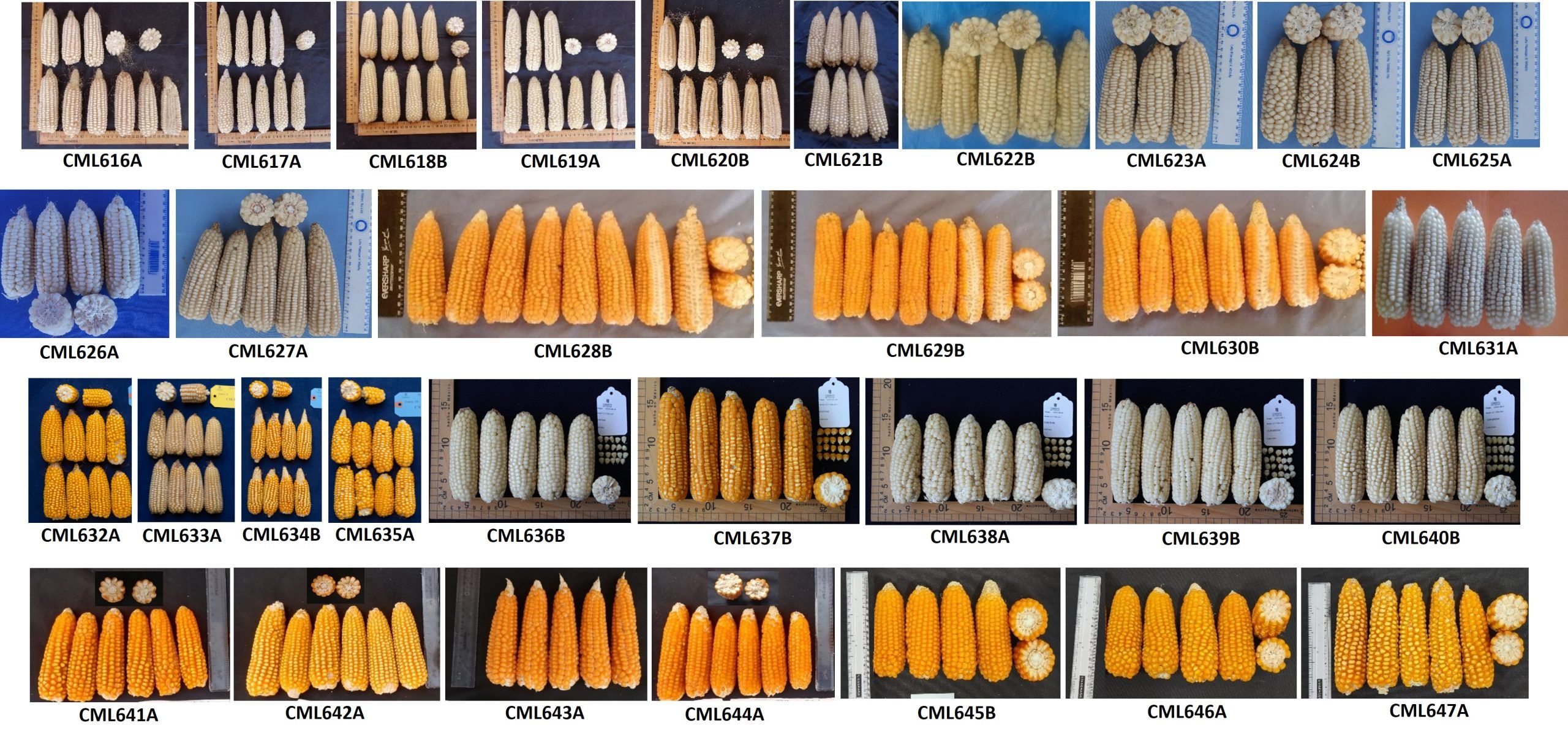
Ten years later: CIMMYT facilities in East Africa continue to make a difference
CIMMYT and partners in Kenya recently marked the 10th anniversary of two major facilities that have been crucial for maize breeding in sub-Saharan Africa. The Maize Doubled-Haploid (DH) facility and the Maize Lethal Necrosis (MLN) screening facility at the Kenya Agriculture and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) centers in Naivasha and Kiboko, respectively, have made immense contributions to the rapid development of higher-yielding, climate-resilient and disease-resistant maize varieties for smallholder farmers across the continent.

“These two facilities have been instrumental in furthering KALRO’s mission to utilize technology in the service of Kenya’s smallholder farmers,” said KALRO Director General/CEO, Eliud Kireger. “They also exhibit the spirit of cooperation and collaboration that is necessary for us to meet all the challenges to our food systems.”
“Deploying a higher yielding maize variety may not be impactful in eastern Africa if that variety does not have resistance to a devastating disease like MLN,” said CIMMYT’s Director General Bram Govaerts. “These two facilities demonstrate the holistic methods which are key to working towards a more productive, inclusive and resilient agrifood system.”
Maize DH facility
Hybrid maize varieties have much higher yields than open-pollinated varieties and are key to unlocking the agricultural potential of maize producing countries. The doubled haploid process is an innovative technology producing within a year genetically true-to-type maize lines that serve as building blocks for improved maize hybrids.
Unlike conventional breeding, which takes at least 7 to 8 generations or crop seasons to develop parental lines, DH lines are generated within two seasons, saving significant time, labor and other resources. DH maize lines are highly uniform, genetically stable, and are more amenable to the application of modern molecular tools, making them perfect resources for breeding elite maize hybrids.

The aim of CIMMYT’s maize DH facility is to empower the breeding programs throughout the low-and middle-income countries in Africa by offering a competitive, accessible, not-for-profit DH production service that will accelerate their rate of genetic gain and fast-track development of improved maize varieties for farming communities.
Since 2017, the DH facility has delivered 280,000 DH lines from 1,840 populations of which 20% were delivered to public and private sector partners. CIMMYT maize breeding programs and partner organizations have embraced the use of DH technology, with many of the newest maize hybrids released in Africa being derived from DH lines. The facility has also served as a training ground so far for over 60 scientists and hundreds of undergraduate students in modern breeding technologies.
“Before 2013, DH technology was mainly employed by private, multinational corporations in North America, Europe, Asia and Latin America,” said CIMMYT’s DH Facility Manager, Vijay Chaikam. “But the DH facility operated by CIMMYT at the KALRO Kiboko research station is specifically targeted at strengthening the maize breeding programs by the public sector institutions as well as small-and medium-size enterprise seed companies in Africa.”
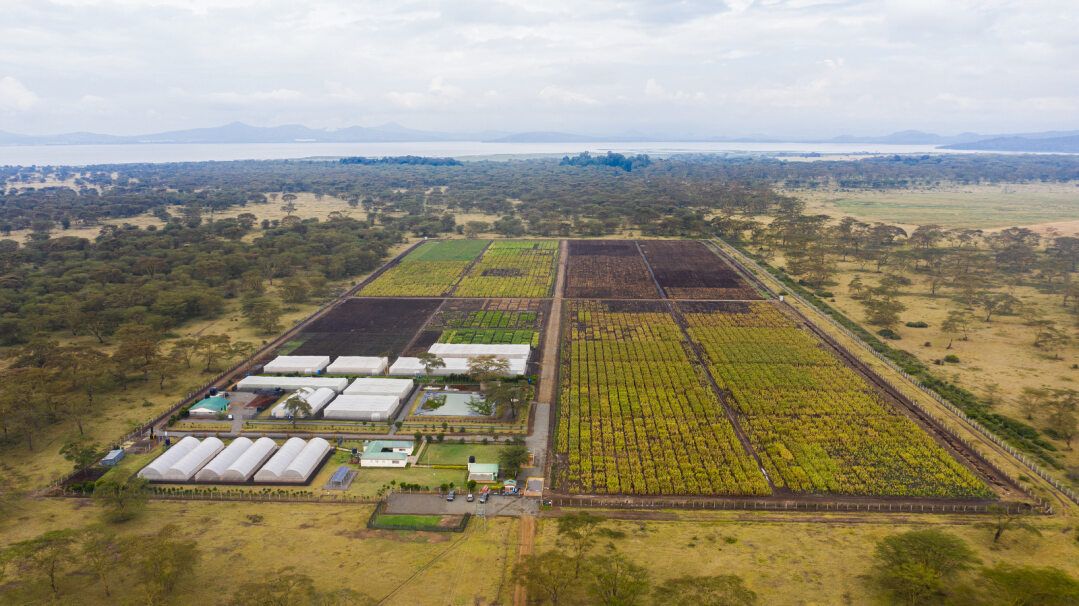
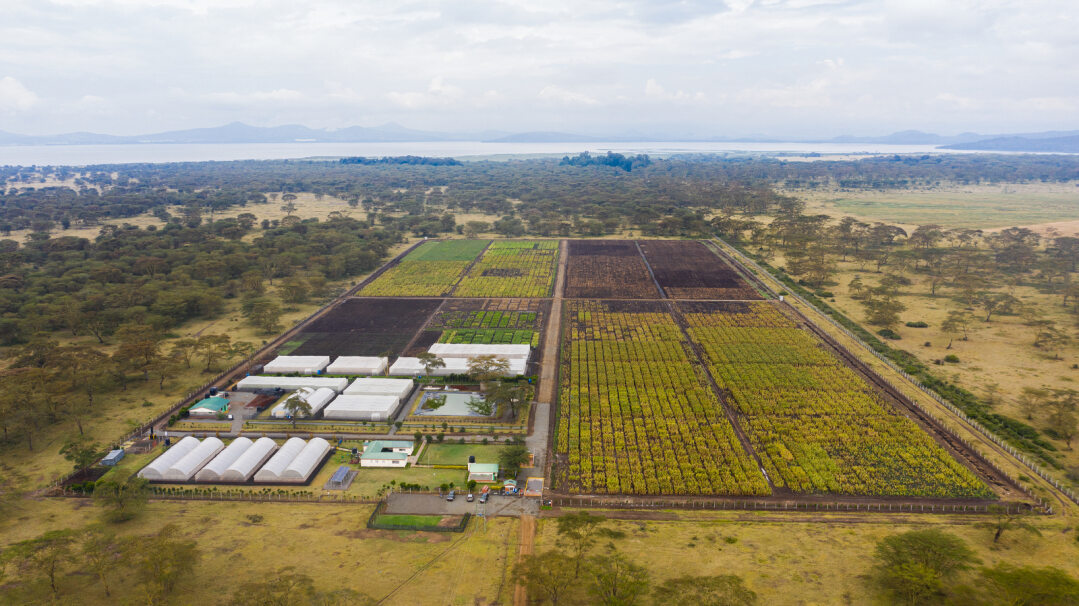
The maize DH facility at Kiboko, Kenya, was established with funding support from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and inaugurated in September 2013. The facility includes an administrative building, seed quality laboratory, training resources, artificial seed dyer, a cold-storage seed room, a chromosome doubling laboratory, greenhouse and a state-of-the-art irrigation system to support year-round DH production in the 17-hectare nursery.
MLN screening facility
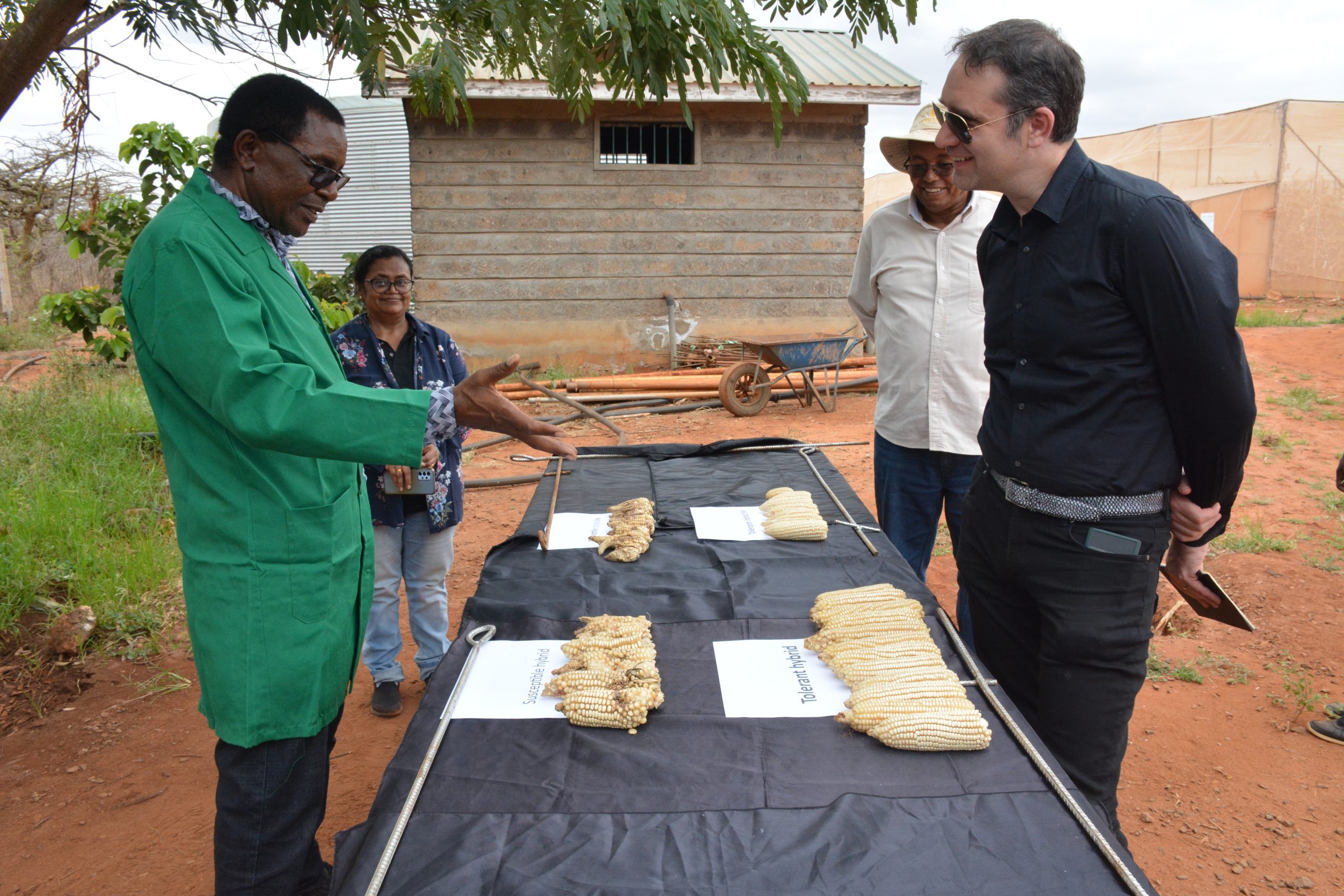
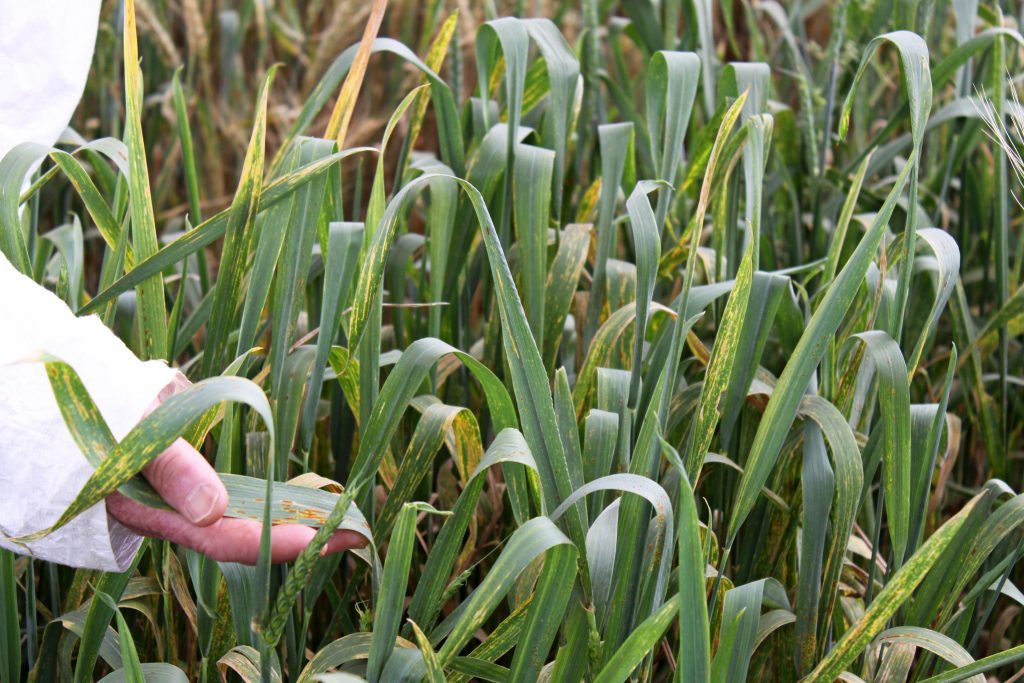
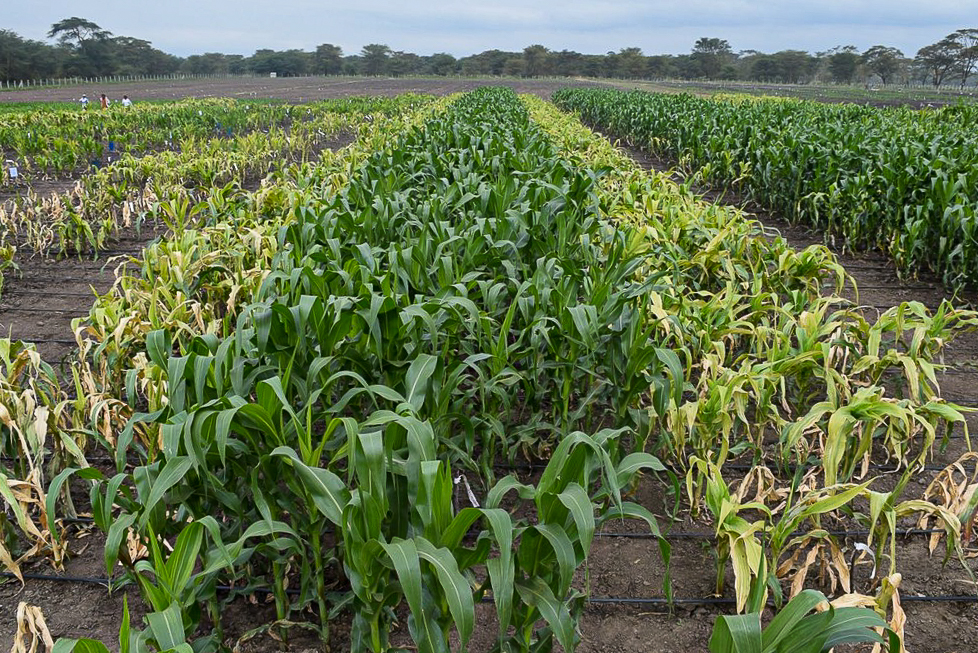
MLN is a devastating viral disease that can decimate farmers’ fields, causing premature plant death and unfilled, poorly formed maize ears, and can lead to up to 100 percent yield loss in farmers’ fields. Though known in other parts of the world for decades, the disease was first identified in eastern Africa in 2011. By 2015, MLN had rapidly spread across eastern Africa, including Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, South Sudan, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of Congo and Ethiopia. CIMMYT scientists quickly discovered that almost all the commercial maize cultivars in eastern Africa were highly susceptible to the disease.
Against this backdrop, CIMMYT and KALRO recognized the urgent need for establishing a screening facility to provide MLN phenotyping service and effectively manage the risk of MLN on maize production through screening of germplasm and identifying MLN-resistant sources. The facility was built with funding support from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the Syngenta Foundation for Sustainable Agriculture, and inaugurated in September 2013.

“The MLN screening facility is a key regional resource in breeding for resistance to a devastating viral disease. The facility is indeed one of the key factors behind successful management of MLN and helping stem the tide of losses in eastern Africa,” said Director of the Global Maize Program at CIMMYT and One CGIAR Plant Health Initiative, B.M. Prasanna. “Fighting diseases like MLN, which do not respect political boundaries, requires strong regional and local collaboration. The successes achieved through the MLN Screening facility in the past 10 years embody that spirit of collaboration.” Indeed, farmers in the region now have access to over twenty genetically diverse, MLN-tolerant/resistant maize hybrids released in eastern and southern Africa.
The facility is the largest dedicated MLN screening facility in Africa and has evaluated over 230,000 accessions (over 330,000 rows of maize) from CIMMYT and partners, including over 15 national research programs, national and multinational seed companies. The facility covers 20 hectares, of which 17 hectares are used for field screening of germplasm. Dedicated laboratories and screen houses cover the remaining 3 hectares.
“MLN phenotyping service is conducted under stringent quarantine standards and the high-quality data is shared with all the CGIAR and public and private partners. The MLN screening service has helped breeding programs across the continent, aided in undertaking epidemiological research activities, and supported capacity building of students from diverse institutions, and regional stakeholders regarding MLN diagnosis and best management practices,” said CIMMYT’s Maize Pathologist in Africa, L.M. Suresh.
“The output of MLN resistant lines and hybrids has been remarkable,” said Director of Phytosanitary and Biosecurity at the Kenya Plant Health Inspectorate Service (KEPHIS), Isaac Macharia. “And the facility has strictly adhered to quarantine regulations.”
In Uganda, the MLN facility was crucial in the “release of the first-generation MLN tolerant hybrids and dissemination of MLN knowledge products that minimized the economic impact of MLN,” said the Director of Research of the National Crops Resources Research Institute, Godfrey Asea.
Peter Mbogo, maize breeder with Seed Co Group, said, “This is the only quarantine facility in the world where you can screen against MLN under artificial inoculation. It has been an excellent return on investment.”