Wheat Disease Early Warning Advisory System (DEWAS)
The Wheat Disease Early Warning Advisory System (Wheat DEWAS) project is bringing new analytic and knowledge systems capacity to one of the world’s largest and most advanced crop pathogen surveillance systems. With Wheat DEWAS, researchers are building an open and scalable system capable of preventing disease outbreaks from novel pathogen strains that threaten wheat productivity in food vulnerable areas of East Africa and South Asia.
The system builds from capabilities developed previously by multi-institutional research teams funded through long-term investments in rust pathogen surveillance, modelling, and diagnostics. Once fully operationalized, the project aims to provide near-real-time, model-based risk forecasts for governments. The result: accurate, timely and actionable advice for farmers to respond proactively to migrating wheat diseases.
The Challenge
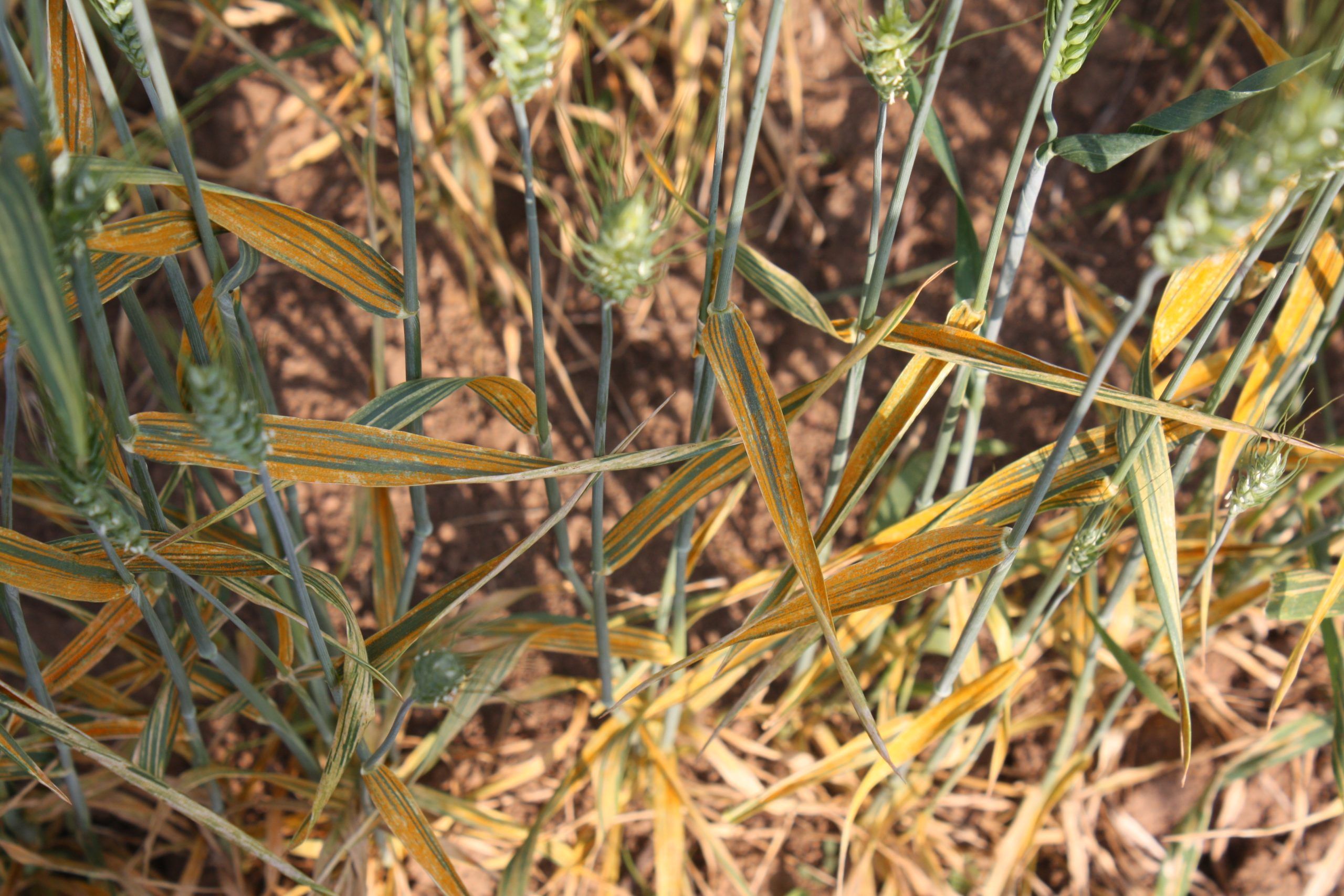
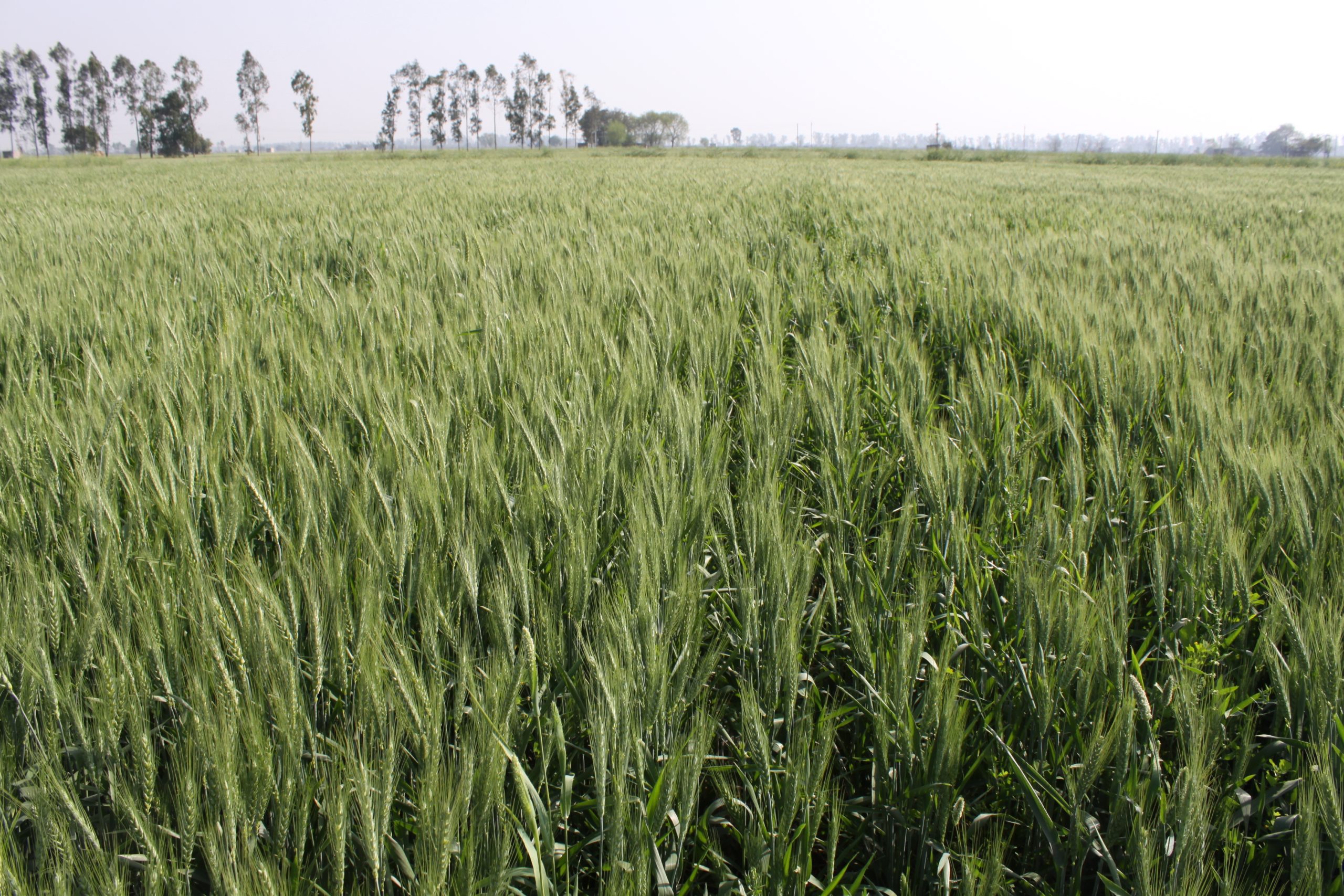
Farmers growing wheat face pathogen pressures from a range of sources. Two of the most damaging are the fungal diseases known as rust and blast. Rust is a chronic issue for farmers in all parts of the world. A study in 2015 estimated that the three rust diseases — stem, stripe and leaf — destroyed more than 15 million tons of wheat at a cost of nearly $3 billion worldwide. Wheat blast is an increasing threat to wheat production and has been detected in both Bangladesh and Zambia. Each of these diseases can destroy entire harvests without warning, wiping out critical income and food security for resource-poor farmers in vulnerable areas.
The Response
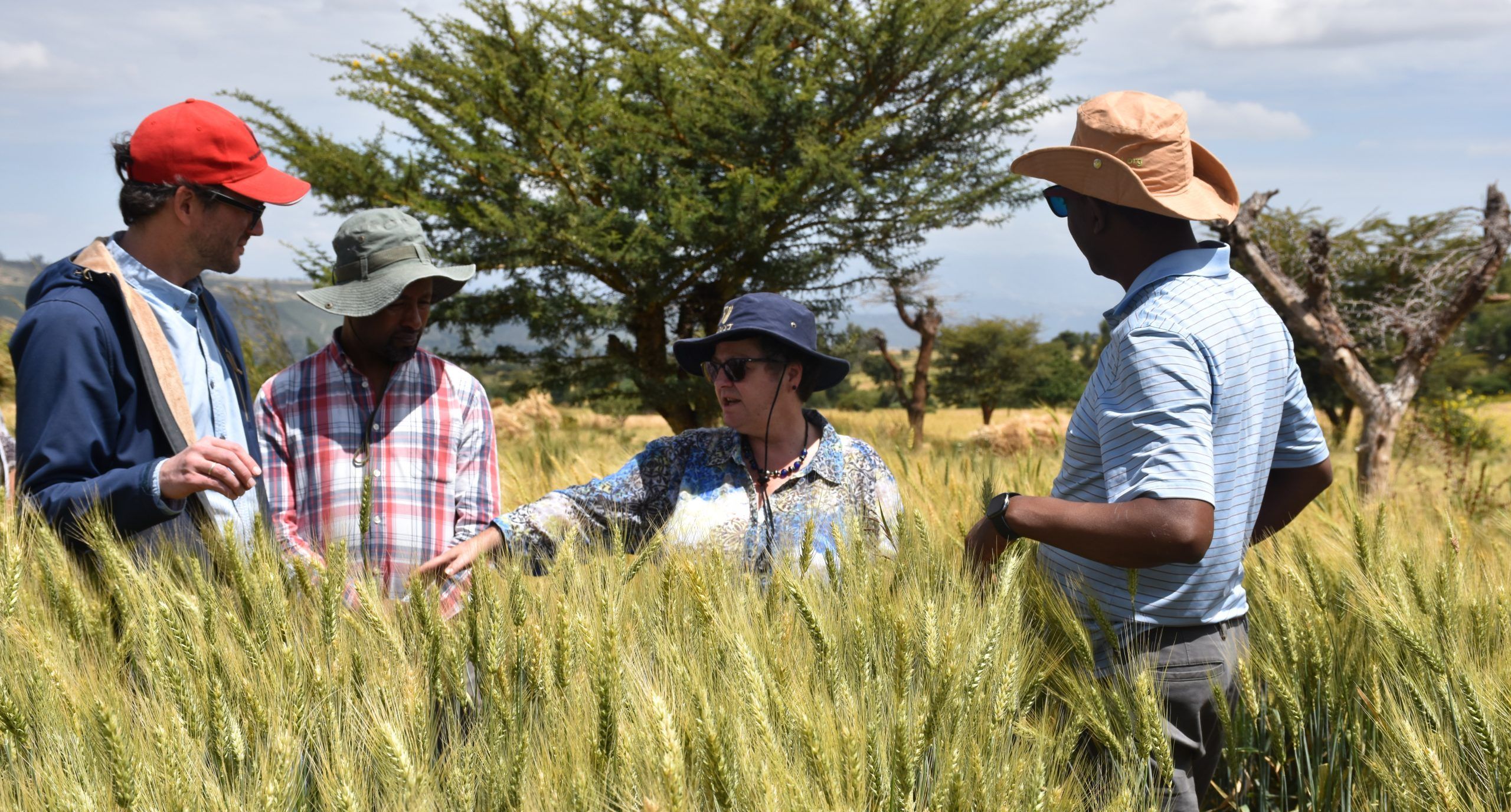
Weather forecasts and early-warning alerts are modern technologies that people rely on for actionable information in the case of severe weather. Now imagine a system that lets farmers know in advance when dangerous conditions will threaten their crop in the field. Wheat DEWAS aims to do just that through a scalable, integrated, and sustainable global surveillance and monitoring system for wheat.
Wheat DEWAS brings together research expertise from 23 research and academic organizations from sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, Europe, the United States and Mexico.
Together, the researchers are focused on six interlinked work packages:
| Work package | Lead | Objectives |
| Data Management | Aarhus University; Global Rust Reference Center |
|
| Epidemiological Models | Cambridge University |
|
| Surveillance (host + pathogen) | CIMMYT |
|
| Diagnostics | John Innes Centre |
|
| Information Dissemination and Visualization Tools | PlantVillage; Penn State |
|
| National Partner Capacity Building | Cornell University |
|
Wheat DEWAS partners
Academic organizations: Aarhus University / Global Rust Reference Center; Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University; Cornell University / School of Integrative Plant Science, Plant Pathology & Plant-Microbe Biology Section; Hazara University; Penn State University / PlantVillage; University of Cambridge; University of Minnesota
Research organizations: Bangladesh Wheat and Maize Research Institute (BWMRI); CIMMYT; Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE), Bangladesh; Ethiopian Agricultural Transformation Institute (ATI); Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR); ICARDA; John Innes Centre (JIC); Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO); National Plant Protection Centre (NPPC), Bhutan; Nepal Agricultural Research Council (NARC); Pakistan Agricultural Research Council (PARC); UK Met Office; Tanzania Agricultural Research Institute (TARI); The Sainsbury Laboratory (TSL) / GetGenome; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service; Zambia Agricultural Research Institute (ZARI)