Tag: project design
Scaling up research for development in CGIAR
“Agricultural research for development is increasingly being held accountable to demonstrate that research goes beyond successful pilots,” said Iain Wright, deputy director general of research and development at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI).
In a bid to scale impact of its research outputs, ILRI has recently undertaken a systematic review of the scaling tools and processes available to help guide and improve the organization’s efforts.
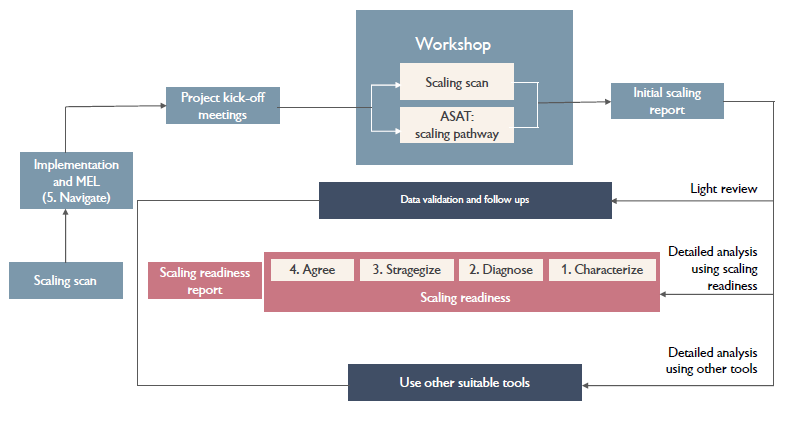
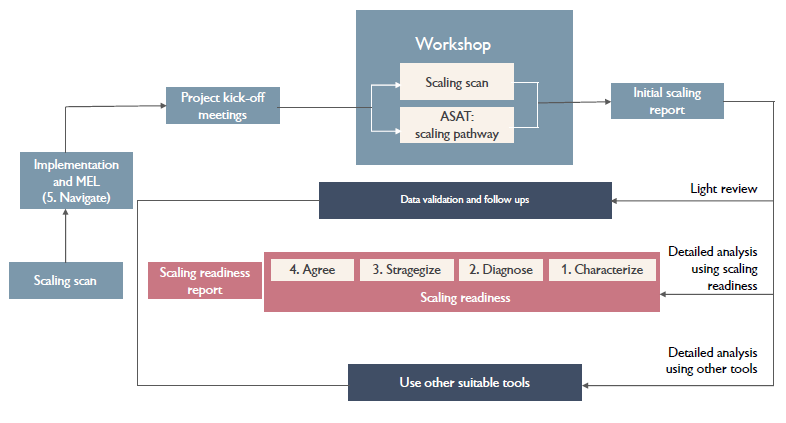
The Scaling Scan has been incorporated into a new scaling framework for ILRI projects and for the CGIAR Research Program on Livestock (Livestock CRP). The Scaling scan, developed in 2017 by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) in collaboration with PPPLab at SNV, is one of three tools that have been identified as most suitable for the ILRI and CGIAR operational contexts.
“ILRI’s scaling framework applies the Scaling Scan and the USAID Scaling Pathway methodology before diving deep using the RTB/Wageningen Scaling Readiness methodology,” explained CIMMYT Scaling Coordinator Maria Boa. “It’s exciting because it aligns some of the best available tools to scale impact with a systems view.”
Designed for use by anyone involved in pro-poor and sustainable development programs looking to scale impact, the CIMMYT Scaling scan is found to be user-friendly and quick to help project implementation teams understand and define their scaling ambitions and asses their scaling environment. Though it is often applied as part of annual project review meetings, the tool can in fact be used at any stage of a project’s lifecycle. This helps stakeholders understand the multiple dimensions of scaling and the significant role nontechnical factors play in a scaling mindset.
CIMMYT shared lessons on how the methodology can be applied in a workshop setting and the Livestock CRP team has already used these to organize two workshops around improving productivity and incomes in Uganda’s pig value chain. The workshops, held in November 2019 and February 2020, brought together value chain actors, CRP researchers and project staff to better understand the multiple dimensions of scaling, develop realistic scaling goals, and identify key bottlenecks and opportunities using the Scaling Scan.
Read more on ILRI’s website:
ILRI adopts new framework for scaling up livestock research for development
Unleashing innovation at CIMMYT
CIMMYT staff share lessons learned at UNLEASH innovation labs with colleagues
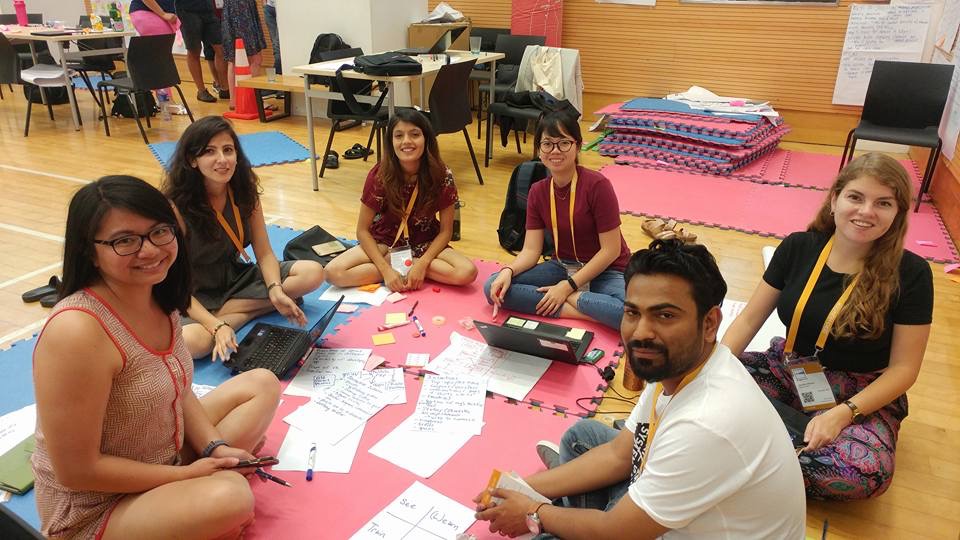

Four young staff members from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) are working to bring home lessons learned at UNLEASH to foster innovation across CIMMYT programs. UNLEASH is a global innovation lab that brings together people from all over the world to transform personal insights into hundreds of ideas and build lasting global networks around the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The annual event, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to occur each year until 2030, brings together 1,000 selected young talents for 10 immersive days of co-creation and problem solving.
Innovation is key to finding solutions to major global challenges such as hunger, climate change and sustainability. However, innovation cannot occur in a vacuum – the strongest and most inclusive solutions are often interdisciplinary approaches developed by a wide range of people from diverse backgrounds and perspectives. What sets UNLEASH apart from other innovation labs and processes is this commitment to diversity, as well as its focus on the Sustainable Development Goals.
While at UNLEASH 2017 in Denmark, CIMMYT staff Aziz Karimov, Daniela Vega and David Guerena were part of 200 teams that were split across 10 ‘folk high schools’ in the Danish countryside. There, they worked through an innovation process with facilitators and experts, refined their ideas to contribute to the SDGs and finally reconvened in the city of Aarhus to pitch the solutions they had developed.
Jennifer Johnson, Maize Communications Officer at CIMMYT, attended the UNLEASH Innovation Lab 2018 in Singapore last June. She worked alongside a diverse team of young people to develop solutions to improve nutrition for adolescent girls in Nepal.
The UNLEASH innovation process has five main phases: problem framing, ideation, prototyping, testing and implementing. “UNLEASH is really about finding and framing the problem,” said Vega, a projects coordinator and liaison officer for the Americas at CIMMYT and UNLEASH 2017 alumna. “Innovation is 90 percent about understanding the problem. Once you get that right, everything that follows becomes easier,” she explained.
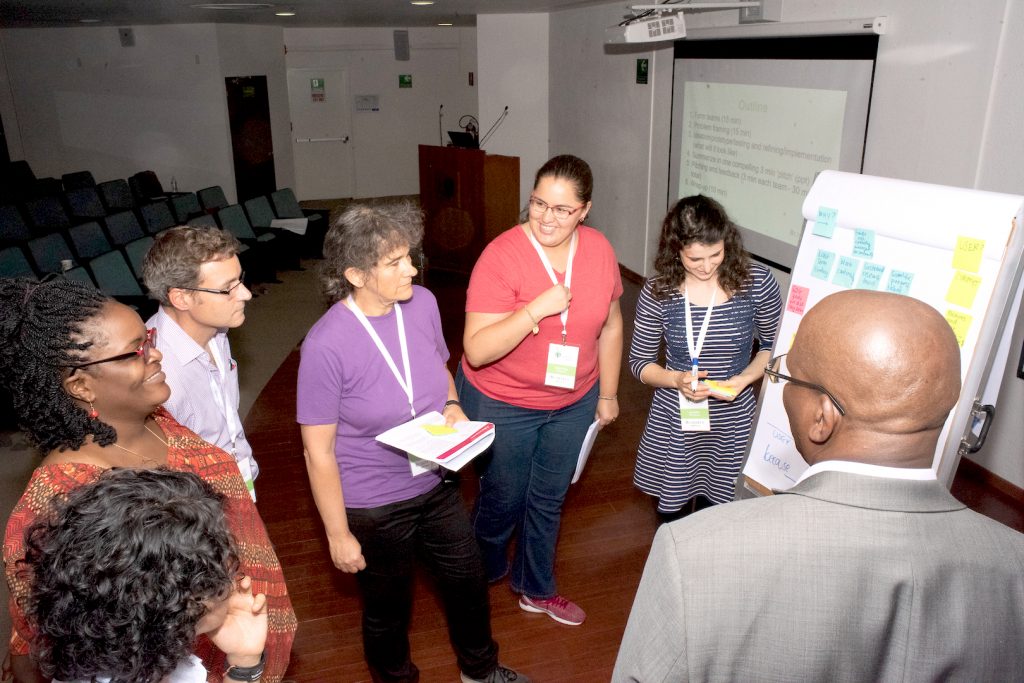

Johnson, Guerena and Vega held a session on innovation and lessons learned at UNLEASH at CIMMYT’s Science Week 2018. Participants were walked through an abridged version of the UNLEASH innovation process to develop creative solutions to real-world problems relating to agriculture. The session emphasized diversity, respect and creativity, which are central tenets of both CIMMYT and UNLEASH.
“One of the key takeaways I got from UNLEASH was the power of diversity and collaboration,” said Guerena, a soil scientist and systems agronomist at CIMMYT who participated in UNLEASH 2017. “The diversity of the participants and collaboration lead to better solutions.”
Vega agreed. “People come from different backgrounds, geographically and professionally, and the level of cooperation and openness with no judgement is essential. We all share a similar value set, we are here because we want to make the world a better place by solving problems on a very hands-on level.”
In just one hour, participants of the CIMMYT session formed diverse teams, developed problem framings, brainstormed potential solutions and gave a three-minute pitch presenting their solution to the audience. Participants expressed extreme satisfaction with what they had learned and the innovation process they had been guided through, as well as interest in participating in similar programs in the future.
“This is a great idea, a very good experience. Often creativity doesn’t get enough attention,” said Lennart Woltering, CIMMYT scaling expert.
“This is fantastic and I’m going to adopt it. This is a great way to introduce concepts such as gender,” said Rahma Adam, CIMMYT gender and development specialist.
In the future, CIMMYT’s UNLEASH alumna hope to continue sharing their experience with colleagues and implementing lessons learned within their work.
“Unleash helps young people to think freely and differently,” said Karimov, a CIMMYT development economist whose team won second place in UNLEASH 2017’s ‘Sustainable Consumption & Production’ category which targeted Goal 12 of the SDGs. “We think innovation is something very complicated but by attending UNLEASH I realized that very simple moves can make a big change. You start believing that what is not possible is actually very possible. You just have to have will and strong desire.”