Exploration of options for functional seed systems and understanding of market needs for cereals and pulses in sub-Saharan Africa

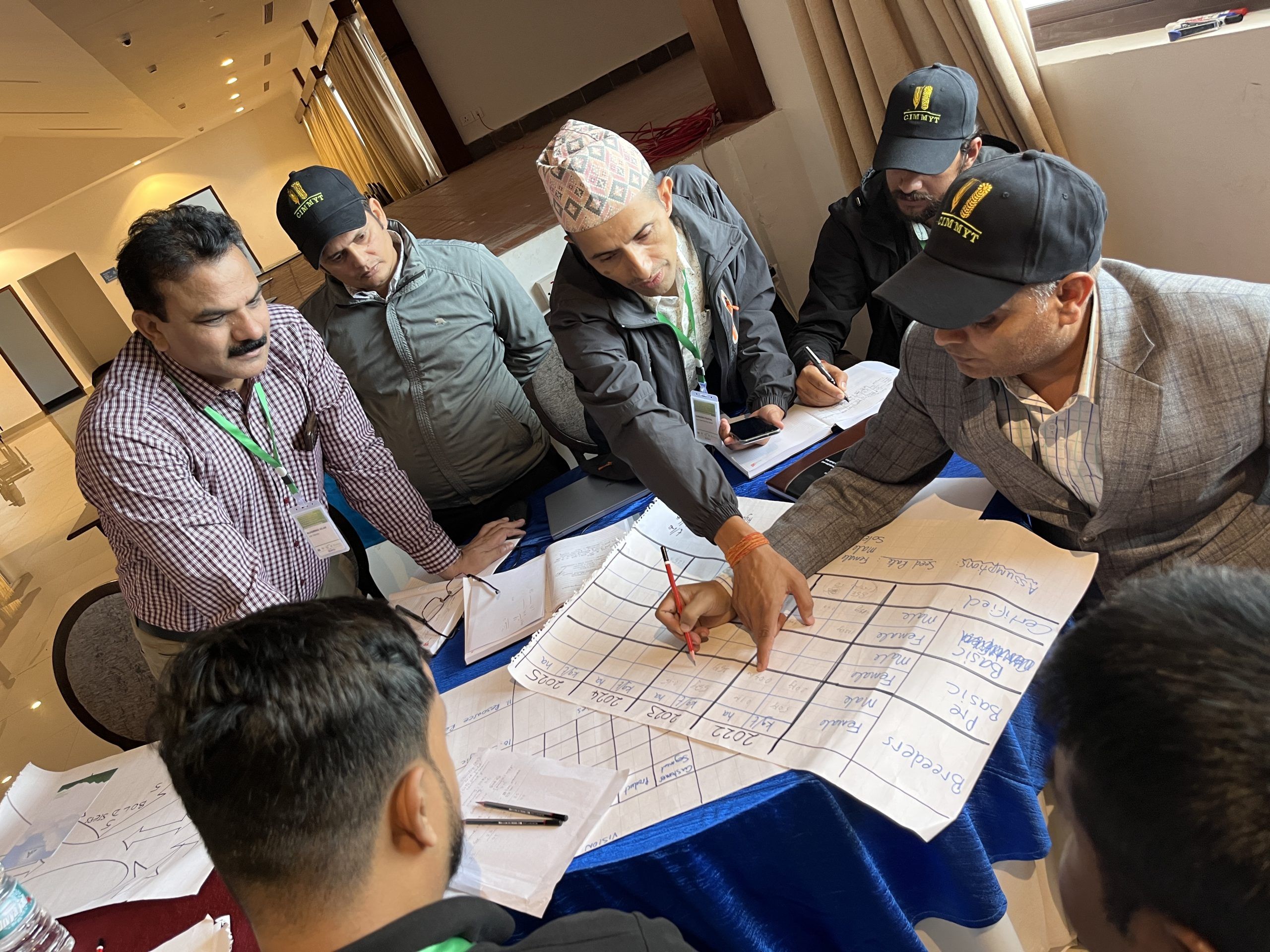
The Seed Systems and Market Intelligence Team of the Sustainable Agrifood Systems (SAS) Program convened for a three-day retreat in Kenya. The retreat provided an opportunity to review ongoing research on seed systems and market intelligence conducted across CIMMYT projcts and CGIAR initiatives.
The event featured oral and poster presentations highlighting key findings from current research activities, fostering constructive feedback from colleagues. Discussion focused on strengthening the team’s technical capacity and ensuring its responsiveness to CIMMYT’s research programs and the broader CGIAR science agenda.
During the retreat, team members presented research spanning a wide range of topics. One key area focused on understanding the demands of farmers, processors, and consumers, for future crop traits, with the aim of informing breeding systems programs to maximize their impact.
The team highlight challenges faced by agro-processors, such as rancidity in pearl millet, which affects the shelf life of processed millet flour. Research also explored groundnut processing across different countries, revealing varied market demands.
In Malawi, groundnut markets prioritize grain size, color and uniformity-driven largely by export requirements-while oil content is less of a focus. In contrast, Nigerian markets demand high oil content for kuli kuli production and show a preference for early maturing varieties. Meanwhile, in Tanzania, an emerging peanut butter market has created opportunities for new groundnut varieties tailored to this product.
Seed systems research in Kenya highlighted how information and economic incentives for farmers and agro-dealers can serve as effective policy options to boost the adoption of new maize hybrids. These strategies have the potential to increase the market share of newly introduced hybrids in the maize seed sector.
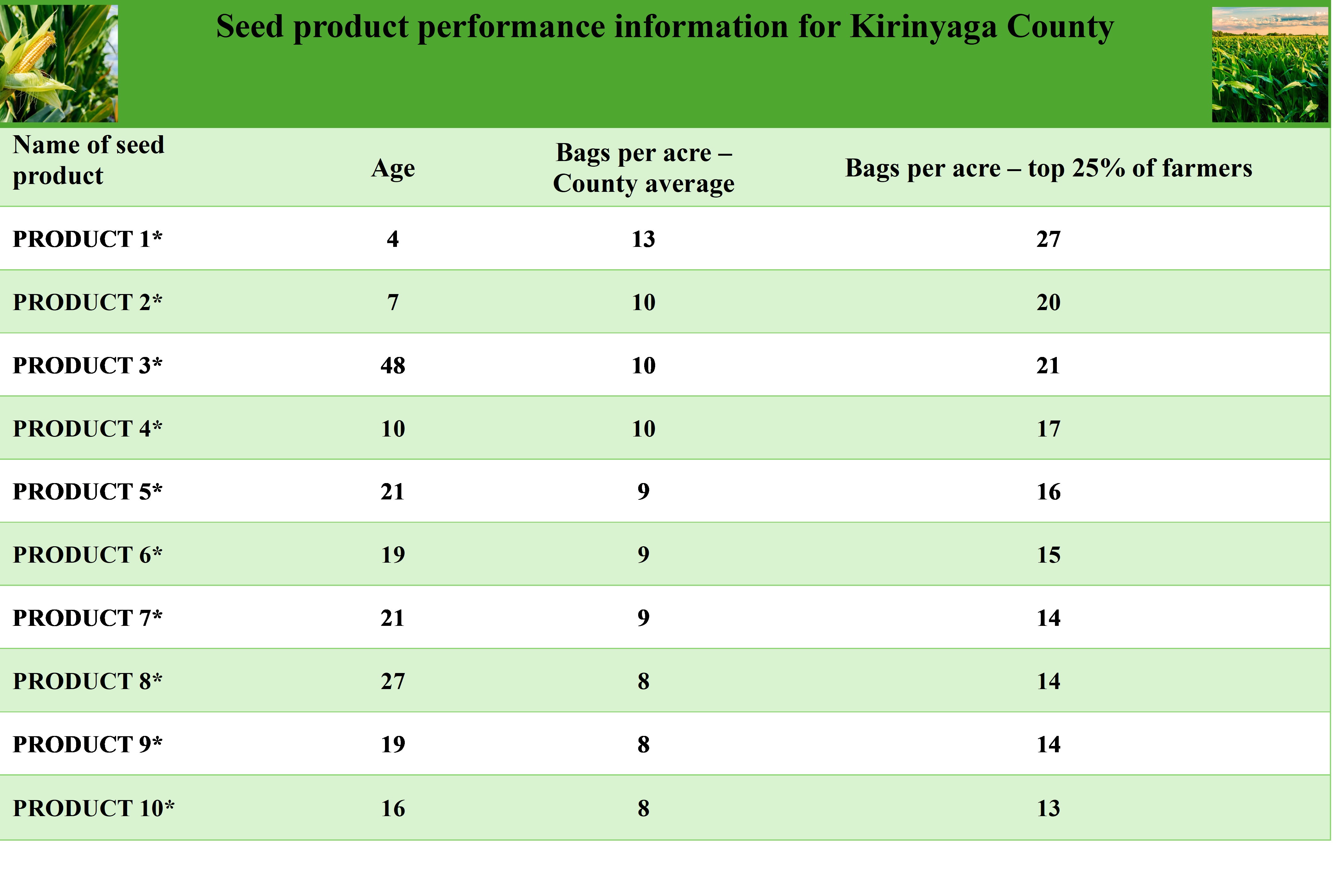
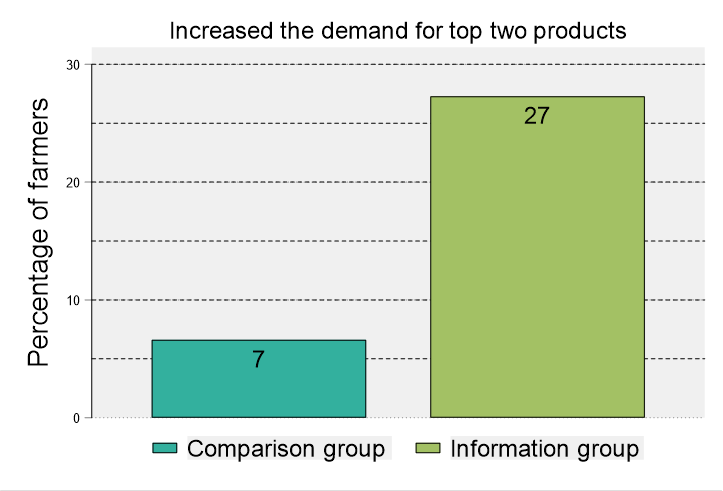
The team showcased the impact of providing variety-specific, independently evaluated yield data for commercially available seed products under local conditions to guide farmers’ seed choices. Additionally, they explored the use of rebates as incentives for agro-dealers to stock new products and actively encourage farmers to try them. The role of price discounts and targeted information at the retail level for newly released varieties was also discussed as a way to promote adoption among farmers.
Another key area of research focused on how farmers perceive existing promotional materials distributed by seed companies. Feedback indicated that most leaflets and posters were not visually engaging. Farmers expressed a preference for materials that include visuals of plant stands, cob sizes, yield potential, and other critical details, presented in local languages like swahili.
Looking ahead, the team outlined a new four-year project supported by the Impact Assessment Group under the Genetic Innovations Action Area. This initiative will build on the current findings to generate further evidence on how information can accelerate farmer adoption of new seed products. It will also examine the role of agro-dealers as key information agents to disseminate knowledge effectively to farmers.
The meeting also highlighted the assessment of varietal turnover in Ethiopia and the role of the DNA Fingerprinting (DNA FP) approach in improving the accuracy of varietal identification. Accurate data generated through this method supports more robust studies on varietal adoption, turnover, and impact. It also enables the assessment of whether released varieties are being cultivated within their target agro-ecologies and contributes to understanding varietal diversity within production systems.
Discussions emphasized the relevance of the DNA FP approach for accurate data collection and its potential for broader application beyond Ethiopia, Tanzania, and Nigeria, where the IMAGE project is currently active. Expanding its use to other regions would further strengthen research efforts in seed systems and market intelligence.
Paswel Marenya, associate program director of SAS Africa, commended the team for the depth and breadth of their research and encouraged greater visibility of results within CIMMYT and beyond. As a key outcome of the meeting, the team committed to increasing its visibility in seed systems and market intelligence research while building a stronger, more qualified team to achieve this goal.
In terms of staffing, the team has a solid presence in Africa but aims to expand its reach through enhanced resource mobilization. Efforts are underway to strengthen the Seed Systems and Market Intelligence team’s presence in other regions where CIMMYT operates, including Latin America (LATAM) and South Asia.