Digitalizing African agriculture: paving the way to Africa’s progress through transforming the agriculture sector
This year’s African Green Revolution Forum (AGRF), which took place from September 3-6, 2019 in Accra, Ghana, focused on the potential of digital agriculture to transform African agriculture through innovations such as precision agriculture solutions for smallholder farmers, access to mobile financial services, data-driven agriculture, and ICT-enabled extension.
Committed to a digital transformation of African agricultural that benefits many, not a few.
The CGIAR has become a new partner of the AGRF and was presenting during the forum its five global challenges: planetary boundaries, sustaining food availability, promoting equality of opportunity, securing public health, and creating jobs and growth.
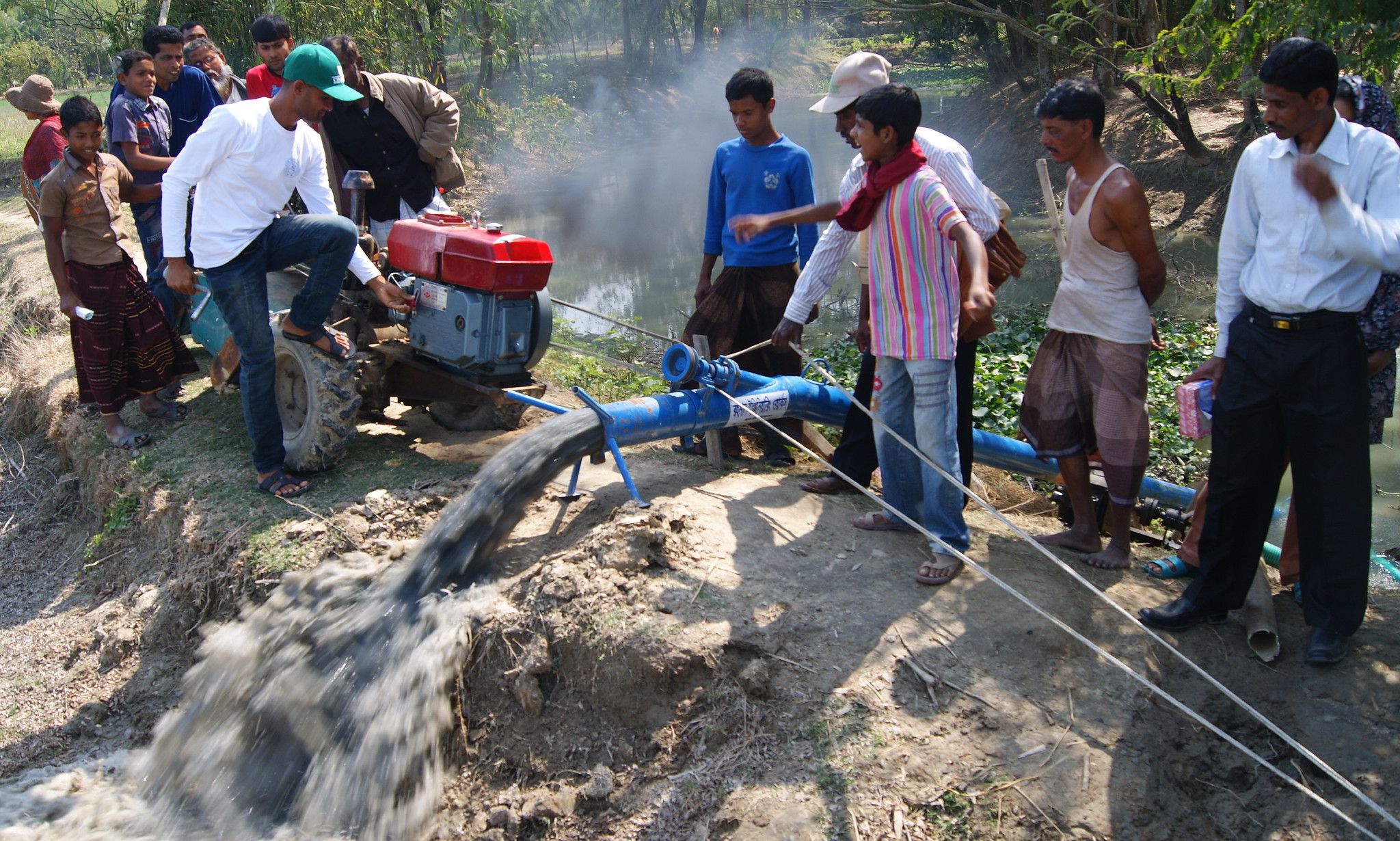
Despite its importance of the continental economy and untapped resources, African farming sector is still dominated by ageing smallholders cultivating few acres of cropland, using not much inputs and lagging far behind productivity world standards.
Many experts believe digital agriculture could help African agriculture leapfrog to overcome its geographical, social and economic bottlenecks, bringing successful technologies to scale faster, and market opportunities even for remote smallholders. Some countries like Ghana or Kenya are becoming digital hubs for agritech-savvy young entrepreneurs along the food value chains, from drone for Ag, linking farmers to the marketplace, or offering mobile mechanization or financial services.
Large initiatives were announced to foster this growth potential, in particular towards the youth in agriculture, like the Mastercard Foundation’s commitment to invest $500 million to support for young agripreneurs within its Young Africa Works initiative, and the World Bank’s One Million Farmer platform in Kenya.
In force at the AGRF 2019, agricultural research organizations such as the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) have a strong role to play in this digital transformation, both as innovator creating for instance new digital maize phenotyping tool for faster yield assessment, and user of tech innovations to improve research targeting and impact.
Improving smallholders’ resilience through digital innovations
The millions of African rainfed farmers are in a risky business, from rising climate shocks to emerging pests and diseases like the invasive fall armyworm or the maize lethal necrosis. CIMMYT Director General Martin Kropff highlighted the importance of digital tools to predict these risks through smart, scalable early warning systems like the award-winning diagnostic tool Marple that helps map wheat rust outbreaks. Researchers can also better predict the farms’ responses to these risks through accurate modelling. They can for instance better assess the potential yield benefits of drought and heat tolerance under different climate change scenarios.
CIMMYT crop breeders use tablet-based disease scoring applications and test new imagery and high-tech sensors for more accurate and cost-effective data collection. Kropff underlined the key role digital tools play to speed up science breakthroughs and impact delivery at the farm level.
Tailored advice for farmers and policy-makers to enable sustainable intensification
“The future is no longer where it used to be. Farmers’ reality has become even more unpredictable,” said Enock Chikava, deputy director, agricultural development at the Bill & Melinda Gates foundation during a vivid debate on how to reshape the future agronomic research so it delivers more site-specific and responsive advice.
Much of the agronomy work within the region remains fragmented across research institutes, commodities and projects, and struggles to go beyond blanket recommendations that are most of the time not adapted to local farming conditions.
However, there is a fast-growing wealth of georeferenced data that can describe the diverse farming landscapes and socio-economic context of each African smallholder farmer. The starting point to exploit these data and get the right solutions for each farmer is to ask the right questions.
Moderated by Samuel Gameda, CIMMYT soil scientist, who shared the lessons from the Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale (TAMASA) project, this session on Agronomy at Scale discussed what public information goods like crop yield prediction maps or extension apps, such as the maize variety selector, would be the most useful for farmers and large-scale agronomic initiatives to trigger this much needed sustainable intensification of millions of African smallholdings. What investments would make a difference to scale the use of these new decision-support tools?
“Agronomic research must be carried out from a broader perspective of large-scale relevance and application. It is also more and more a joint effort and responsibility between smallholder farmers, the research community and public and private sectors, with each component playing specific and interacting roles. The current era of powerful and accessible ICT tools and big data analytics make this much more feasible and should be incorporated to enable precision agronomy for all, this is my take home message,” said Gameda.
“This data revolution will only work if we invest in research data quality and data management,” stressed Bram Govaerts, CIMMYT’s Integrated Development Program director. “That will generate better evidence for decision-makers to guide impact investment plans, deciding on which technology e.g. a new drought-tolerant crop variety and put the money in the right leveraging point,” Govaerts concluded.
The largest forum on African agriculture, AGRF 2019 gathered more than 2,200 delegates and high-level dignitaries, from heads of State and government officials to leaders of global and regional development institutions; top agri-food businesses and local entrepreneurs; financial institutions; mobile network operators and tech leaders, as well as lead representatives of farmer organizations.
Cover photo: Delegation from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) at the African Green Revolution Forum (AGRF) 2019.