CIMMYT and WorldVeg Unite for Better Nutrition and Farmer Incomes
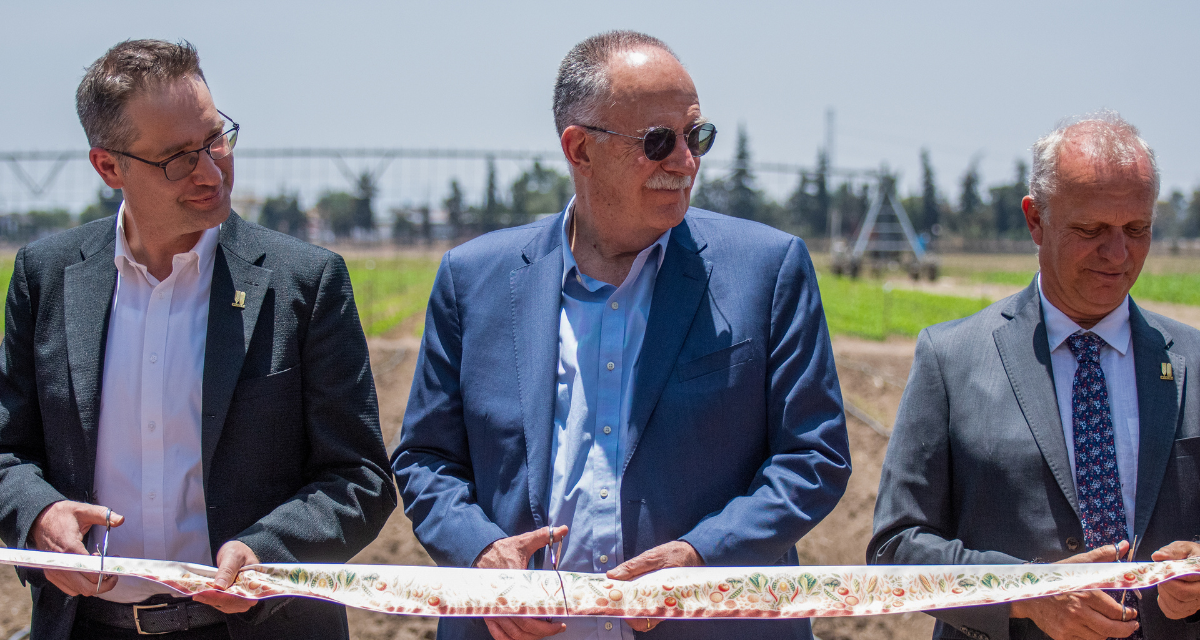
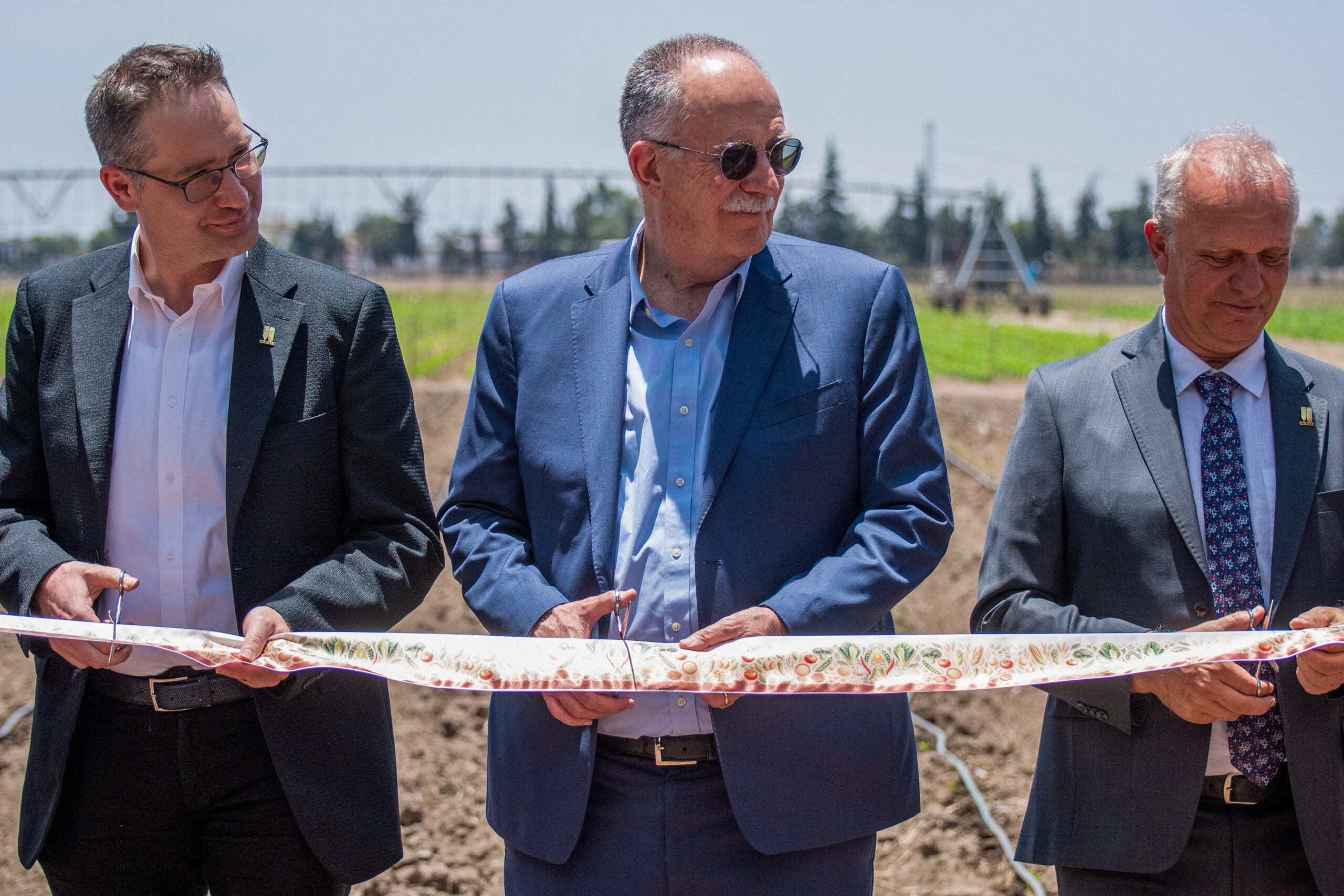
MEXICO CITY — CIMMYT and the World Vegetable Center (WorldVeg ) accelerated its global partnership by launching a new WorldVeg office in Mexico at CIMMYT’s headquarters. This joint location will provide improved nutrition, soil health and earning potential for global farmers.
“When vegetables and cereals grow together, the benefits multiply for people and the planet,” said Bram Govaerts, Director General of CIMMYT.
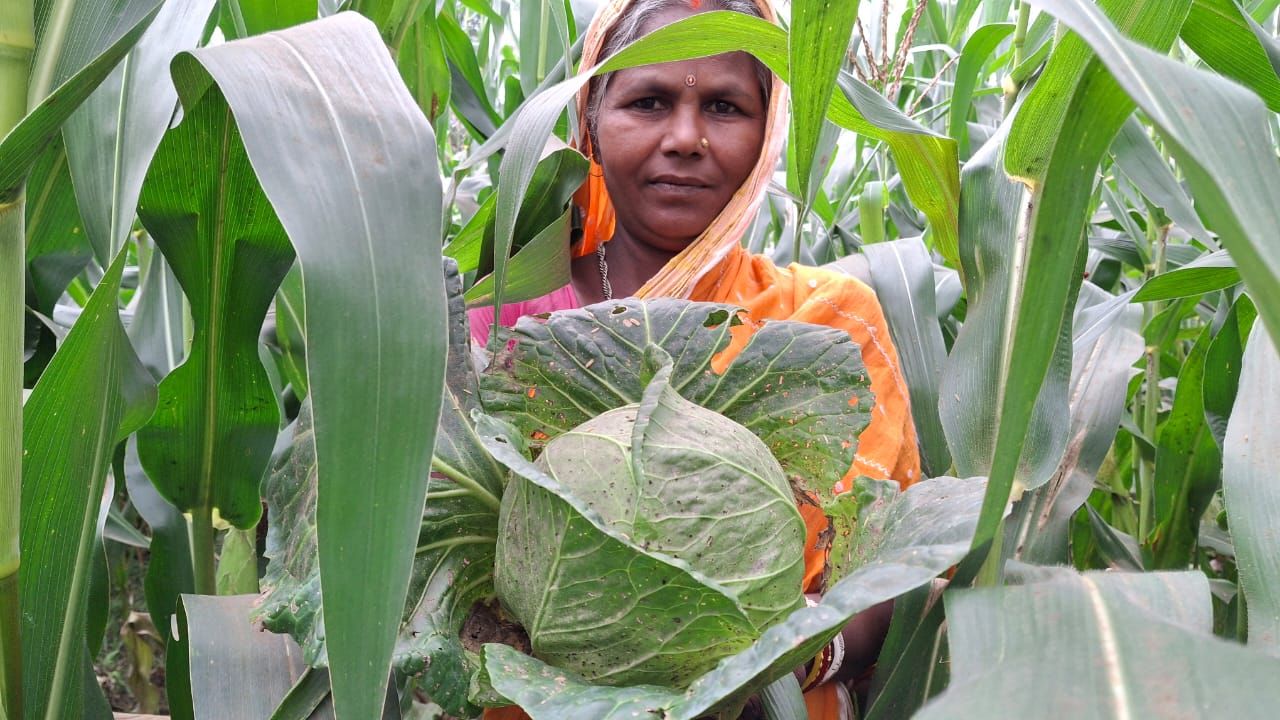
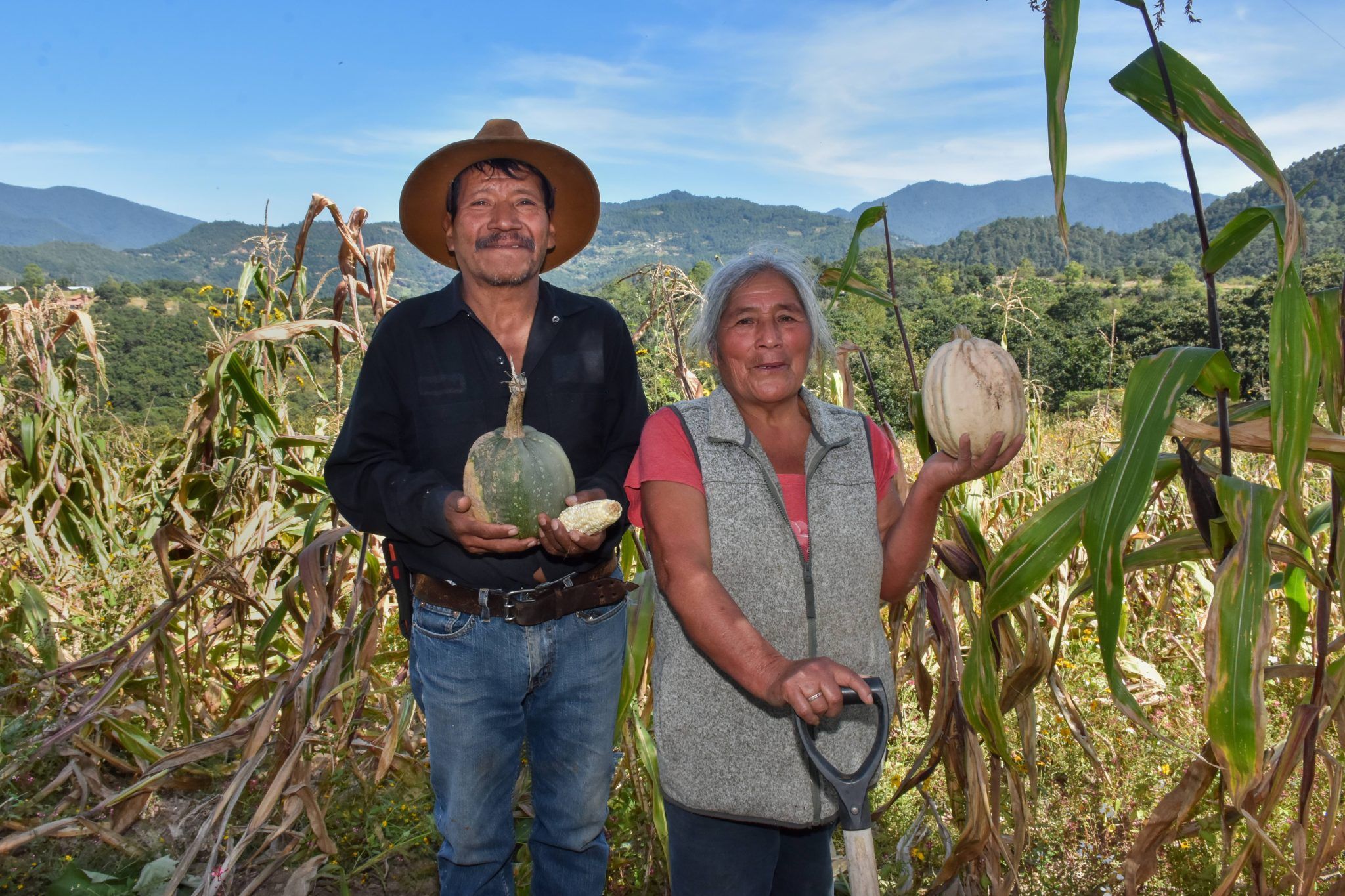
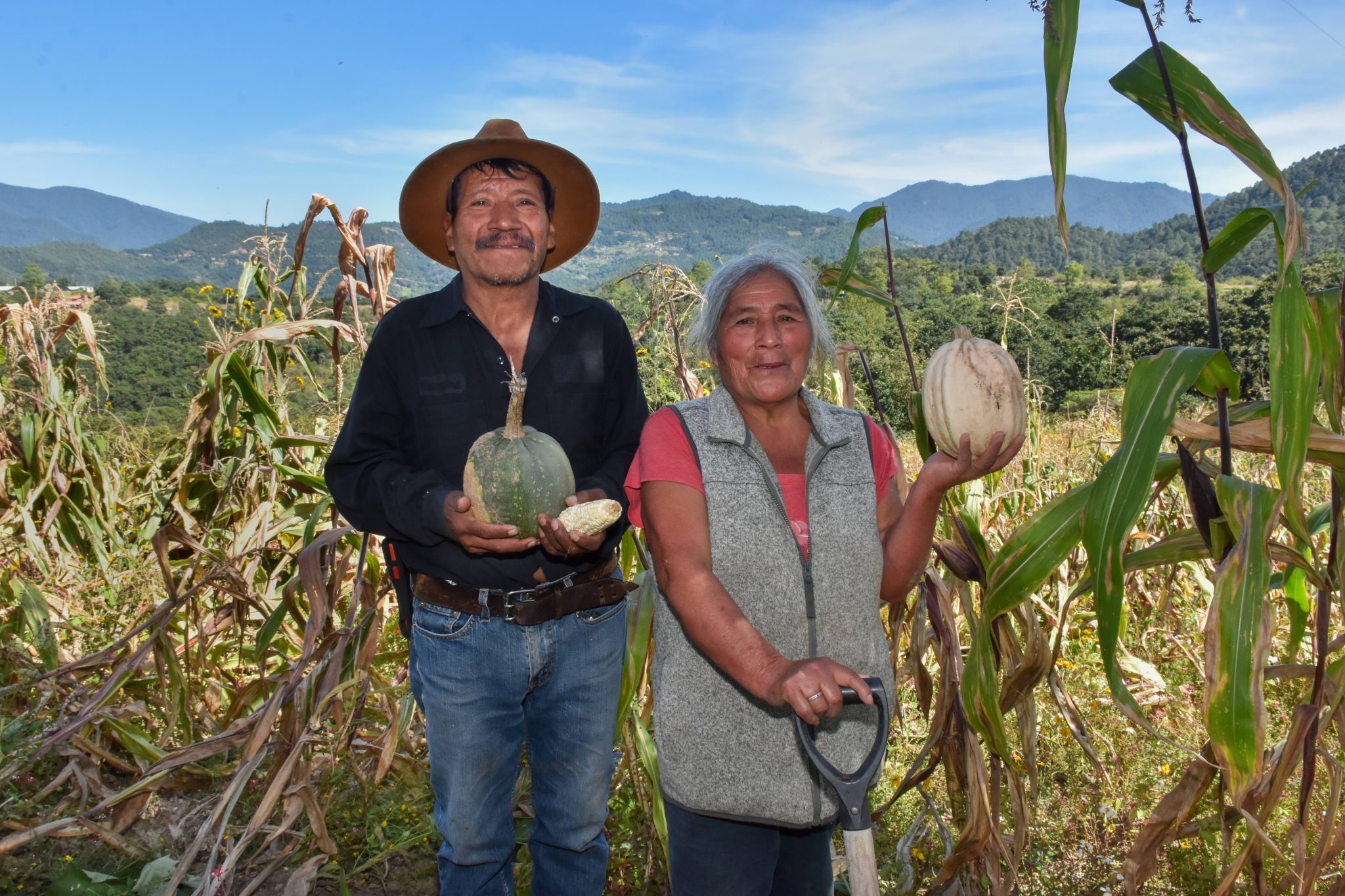
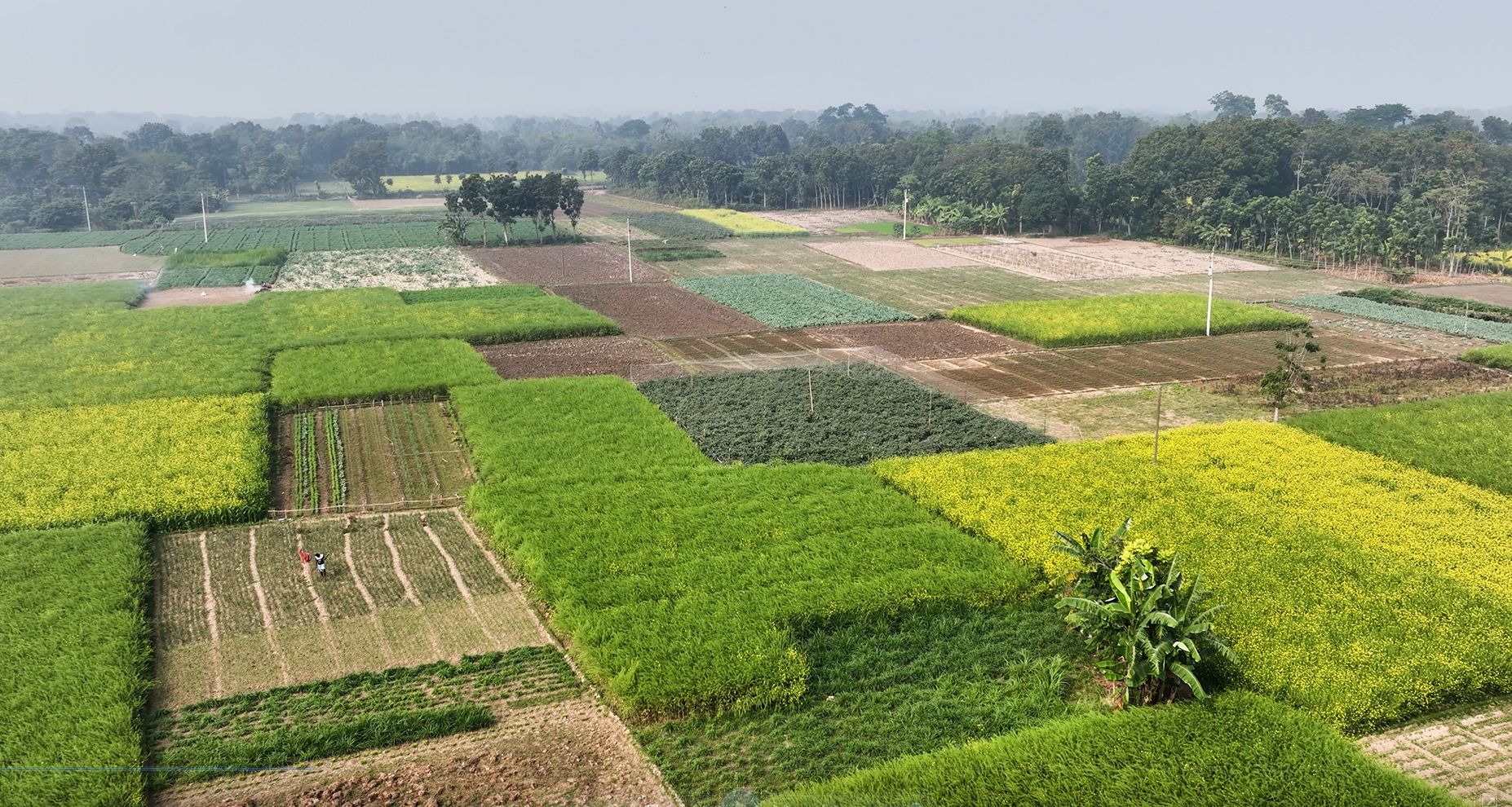
Govaerts said he is eager to scale a proven global track record of collaboration across Mexico, Latin America and the wider world. CIMMYT and WorldVeg’s partnership is already delivering results in Mexico and Central America. For years, the organizations have collaborated to improve production in the traditional milpa system—where maize is grown with beans and squash, often known as the “three sisters.” Collaboration increased yields, helped balance diets and conserved biodiversity.
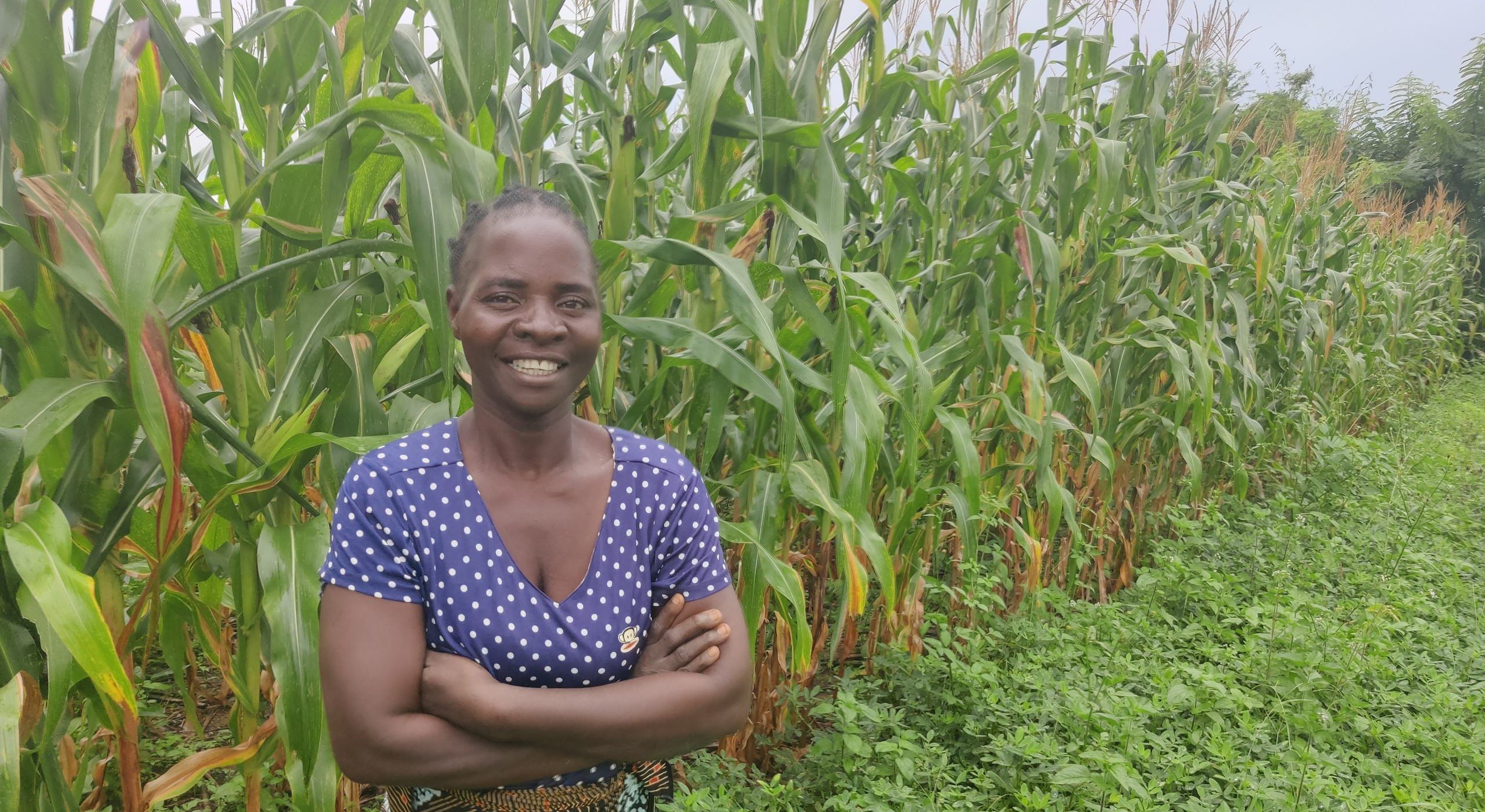
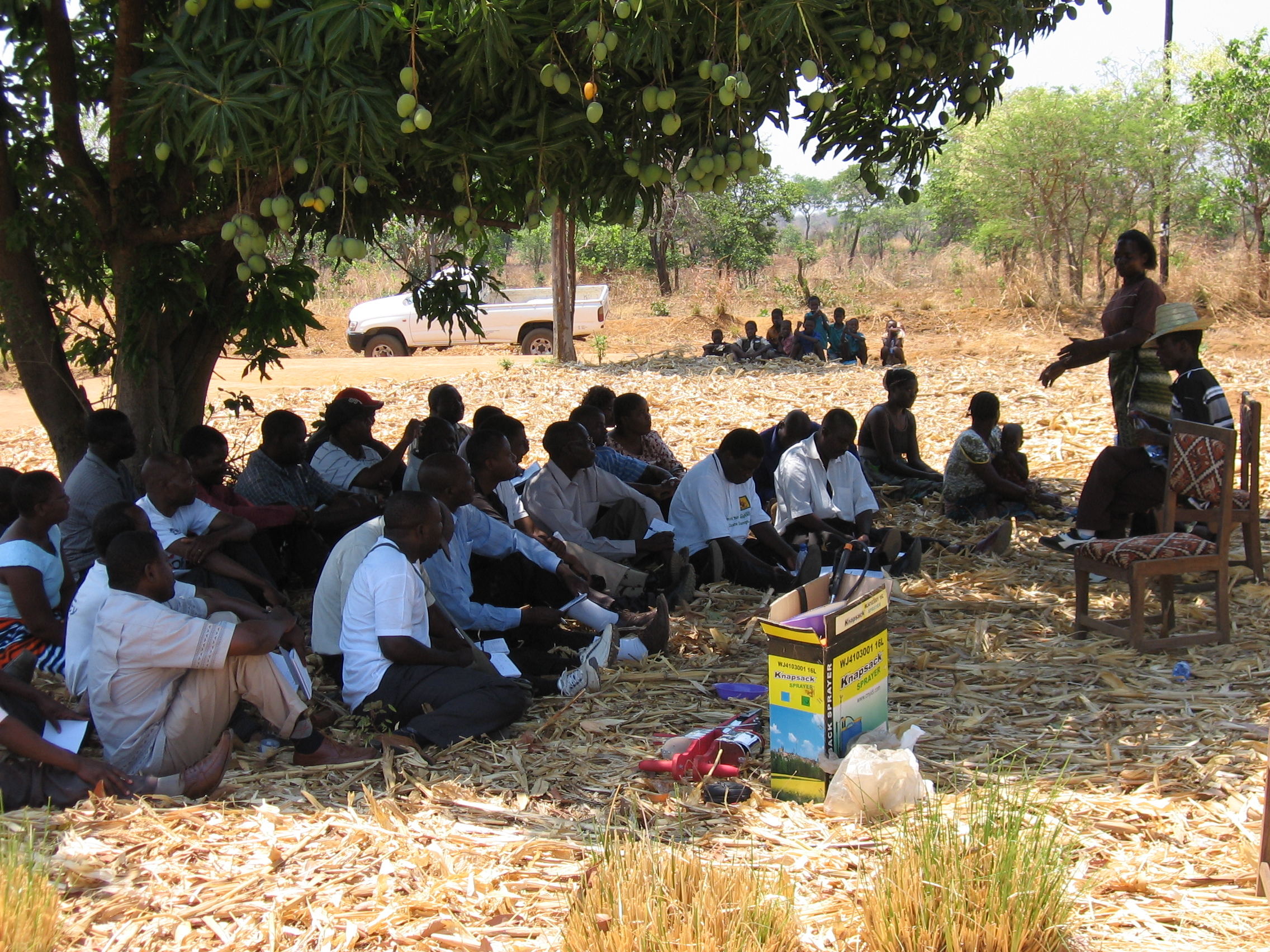
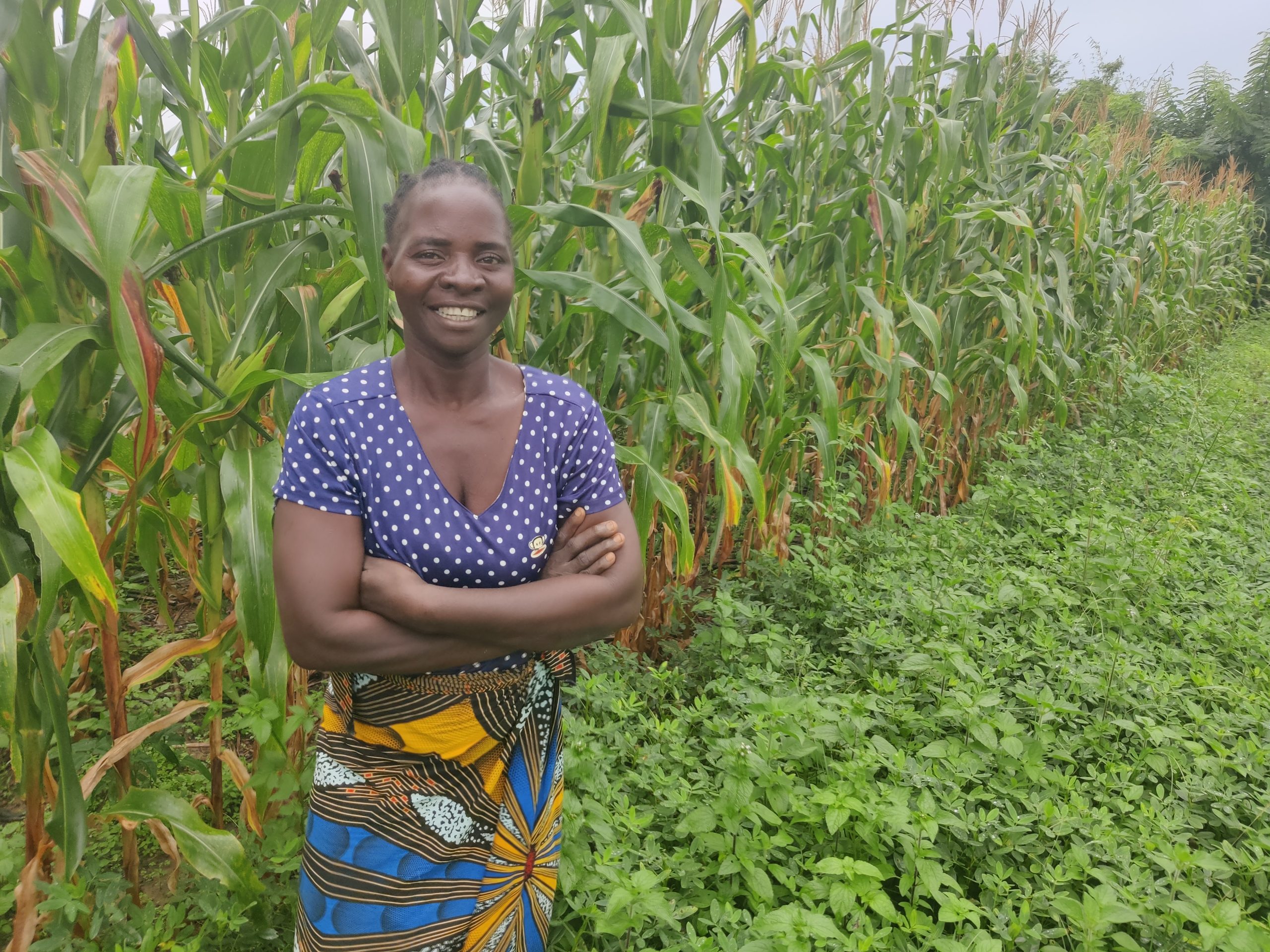
The collaboration also builds on the more than 100,000 people reached in Sudan, Malawi, Tanzania, and Zambia through CIMMYT and WorldVeg collaboration. These joint projects have improved dietary diversity, soil health and incomes by cultivating both vegetables and cereals. In Tanzania alone, the collaboration has increased the sales of value-added products by 50%.
“This partnership represents tangible, scalable diversification options for farmers,” said Marco Wopereis, Director General of WorldVeg. “Integrating vegetables into cereal systems improves nutrition, raises incomes, and builds sustainability, beginning in Mexico and expanding globally.”
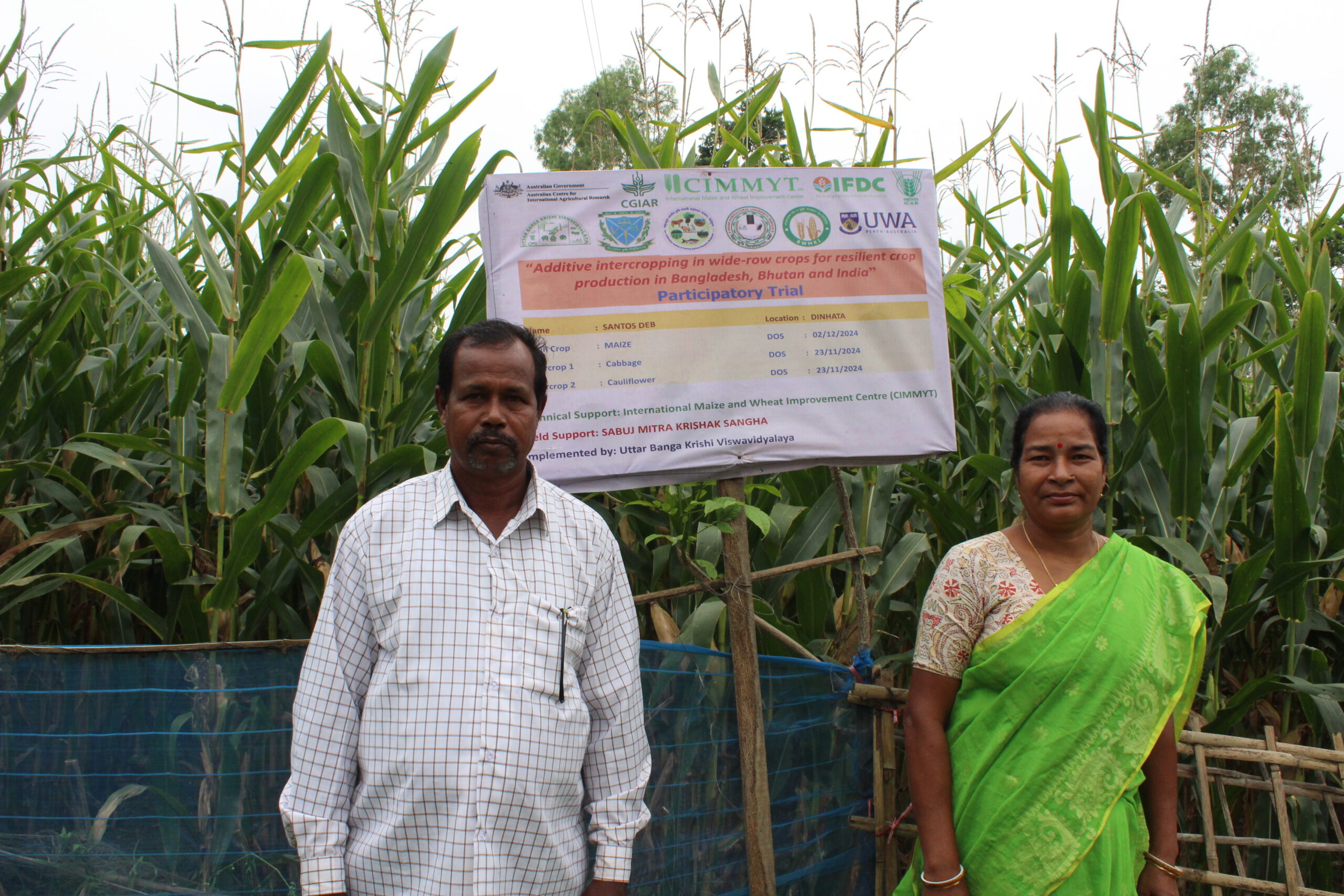
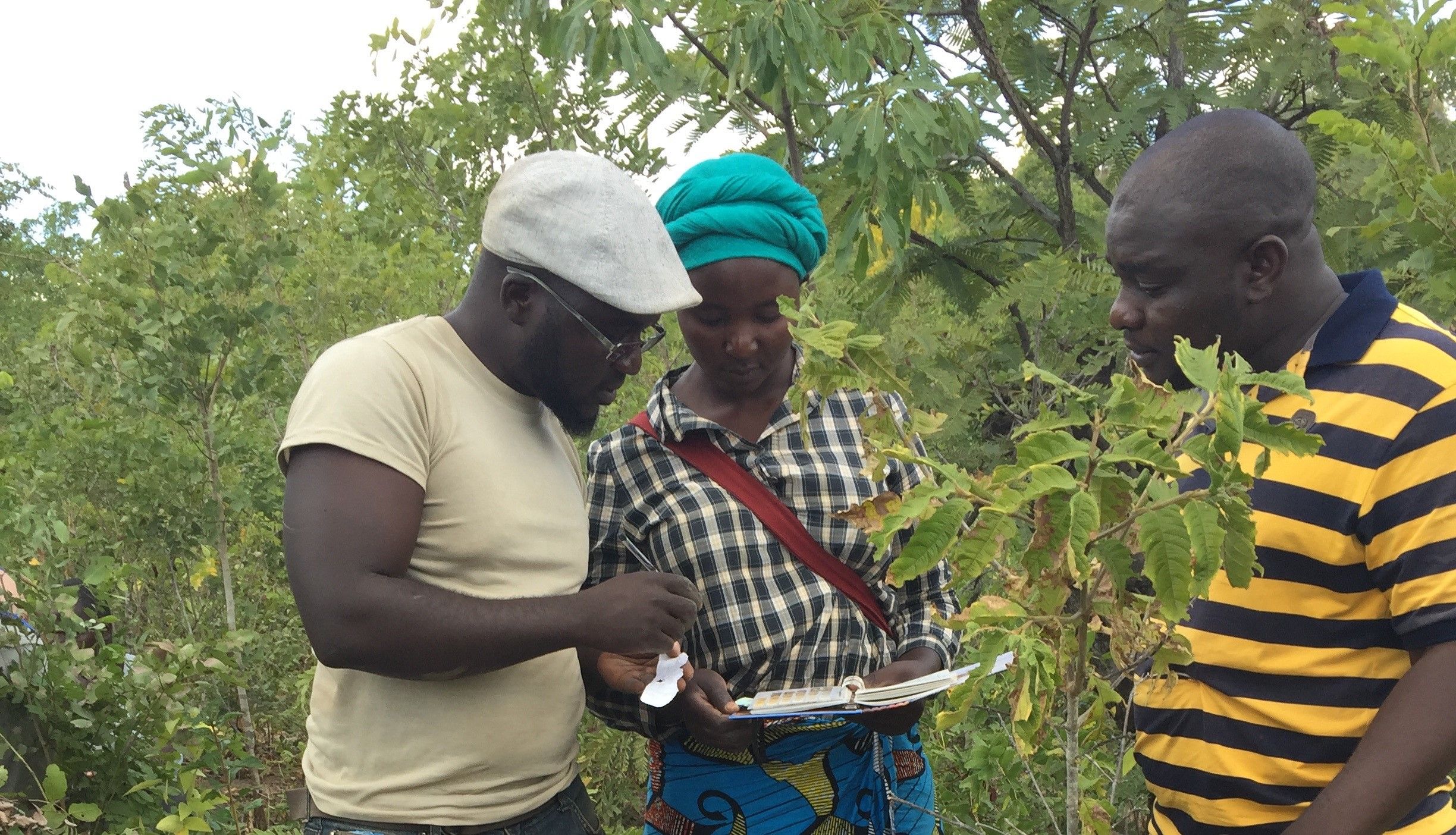
Led by WorldVeg Scientist Roland Schafleitner, the WorldVeg Mexico office in partnership with CIMMYT, local universities, research organizations and farmers will identify and promote adapted vegetable varieties suitable for smallholder production, as well as intercropping systems.
This initiative will improve supply of nutrient-rich vegetables that directly address the pressing global challenge highlighted by a 2020 FAO report—that over 3 billion people worldwide lack affordable access to diverse and nutritious diets.
“Whether it is in the field or on plates – cereals and vegetables go better together,” said Govaerts. “This marks an acceleration CIMMYT’s efforts to work with other organizations that share in our mission to advance a more food- and nutrition-secure world for all. We are eager to partner with other organizations that share this focus.”
The strategic alliance between CIMMYT and WorldVeg marks the first of several anticipated collaborations, transforming CIMMYT’s global headquarters into a hub for food and agricultural innovation.

About CIMMYT
CIMMYT is a cutting edge, nonprofit, international organization dedicated to solving tomorrow’s problems today. It is entrusted with fostering improved quantity, quality, and dependability of production systems and basic cereals such as maize, wheat, triticale, sorghum, millets and associated crops through applied agricultural science, particularly in the Global South, building strong partnerships. This combination enhances the livelihood trajectories and resilience of millions of resource-poor farmers while working toward a more productive, inclusive, and resilient agrifood system within planetary boundaries. For more information, visit: cimmyt.org.
About WorldVeg
WorldVeg is an international non-profit institute for research and development of vegetable technologies. It mobilizes resources from the public and private sectors to realize the potential of vegetables for healthier lives and more resilient livelihoods. WorldVeg’s improved varieties, production and postharvest methods help farmers increase vegetable harvests, raise incomes in poor rural and urban households, create jobs, and provide healthier, more nutritious diets for families and communities. Headquartered in Taiwan, it operates in 15 countries. More information: worldveg.org.