Collective efforts to fight fall armyworm in Nepal
Three years ago, farmers in the country were combatting the threats of a destructive tomato pest, Tuta Absoluta, and are now battling their way to manage the attack of fall armyworm on maize fields across the country. Since the government’s Plant Quarantine and Pest Management Centre (PQPMC) declared the arrival of fall armyworm on August 2019, this pest is reported to have infested almost half the districts of Nepal and continues to spread further.
“I wasn’t able to gather even half the yields I used to get from my maize field following the fall armyworm outbreak last year,” said Pavitra, a farmer from Sindhupalchowk district, Nepal.
The level of incidence and damage varies from place to place, but farmers have reported up to 80% crop loss in extreme cases. In Nepal, the fall armyworm has the potential to cause maize yield losses of 20-25%, which translates to the loss of more than half a million tons of the annual maize production — estimated at around $200 million. If the pest is left unrestrained, its impact will be huge for farmers and the economy.
This calls for a collective effort and broad mobilization to effectively manage fall armyworm and limit its spread across the country. Since the pest was expected to reach Nepal, partners have conducted workshops and community mobilization initiatives.
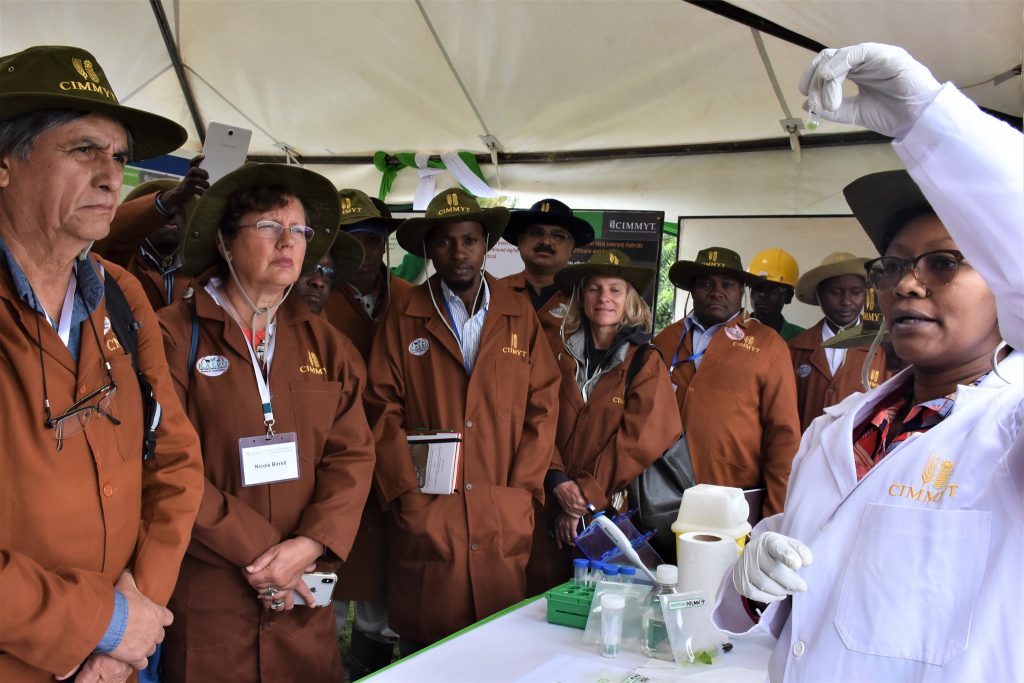
Experts at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) have been working with public and private partners before and after the arrival of the invasive pest in Nepal. The shared efforts have focused on creating awareness, disseminating appropriate technologies and management techniques, and strengthening the capacity of communities, institutions and governments.
The Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development has established a national taskforce to fight the pest. Most provinces have established similar taskforces that include researchers, agriculture extension agents, farmers and entrepreneur associations.
Gearing up to fight the very hungry caterpillar
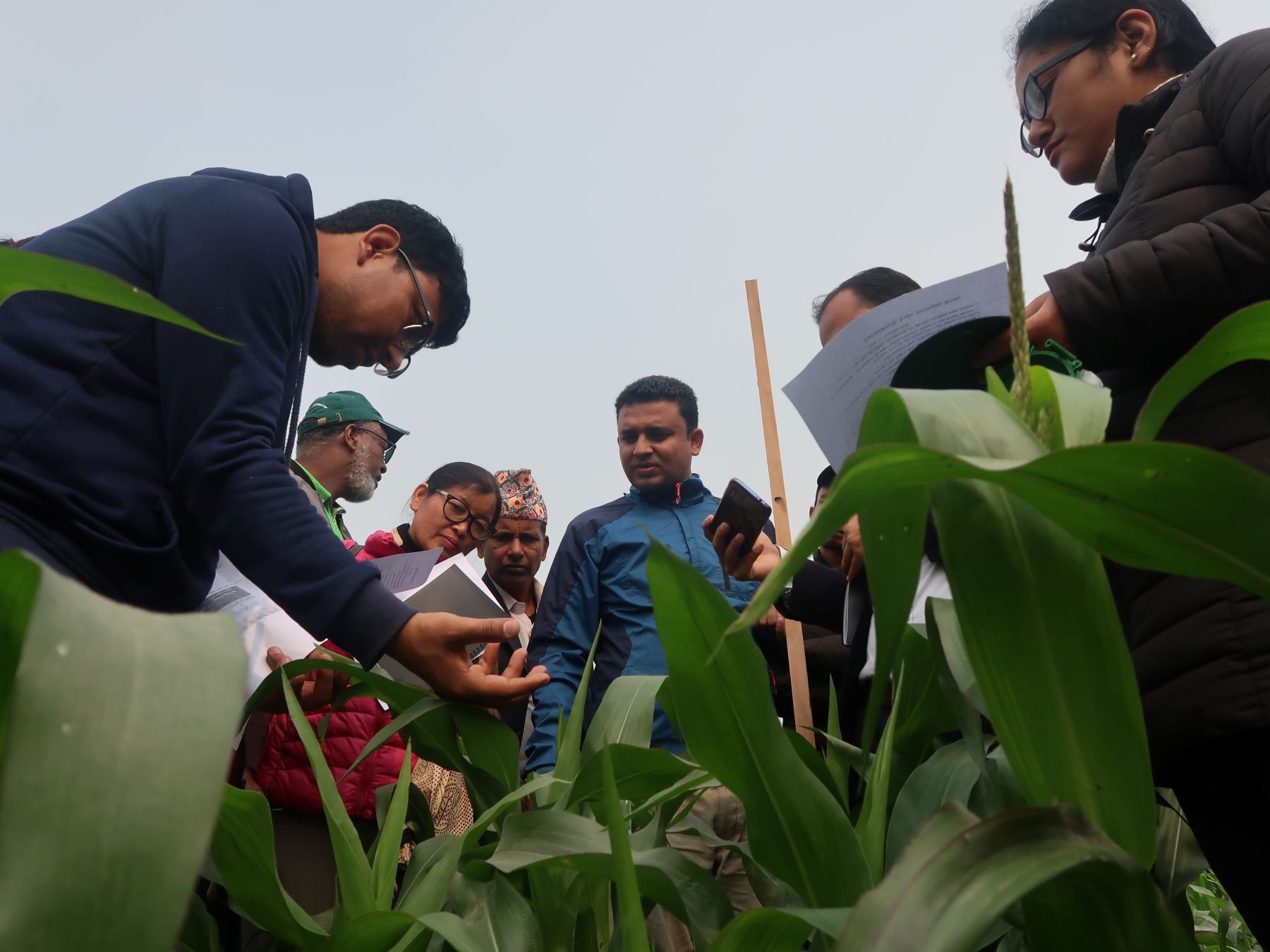
In collaboration with national and provincial governments, CIMMYT has trained 426 agricultural professionals, including lead farmers, on how to identify and manage fall armyworm.
In February 2020, CIMMYT partnered with agricultural development directorates in two provinces to train 130 people on how to scout for fall armyworm and recommended solutions, based on integrated pest management principles.
In late 2019, CIMMYT engaged with the public and private sector through training workshops to disseminate proven practices to control the pest.
“Before, I was unable to recognize the pest that had destroyed my maize field. The hands-on training has been very informative,” said Urmila Banjgayu, a lead farmer who participated in one of the trainings. “I am certain to share the knowledge and practices that I learned with other farmers in my locality. They need to know what to do and what not to.”
Through the Nepal Seed and Fertilizer (NSAF) project, CIMMYT staff is working closely with the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development, the Nepal Agricultural Research Council (NARC), the PQPMC, provincial governments, and other USAID-funded projects and development partners in Nepal. Together, they have developed integrated pest management packages, informative factsheets and surveillance guidelines. CIMMYT researchers have shared experiences on pest management, surveillance and scouting techniques from other countries in Asia and Africa. They have also demonstrated digital tools that will help map the spread of the pest and build accurate interpretation for better management.
Fall armyworm awareness campaign
Farmers must learn how to identify and manage this pest. Bijaya Ghimire, a lead farmer from Kanchanpur district, had heard about fall armyworm from a nearby seed company and a few of his friends. He informed the Agriculture Knowledge Center about the symptoms he observed in his maize field, and verification of the larvae and damage confirmed the presence of fall armyworm. Luckily, Ghimire was able to control the pest before severe damage was done.
CIMMYT researchers collaborated with the Prime Minister Agricultural Modernization Project (PMAMP) to implement outreach campaigns in Banke district. This included a mobile information booth, local dissemination of audio messages, and distribution of posters and fact sheets about fall armyworm. The two-day campaign successfully raised awareness about the pest, reaching more than 1,000 farmers from four villages in maize growing areas.
Researchers also worked with Scientific Animations Without Borders (SAWBO) and adapted an educational video on how to identify and scout for fall armyworm in a field into Nepali. In collaboration with the PQPMC, the video was broadcast 42 times on three local TV channels, to an estimated audience of more than one million viewers in June 2019. The video has also received over 2,000 online views. The animated video is being shown to farmers using mobile phones and displayed on big screens during community events and workshops.
“Seamless collaboration is required among the major stakeholders in the country to collectively fight the pest,” said AbduRahman Beshir, CIMMYT seed systems lead for the NSAF project and member of the national fall armyworm taskforce. “The potential impact of fall armyworm poses a fundamental challenge for smallholder farmers in Nepal. If unattended, it is going to be a food security issue and an equally daunting task to safeguard livelihoods.”