Tag: resistant varieties
Fall armyworm research, development and extension for horticulture
Breeding for fall armyworm resistance in maize: an update from CIMMYT
Staff from the Queensland Department of Agriculture and Fisheries (DAF), Agriculture Victoria, Food and Fibre Gippsland, and Bowen Gumlu Growers Association joined B.M. Prasanna (Maize Program Director at CIMMYT & CGIAR Plant Health Initiative Lead) on 19th October 2023 to learn about CIMMYT’s efforts and experiences with fall armyworm management at the global scale, and to build partnerships between CIMMYT and Australian institutions for future collaboration on plant health management.
At the online meeting, Prasanna shared CIMMYT’s research and development on FAW management in maize, including breeding for insect-pest resistance, screening maize germplasm against FAW under artificial infestation, and collaborative approaches on integrated pest management of FAW.
Key points from the discussion:
- Collaborative efforts are important in managing FAW, and international R&D collaboration is as important as country-level research efforts.
- CIMMYT has made significant progress in breeding FAW-tolerant maize hybrids (with native genetic resistance); three such hybrids have been released by national partners in Kenya, Zambia, Malawi, South Sudan, and Ghana, and several more countries in Africa are in the pipeline for release and deployment of these hybrids.
- Insect resistance management is critical wherever Bt maize varieties have been already released or in the process of release.
- Both conventionally derived and Bt-based resistant maize varieties have their own importance in FAW management.
- Need to intensify breeding activities for developing elite maize germplasm with FAW resistance together with other important traits, and fast-track deployment of FAW-tolerant elite maize hybrids.
- Possible to achieve synergies between host plant resistance and other IPM approaches for sustainable management of FAW.
- Researchers interested in accessing germplasm from CIMMYT’s breeding program can source through a standard material transfer agreement.
Dr Prasanna responded to several queries from the participants of the meeting. Australian researchers and CIMMYT showed interest in further research collaboration. Dr Ramesh Raj Puri, DAF Extension Officer, facilitated the meeting.
Pilot of new wheat variety improves yield for farmers in Ethiopia
“I am happy with this wheat variety and all the support from the project,” said Agere Worku, a female farmer in Ethiopia working with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT). “It is a lot of money that I will earn as a female farmer in my life.”
Worku is just one farmer taking part in a pilot intervention as part of CIMMYT’s Adaptation, Demonstration, and Piloting of Wheat Technologies for Irrigated Lowlands of Ethiopia (ADAPT-Wheat) project. Four female and four male farmers were chosen to take part from the Melke Yegna Tesfa Association, a membership group of 83 smallholder farmers, nearly half of which are female.
Participants were given Kingbird seeds, a new wheat variety, to plant in their smallholdings. The project then supported them through capacity building and advice on smart soil, water management, plant protection and agronomic packages.
“We prepared six hectares of land and sowed 1.1 tons of Kingbird seed,” said Yeshiwas Worku, chair of the Melke Yegna Tefsa Association. “There were other wheat varieties, such as Danda’a, adjacent to our experimental plot and the difference in yields was very visible. The other members of the association were eager to get Kingbird seeds, which are very different in terms of quality, yields, maturity, and disease tolerance.”
“CIMMYT is a life changer for me,” said Buzayehu Getahun, a farmer in Jeju, in the Oromia region. “I produced 3.7 tons on 0.75 hectares. Interestingly, I earned around 132,000 Ethiopian Birr (US$2,500) from this yield. I plan to build a new house for my mother in my village and will be blessed by her at her old age,” said Getahun.
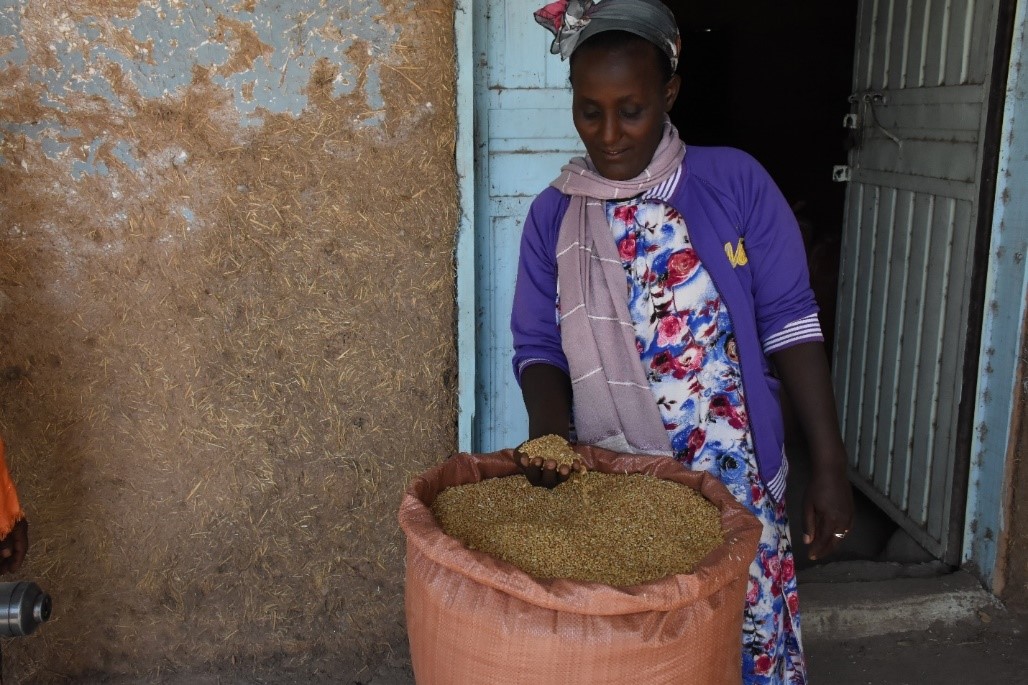

The impact on female farmers
After involvement in the pilot, the female farmers produced higher yields than they had experienced before.
“I used to harvest wheat three times in the previous years and earned only 0.66 tons of wheat per 0.75 hectare using seeds of other wheat varieties,” explained Worku. “But now thanks to support from CIMMYT, the yield has increased four times than the previous years; I produced 2.4 tons per 0.75 hectares. I am very happy with the high yield and feel encouraged to reinvest in other agricultural activities.”
A second female farmer, Melishew Tedela, said, “I am happy with this seed and all the support from the project. I can be witness that the other farmers who didn’t get this variety were not happy with their low yields of wheat.”
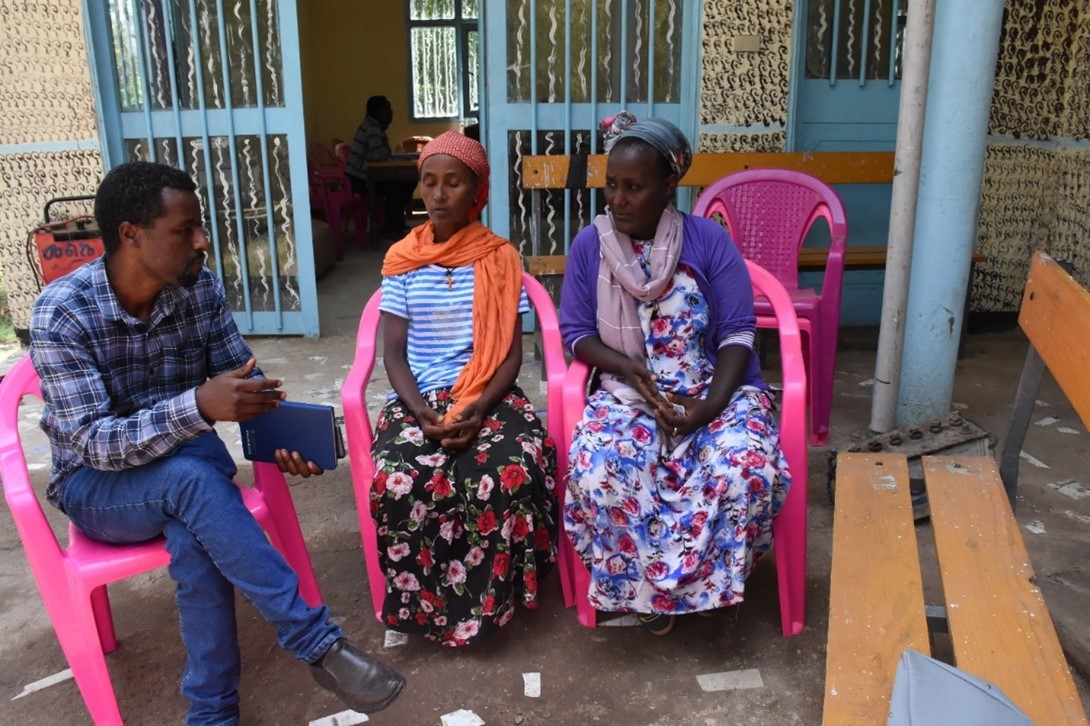

The future of lowland wheat farming
Bekele Geleta Abeyo, wheat breeder and Ethiopia Country Representative at CIMMYT, said, “The Government of Ethiopia is emphasizing increasing irrigated wheat production and productivity in the lowlands to complement the intensification of rainfed wheat production in the highlands in order to achieve self-sufficiency by 2023 and feed the ever-growing population.”
With world wheat prices skyrocketing due to the Ukraine conflict, wheat technology generation and dissemination are key for sustainable agricultural practices.
CIMMYT is working to replace obsolete wheat varieties in Ethiopia that are susceptible to wheat rust, particularly yellow and stem rust, with disease-resistant products. Newer varieties like Kingbird are rust-resistant and therefore produce higher yields.

How interactions among hidden enemies and drought effects grain yield and disease severity in bread wheat
In nature, plants are simultaneously exposed to a complex system of biotic and abiotic stresses that limit crop yield. The cereal cyst nematode Heterodera filipjevi and dryland crown rot, caused by Fusarium, are important diseases facing cereal production around the world that cause significant yield loss. Yield loss accelerates when those diseases coexist with other abiotic stresses, such as drought.
Hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is an essential staple food for a large part of the world’s population, covering around 20% of daily caloric intake in the human diet, with global production at about 670.8 million tons per year, produced over 215.4 million hectares of land worldwide. Therefore, the program studying soil-borne pathogens at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT)’s Turkey office initiated a study to investigate the effect of soil borne diseases (H. filipjevi and Fusarium culmorum) individually and in combination with drought on some morphological and physiological traits in wheat germplasm with different genetic tolerances to the three studied factors.
In this study, yield components included thousand kernel weight, spike weight, seed per spike and total grain yield. Morphological parameters, including plant height, final plant number (seedling emergence), relative water content, leaf chlorophyll content, H. filipjevi cyst number and presence of crown rot, were studied under greenhouse conditions in Turkey.
The main findings of the study showed that the interaction among water stress, F. culmorum and H. filipjevi increased the damage on the wheat parameters studied when compared with each stress applied alone. One of the most significant damages was seen in high seedling mortality under the three combined stresses (56% seedling death rate), which indicates the damage on wheat yield might occur at the seedling stage rather than later stages. This reduces plant density per area, which was ultimately responsible for low grain yield produced. The known dryland disease, crown rot, caused by F. culmorum, was significantly pronounced under water-stressed conditions.
In all studied parameters, the lowest damage was found among the resistant cultivars to biotic or abiotic stresses. This underscores the importance of wheat breeding programs to develop resistant germplasm, and reminds farmers to replace their old, susceptible varieties with new, resistant ones.
Based on our intensive experience in the CWANA region, most wheat growers basically do not recognize soil borne pathogens as a problem. In fact, most of them do not know that what nematode or soil fungal species are in their fields affecting yield. The term “hidden enemy” perfectly applies to the problems in the region and beyond. Integrated pest management (IPM) is, however, not practiced in the entire region and soil borne pathogen-induced yield losses are simply accepted.
We can conclude from this study that yield reduction in wheat due to soil borne pathogens could be lessened by improving and understanding the concept of IPM in the region where the practice of winter mono-culturing of wheat is the norm. Management of cereal soil-borne pathogens, especially cereal cyst nematode and crown rot, could involve an integrated approach that includes crop rotation, genetic resistance, crop nutrition and appropriate water supply.
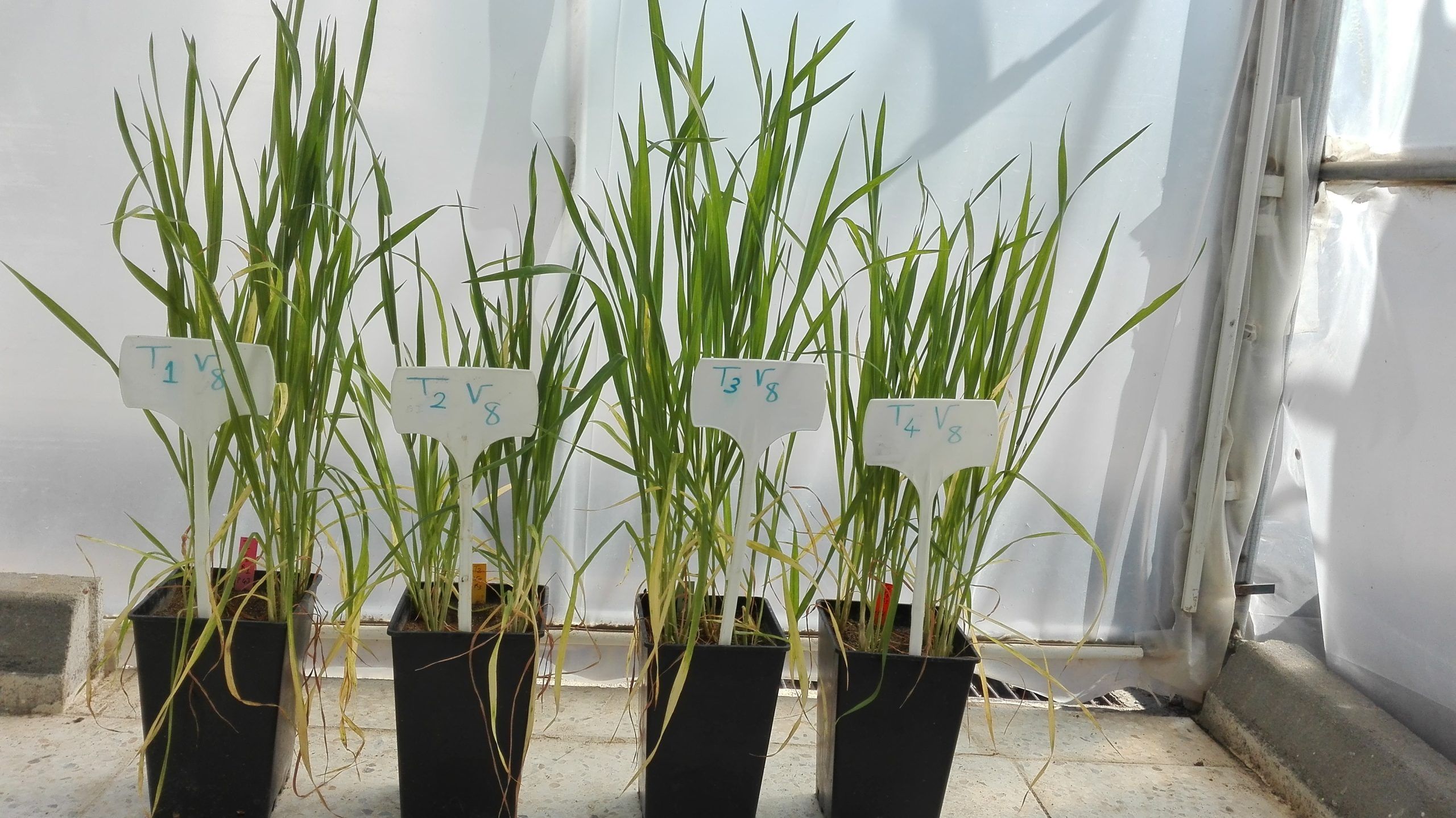
Cover photo: Four different test crops show different stresses: T1V8 = Drought, T2V8 = Drought and Nematodes, T3V8 = Drought and fungus, T4V8 = Drought and nematode and fungus together. (Credit: CIMMYT)
Adaptation, Demonstration and Piloting of Wheat Technologies for Irrigated Lowlands of Ethiopia (ADAPT-Wheat)
Wheat is the second most important staple crop in Ethiopia and a major pillar for food security. Based on fingerprinting analysis from 2018, about 87% of all wheat varieties grown in Ethiopia are CIMMYT-derived.
Domestic wheat production and productivity has nearly doubled over the past 15 years, due to improved farmer access to better varieties, agronomic practice recommendations and conducive marketing and supply chain policies. Nevertheless, due to population growth, higher incomes and accelerated urbanization, the demand for wheat in Ethiopia is increasing faster than productivity, with the demand for an additional 1.5 million tons of wheat per year satisfied through imports.
In 2018, the Government of Ethiopia set a policy to achieve wheat national self-sufficiency by 2023. Additional production would come primarily from the irrigated lowlands of the Awash valley, in the Afar and Oromia regions, where the current cotton mono-culture would be converted to a cotton-wheat rotation.
Preliminary yield trials conducted by Werer Agricultural Research Center and based on experiences in Sudan where climate conditions are similar, on-farm wheat grain yields of 4 tons per hectare can be achieved. The potential area for irrigated wheat-cotton is at present around 500,000 hectares, which, when fully implemented, has the potential to make Ethiopia self-sufficient for wheat production.
The challenges to develop the current lowland into productive farming systems are significant and include identifying high yielding, early maturing, heat-tolerant, rust-resistant wheat varieties with appropriate end-use quality.
Appropriate mechanization will be required to allow farmers to facilitate rapid preparation of fields for wheat sowing after harvesting cotton, as well as for mechanized harvesting. Tested packages of agronomic and land management practices will be needed to optimize the production systems while mitigating against soil salinization.
In coordination with the national research and extension systems, this project will evaluate and pilot wheat technologies and packages of practices to reach 1,000 smallholders and medium commercial farmers in the Awash valley, and enable them to use these technologies and practices on 10,000 hectares of irrigated land in the first year, following the conclusion of this project.
Objectives
- Capacity of research and development practitioners working on irrigated lowland wheat developed.
- Improved wheat elite lines evaluated, and pre-release seed multiplication initiated of variety candidates.
- Tested package of agronomic practices are ready for scaling.
- Demonstration and piloting of appropriate machineries (modern mechanization) for irrigated wheat production.
Taming wheat blast
As wheat blast continues to infect crops in countries around the world, researchers are seeking ways to stop its spread. The disease — caused by the Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum — can dramatically reduce crop yields, and hinder food and economic security in the regions in which it has taken hold.
Researchers from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and other international institutions looked into the potential for wheat blast to spread, and surveys existing tactics used to combat it. According to them, a combination of methods — including using and promoting resistant varieties, using fungicides, and deploying strategic agricultural practices — has the best chance to stem the disease.
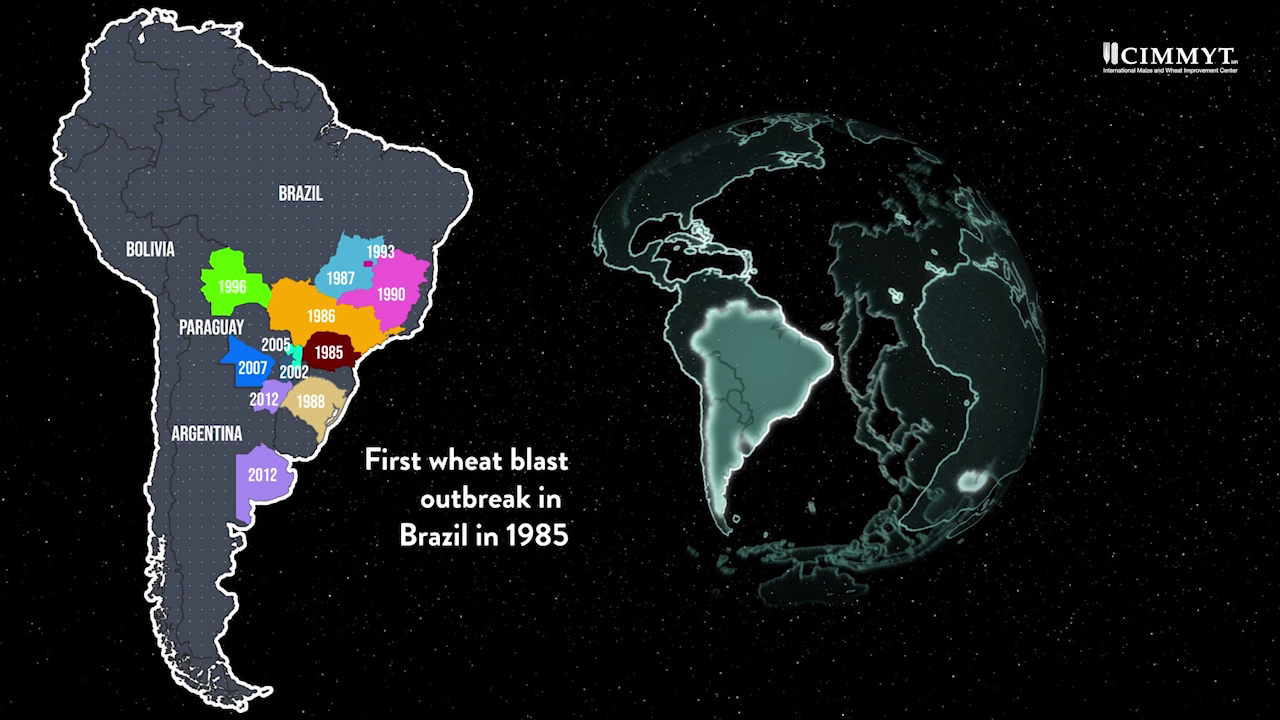
The disease was originally identified in Brazil in 1985. Since then, it has spread to several other countries in South America, including Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay. During the 1990s, wheat blast impacted as many as three million hectares in the region. It continues to pose a threat.
Through international grain trade, wheat blast was introduced to Bangladesh in 2016. The disease has impacted around 15,000 hectares of land in the country and reduced average yields by as much as 51% in infected fields.
Because the fungus’ spores can travel on the wind, it could spread to neighboring countries, such as China, India, Nepal and Pakistan — countries in which wheat provides food and jobs for billions of people. The disease can also spread to other locales via international trade, as was the case in Bangladesh.
“The disease, in the first three decades, was spreading slowly, but in the last four or five years its pace has picked up and made two intercontinental jumps,” said Pawan Singh, CIMMYT’s head of wheat pathology, and one of the authors of the recent paper.
In the last four decades, wheat blast has appeared in South America, Asia an Africa. (Video: Alfonso Cortés/CIMMYT)
The good fight
Infected seeds are the most likely vector when it comes to the disease spreading over long distances, like onto other continents. As such, one of the key wheat blast mitigation strategies is in the hands of the world’s governments. The paper recommends quarantining potentially infected grain and seeds before they enter a new jurisdiction.
Governments can also create wheat “holidays”, which functionally ban cultivation of wheat in farms near regions where the disease has taken hold. Ideally, this would keep infectable crops out of the reach of wheat blast’s airborne and wind-flung spores. In 2017, India banned wheat cultivation within five kilometers of Bangladesh’s border, for instance. The paper also recommends that other crops — such as legumes and oilseed — that cannot be infected by the wheat blast pathogen be grown in these areas instead, to protect the farmers’ livelihoods.
Other tactics involve partnerships between researchers and agricultural workers. For instance, early warning systems for wheat blast prediction have been developed and are being implemented in Bangladesh and Brazil. Using weather data, these systems alert farmers when the conditions are ideal for a wheat blast outbreak.
Researchers are also hunting for wheat varieties that are resistant to the disease. Currently, no varieties are fully immune, but a few do show promise and can partially resist the ailment depending upon the disease pressure. Many of these resistant varieties have the CIMMYT genotype Milan in their pedigree.
“But the resistance is still limited. It is still quite narrow, basically one single gene,” Xinyao He, one of the co-authors of the paper said, adding that identifying new resistant genes and incorporating them into breeding programs could help reduce wheat blast’s impact.

The more the merrier
Other methods outlined in the paper directly involve farmers. However, some of these might be more economically or practically feasible than others, particularly for small-scale farmers in developing countries. Wheat blast thrives in warm, humid climates, so farmers can adjust their planting date so the wheat flowers when the weather is drier and cooler. This method is relatively easy and low-cost.
The research also recommends that farmers rotate crops, alternating between wheat and other plants wheat blast cannot infect, so the disease will not carry over from one year to the next. Farmers should also destroy or remove crop residues, which may contain wheat blast spores. Adding various minerals to the soil, such as silicon, magnesium, and calcium, can also help the plants fend off the fungus. Another option is induced resistance, applying chemicals to the plants such as jasmonic acid and ethylene that trigger its natural resistance, much like a vaccine, Singh said.
Currently, fungicide use, including the treatment of seeds with the compounds, is common practice to protect crops from wheat blast. While this has proven to be somewhat effective, it adds additional costs which can be hard for small-scale farmers to swallow. Furthermore, the pathogen evolves to survive these fungicides. As the fungus changes, it can also gain the ability to overcome resistant crop varieties. The paper notes that rotating fungicides or developing new ones — as well as identifying and deploying more resistant genes within the wheat — can help address this issue.
However, combining some of these efforts in tandem could have a marked benefit in the fight against wheat blast. For instance, according to Singh, using resistant wheat varieties, fungicides, and quarantine measures together could be a time-, labor-, and cost-effective way for small-scale farmers in developing nations to safeguard their crops and livelihoods.
“Multiple approaches need to be taken to manage wheat blast,” he said.