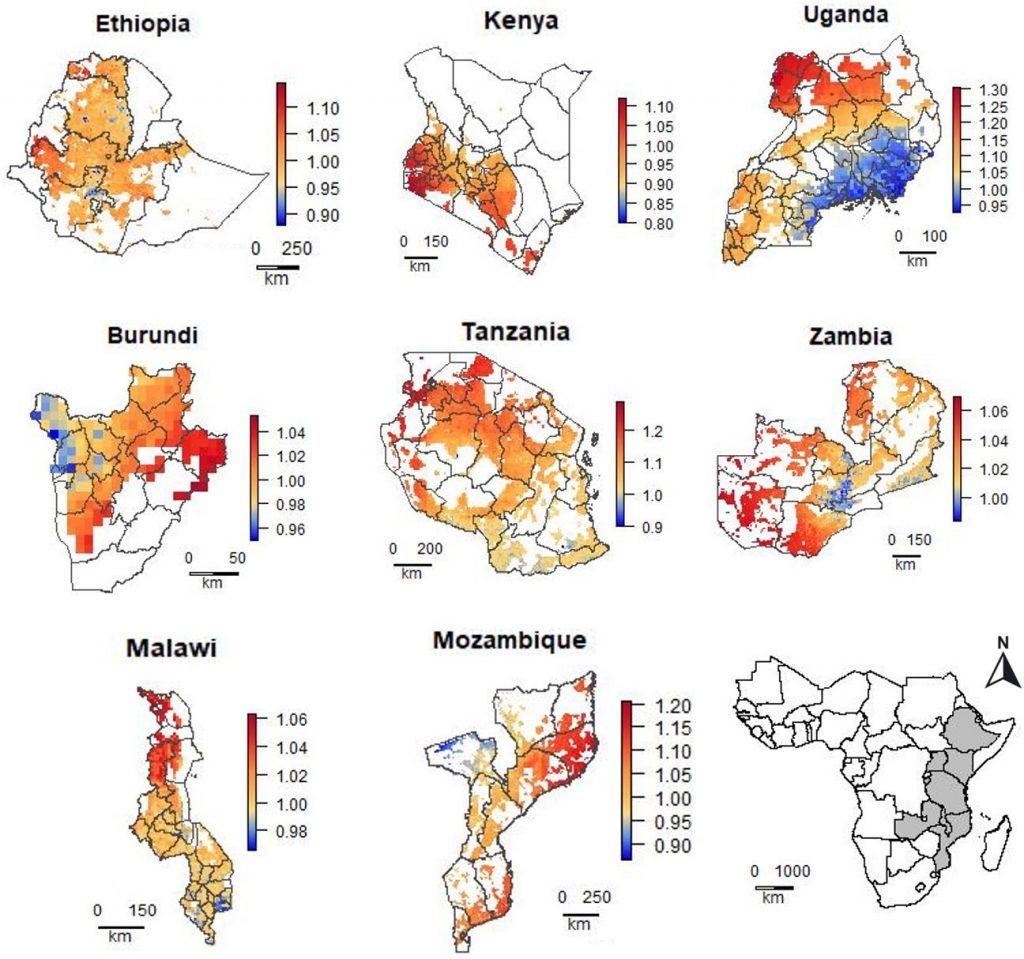
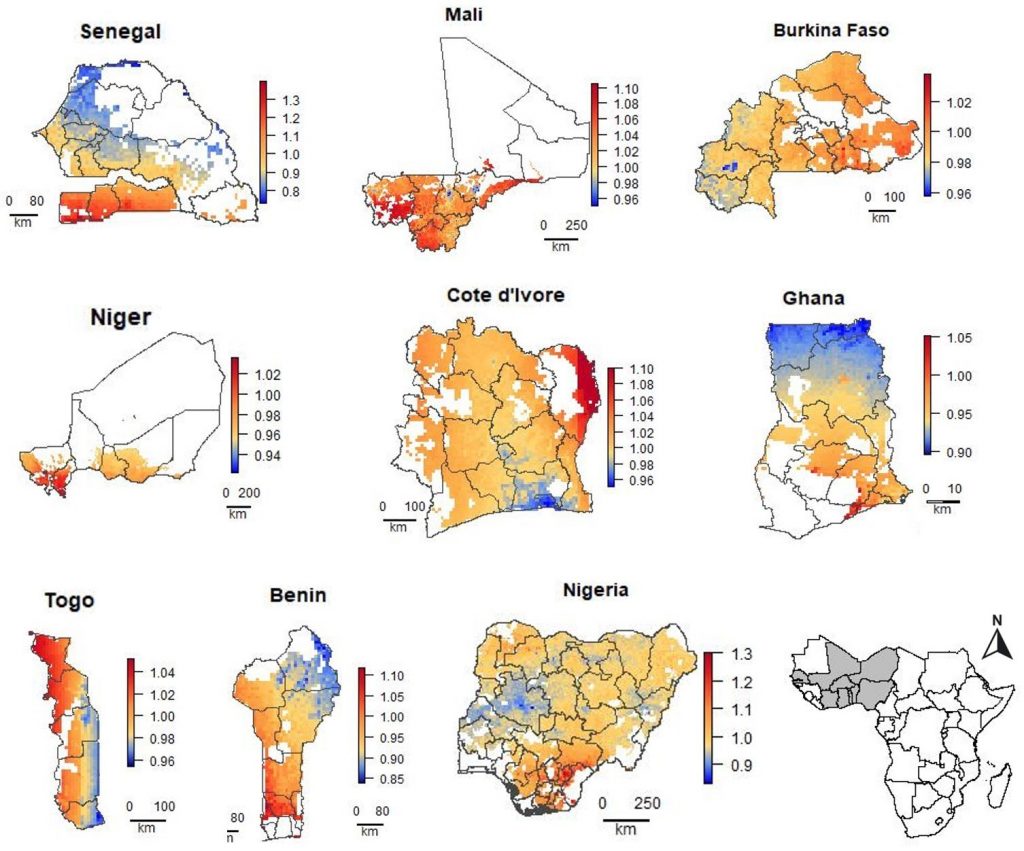
What price wheat?

When wheat prices rise, so do global food prices, along with conflict, inequality and instability. Over the past two decades, the world has witnessed multiple crises erupt over the social and political instability caused by rising costs for staple cereals. The global food crisis that impacted many parts of the world in 2007–2008 was a response, in part, to the prices for wheat and rice which had increased 130% and 70%, respectively, compared to the year before. More recently, spikes in grain prices catalyzed the 2011 Arab Spring.
With the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and the resulting longer-term disruptions of the country’s rural economy, there is potential for another round of turmoil linked to prices for staple cereals.
Ukraine is a breadbasket for the world, with 57% of its land area arable for agriculture. Wheat production in the country increased roughly 10%, on average, between 2000 and 2020. In 2022, Ukraine ranked as the fifth largest wheat exporter globally, exporting $3.59 billion of wheat.
Today, global wheat prices are at their highest levels since 2012: $9 per bushel, based on data from the Chicago Board of Trade.
Wheat is a staple crop, essential to food security. It is consumed by over 2.5 billion people worldwide, including large proportions of the populations of many food-insecure regions in the world. Many of the wheat-consuming countries in these regions are far from wheat self-sufficient, relying on global imports to meet demand. This causes significant vulnerability in food supply and increases associated humanitarian risks. In 2019, important quantities of Ukrainian wheat were exported to low- and middle-income countries in North Africa and the Middle East. Although the impacts of current price increases are anticipated to be short-term, they are likely to be inequitably felt, as not all buyers are able to pay higher prices.
There are over 6 million hectares of wheat planted in farmers’ fields across Ukraine that will be due for harvest in June and July of 2022. The length and depth of the current crisis has potential implications for the fate of this in-field crop, and for its subsequent harvest and global distribution. Likewise, sanctions and trading restrictions on Russia, the world’s largest wheat exporter — exporting $7.92 billion of wheat in 2020 — are likely to place added pressure on international wheat markets. This comes at a time of rising costs in agriculture, including the soaring price of nitrogen fertilizer and increasing fuel and supply chain costs. The gap between supply and demand is also becoming wider with climatic instability — such as drought conditions — hitting both domestic production and export stocks in several countries.
Rising prices for staple cereals have historically led to instability, particularly in fragile regions where food security is low. The impacts of current high wheat prices are likely to be felt most significantly by populations in the Global South who rely on wheat imports.
The potential humanitarian crisis beyond the borders of the current conflict needs to be addressed to avoid deepening global divisions in equality of access to food. In the case of wheat, long-term solutions will require much higher levels of investment, coordination and cooperation between governments, development organizations and agro-industry. Without doubt, part of the solution lies in increasing wheat productivity and profitability in food-insecure regions where wheat has traditionally been grown, as well as supporting the expansion of wheat production into climatically suitable areas in countries which have traditionally relied on imports to meet local demand.