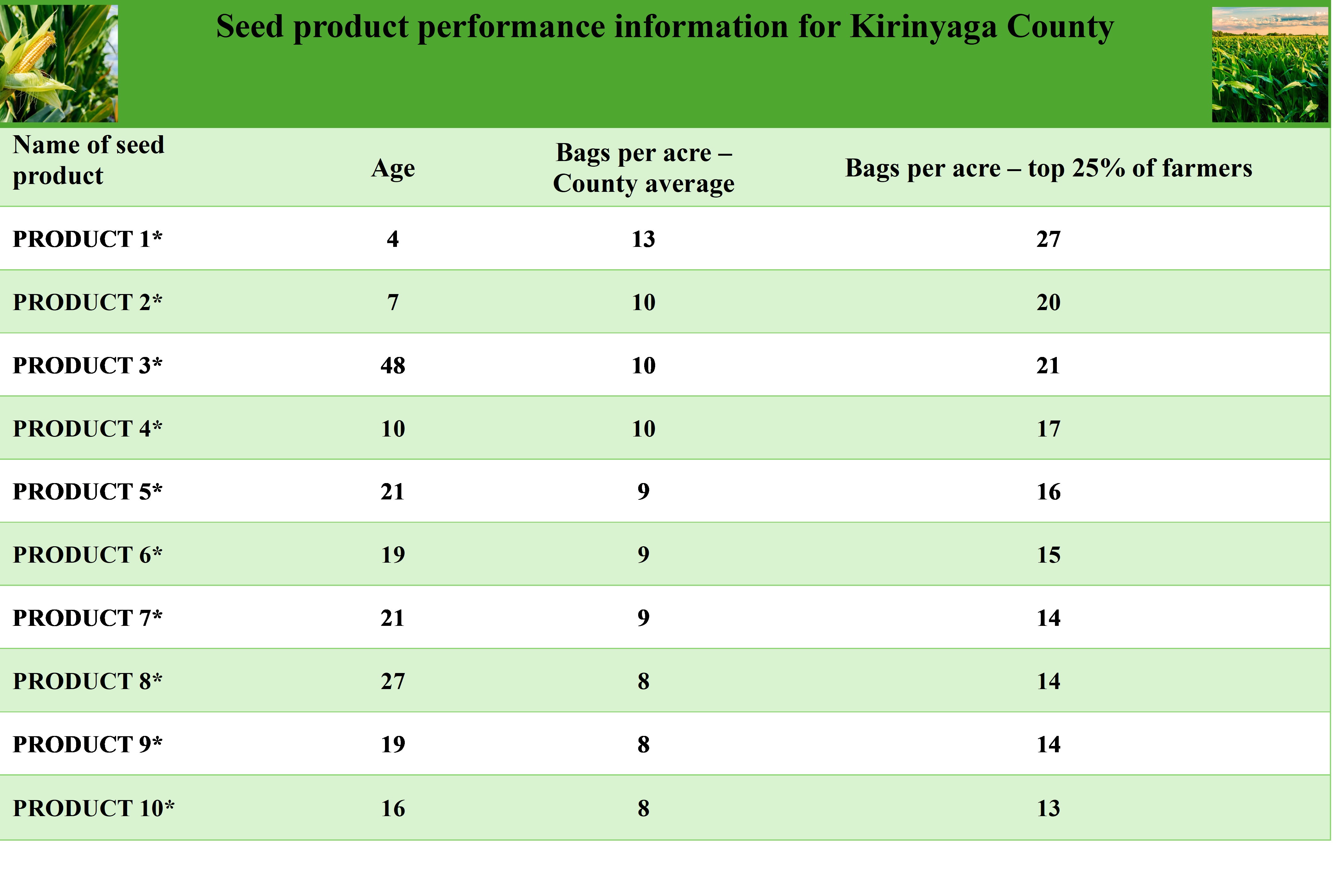
Before they made any purchases, the customers were asked about which maize seed they intended to buy. After purchase, they were interviewed again to find out which maize seeds they bought and how they had used the voucher.

What we found
Majority of the treatment farmers had a very positive evaluation of the information they received, indicating that they found it relevant and useful when making seed choice. Specifically, over 90% of them said that the information was trustworthy and easy to understand while about 80% said that the information was easy to recall. Over 80% of them disagreed that the list of varieties was too long to comprehend, the information on varieties was similar and hard to differentiate and that it was hard for them to choose a variety from the list.
This positive evaluation of the information is also reflected in their seed choices. Pre-purchases (before they entered the agrodealer store), farmers who were exposed to the performance information showed increased certainty in their choices and a higher inclination towards products listed in the product performance data, particularly the top-performing varieties. While 5% of the comparison farmers indicated that they did not know what to buy with their vouchers, only 2% of the treatment farmers suffered the same uncertainty. Such farmers relied mostly on agro-dealers to recommend a product they could experiment with.
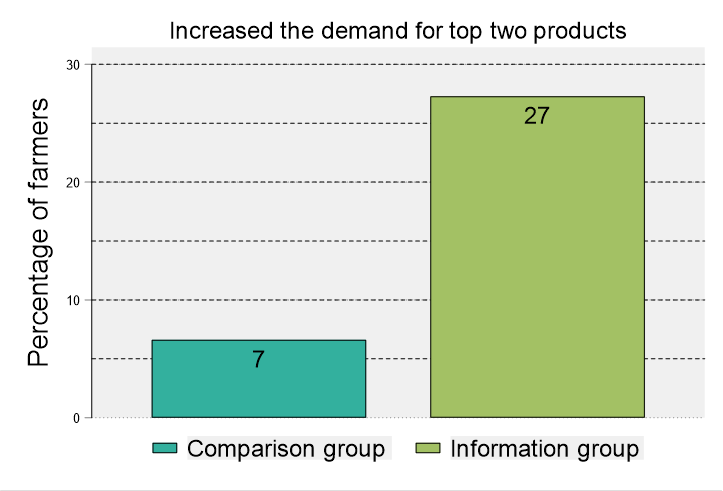
As shown by the bar chat below, only 7% of comparison group farmers desired to use their vouchers on (or had an effective demand for) products which were the top two in the product performance lists. This increased to 27% among the information group farmers, representing an increase of 286% in the demand of top performing products.
However, although our intervention relaxed an essential constraint (product performance information) and increased the demand for some seed products, the actual purchases were subject to other constraints, stock-outs key among them. As a result, both groups showed shifts from initially desired products in their actual purchases. Even so, the treatment group maintained a stronger alignment with the listed products, exhibiting a higher likelihood of purchasing top-performing products. Only 5% of farmers in comparison group used their vouchers to purchase products which were top two in the product performance lists. This increased to 13% among farmers in the treatment group, representing a 160% increase in the likelihood of purchasing the best performing products in the lists.
Reflections
Slow varietal turnover among maize farmers in E. Africa is a pervasive problem and there is no one solution to it. This research shows that information on product performance can be an effective approach in bringing to the attention of farmers newer, more adapted and better yielding seed products. Dissemination of such information can be incorporated in extension programs, shared at the point of sale, shared through SMSs and WhatsApp messages, displayed in posters fixed in public places, etc.
The findings offer clear recommendations for future investments in seed systems development. These include the implementation of new product testing regimes to ensure quality and objectivity of performance data, testing what other information would be useful to farmers – beyond yield data, exploring new marketing options to reach farmers more effectively, and considering additional approaches to empower farmers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions thus leading to improved agricultural productivity, resilience, and livelihoods.




