Assessing the effectiveness of a “wheat holiday” for preventing blast in the lower Gangetic plains
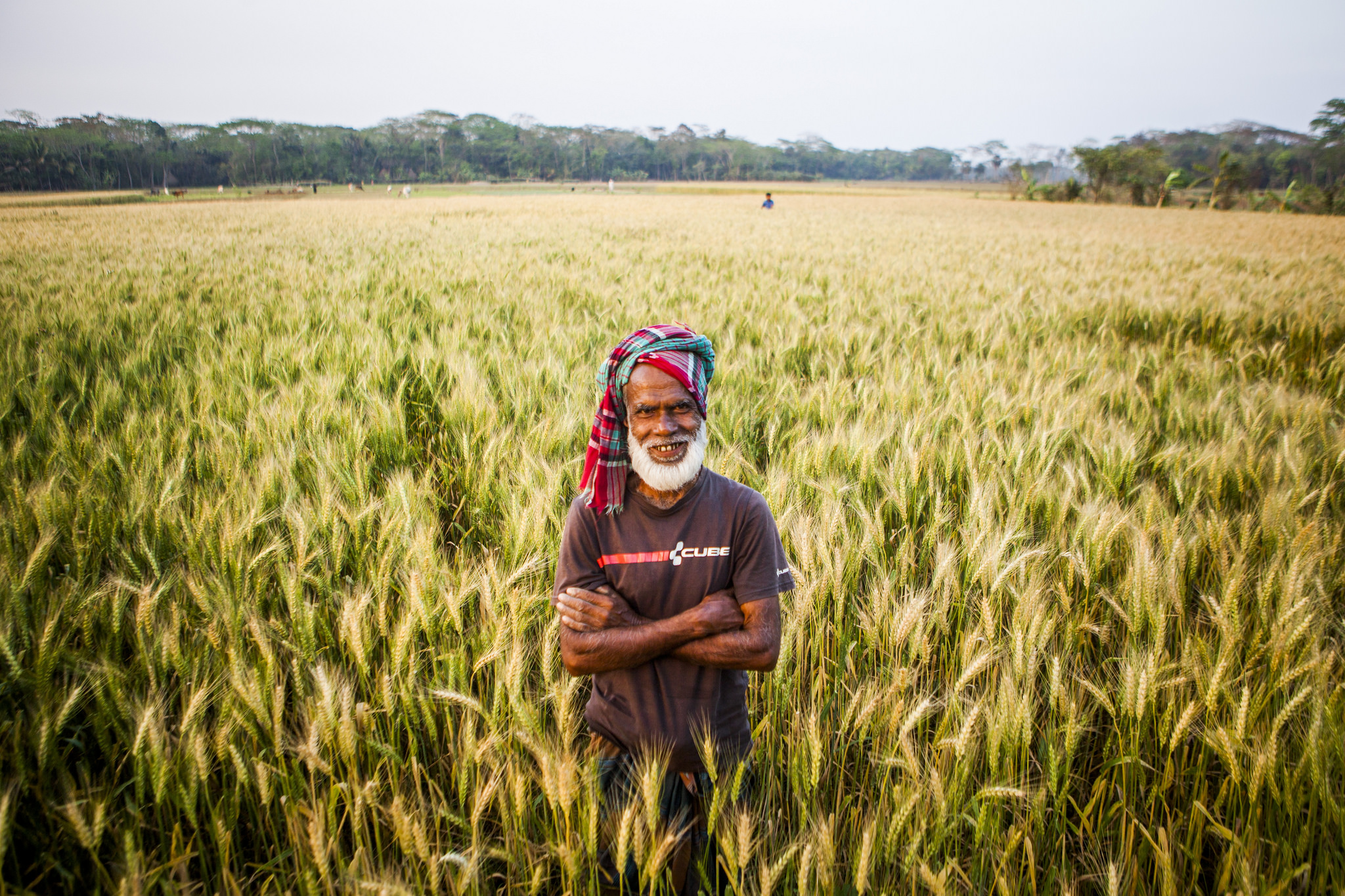

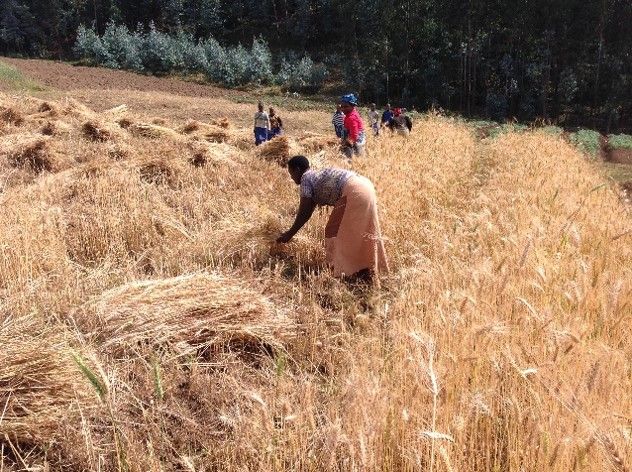
Wheat blast — one of the world’s most devastating wheat diseases — is moving swiftly into new territory in South Asia.
In an attempt to curb the spread of this disease, policymakers in the region are considering a “wheat holiday” policy: banning wheat cultivation for a few years in targeted areas. Since wheat blast’s Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype triticum (MoT) fungus can survive on seeds for up to 22 months, the idea is to replace wheat with other crops, temporarily, to cause the spores to die. In India, which shares a border of more than 4,000 km with Bangladesh, the West Bengal state government has already instituted a two-year ban on wheat cultivation in two districts, as well as all border areas. In Bangladesh, the government is implementing the policy indirectly by discouraging wheat cultivation in the severely blast affected districts.
CIMMYT researchers recently published in two ex-ante studies to identify economically feasible alternative crops in Bangladesh and the bordering Indian state of West Bengal.
Alternative crops
The first step to ensuring that a ban does not threaten the food security and livelihoods of smallholder farmers, the authors assert, is to supply farmers with economically feasible alternative crops.
In Bangladesh, the authors examined the economic feasibility of seven crops as an alternative to wheat, first in the entire country, then in 42 districts vulnerable to blast, and finally in ten districts affected by wheat blast. Considering the cost of production and revenue per hectare, the study ruled out boro rice, chickpeas and potatoes as feasible alternatives to wheat due to their negative net return. In contrast, they found that cultivation of maize, lentils, onions, and garlic could be profitable.
The study in India looked at ten crops grown under similar conditions as wheat in the state of West Bengal, examining the economic viability of each. The authors conclude that growing maize, lentils, legumes such as chickpeas and urad bean, rapeseed, mustard and potatoes in place of wheat appears to be profitable, although they warn that more rigorous research and data are needed to confirm and support this transition.
Selecting alternative crops is no easy task. Crops offered to farmers to replace wheat must be appropriate for the agroecological zone and should not require additional investments for irrigation, inputs or storage facilities. Also, the extra production of labor-intensive and export-oriented crops, such as maize in India and potatoes in Bangladesh, may add costs or require new markets for export.
There is also the added worry that the MoT fungus could survive on one of these alternative crops, thus completely negating any benefit of the “wheat holiday.” The authors point out that the fungus has been reported to survive on maize.
A short-term solution?

In both studies, the authors discourage a “wheat holiday” policy as a holistic solution. However, they leave room for governments to pursue it on an interim and short-term basis.
In the case of Bangladesh, CIMMYT agricultural economist and lead author Khondoker Mottaleb asserts that a “wheat holiday” would increase the country’s reliance on imports, especially in the face of rapidly increasing wheat demand and urbanization. A policy that results in complete dependence on wheat imports, he and his co-authors point out, may not be politically attractive or feasible. Also, the policy would be logistically challenging to implement. Finally, since the disease can potentially survive on other host plants, such as weeds and maize, it may not even work in the long run.
In the interim, the government of Bangladesh may still need to rely on the “wheat holiday” policy in the severely blast-affected districts. In these areas, they should encourage farmers to cultivate lentils, onions and garlic. In addition, in the short term, the government should make generic fungicides widely available at affordable prices and provide an early warning system as well as adequate information to help farmers effectively combat the disease and minimize its consequences.
In the case of West Bengal, India, similar implications apply, although the authors conclude that the “wheat holiday” policy could only work if Bangladesh has the same policy in its blast-affected border districts, which would involve potentially difficult and costly inter-country collaboration, coordination and logistics.
Actions for long-term success
The CIMMYT researchers urge the governments of India and Bangladesh, their counterparts in the region and international stakeholders to pursue long-term solutions, including developing a convenient diagnostic tool for wheat blast surveillance and a platform for open data and science to combat the fungus.
A promising development is the blast-resistant (and zinc-enriched) wheat variety BARI Gom 33 which the Bangladesh Agricultural Research Institute (BARI) released in 2017 with support from CIMMYT. However, it will take at least three to five years before it will be available to farmers throughout Bangladesh. The authors urged international donor agencies to speed up the multiplication process of this variety.
CIMMYT scientists in both studies close with an urgent plea for international financial and technical support for collaborative research on disease epidemiology and forecasting, and the development and dissemination of new wheat blast-tolerant and resistant varieties and complementary management practices — crucial steps to ensuring food security for more than a billion people in South Asia.
| Wheat blast impacts
First officially reported in Brazil in 1985, where it eventually spread to 3 million hectares in South America and became the primary reason for limited wheat production in the region, wheat blast moved to Bangladesh in 2016. There it affected nearly 15,000 hectares of land in eight districts, reducing yield by as much as 51 percent in the affected fields. Blast is devilish: directly striking the wheat ear, it can shrivel and deform the grain in less than a week from the first symptoms, leaving farmers no time to act. There are no widely available resistant varieties, and fungicides are expensive and provide only a partial defense. The disease, caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype triticum (MoT), can spread through infected seeds as well as by spores that can travel long distances in the air. South Asia has a long tradition of wheat consumption, especially in northwest India and Pakistan, and demand has been increasing rapidly across South Asia. It is the second major staple in Bangladesh and India and the principal staple food in Pakistan. Research indicates 17 percent of wheat area in Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan — representing nearly 7 million hectares – is vulnerable to the disease, threatening the food security of more than a billion people. |
CIMMYT and its partners work to mitigate wheat blast through projects supported by U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR), the Indian Council for Agricultural Research (ICAR), the CGIAR Research Program on Wheat and the CGIAR Platform for Big Data in Agriculture.
Read the full articles:
- Averting Wheat Blast by Implementing a ‘Wheat Holiday’: In Search of Alternative Crops in West Bengal, India by Khondoker A. Mottaleb, Pawan K. Singh, Kai Sonder, Gideon Kruseman, Olaf Erenstein (PLOS One, February 2019)
- Alternative use of wheat land to implement a potential wheat holiday as wheat blast control: In search of feasible crops in Bangladesh by Khondoker Abdul Mottaleb, Pawan Kumar Singh, Xinyao He, Akbar Hossain, Gideon Kruseman, Olaf Erenstein (Land Use Policy, March 2019)
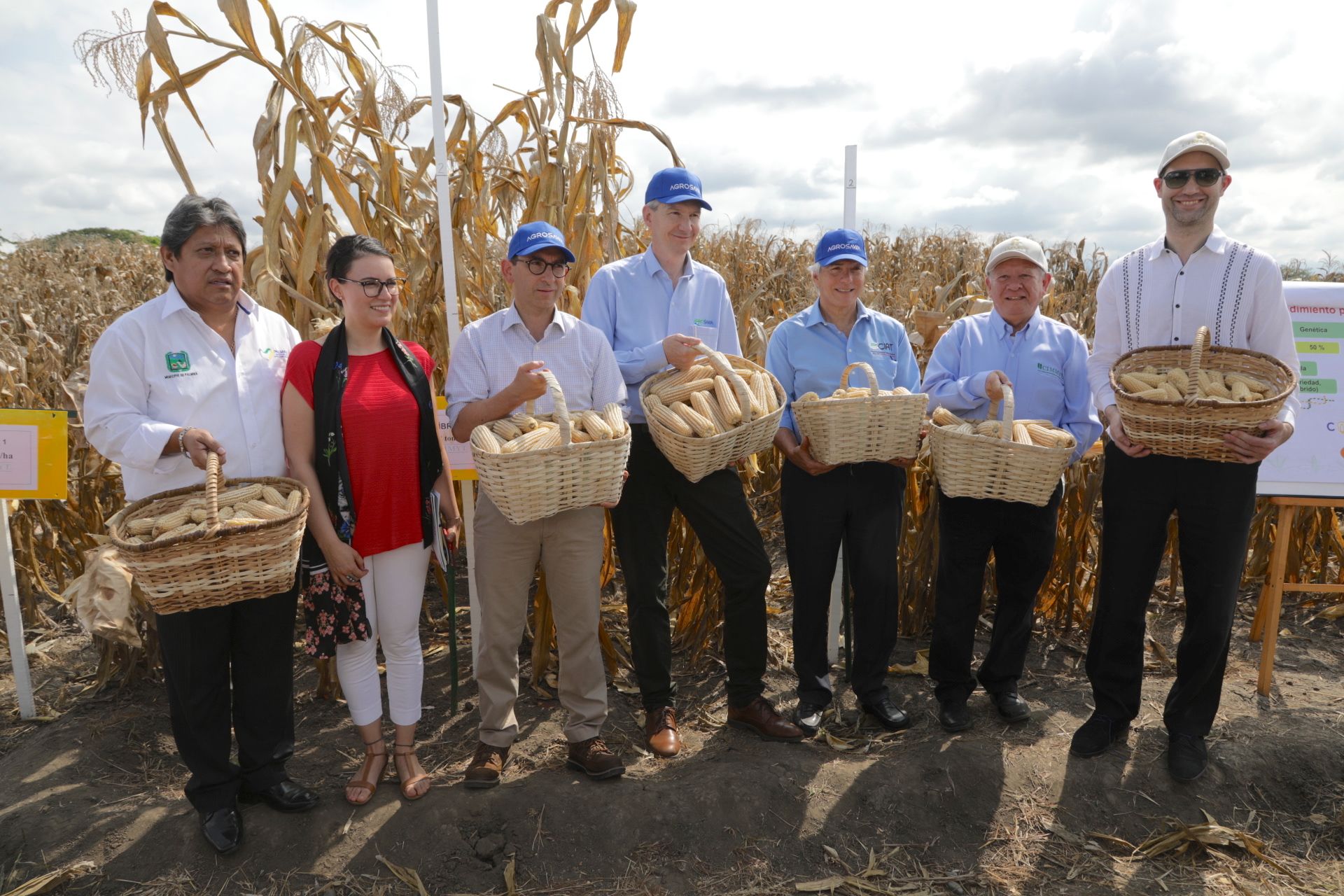
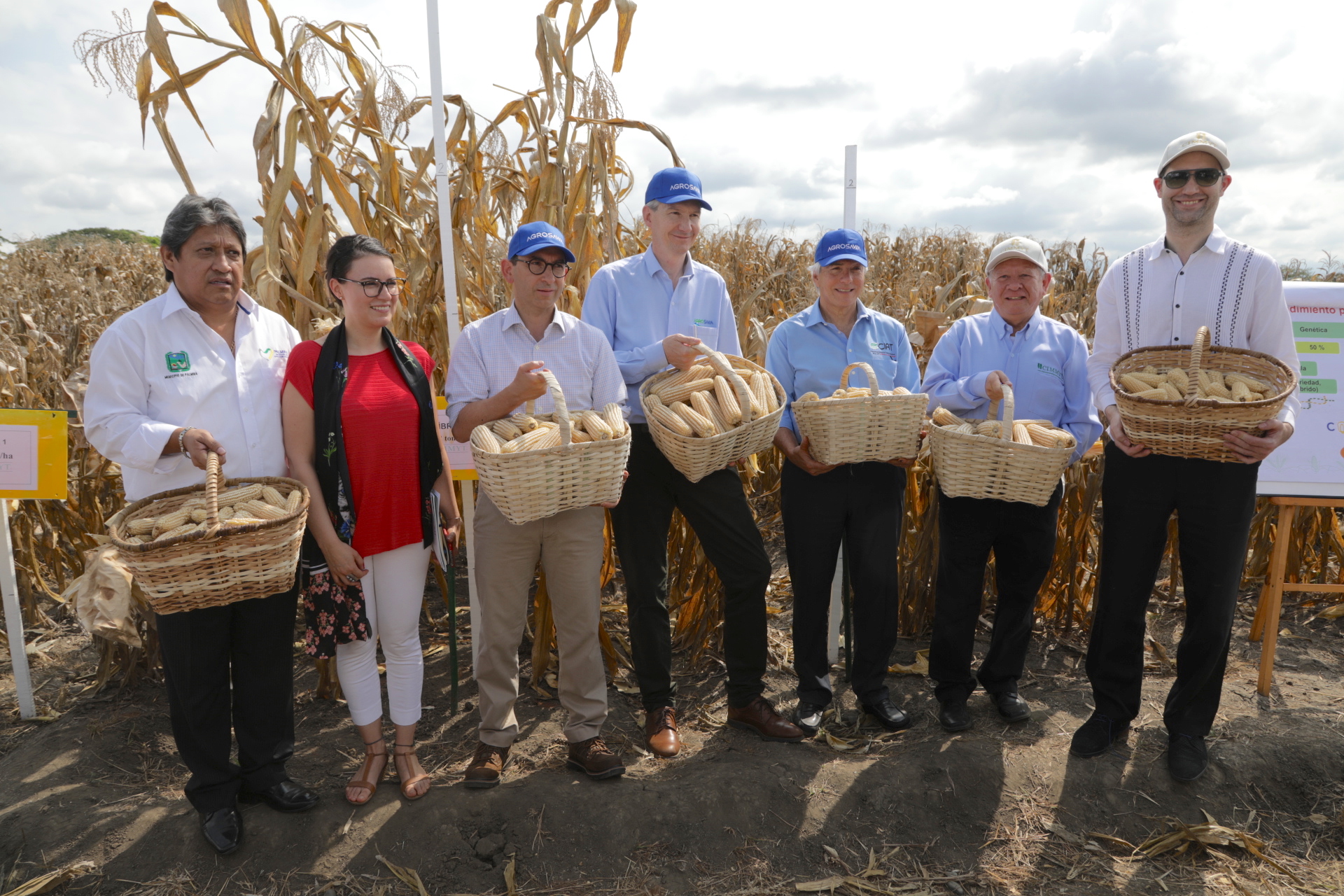


 Palmira (Colombia), February 14, 2019 — AGROSAVIA, Colombia’s leading not-for-profit organization for agricultural research and technology transfer, the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) and the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) have signed a five-year agreement that aims to boost maize production.
Palmira (Colombia), February 14, 2019 — AGROSAVIA, Colombia’s leading not-for-profit organization for agricultural research and technology transfer, the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) and the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) have signed a five-year agreement that aims to boost maize production.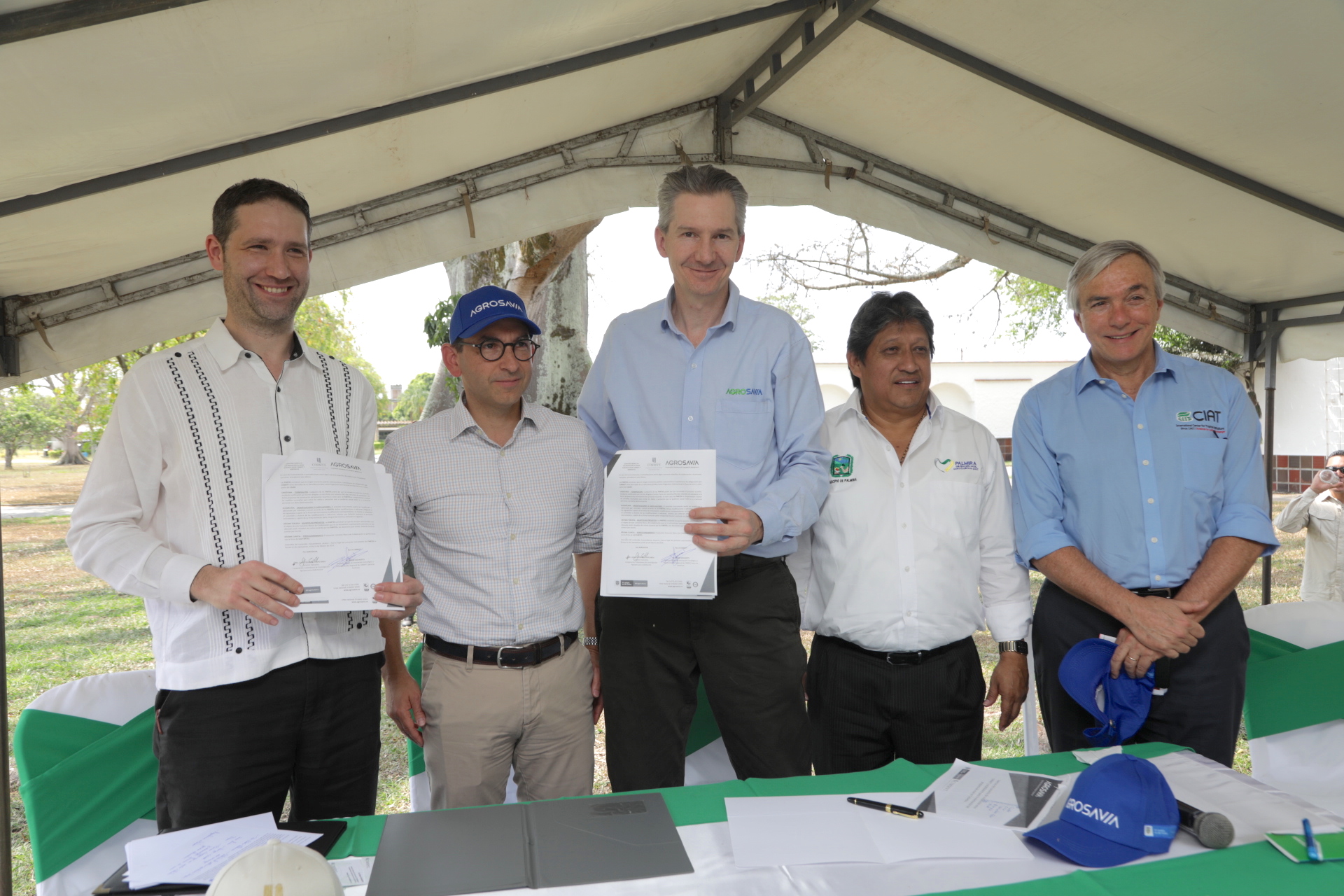 INTERVIEW OPPORTUNITIES:
INTERVIEW OPPORTUNITIES: