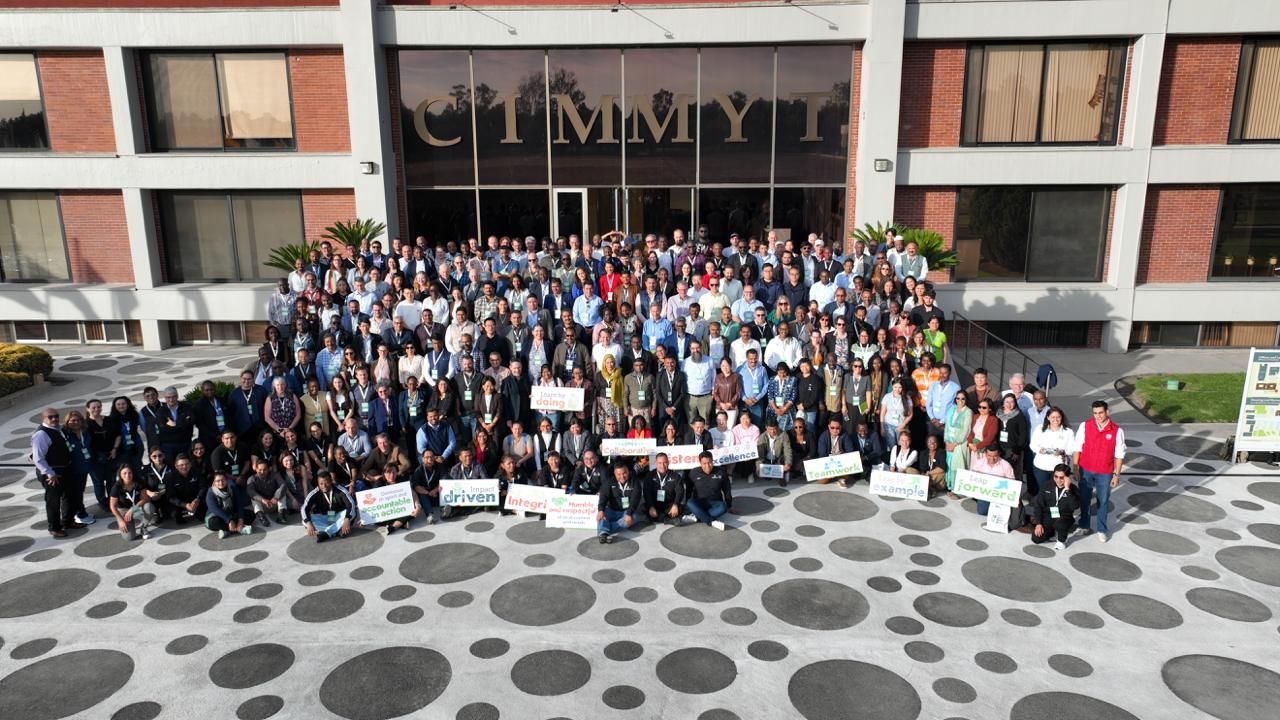
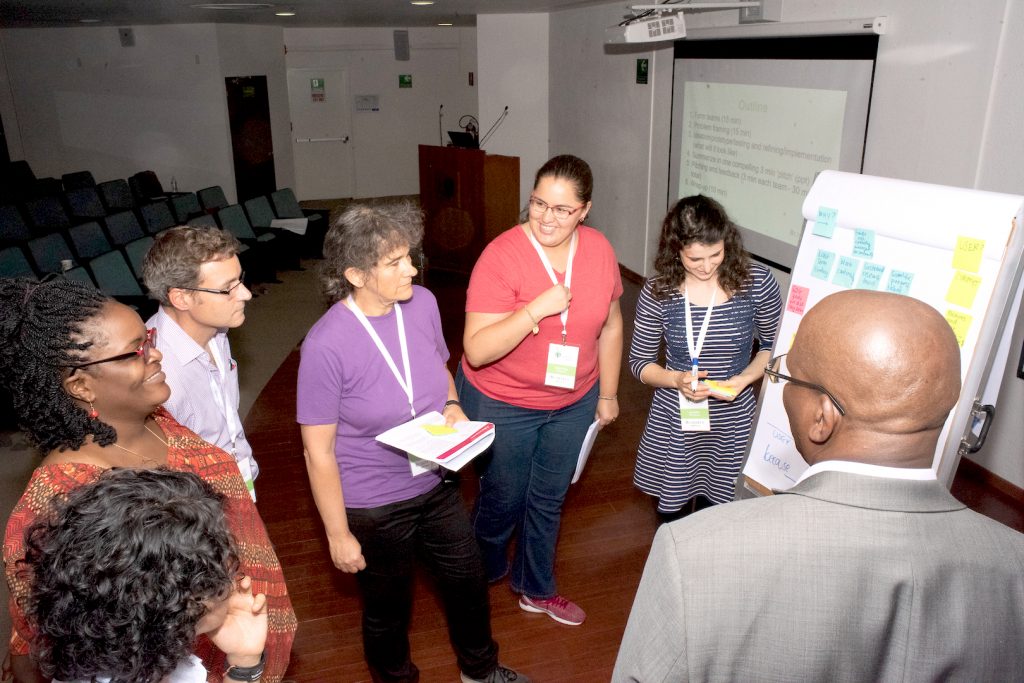
Every two years, CIMMYT hosts its Science and Innovation Week (SIW), a moment not only for reflection but also for action. SIW2025 is more than a gathering; it is a call to action, challenging us to create lasting change and transformative impact. Each day, we wake up with a bold mission: to make our work meaningful to the ultimate beneficiaries – smallholder farmers.
To kick off this year’s Science Week, CIMMYT Director General Bram Govaerts reminded participants that at the heart of our work is real-world impact. More than an opportunity to evaluate strategies, Science Week is about envisioning and driving the future of food systems.
“CIMMYT’s work connects communities worldwide, from labs to corn harvests. Your tireless research deserves accolades as profound as a Nobel Prize” said Ted McKinney, CEO of the JS National Association of State Departments of agriculture, NASDA & Former USDA Undersecretary. Recognizing this urgency, CIMMYT convened leading scientists, researchers, and decision-makers at its headquarters in Texcoco, Mexico, for Science Week 2025.
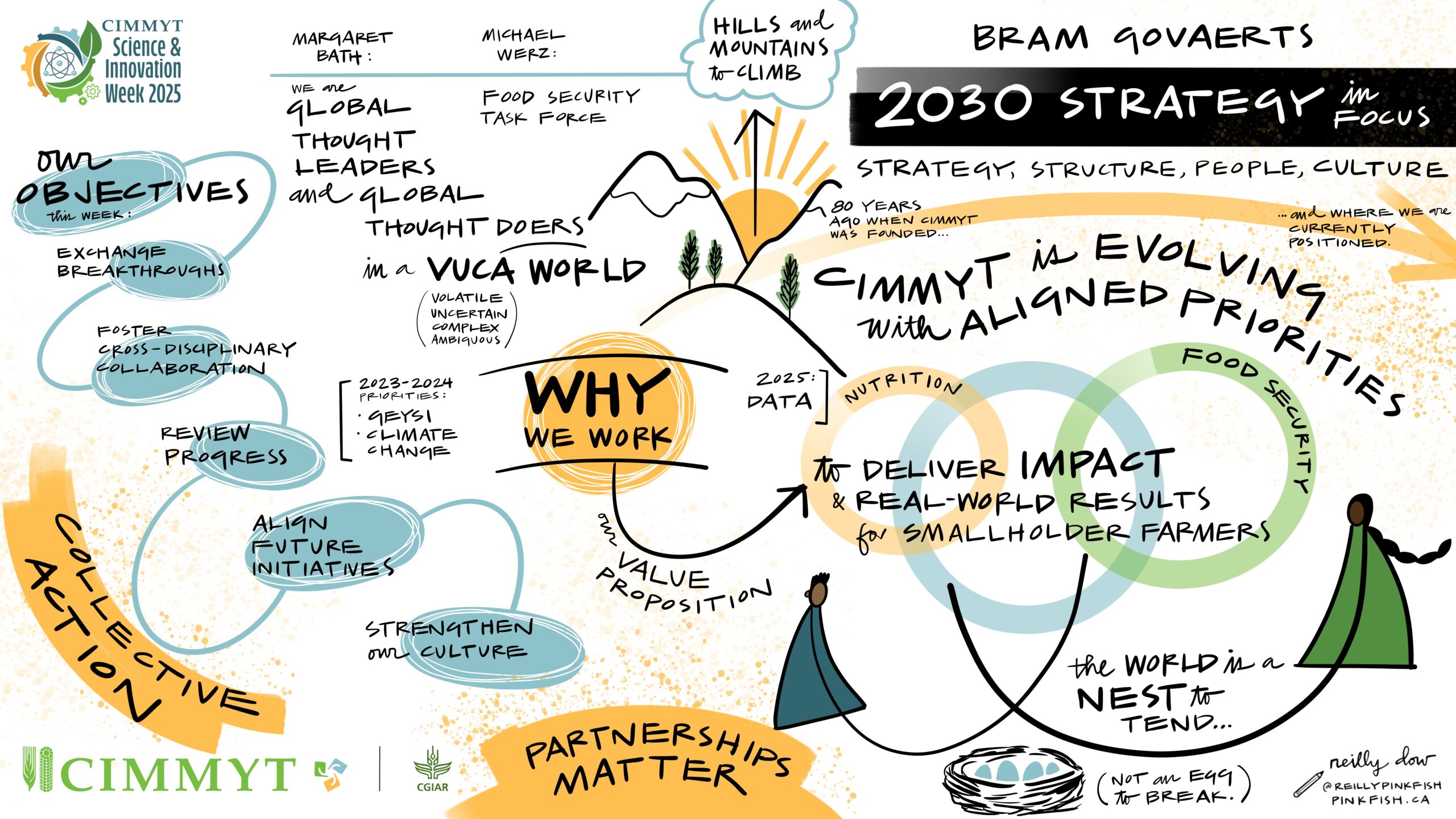
This flagship event brought together experts at the intersection of agriculture, climate and food security to foster collaboration and inspire action for resilient food systems. With CIMMYT’s research agenda focused on addressing the world’s most pressing agricultural challenges, Science Week served as a key platform to shape the future of innovation, strengthen partnerships, and accelerate impact on global food security. Through knowledge sharing and strategic discussions, participants explored transformative solutions that will empower smallholder farmers, build crop resilience, and ensure a sustainable future for food systems worldwide.
A platform for collaboration and innovation
The first day set the stage for a dynamic exchange of ideas, bringing together global experts to address agriculture’s most pressing challenges. Discussions explored climate-smart agriculture, the role of digital transformation, and the resilience of seed systems, highlighting the need for innovation to ensure food security. Advances in crop breeding and cutting-edge research took center stage, reinforcing CIMMYT’s commitment to developing scalable, science-based solutions that empower farmers.
Sessions covered a wide range of topics, including climate-smart agriculture, digital transformation in agriculture, resilience of seed systems, and advances in crop breeding. High-level panels and thought leaders highlighted the importance of collaboration, from integrating AI and strategic partnerships to amplifying research impact, while deep diving into CIMMYT’s scientific breakthroughs. The challenge was clear: think beyond the event, push boundaries, and make a meaningful impact that extends far beyond this week.
From data-driven decision-making to sustainable food production, discussions reinforced the need for strategic collaboration, digital transformation, and responsible innovation. With a strong focus on open data and climate resilience, day two underscored CIMMYT’s commitment to translating science into real-world impact for farmers and food systems worldwide.
With CIMMYT generating around 122 datasets annually, experts stressed the importance of improving data quality, integrating new information, and standardizing workflows for greater transparency and efficiency. The discussions also tackled food security, conflict, and economic instability. With 8.4 million people affected by food insecurity in Latin America and the Caribbean, experts highlighted the urgent need for social protection systems, digital solutions, and adaptive policies.
Moving forward, CIMMYT must bridge science and action, ensuring that research translates into tangible solutions for farmers and food systems worldwide – because resilience is not just an option; it is the foundation of sustainable agriculture.
Scientific excellence in action
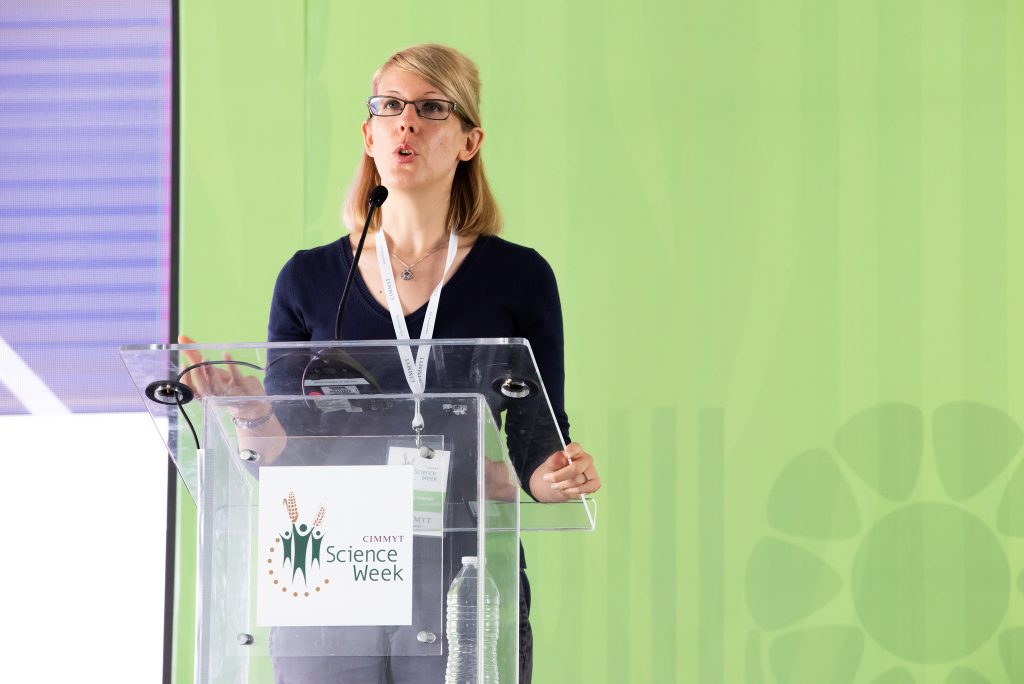
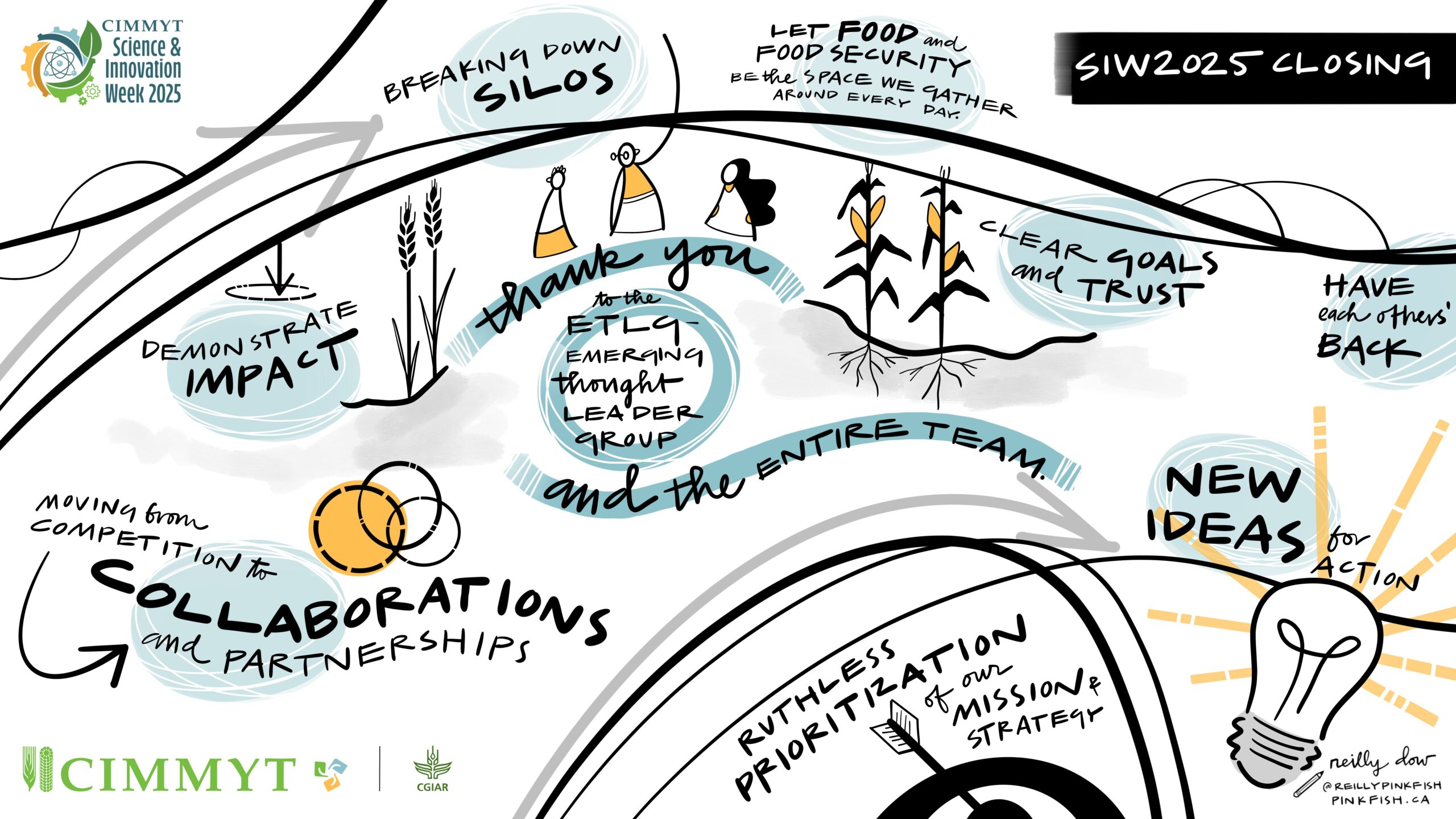
As Science Week 2025 drew to a close, discussions focused on two key themes: partnerships and communicating impact. To kick off the session, Aaron Maniam, Fellow of Practice and Director, Digital Transformation Education, Oxford University Blavatnik School, challenged participants to rethink collaboration – not just as coordination but as a balance between integration and fragmentation. Collaboration is non-negotiable, and positioning CIMMYT as the partner of choice will be critical to advancing its mission.
Today’s challenges are too complex to tackle alone, and strategic partnerships are essential to amplify impact, leverage resources, and scale innovation. But successful partnerships go beyond collaboration – they require trust and shared goals. Science must be accessible, compelling, and strategically packaged to engage diverse audiences and drive real-world change. As we move forward, the challenge is clear: Embrace, amplify, and boldly communicate our impact to shape the future of food and agriculture. The work does not stop here, this is just the beginning of the next chapter in transforming global food systems for a food and nutrition secure world.








