Digital imaging tools make maize breeding much more efficient

To keep up with growing maize demand, breeders aim at optimizing annual yield gain under various stress conditions, like drought or low fertility soils. To that end, they identify the genetic merit of each individual plant, so they can select the best ones for breeding.
To improve that process, researchers at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) are looking at cost-effective ways to assess a larger number of maize plants and to collect more accurate data related to key plant characteristics. Plant phenotyping looks at the interaction between the genetic make-up of a plant with the environment, which produces certain characteristics or traits. In maize, for example, this may manifest in different leaf angles or ear heights.
Recent innovations in digital imagery and sensors save money and time in the collection of data related to phenotyping. These technologies, known as high-throughput phenotyping platforms, replace lengthy paper-based visual observations of crop trials.
Authors of a recent review study on high-throughput phenotyping tools observe that obtaining accurate and inexpensive estimates of genetic value of individuals is central to breeding. Mainassara Zaman-Allah, an abiotic stress phenotyping specialist at CIMMYT in Zimbabwe and one of the co-authors, emphasizes the importance of improving existing tools and developing new ones. “Plant breeding is a continuously evolving field where new tools and methods are used to develop new varieties more precisely and rapidly, sometimes at reduced financial resources than before,” he said. “All this happens to improve efficiency in breeding, in order to address the need for faster genetic gain and reduction of the cost of breeding.”
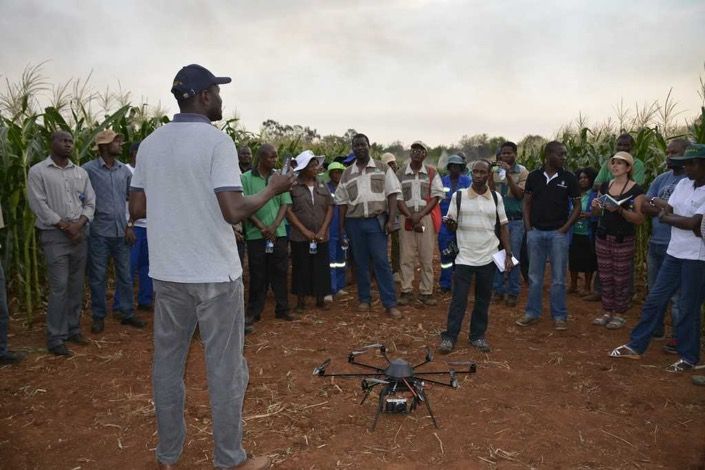
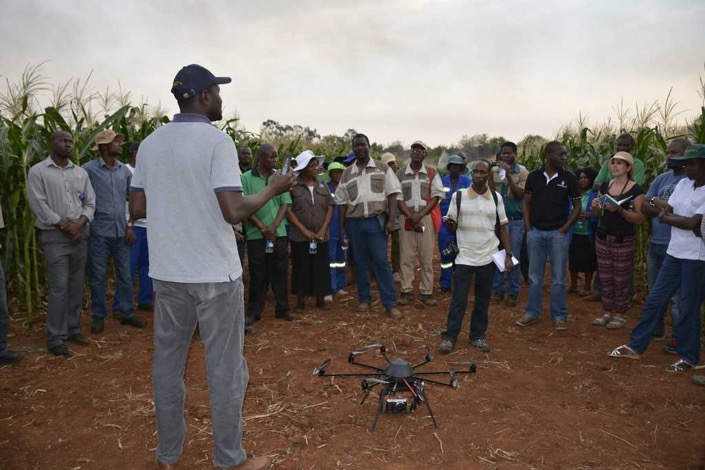
“Under the Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) project, we are working on implementing the use of drone-based sensing, among other breeding innovations, to reduce time and cost of phenotyping, so that the development of new varieties costs less,’’ said Zaman-Allah. “The use of drones cuts time and cost of data collection by 25 to 75 percent compared to conventional methods, because it enables to collect data on several traits simultaneously — for example canopy senescence and plant count,” he explained.
Another great innovation developed under this CIMMYT project is what Zaman-Allah calls the ear analyzer. This low-cost digital imaging app allows to collect maize ear and kernel trait data 90 percent faster. This implies higher productivity and rigor, as more time is dedicated to data analysis rather than time spent on data collection. Using digital image processing, the ear analyzer gives simultaneous data of more than eight traits, including ear size and number, kernel number, size and weight.
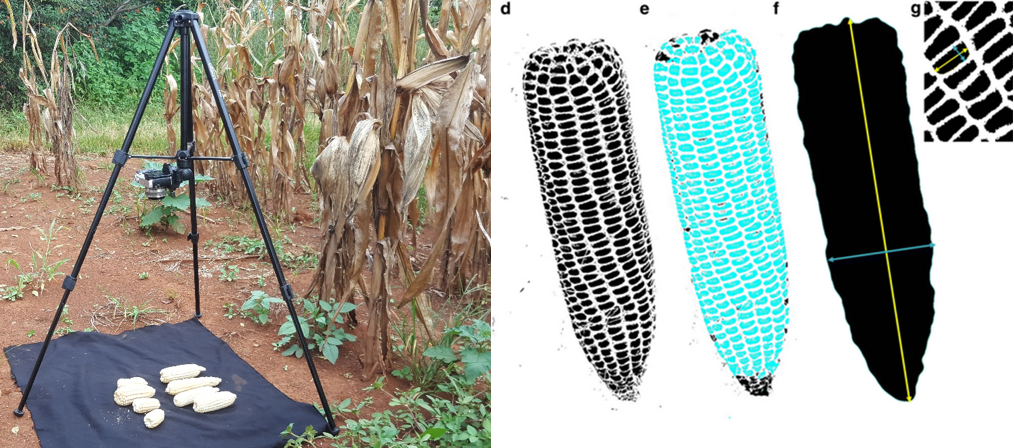

Some national agricultural research systems and NGOs have adopted this digital imagery tool to better assess maize yields in farmers’ fields. For instance, CIMMYT and GOAL have used this tool to assess the extent of fall armyworm impact on maize crops yield in eastern Zimbabwe.
Scientists are exploring the use of different sensors for phenotyping, such as Red, Green and Blue (RGB) digital imaging or Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) devices. Infrared thermal and spectral cameras could lead to further progress towards faster maize breeding.
Such sensors can help collect numerous proxy data relating to important plant physiological traits or the plant environment, like plant height and architecture, soil moisture and root characteristics. This data can be used to assess the maize crop yield potential and stress tolerance.
Such breeding innovations are also making maize research more responsive to climate change and emerging pests and diseases.