Precision spreader for fertilizer set to change the agriculture scene in Nepal

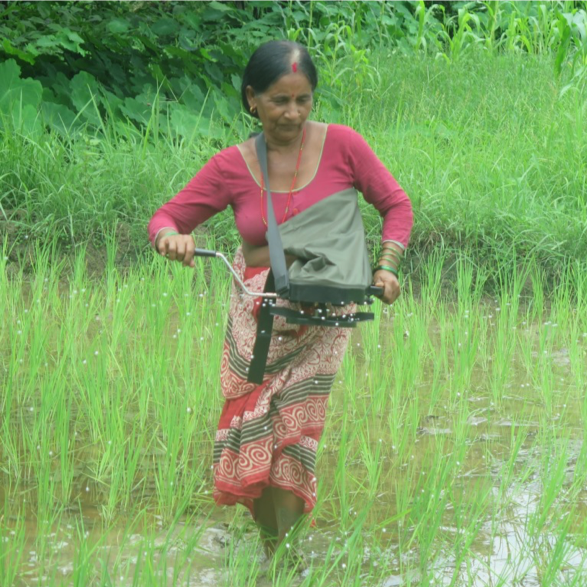
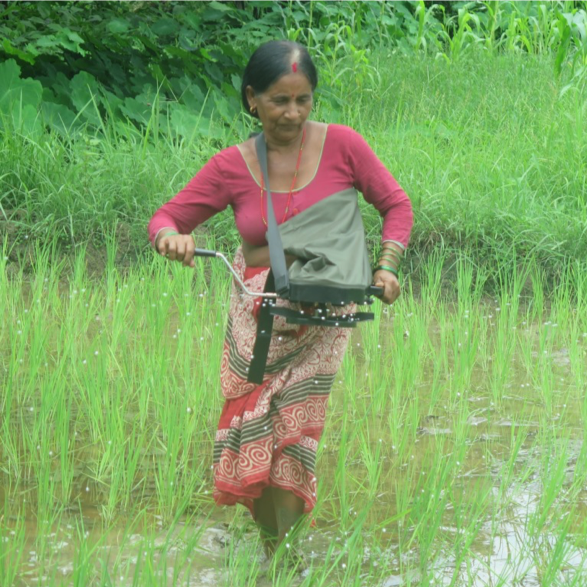
Smallholder farmers in Nepal tend to apply fertilizer by hand, spreading it as they walk through the field. Under this practice, fertilizer is dispersed randomly and is therefore unevenly distributed among all the seedlings. A recently introduced method, however, helps farmers spread fertilizer in a more uniform, faster and easier way.
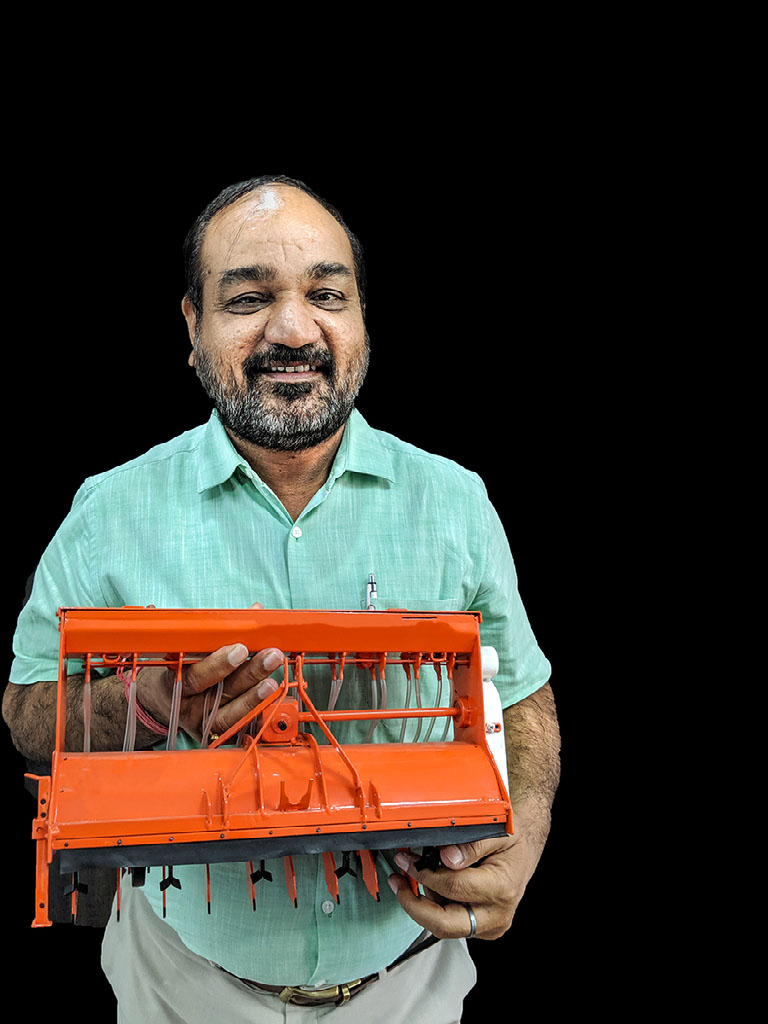
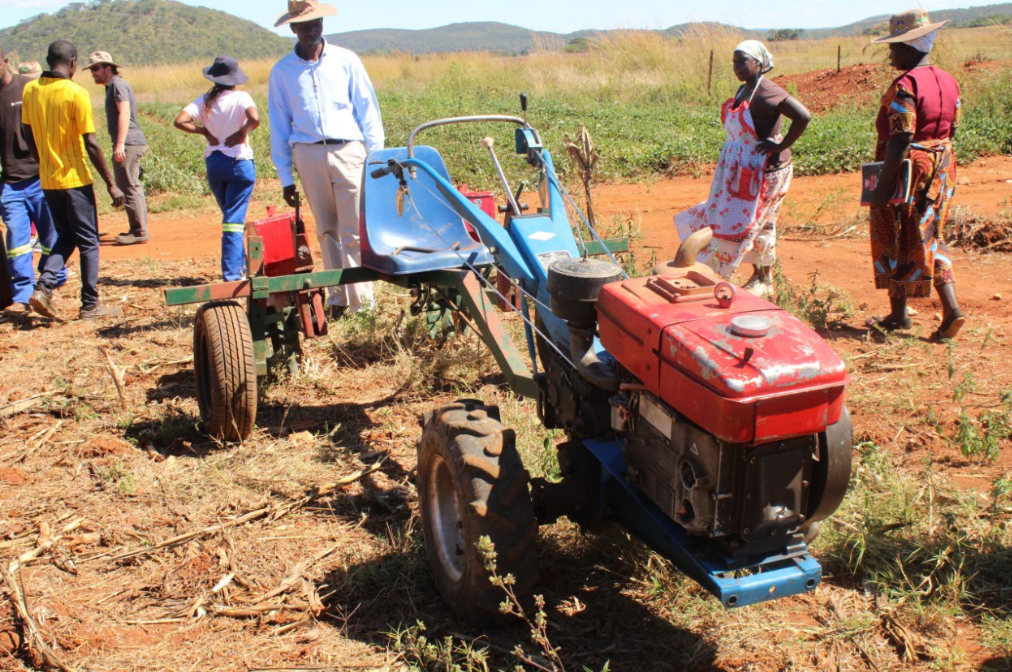
The precision spreader is a hand-operated device that ensures an even distribution of fertilizer and is easy to operate. This technology is endorsed by the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA), a project led by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) which helps Nepalese farmers adapt measures that are efficient, effective and resilient to the impacts of climate change.
In addition to more consistent distribution, the precision spreader regulates the exact amount of fertilizer required and helps the farmer cover a considerable area with limited movement. This technology has been proven to require less time and effort than the traditional method of broadcasting by hand.
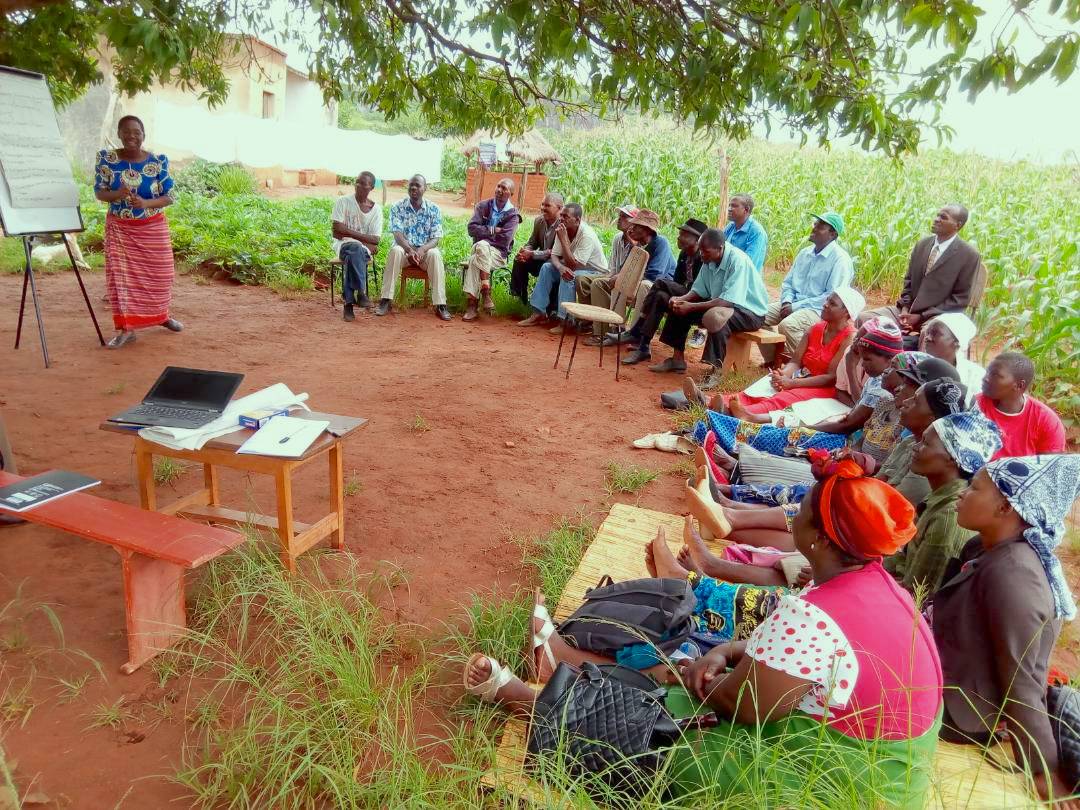
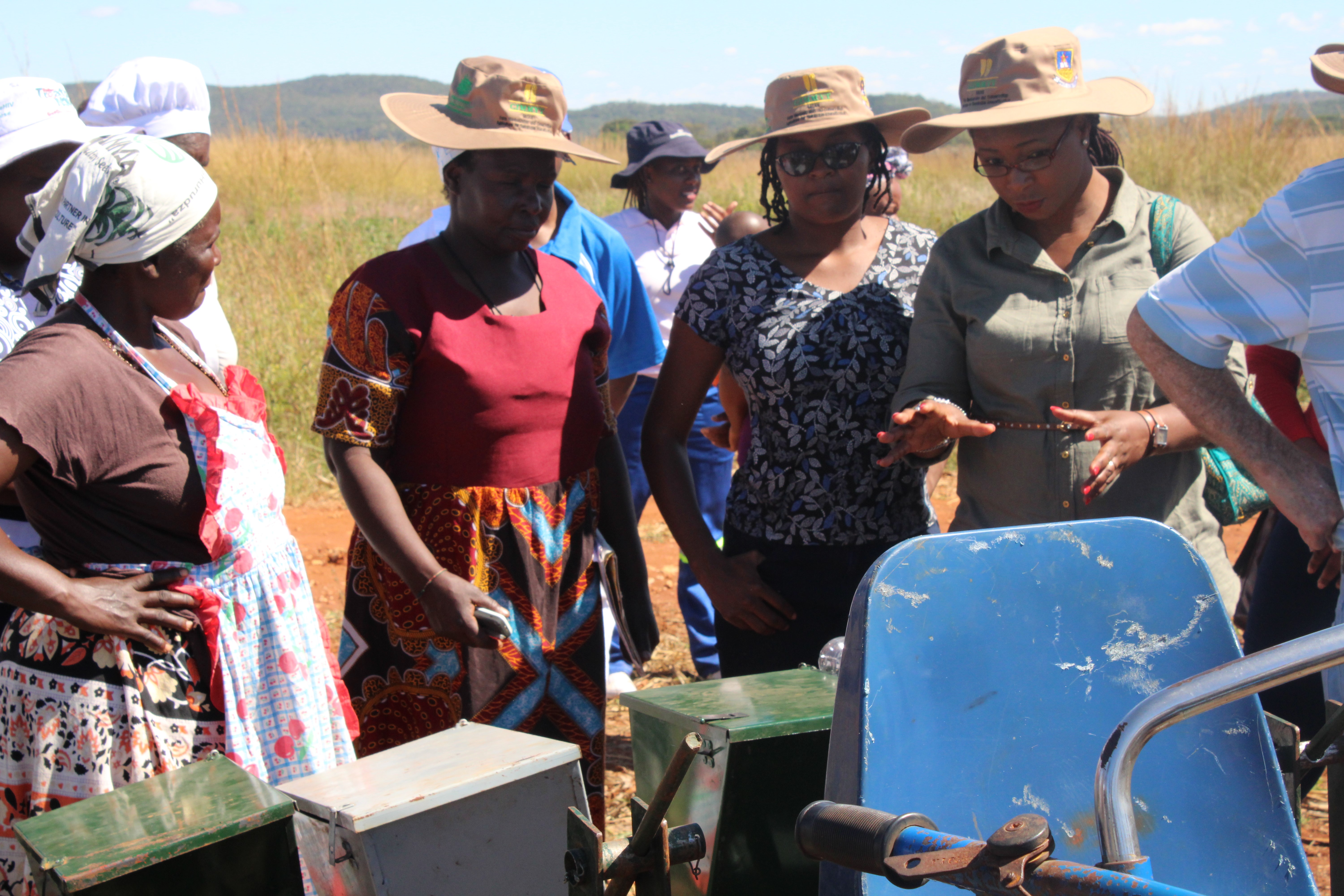
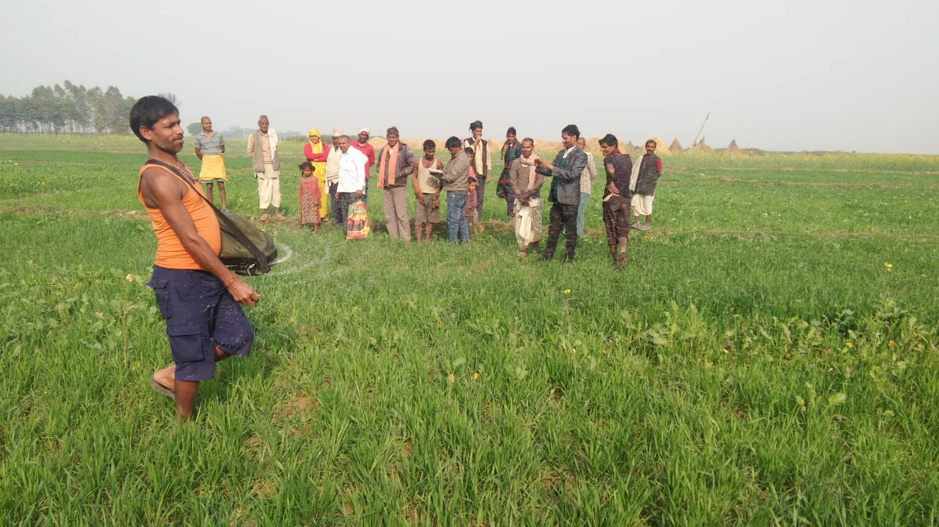
Considering the potential benefits, the CSISA team introduced farmers in Nepal to the precision spreader through training sessions followed by demonstrations of its use. They took place in wheat fields in Bansgadhi, Barbardiya and Duduwa, in Lumbini province, in collaboration with multipurpose cooperative Janaekata and the local governments. Through these sessions, conducted in 45 different sites, more than 650 farmers had a chance to familiarize themselves with the precision spreader, and most of them took a keen interest in incorporating the device into their cropping management practices.
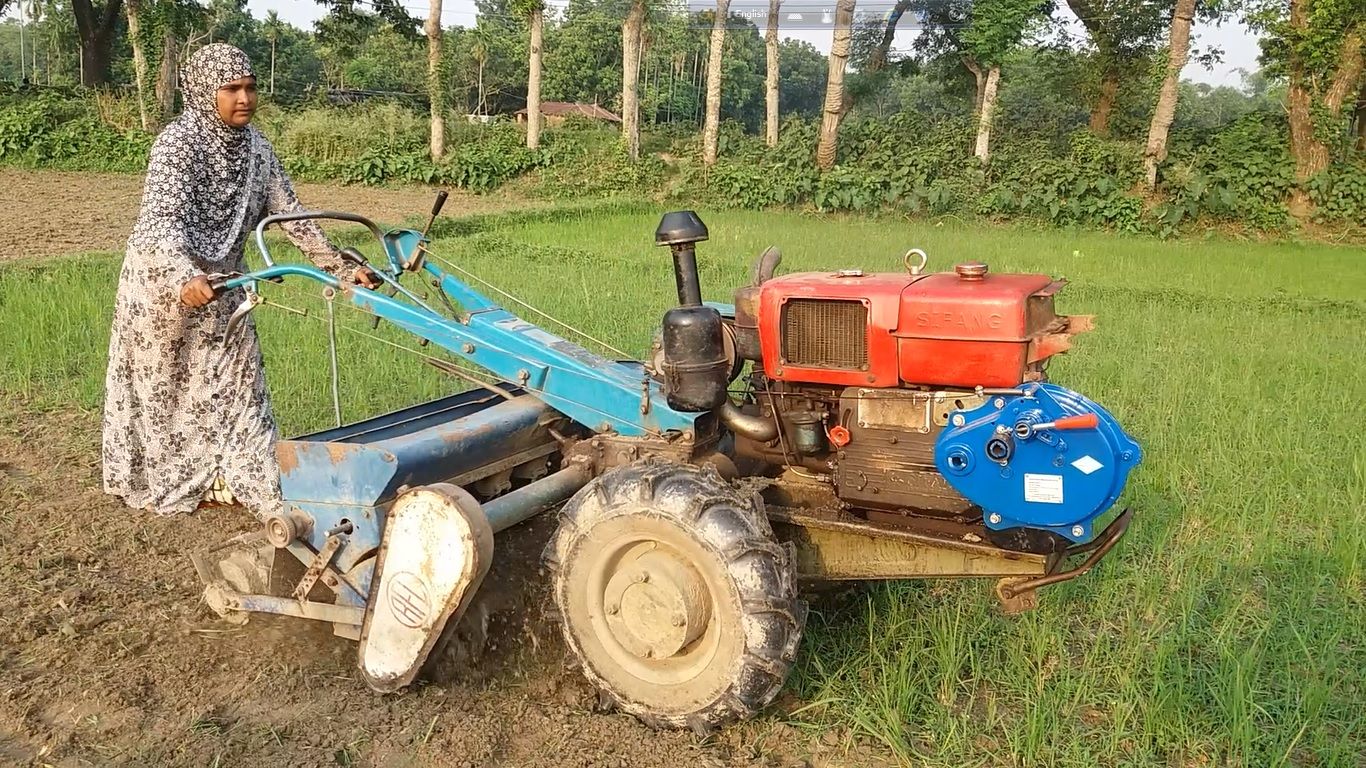
Perhaps the most prominent reason why the precision spreader sparked such interest is that women can easily use it. Most men in rural areas have migrated to the city or abroad in hopes of higher income, so work in the fields has been inadvertently transferred to women. Since Nepal is a predominantly conservative patriarchal society, women have not yet become comfortable and familiarized with all farming practices, especially operating heavy agricultural machinery. However, as expressed by women themselves, the precision spreader is highly convenient to use. Its use could help ease women into the agriculture scene of Nepal and consequently reduce farming drudgery.

Healthier crops, healthier people
Nestled between China and India, Nepal predominantly relies on agriculture for employment. With the majority of its population engaged in the agricultural sector, the country still struggles to produce an adequate food supply for its people, resulting in depressed rural economies, increased malnutrition and widespread hunger.
Sustainable intensification, therefore, is necessary to increase the overall yield and to accelerate agricultural development.
Better distribution of fertilizer in the fields results in a higher chance of healthier crops, which are the source of better nutrition.
A wider use of a seemingly small technology like the precision spreader would not only reduce hardships in farming, but it would also help farmers become more resilient towards the natural and economic adversities they face.
The Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA) is a regional project in Bangladesh, India and Nepal that was established in 2009 with the goal of benefiting more than 8 million farmers by the end of 2020. Funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, CSISA is led by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and implemented jointly with the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) and the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI).