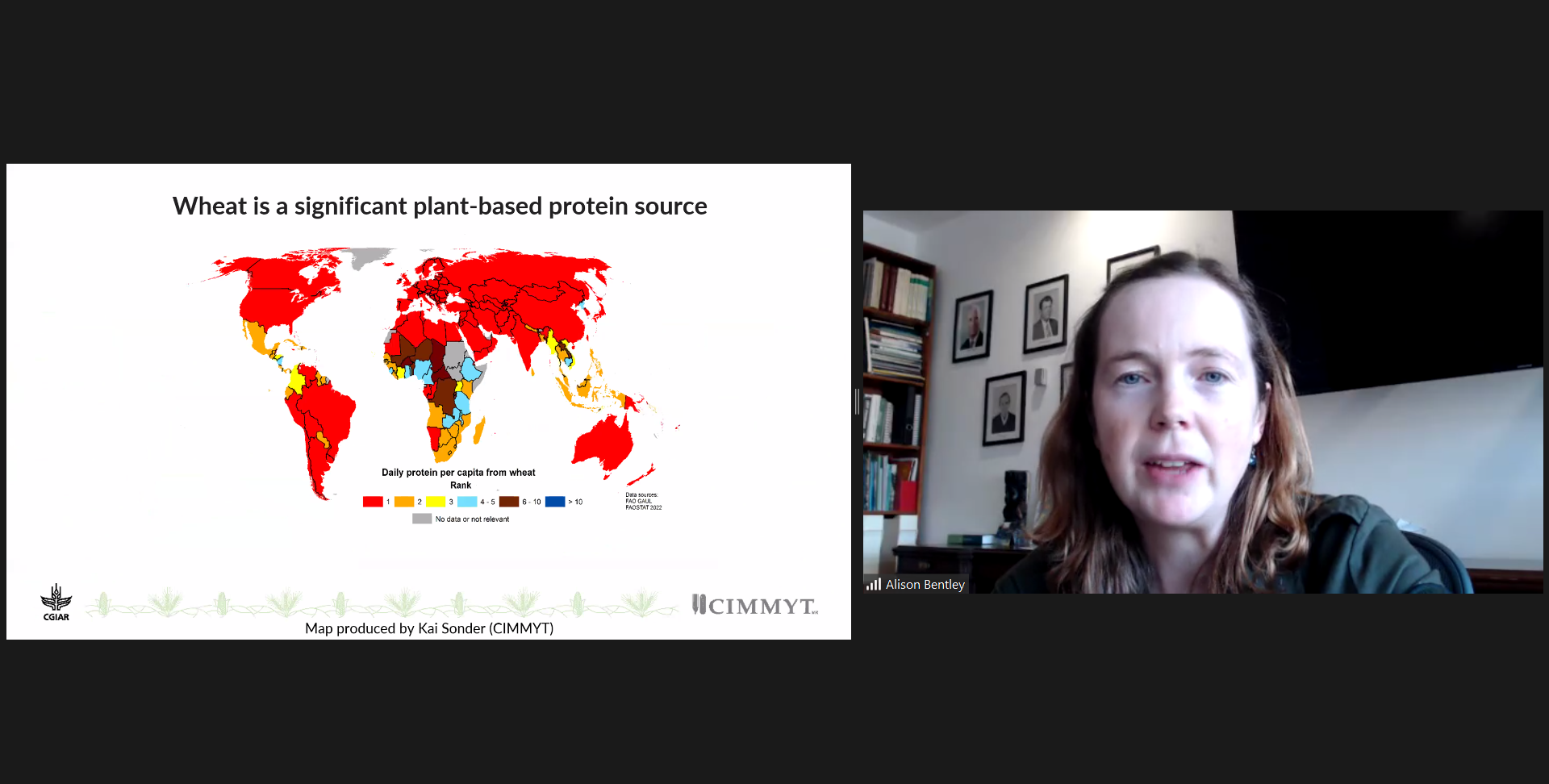
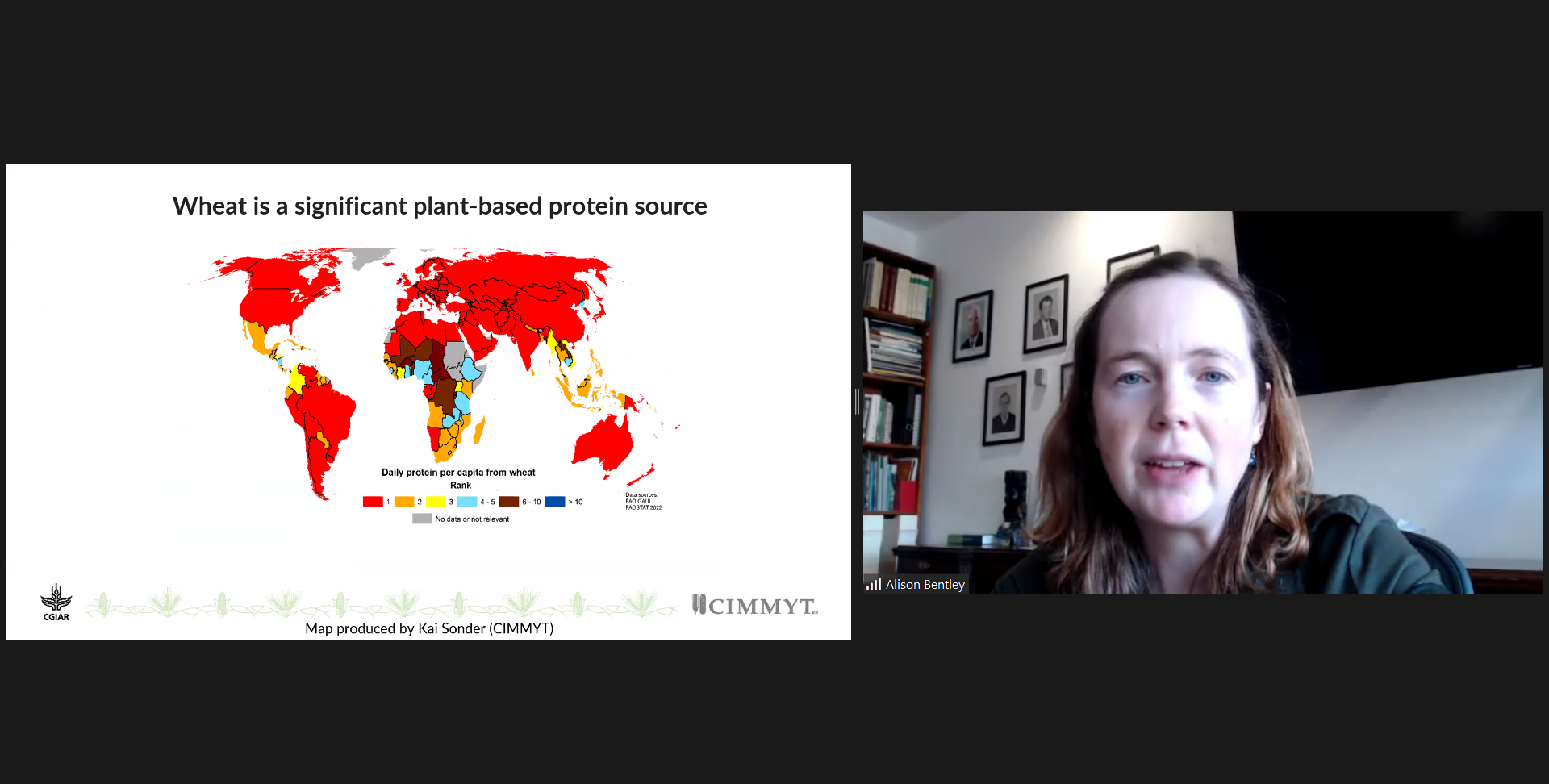
Novel technology to reduce the complexity of maize seed production and increase maize hybrid yields in farmer’s fields
A recently published study in Nature Communications Biology journal demonstrates the potential of a novel seed production technology to transform Africa’s seed production system, conferring important benefits to smallholder maize farmers and seed companies in sub-Saharan Africa.
The Seed Production Technology for Africa (SPTA) process enables production of non-pollen-producing inbred seed that can be used in a two-step multiplication process to produce commercial seed of hybrid varieties containing equal parts pollen producing and non-pollen producing plants. The pollen producing plants provide pollen for the entire field, while the non-pollen producing plants deliver additional grain since they save energy by not producing pollen. Hybrids in which fifty percent of the plants are non-pollen producing have a significant grain yield advantage compared with hybrids in which all plants produce pollen.
Farmers and researchers evaluated the performance of fifty percent non-pollen producing (FNP) hybrids in side-by-side comparisons across diverse farm sites in Kenya, South Africa, and Zimbabwe between 2016 and 2019. The results demonstrate that FNP hybrids deliver an average yield increase of 200 kg per hectare, representing a 10-20% increase at current sub-Saharan Africa yield levels where farmers face frequent drought and sub-optimal soil fertility. The FNP yield advantage was consistent in both low yielding and higher yielding conditions. Additionally, in extensive farmer surveys, farmers rated the FNP hybrids higher than the pollen producing counterparts, recognizing the grain yield advantage. Favorable rating of FNP hybrids suggests that farmers are likely to adopt them once available.
Although consistent and steady improvement is being made for grain yield potential through plant breeding, the yield benefit of FNP hybrids is the equivalent of approximately six years of breeding progress under stressful conditions. The FNP trait provided a consistent yield advantage in several genetically unique hybrids evaluated, indicating that the yield advantage from FNP will be complementary to and additive with progress from maize breeding efforts.
In sub-Saharan Africa, the challenge of delivering genetically pure, high-quality seed is substantial. Seed companies in the region contend with a complex and costly system to produce commercial seed. In addition to delivering higher grain yield to farmers through the FNP trait, the SPTA process will reduce the complexity of seed production, enabling seed producers to deliver higher purity improved hybrid seeds in sufficient quantities for smallholder farmers.
Hybrid seed production requires that one of the parents of the hybrid is prevented from producing pollen, ensuring that the seed harvested has been cross-fertilized by the pollen parent. Most hybrid seed production in sub-Saharan Africa involves physical removal of the tassels of the seed parent prior to the release of pollen, a process known as detasseling. Detasseling is important in commercial seed production to prevent self-fertilization of the seed parent plants. Nearly all detasseling in sub-Saharan Africa is done by hand, which is a labor-intensive and time-sensitive process. Poorly executed or ill-timed detasseling results in unwanted self-fertilization of the seed parent, leading to rejection of seed and incurring losses to the seed producer. Furthermore, timely detasseling typically involves removal of one or more leaves together with the tassel, reducing the photosynthetic capacity of the plant, and lowering the seed yield.
Use of the SPTA process ensures that the seed parent of the hybrid will not produce pollen, thereby eliminating the need for detasseling. This means seed producers can ensure higher integrity of hybrid seed while reducing costs and increasing seed yield. The technology is well suited for the three-way hybrid production commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa. Economic advantages to seed companies of using seed from the SPTA process is also expected to provide incentive to replace older, lower yielding varieties with more recently developed hybrids. Providing improved quality seed of better hybrids while delivering the yield advantage of the FNP trait can benefit smallholder maize farmers throughout the region. Saving costs can help the seed sector remain strong and competitive, which leads to increasingly better options for farmers in the future.
Read the full study: Incorporating male sterility increases hybrid maize yield in low input African farming systems
The research was conducted by scientists from the Seed Production Technology for Africa project, a collaborative initiative of the Agricultural Research Council of South Africa (ARC), International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), CortevaTM Agriscience, Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO), and QualiBasic Seed Company (QBS).
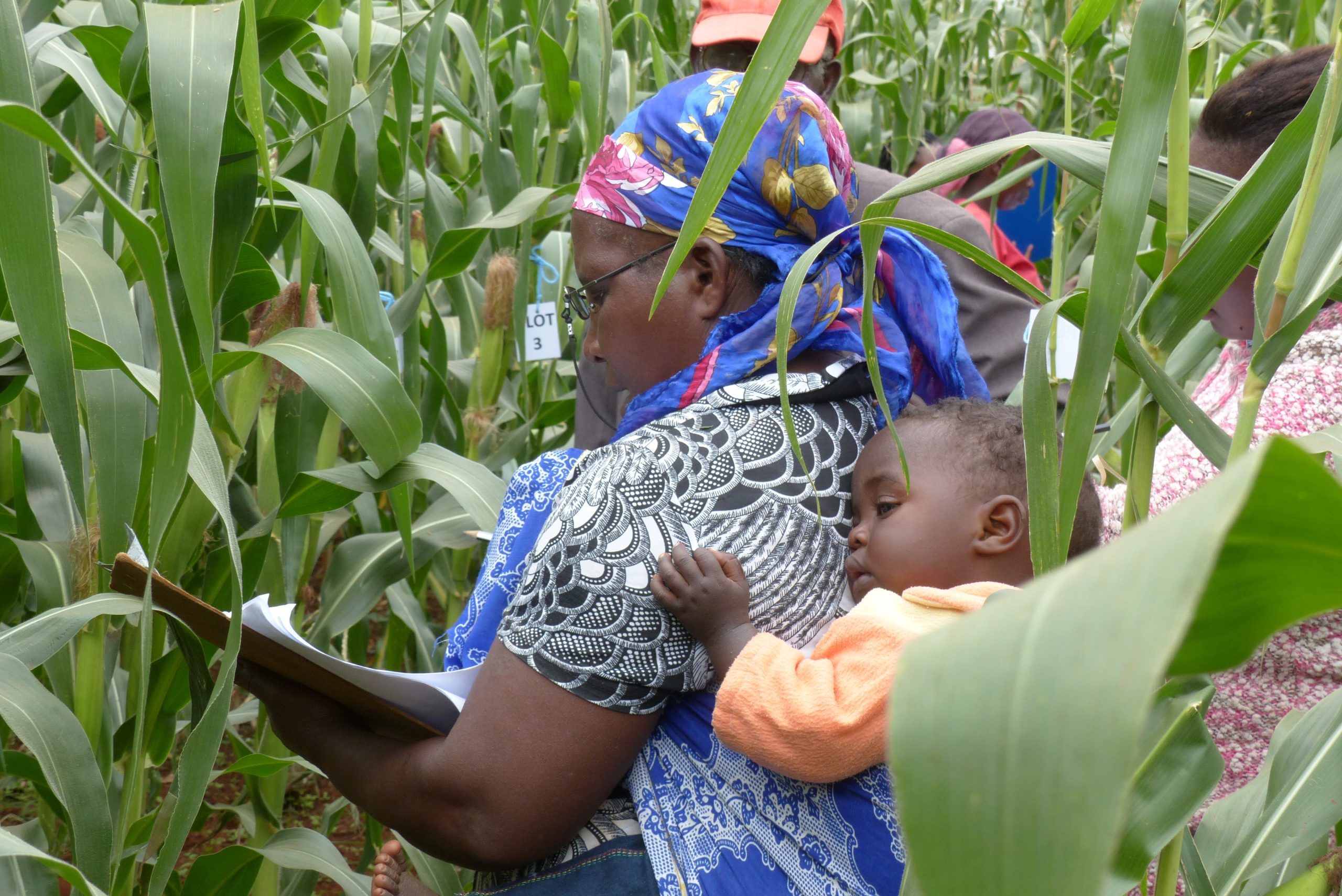
Cover photo: A woman with a baby on her back evaluating maize plants farmer’s plots hosting FNP trials in Embu, Kenya. Photo: Hugo DeGroote/CIMMYT