Sustainable and Resilient Farming Systems Intensification in the Eastern Gangetic Plains (SRFSI)
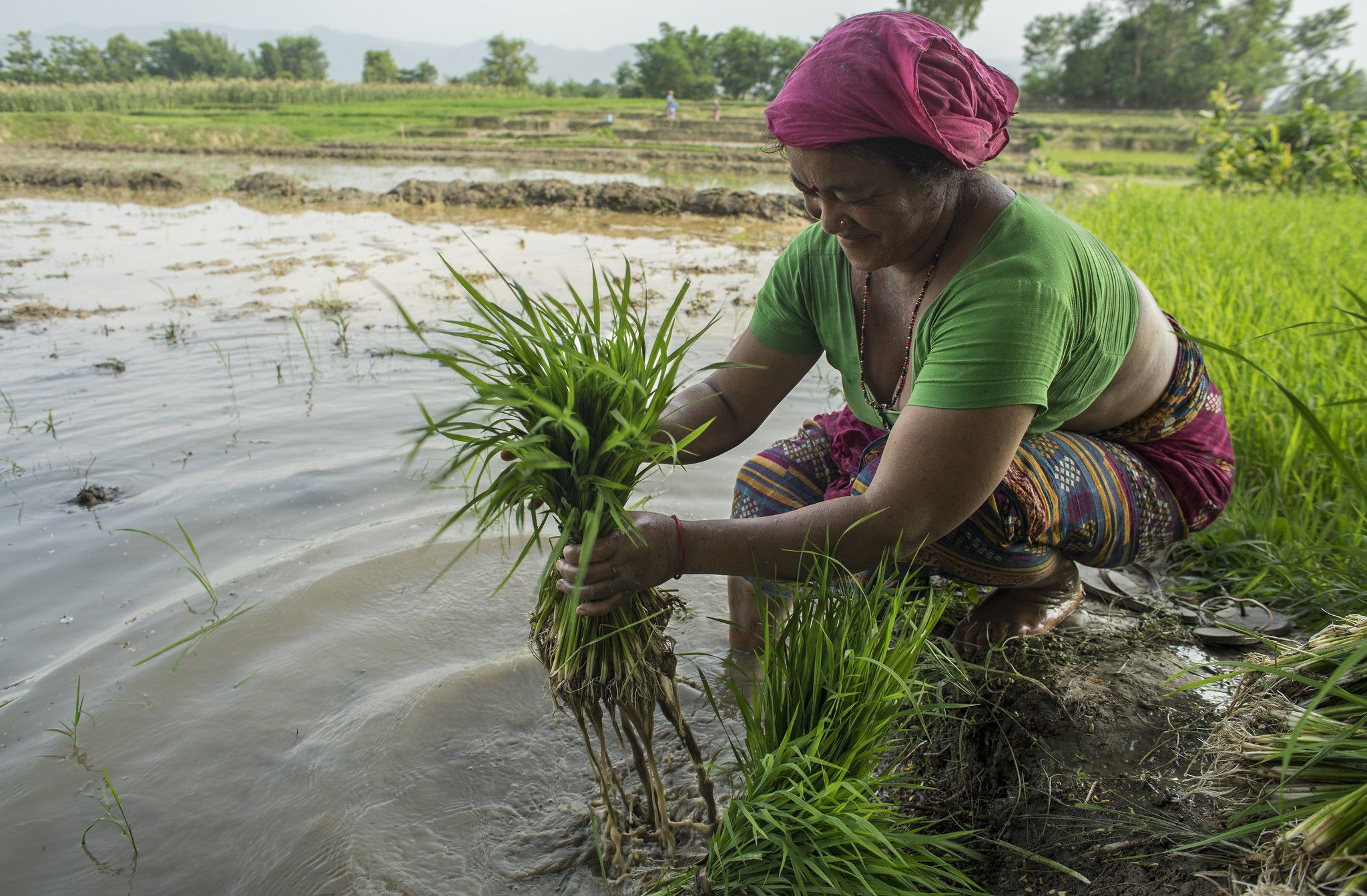
The Eastern Gangetic Plains region of Bangladesh, India, and Nepal is home to the greatest concentration of rural poor in the world. This region is projected to be one of the areas most affected by climate change. Local farmers are already experiencing the impact of climate change: erratic monsoon rains, floods and other extreme weather events have affected agricultural production for the past decade. The region’s smallholder farming systems have low productivity, and yields are too variable to provide a solid foundation for food security. Inadequate access to irrigation, credit, inputs and extension systems limit capacity to adapt to climate change or invest in innovation. Furthermore, large-scale migration away from agricultural areas has led to labor shortages and increasing numbers of women in agriculture.
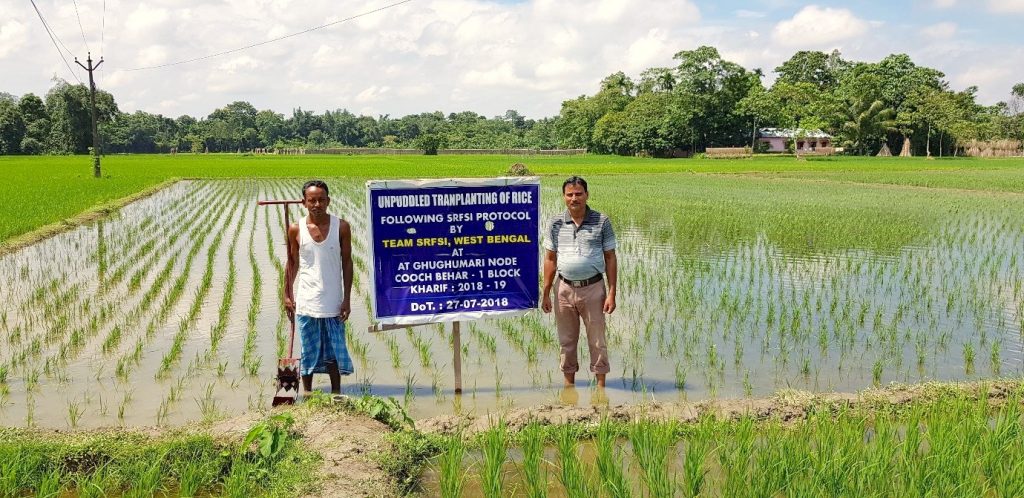
The Sustainable and Resilient Farming Systems Intensification (SRFSI) project aims to reduce poverty in the Eastern Gangetic Plains by making smallholder agriculture more productive, profitable and sustainable while safeguarding the environment and involving women. CIMMYT, project partners and farmers are exploring Conservation Agriculture-based Sustainable Intensification (CASI) and efficient water management as foundations for increasing crop productivity and resilience. Technological changes are being complemented by research into institutional innovations that strengthen adaptive capacity and link farmers to markets and support services, enabling both women and men farmers to adapt and thrive in the face of climate and economic change.
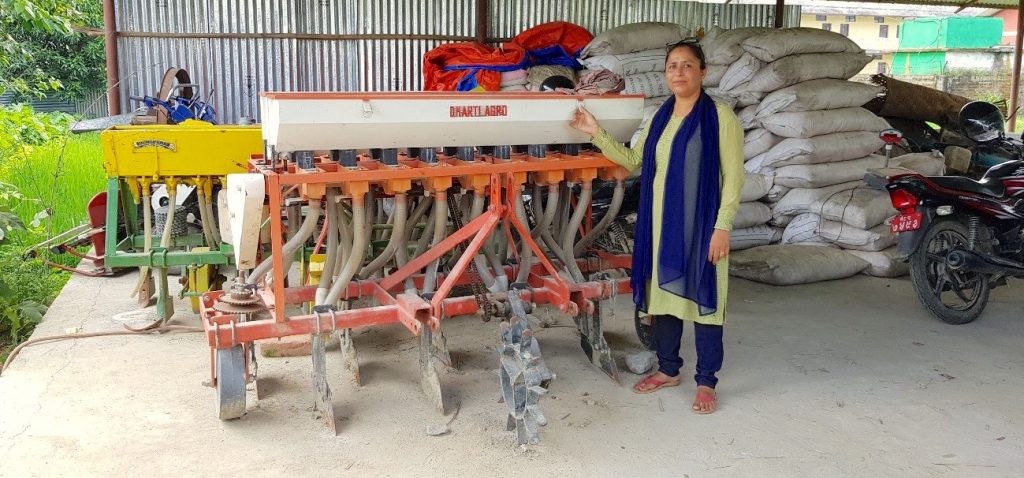
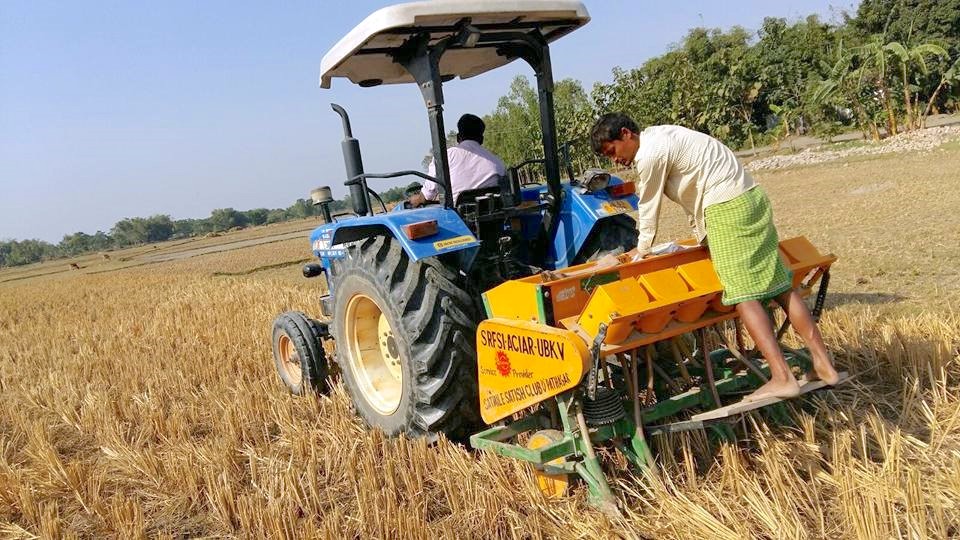
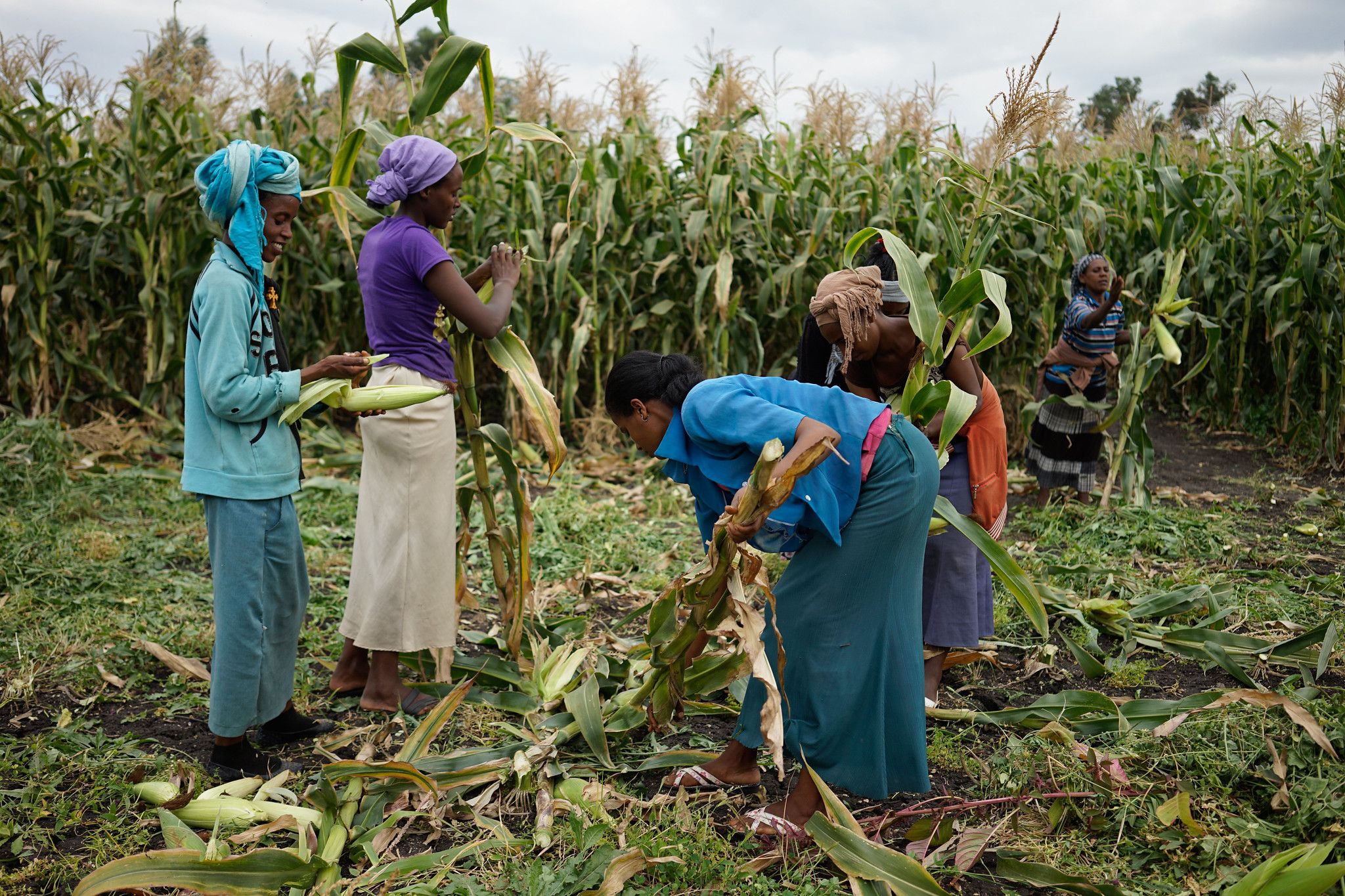
In its current phase, the project team is identifying and closing capacity gaps so that stakeholders can scale CASI practices beyond the project lifespan. Priorities include crop diversification and rotation, reduced tillage using machinery, efficient water management practices, and integrated weed management practices. Women farmers are specifically targeted in the scaling project: it is intended that a third of participants will be women and that at least 25% of the households involved will be led by women.
The 9.7 million Australian dollar (US$7.2 million) SRFSI project is a collaboration between CIMMYT and the project funder, the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research. More than 20 partner organizations include the Departments of Agriculture in the focus countries, the Bangladesh Agricultural Research Institute, the Indian Council for Agricultural Research, the Nepal Agricultural Research Council, Uttar Banga Krishi Vishwavidyalaya, Bihar Agricultural University, EcoDev Solutions, iDE, Agrevolution, Rangpur-Dinajpur Rural Services, JEEViKA, Sakhi Bihar, DreamWork Solutions, CSIRO and the Universities of Queensland and Western Australia.
OBJECTIVES
- Understand farmer circumstances with respect to cropping systems, natural and economic resources base, livelihood strategies, and capacity to bear risk and undertake technological innovation
- Develop with farmers more productive and sustainable technologies that are resilient to climate risks and profitable for smallholders
- Catalyze, support and evaluate institutional and policy changes that establish an enabling environment for the adoption of high-impact technologies
- Facilitate widespread adoption of sustainable, resilient and more profitable farming systems