New publications: Breeders can benefit much more from phenotyping tools
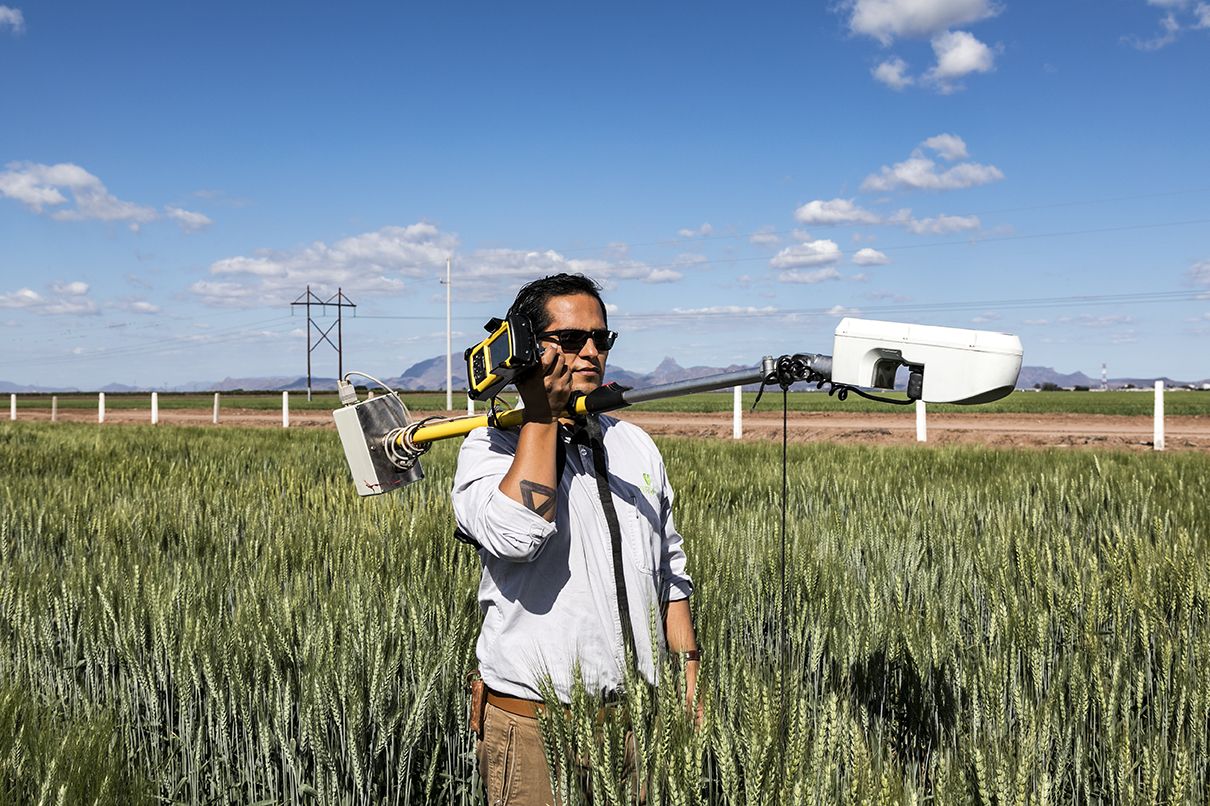
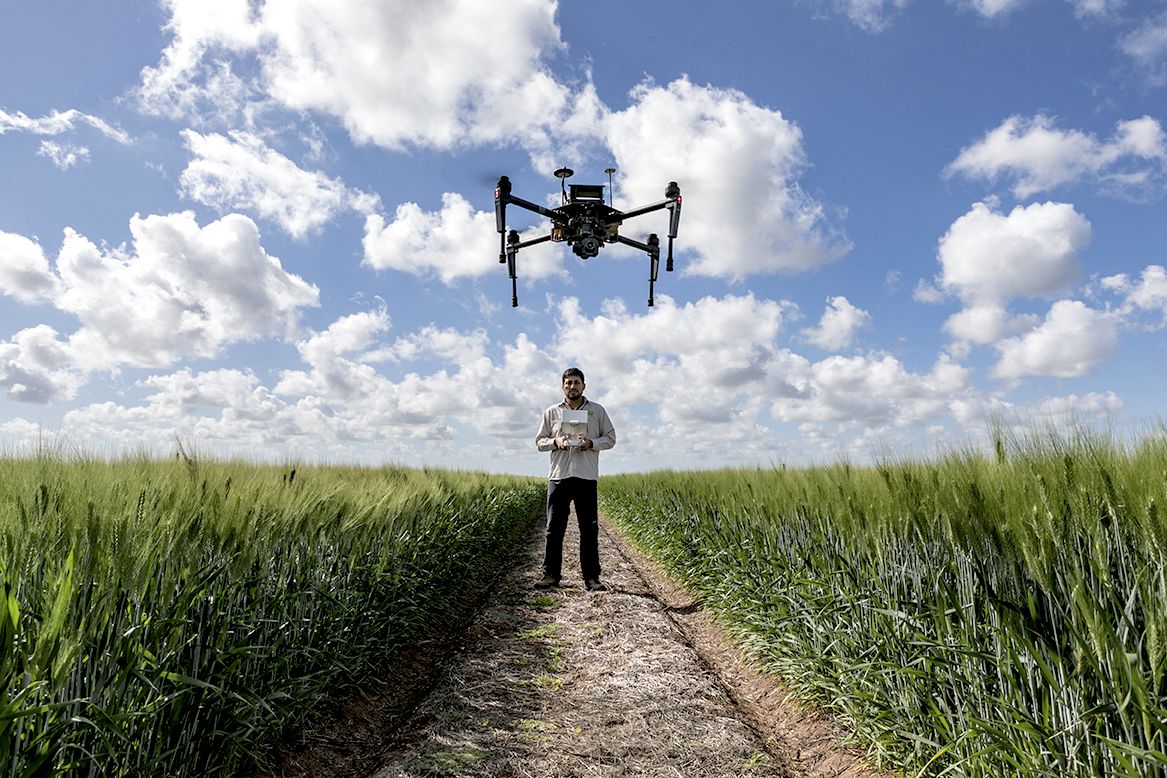
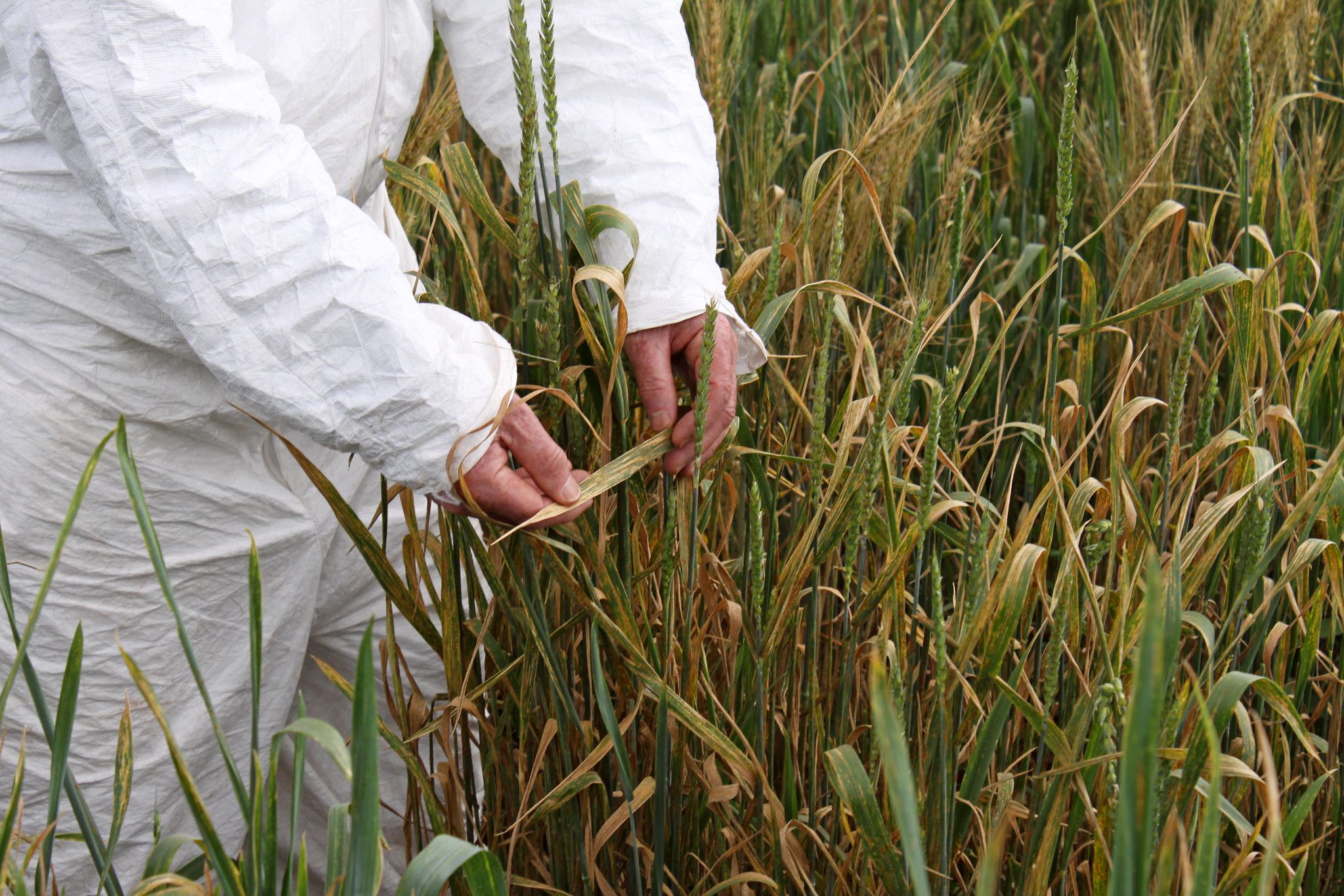
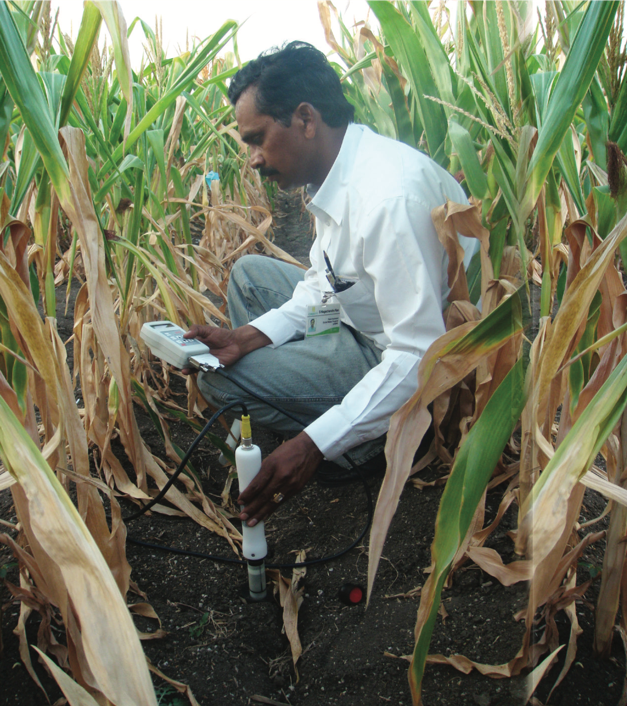
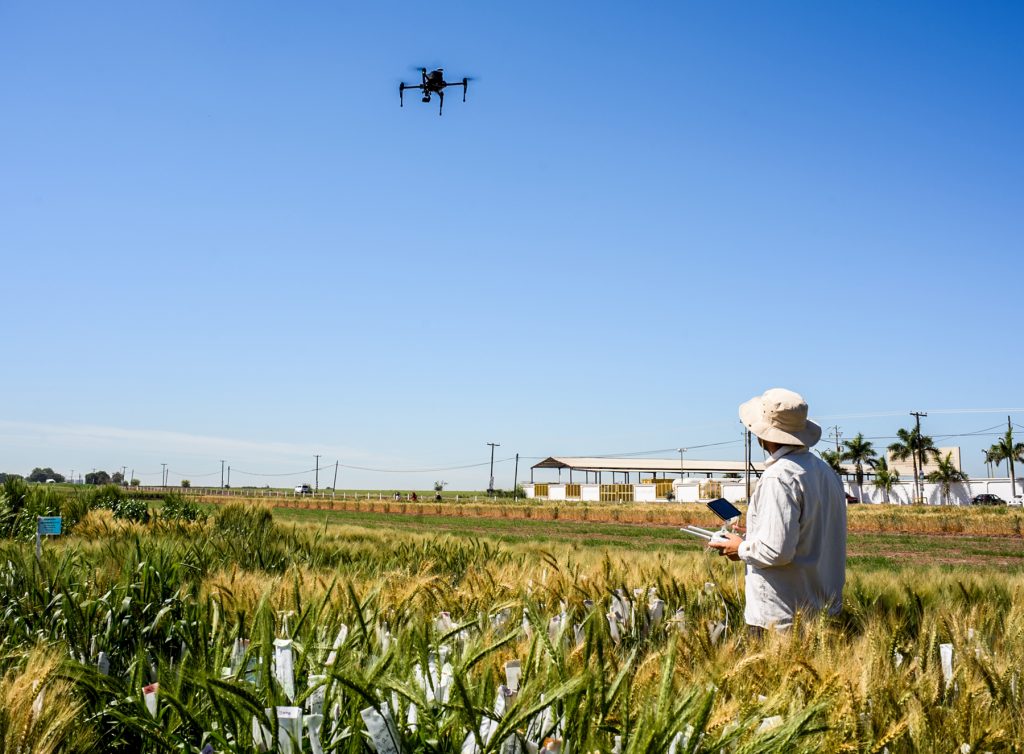
In crop research fields, it is now a common sight to see drones or other high-tech sensing tools collecting high-resolution data on a wide range of traits — from simple measurement of canopy temperature to complex 3D reconstruction of photosynthetic canopies.
This technological approach to collecting precise plant trait information, known as phenotyping, is becoming ubiquitous, but according to experts at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and other research institutions, breeders can profit much more from these tools, when used judiciously.
In a new article in the journal Plant Science, CIMMYT researchers outline the different ways in which phenotyping can assist breeding — from large-scale screening to detailed physiological characterization of key traits — and why this methodology is crucial for crop improvement.
“While having been the subject of debate in the past, extra investment for phenotyping is becoming more accepted to capitalize on recent developments in crop genomics and prediction models,” explain the authors.
Their review considers different contexts for phenotyping, including breeding, exploration of genetic resources, parent building and translations research to deliver other new breeding resources, and how these different categories of phenotyping apply to each. Some of the same tools and rules of thumb apply equally well to phenotyping for genetic analysis of complex traits and gene discovery.
The authors make the case for breeders to invest in phenotyping, particularly in light of the imperative to breed crops for warmer and harsher climates. However, wide scale adoption of sophisticated phenotyping methods will only occur if new techniques add efficiency and effectiveness.
In this sense, “breeder-friendly” phenotyping should complement existing breeding approaches by cost-effectively increasing throughput during segregant selection and adding new sources of validated complex traits to crossing blocks. With this in mind, stringent criteria need to be applied before new traits or phenotyping protocols are incorporated into mainstream breeding pipelines.
Read the full article in Plant Science:
Breeder friendly phenotyping.

See more recent publications from CIMMYT researchers:
- Genome-wide association study to identify genomic regions influencing spontaneous fertility in maize haploids. 2019. Chaikam, V., Gowda, M., Nair, S.K., Melchinger, A.E., Prasanna, B.M. In: Euphytica v. 215, no. 8, art. 138.
- Adapting irrigated and rainfed wheat to climate change in semi-arid environments: management, breeding options and land use change. 2019. Hernandez-Ochoa, I.M., Pequeno, D.N.L., Reynolds, M.P., Md Ali Babar, Sonder, K., Molero, A., Hoogenboom, G., Robertson, R., Gerber, S., Rowland, D.L., Fraisse, C.W., Asseng, S. In: European Journal of Agronomy.
- Integrating genomic resources to present full gene and putative promoter capture probe sets for bread wheat. 2019. Gardiner, L.J., Brabbs, T., Akhunova, A., Jordan, K., Budak, H., Richmond, T., Sukhwinder-Singh, Catchpole, L., Akhunov, E., Hall, A.J.W. In: GigaScience v. 8, no. 4, art. giz018.
- Rethinking technological change in smallholder agriculture. 2019. Glover, D., Sumberg, J., Ton, G., Andersson, J.A., Badstue, L.B. In: Outlook on Agriculture v. 48, no. 3, p. 169-180.
- Food security and agriculture in the Western Highlands of Guatemala. 2019. Lopez-Ridaura, S., Barba‐Escoto, L., Reyna, C., Hellin, J. J., Gerard, B., Wijk, M.T. van. In: Food Security v. 11, no. 4, p. 817-833.
- Agronomic, economic, and environmental performance of nitrogen rates and source in Bangladesh’s coastal rice agroecosystems. 2019. Shah-Al Emran, Krupnik, T.J., Kumar, V., Ali, M.Y., Pittelkow, C. M. In: Field Crops Research v. 241, art. 107567.
- Highlights of special issue on “Wheat Genetics and Breeding”. 2019. He Zhonghu, Zhendong Zhao, Cheng Shun-He In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering v. 6, no. 3, p. 207-209.
- Progress in breeding for resistance to Ug99 and other races of the stem rust fungus in CIMMYT wheat germplasm. 2019. Bhavani, S., Hodson, D.P., Huerta-Espino, J., Randhawa, M.S., Singh, R.P. In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering v. 6, no. 3, p. 210-224.
- China-CIMMYT collaboration enhances wheat improvement in China. 2019. He Zhonghu, Xianchun Xia, Yong Zhang, Zhang Yan, Yonggui Xiao, Xinmin Chen, Li Simin, Yuanfeng Hao, Rasheed, A, Zhiyong Xin, Zhuang Qiaosheng, Ennian Yang, Zheru Fan, Yan Jun, Singh, R.P., Braun, H.J. In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering v. 6. No. 3, p. 233-239.
- International Winter Wheat Improvement Program: history, activities, impact and future. 2019. Morgounov, A.I., Ozdemir, F., Keser, M., Akin, B., Payne, T.S., Braun, H.J. In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering v. 6, no. 3, p. 240-250.
- Genetic improvement of wheat grain quality at CIMMYT. 2019. Guzman, C., Ammar, K., Velu, G., Singh, R.P. In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering v. 6, no. 3, p. 265-272.
- Comments on special issue on “Wheat Genetics and Breeding”. 2019. He Zhonghu, Liu Xu In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, v. 6. No. 3, p. 309.
- Spectral reflectance indices as proxies for yield potential and heat stress tolerance in spring wheat: heritability estimates and marker-trait associations. 2019. Caiyun Liu, Pinto Espinosa, F., Cossani, C.M., Sukumaran, S., Reynolds, M.P. In: Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, v. 6, no. 3, p. 296-308.
- Beetle and maize yield response to plant residue application and manual weeding under two tillage systems in northern Zimbabwe. 2019. Mashavakure, N., Mashingaidze, A.B., Musundire, R., Gandiwa, E., Thierfelder, C., Muposhi, V.K. In: Applied Soil Ecology v. 144, p. 139-146.
- Optimizing dry-matter partitioning for increased spike growth, grain number and harvest index in spring wheat. 2019. Rivera Amado, A.C., Trujillo, E., Molero, G., Reynolds, M.P., Sylvester Bradley, R., Foulkes, M.J. In: Field Crops Research v. 240, p. 154-167.
- Small businesses, potentially large impacts: the role of fertilizer traders as agricultural extension agents in Bangladesh. 2019. Mottaleb, K.A., Rahut, D.B., Erenstein, O. In: Journal of Agribusiness in Developing and Emerging Economies v. 9, no. 2, p. 109-124.
- Heterogeneous seed access and information exposure: implications for the adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties in Uganda. 2019. Simtowe, F.P., Marenya, P. P., Amondo, E., Regasa, M.W., Rahut, D.B., Erenstein, O. In: Agricultural and Food Economics v. 7. No. 1, art. 15.
- Hyperspectral reflectance-derived relationship matrices for genomic prediction of grain yield in wheat. 2019. Krause, M., Gonzalez-Perez, L., Crossa, J., Perez-Rodriguez, P., Montesinos-Lopez, O.A., Singh, R.P., Dreisigacker, S., Poland, J.A., Rutkoski, J., Sorrells, M.E., Gore, M.A., Mondal, S. In: G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics v.9, no. 4, p. 1231-1247.
- Unravelling the complex genetics of karnal bunt (Tilletia indica) resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum) by genetic linkage and genome-wide association analyses. 2019. Emebiri, L.C., Sukhwinder-Singh, Tan, M.K., Singh, P.K., Fuentes Dávila, G., Ogbonnaya, F.C. In: G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics v. 9, no. 5, p. 1437-1447.
- Healthy foods as proxy for functional foods: consumers’ awareness, perception, and demand for natural functional foods in Pakistan. 2019. Ali, A., Rahut, D.B. In: International Journal of Food Science v. 2019, art. 6390650.
- Northern Himalayan region of Pakistan with cold and wet climate favors a high prevalence of wheat powdery mildew. 2019. Khan, M.R., Imtiaz, M., Farhatullah, Ahmad, S., Sajid Ali.In: Sarhad Journal of Agriculture v. 35, no. 1, p. 187-193.
- Resistance to insect pests in wheat—rye and Aegilops speltoides Tausch translocation and substitution lines. 2019. Crespo-Herrera, L.A., Singh, R.P., Sabraoui, A., Moustapha El Bouhssini In: Euphytica v. 215, no. 7, art.123.
- Productivity and production risk effects of adopting drought-tolerant maize varieties in Zambia. 2019. Amondo, E., Simtowe, F.P., Rahut, D.B., Erenstein, O. In: International Journal of Climate Change Strategies and Management v. 11, no. 4, p. 570-591.
- Review: new sensors and data-driven approaches—A path to next generation phenomics. 2019. Roitsch, T., Cabrera-Bosquet, L., Fournier, A., Ghamkhar, K., Jiménez-Berni, J., Pinto Espinosa, F., Ober, E.S. In: Plant Science v. 282 p. 2-10.
- Accountability mechanisms in international climate change financing. 2019. Basak, R., van der Werf, E. In: International Environmental Agreements: Politics, Law and Economics v. 19, no. 3, p. 297-313.
- Enhancing the rate of genetic gain in public-sector plant breeding programs: lessons from the breeder’s equation. 2019. Cobb, J.N., Juma, R.U., Biswas, P.S., Arbelaez, J.D., Rutkoski, J., Atlin, G.N., Hagen, T., Quinn, M., Eng Hwa Ng. In: Theoretical and Applied Genetics v. 132, no. 3, p. 627-645.