The other revolution that was born in Mexico: The legacy of sustainable transformation and its new roots

The Mexican Revolution was not the only transformative movement to emerge in Mexico. Another profound transformation began in the Mexican countryside, and today, far from guns, today it continues to drive a more peaceful and resilient society through the integration of science, innovation and ancestral knowledge.
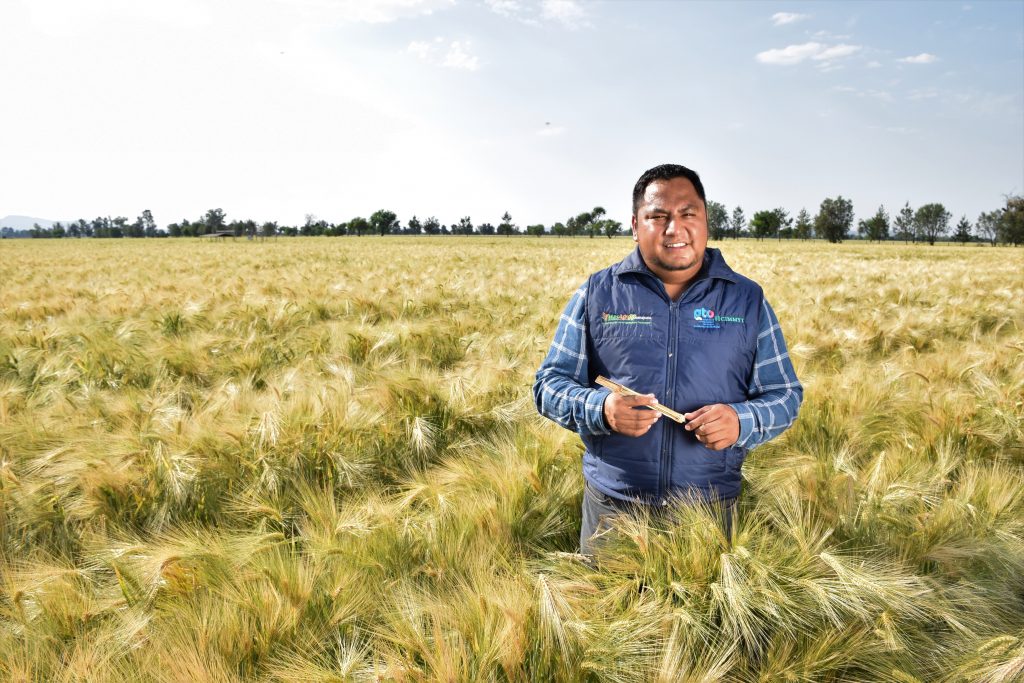
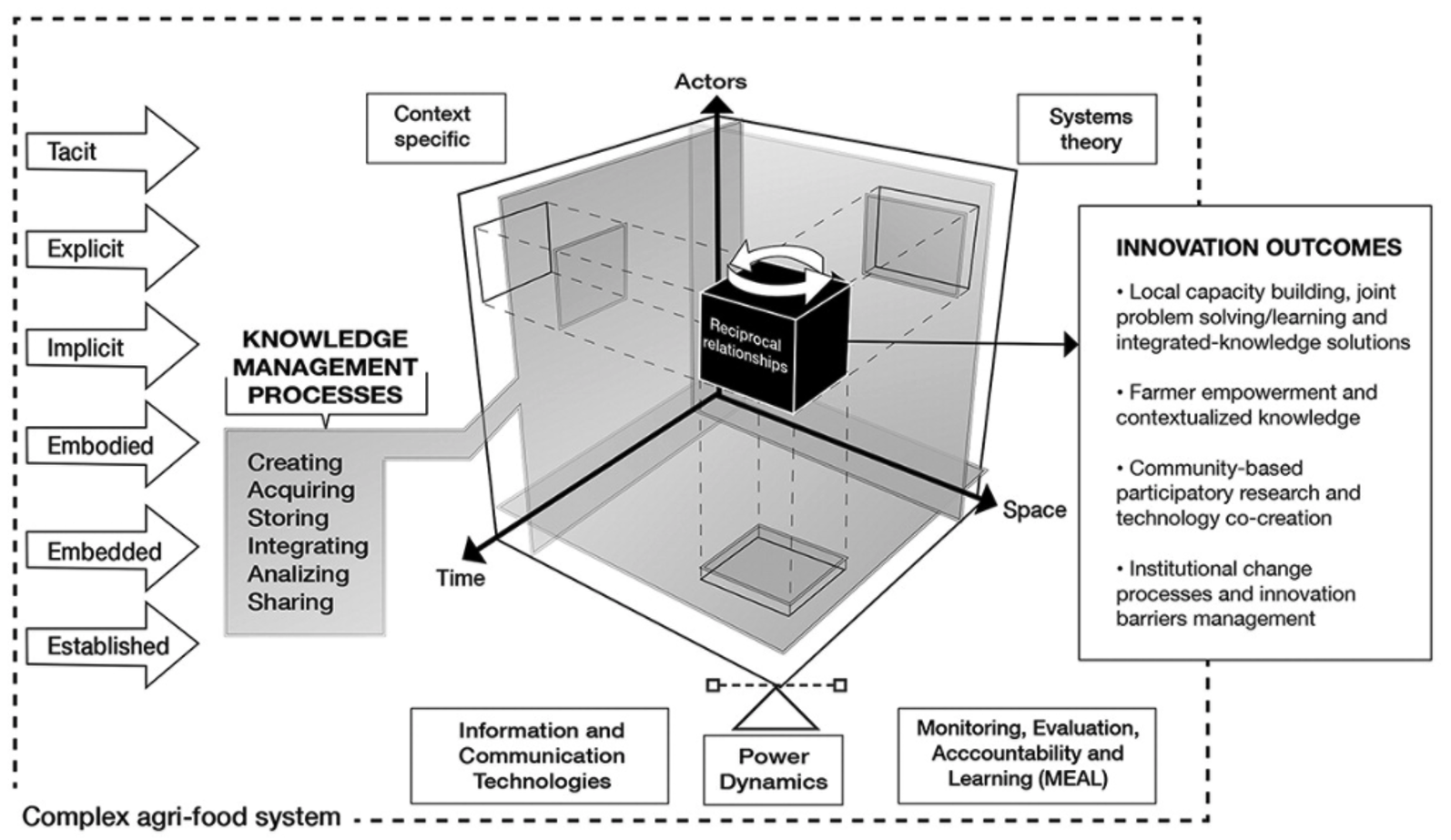
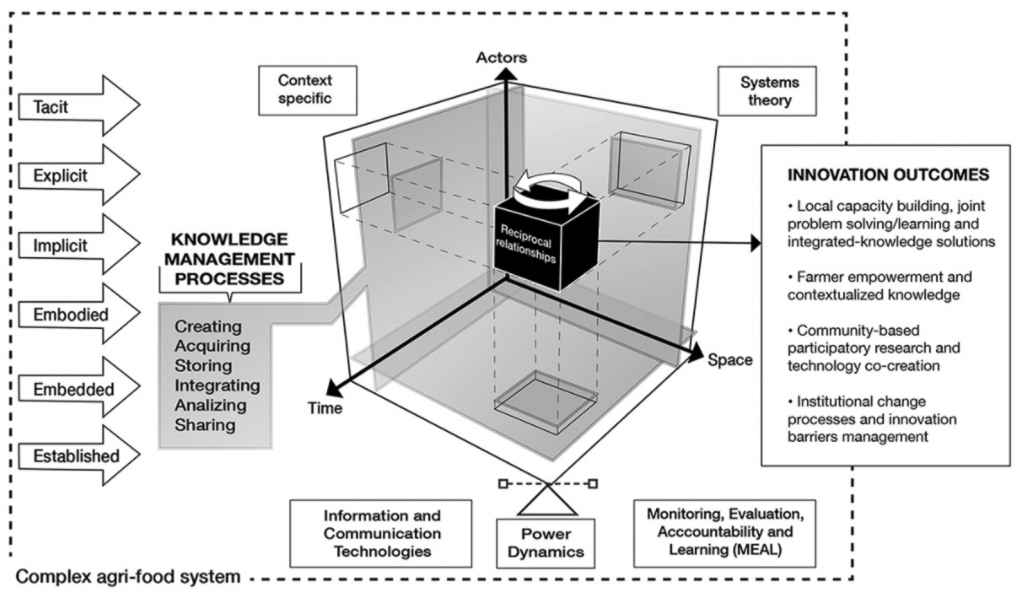
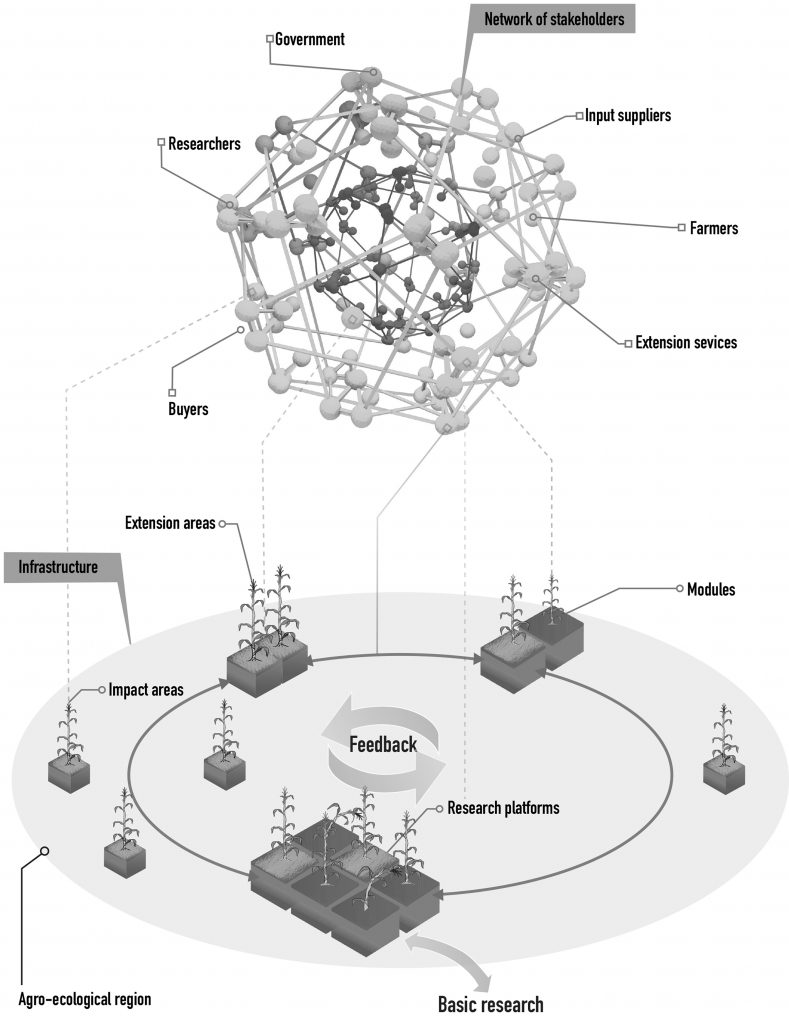
In the 1960s, Mexico set a precedent for global agricultural change. Today, that movement has evolved into a sustainability approach that responds to today’s challenges: climate change, biodiversity loss and the need to ensure food security. Under CIMMYT’s leadership, the Hub model has established itself as a key tool for delivering scientific solutions to producers, strengthening resilient and sustainable agricultural systems.
At CIMMYT, we believe that ensuring food security means not only producing healthier food but also conserving natural resources such as soil and water and promoting the well-being of farmers and their communities. Through the Hub model, we have promoted practices such as the sustainable management of staple crops such as maize and related crops, and the use of strategies to strengthen the seed system to meet the challenges of the agricultural sector.
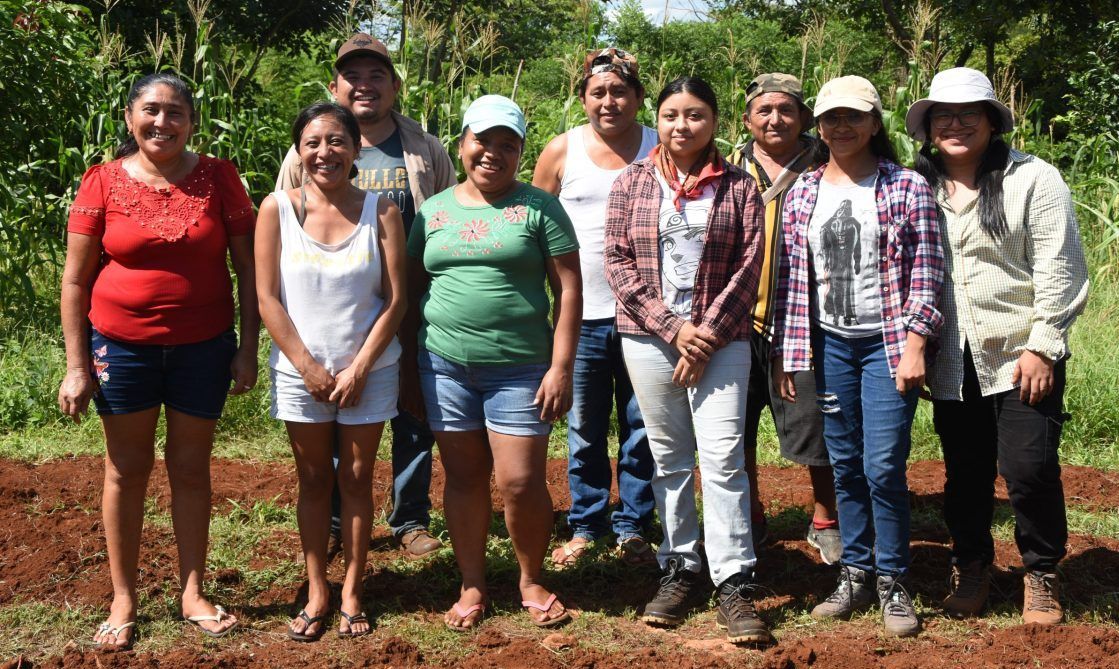
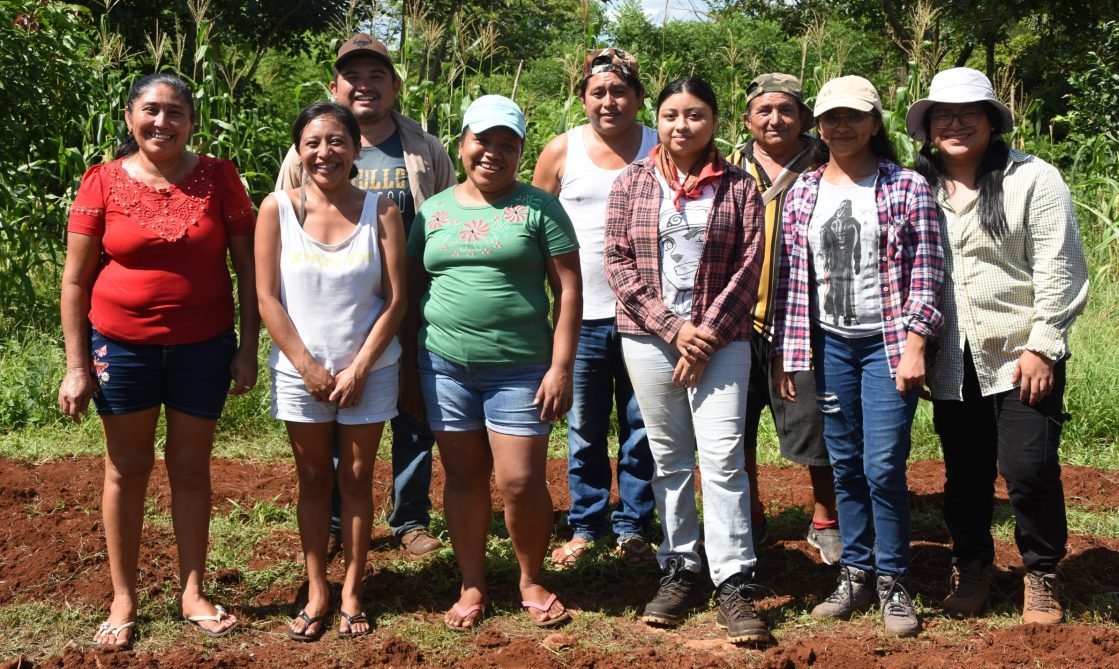
A clear example of this approach is the Maíz Criollo Kantunil group in Yucatán. Led by Edgar Miranda, this collective of eight families has adopted innovative practices such as regenerative agriculture, efficient water use and agroecological pest management. By linking with the Hub model, the group has been able to conserve native seeds, strengthen local agroecology and generate social and productive benefits for their community.
“Our main objective is that the next generations will have seeds available to meet their food needs,” said Edgar Miranda. “We work with sustainable practices that allow us to conserve our resources and produce healthy crops,” he added.
In addition to supporting producers, the Hub model fosters associativity and community participation, essential pillars for building inclusive and resilient food systems. These activities are in line with national initiatives such as strengthening production chains, but also reflect CIMMYT’s commitment to a global approach to sustainable development.
CIMMYT’s strategy in Mexico not only supports producers in transforming their agricultural systems, but also promotes strategic alliances with public and private actors. These collaborations strengthen the integration of scientific solutions and sustainable practices, stimulate innovation in rural communities, and promote resilience to the challenges of climate change. With an approach based on science, inclusiveness and continuous learning, CIMMYT continues to contribute to building a more equitable, sustainable and prosperous future for Mexico and the world.