Untapped potential of genome-edited crops explored in new research
Analysis of evidence by scientists of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and CGIAR concludes that the scientific risks of genome editing are similar to those of traditional breeding: all new varieties, however developed, need to be tested for agronomic performance in a range of environments.
Social risks are mainly that these powerful technologies may be rendered inaccessible to less-commercial crops and farmers if intellectual property (IP) and regulatory policies make them expensive or difficult to use.
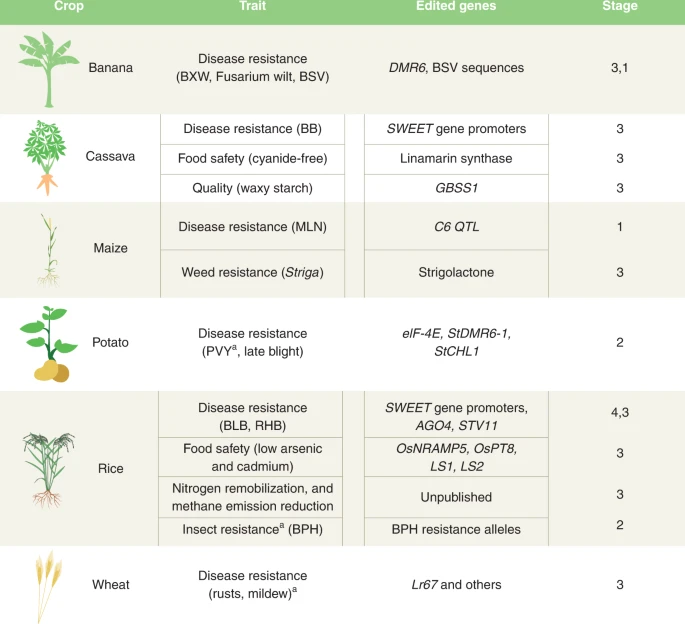
Genome editing has demonstrated potential to contribute to food security, improved nutrition, and value addition for farmers and consumers.
Many countries are still uncertain about whether to grow, or if and how to regulate genome-edited crop varieties. The Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) has stated that genome-edited crops should be considered as transgenics in the EU for regulatory purposes, a decision that could limit their use in Africa. On the other hand, several countries, including USA, Canada, Brazil, Colombia, Argentina, Chile, Kenya, Nigeria, Israel, India, and Japan have determined that genome-edited crops should not be regulated like transgenics if they do not contain foreign DNA.
Policies should enable choice and avoid the risk that genome editing technologies for crops benefit only those who can pay premium price. Smallholder farmers should have equal access to advanced technologies, should they wish to use them, as well as relevant and objective information about their value and how to use them.
Read the full study: Genome-edited crops for improved food security of smallholder farmers
CIMMYT Position Statement on Novel Genome Editing Technologies in Crops