The Scaling Scan — launch of 3rd edition
 How many times have we seen innovative ideas launched into the marketplace, seeming to offer answers to key problems, only to see them fail to make the impact that we expected? In the modern world, having a great idea is not enough to ensure market success. Even when new products, processes or technologies have been carefully and successfully tested in trials and studies, the process of scaling and launching them often leads to disappointing results.
How many times have we seen innovative ideas launched into the marketplace, seeming to offer answers to key problems, only to see them fail to make the impact that we expected? In the modern world, having a great idea is not enough to ensure market success. Even when new products, processes or technologies have been carefully and successfully tested in trials and studies, the process of scaling and launching them often leads to disappointing results.
History of the Scaling Scan
“The Scaling Scan is a necessary breakthrough for those connected with meaningful impact. The Scaling Scan is accessible, practical, grounded in the reality, and most importantly, a watershed rethinking the ‘bigger is better’ logic of scaling.”
Rob McLean, CIMMYT scaling coordinator senior program specialist in Policy and Evaluation at IDRC and author of “Scaling Impact”
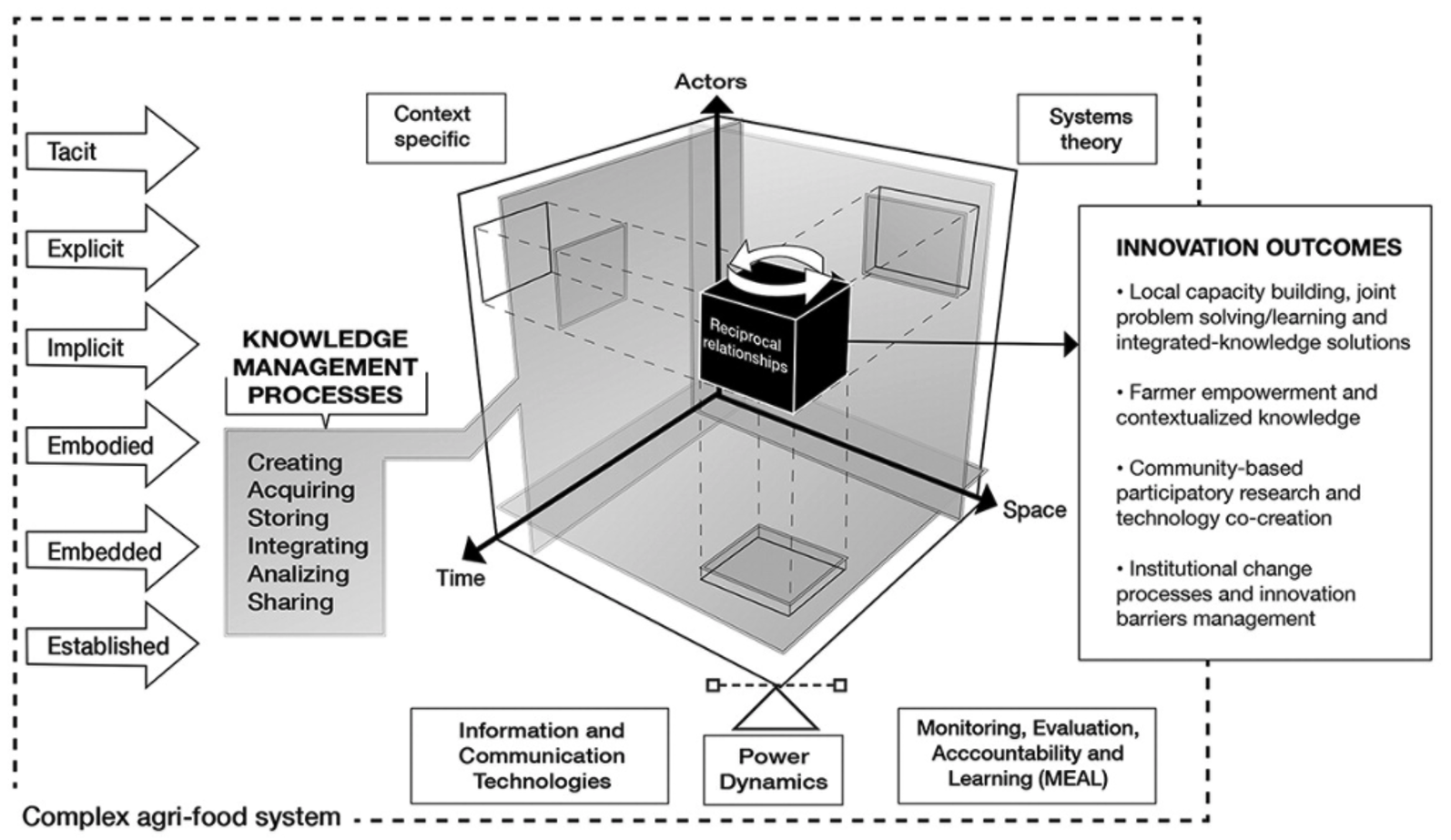
The Scaling Scan was developed to improve this process and ensure that new innovations have the best chance of success. Traditionally, scaling an innovation has often resulted in “linear” thinking, where the project team focuses on the advantages of their new product and relies on these for launch. The Scaling Scan encourages teams to broaden their thinking into areas within the overall private and public sector environments where they may have less experience, but which can greatly help or hinder the success of new ideas. It looks at 10 “ingredients” to consider, discuss, and develop strategies to address — ranging from end-user financing and business cases to national strategies and regulations.
The first version of the Scaling Scan was launched in 2017 following cooperation between scaling expert Lennart Woltering at CIMMYT and the Public Private Partnership Lab (PPPLab), a research consortium based in the Netherlands. A second, updated version was released the following year. The tool has been implemented through workshops held around the world, with trained moderators to encourage discussion, share ideas and develop expertise. These discussions resulted in five action steps:
- Evaluation of realistic targets for the scaling — is the team’s thinking too ambitious, or alternatively, has the analysis identified further opportunities?
- Consideration of the impact on other areas of concern — for example, the environment or social dynamics (such as gender roles and relations).
- Identification of weak areas of expertise that hold back scaling — for example poor access to finance or lack of evidence that would convince others to join the cause.
- New and better-informed directions for project management, taking into consideration their own capacities, networks, and power.
- Identification of knowledge and expertise that would be of benefit to the scaling team.
More than 1,200 participants attended the workshops that were held in English, Spanish and French. Half of the workshops were held in Africa, with the rest divided between Asia and North and South America, including 11 in Mexico. In 2022, an online version was made available through the launch of a new website, https://scalingscan.org/ with support from the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) and the One CGIAR Mitigate initiative. This has further increased the availability of and access to scaling information.
“The Scaling Scan pushes users to go beyond a narrow focus on scaling an innovation. It is a great tool that enables practical thinking about the multiple pathways to impact at scale and the range of stakeholders that need to be considered in scaling process.”
Kelly Hayley Price, DRC senior evaluation officer
3rd edition Scaling Scan Launch
On September 14, 2023, the 3rd edition of the Scaling Scan will be launched. With the support of GIZ, FAO, Alliance, and SNV, the tool has been enhanced to include some changes inspired by discussions at the workshops. There is increased consideration of gender roles and how these might affect, or be affected by, a scaling program. Likewise, the impact of climate change is also included. In terms of usability, the Scaling Scan has been adapted to make it more accessible to use without a moderator, meaning that users will be able to benefit even if they have difficulty getting to a workshop. It has also been designed to make it easier to customize the Scaling Scan to fit one’s own needs, rather than requiring the standard version used in workshops.
To find out more about the Scaling Scan, please visit https://scalingscan.org/, or email e.valencia@cgiar.org for more information.