Driving Varietal Turnover: Insights from Market Intelligence and Seed Systems in Tanzania
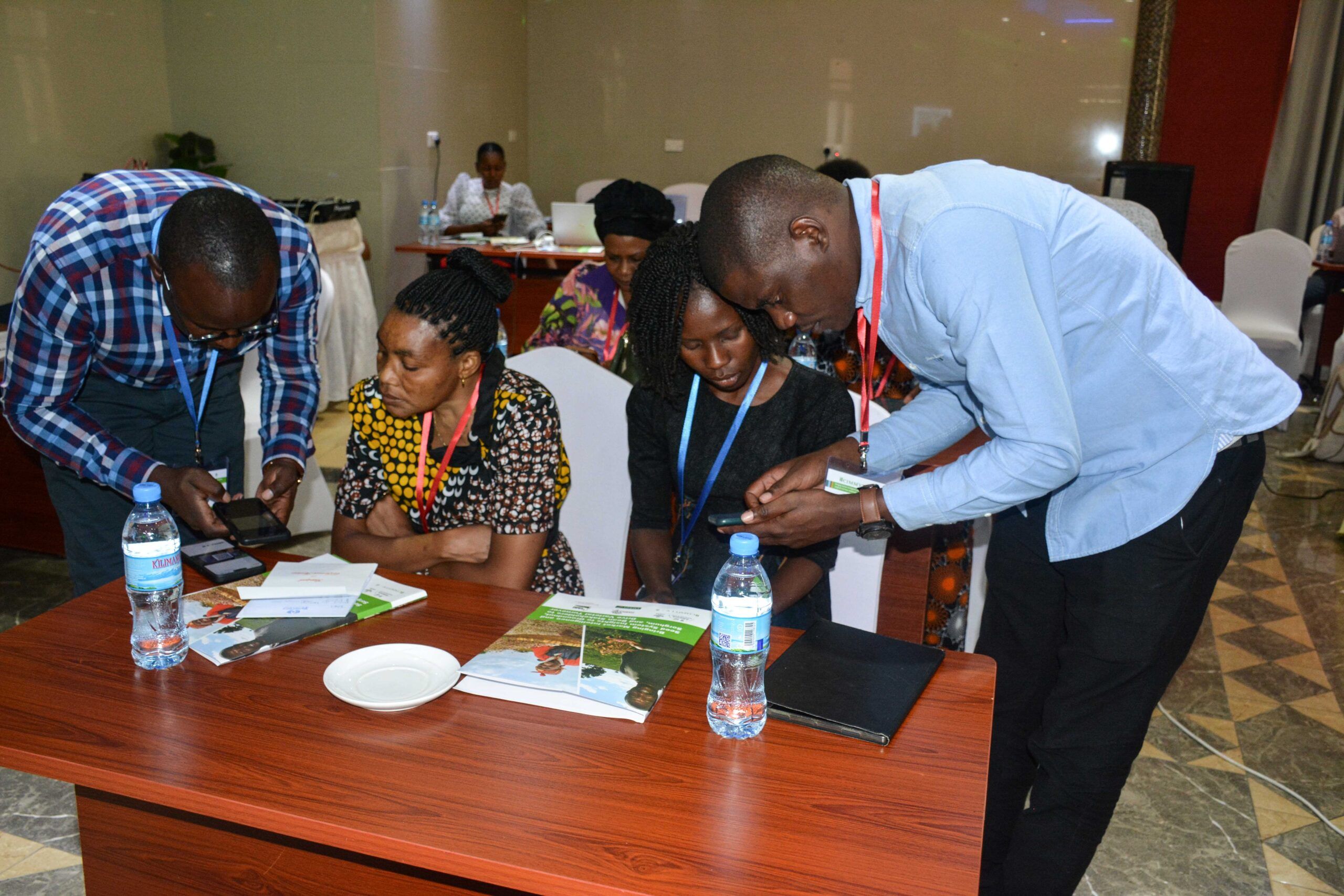
How can market intelligence and seed system insights drive varietal turnover for groundnut, sorghum, and bean stakeholders? This was the central question explored during a series of workshops convened by the Accelerated Varietal Improvement and Seed Systems in Africa (AVISA) and The Accelerated Varietal Adoption and Turnover for Open-Pollinated Varieties (ACCELERATE) projects.
Held from October 21-25, 2024, across three locations in Tanzania, these workshops were designed to identify practical solutions for improving varietal turnover.
Organized by CIMMYT in collaboration with the Tanzania Agricultural Research Institute (TARI), the Alliance of Bioversity & CIAT, the Pan-Africa Bean Research Alliance (PABRA), and the Tanzania Official Seed Certification Institute (TOSCI), the workshops brought together stakeholders across the agricultural value chain.
The AVISA Project focuses on modernizing crop breeding programs and strengthening seed systems to enhance the productivity, resilience, and marketability of key dryland cereals and legumes in sub-Saharan Africa. By ensuring that smallholder farmers have access to high-quality improved varieties, AVISA contributes to better food security, nutrition, and economic development.
ACCELERATE, complementing AVISA’s efforts, focuses on market-driven adoption strategies by analyzing the requirements and constraints of both large- and small-scale marketplace traders. It aims to catalyze the uptake of new varieties through market intelligence-driven interventions and foster partnerships across formal, semi-formal, and informal seed sectors to accelerate varietal adoption and turnover.
The workshops opened with expert presentations from breeders and seed system specialists from CIMMYT, CIAT, and TARI. Key topics included the adoption of improved seeds for groundnuts, sorghum, and beans; groundnut processing for peanut butter; the sustainability of digital inclusion initiatives; challenges and opportunities in seed systems; and the increasing demand for crops such as groundnuts, sorghum, and beans. The speakers provided valuable insights into crop production, seed availability, market demand, and the desired traits for improved crop varieties.

Three separate sessions were held in Arusha, Dodoma, and Dar es Salaam, bringing together farmers, processors, traders, and researchers to deliberate on systemic challenges affecting varietal turnover. Participants then identified practical solutions to enhance the adoption of improved varieties of sorghum, beans, and groundnuts.
Opening each workshop session, TARI representatives emphasized the critical role of high-quality seeds in realizing higher crop yields and achieving agricultural growth.
“We are here to ensure improved varieties leave shelves and reach farmers’ fields in efforts to support the envisaged 5% annual growth in agriculture,” remarked Fred Tairo, the TARI Manager in Dar es Salaam. In Arusha, Nicholaus Kuboja, TARI Center Director, Selian, highlighted the importance of market intelligence. “Market intelligence is crucial, as market access has been a persistent challenge across African countries, particularly for smallholder farmers, in securing profitable markets for their produce.”
The Director General of TARI, Thomas Bwana, speaking in Dodoma, focused on partnerships. “We are actively promoting the production and distribution of early generation seed, particularly breeder seed, for access by downstream seed producers. Through collaborations with other value chain actors, we strive to ensure that these seeds meet the quality standards needed by both seed and grain producers, as well as consumers who are keen on specific varietal traits,” he noted.
The subsequent discussions underscored the importance of collaboration and innovation to meet the rising demand for these vital crops.
Identifying Challenges
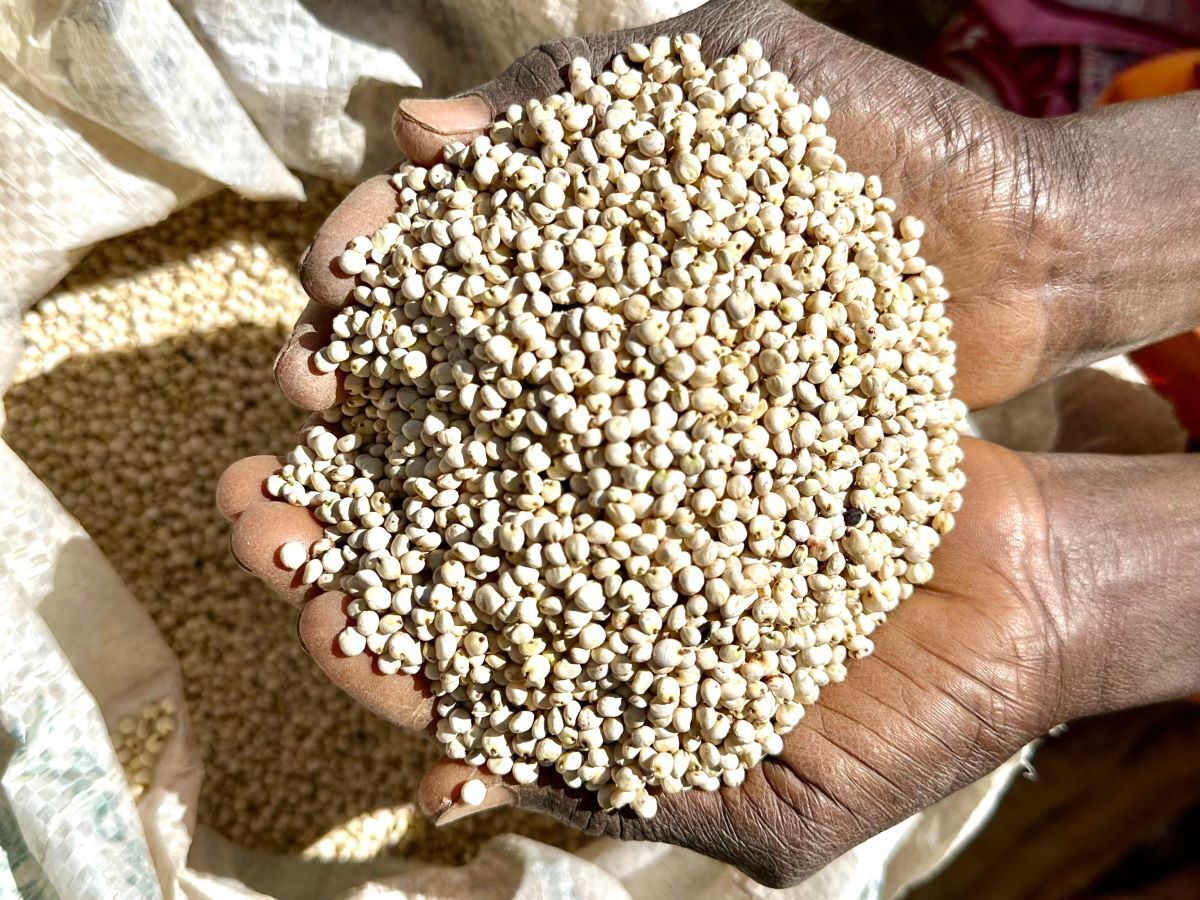
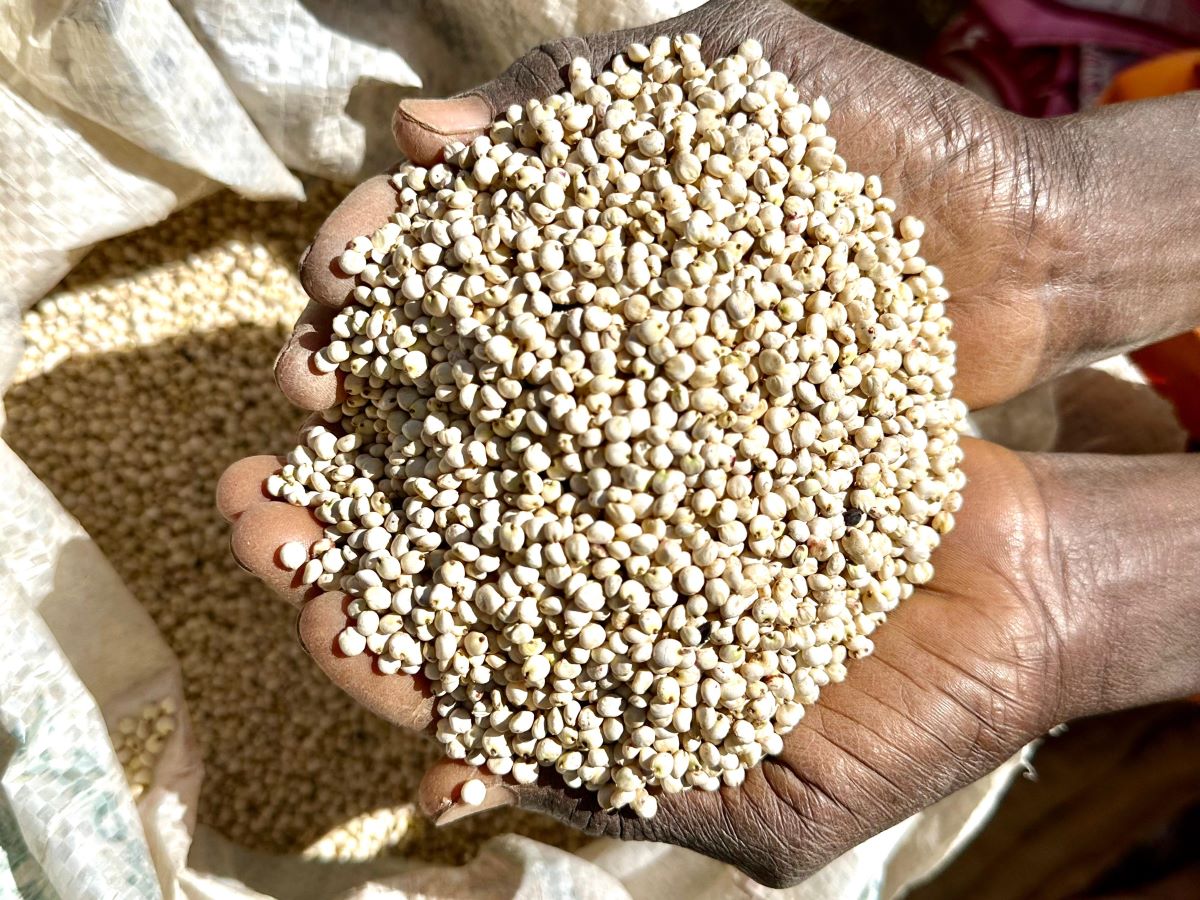
In experience sharing among participants across the three workshops, some key challenges were brought to light. For instance, farmers reported limited access to certified seeds as a major barrier to increasing productivity. A farmer from Dodoma expressed concern that current seed distribution networks often do not reach remote areas, leaving farmers with no option but to use inferior seeds from the sources available.
“We want to use quality seed, but the distribution networks don’t reach us,” he said. On the other hand, traders expressed frustration over inconsistent supplies of high-quality grain produce, which is also aggravated by poor grain handling due to inadequate storage conditions leading to contamination.

One groundnut trader noted, “Poor pre- and post-harvest handling has led to smaller, shriveled nuts, making it difficult for traders to meet market expectations.” Processors echoed these concerns, highlighting aflatoxin contamination as a significant problem that undermines both product safety and marketability. They stressed the need for better practices. “We need better practices at every stage of the value chain to minimize aflatoxin contamination in the grains sourced for processing,” emphasized one processor.
Additional challenges emerged, with common bean farmers highlighting difficulties with post-harvest storage and pest damage, which reduced both quality and market value. Processors, meanwhile, pointed out consumer misconceptions that hinder the acceptance of improved varieties. For instance, white sorghum varieties that naturally turned brown during processing were sometimes perceived as inferior, underscoring the need for better consumer education.
Unveiling Solutions
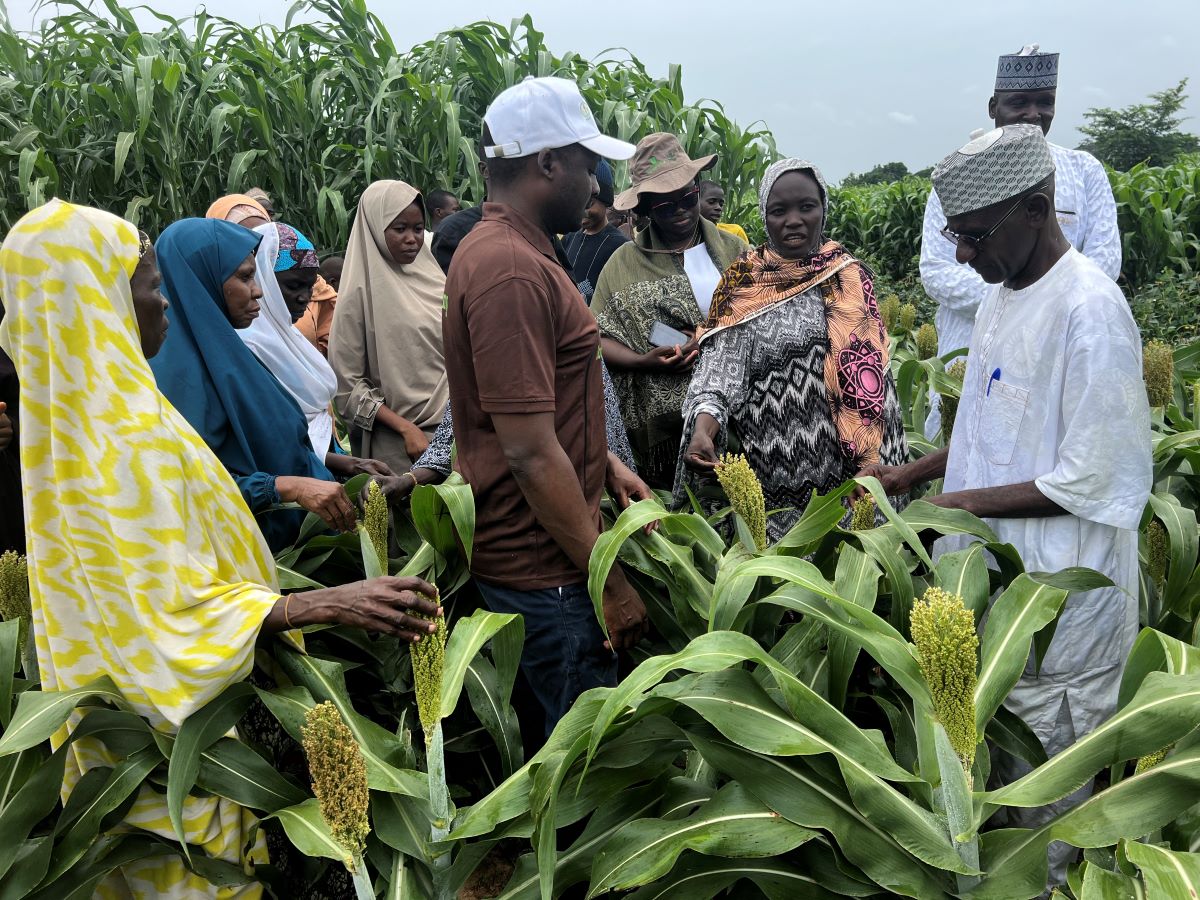
Despite the challenges, the workshops were a source of optimism, as well as underscoring viable, innovative solutions and actionable strategies to drive progress. Participants explored newly released crop varieties, including TARI Sorg 1 and TARI Bean 6, which offer higher yields, disease resistance, and improved nutritional content. Stakeholders in Dodoma emphasized the use of digital tools such as WhatsApp channels and SMS for real-time updates on seed availability and agronomic practices. “Modernizing how we share knowledge can bridge gaps between farmers and researchers,” remarked one participant.
Capacity building emerged as a key strategy for tackling many of the systemic issues discussed. Farmers called for more training on seed handling and post-harvest practices to reduce losses and improve crop quality. Processors stressed the need for targeted interventions for aflatoxin management, a critical step in ensuring the safety and marketability of groundnuts. Researchers and agricultural organizations underscored the importance of aligning breeding programs with market needs.
In Arusha, discussions centered on developing groundnut varieties tailored to specific processing needs, such as improving peanut butter quality to meet consumer preferences and market standards.

Expanding the seed distribution network also emerged as a key priority. TARI committed to scale up the production of Quality Declared Seed (QDS) and strengthen partnerships with private seed companies to ensure a consistent supply of high-quality seeds across the country. “Quality seeds must reach every corner of the country,” affirmed a TARI scientist. The stakeholders also called on breeding programs to align with market demands, emphasizing the need to tailor improved varieties to specific consumer and processor requirements.
Insights from Stakeholders and Actionable Strategies
Breakout sessions provided a platform for stakeholders to articulate their specific needs. Farmers from Dodoma and Dar es Salaam shared a common observation of increasing demand for groundnuts, sorghum, and beans, largely driven by population growth and international market expansion. In Dodoma, farmers emphasized that improved crop varieties had significantly boosted cultivation over the past decade.
Despite this progress, they highlighted the lack of drought-resistant varieties and limited access to affordable, high-quality seeds as persistent challenges. In Dar es Salaam, farmers noted that while demand for the crops had risen, their ability to meet this demand was hampered by limited seed availability and education on effective usage. Both groups agreed that weak seed distribution networks, high seed prices, and insufficient knowledge undermine productivity.

Processors and traders from both Arusha and Dar es Salaam echoed these concerns but added insights into market dynamics. In Arusha, processors identified aflatoxin as a critical challenge, with inadequate farmer knowledge on grain handling practices exacerbating the issue. Processors also emphasized the need for nutrient-enhanced beans and groundnuts suited for specific products like peanut butter and flour. Traders in Arusha highlighted the need for pure white sorghum and beans free from pests to meet growing demand, particularly for export markets.
As the workshops concluded, participants identified key strategies to strengthen agricultural resilience. These included improving the seed supply chains, enhancing market linkages, and investing in continuous learning and education initiatives.
Echoing this vision, the TARI Director General emphasized in Dodoma, “This is just the beginning. By working together, we can ensure that every farmer, processor, and trader has the tools and knowledge needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving agricultural landscape.”