Archives: Projects
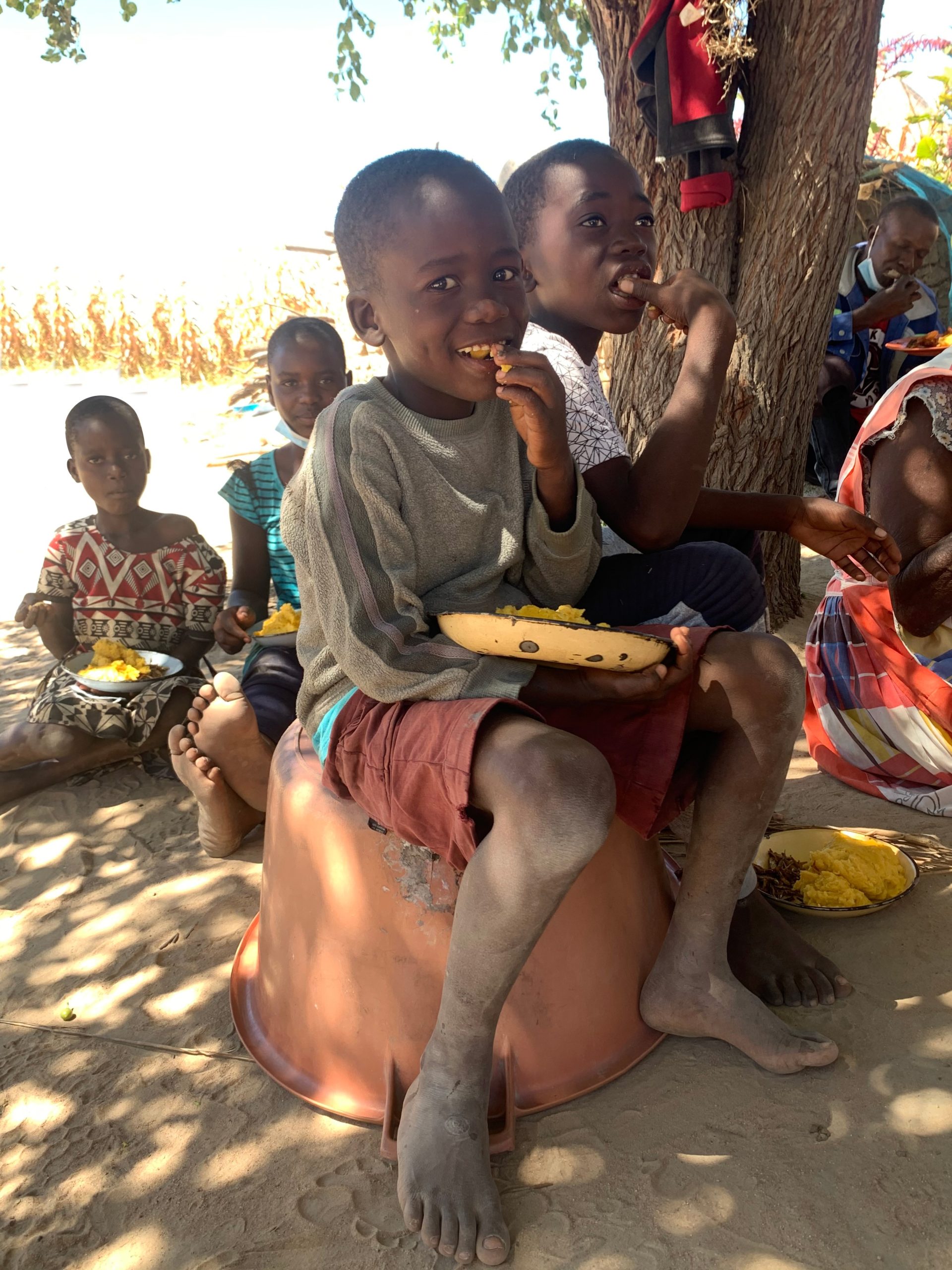
Climate Change and Child Malnutrition in Zimbabwe: Evidence to Action
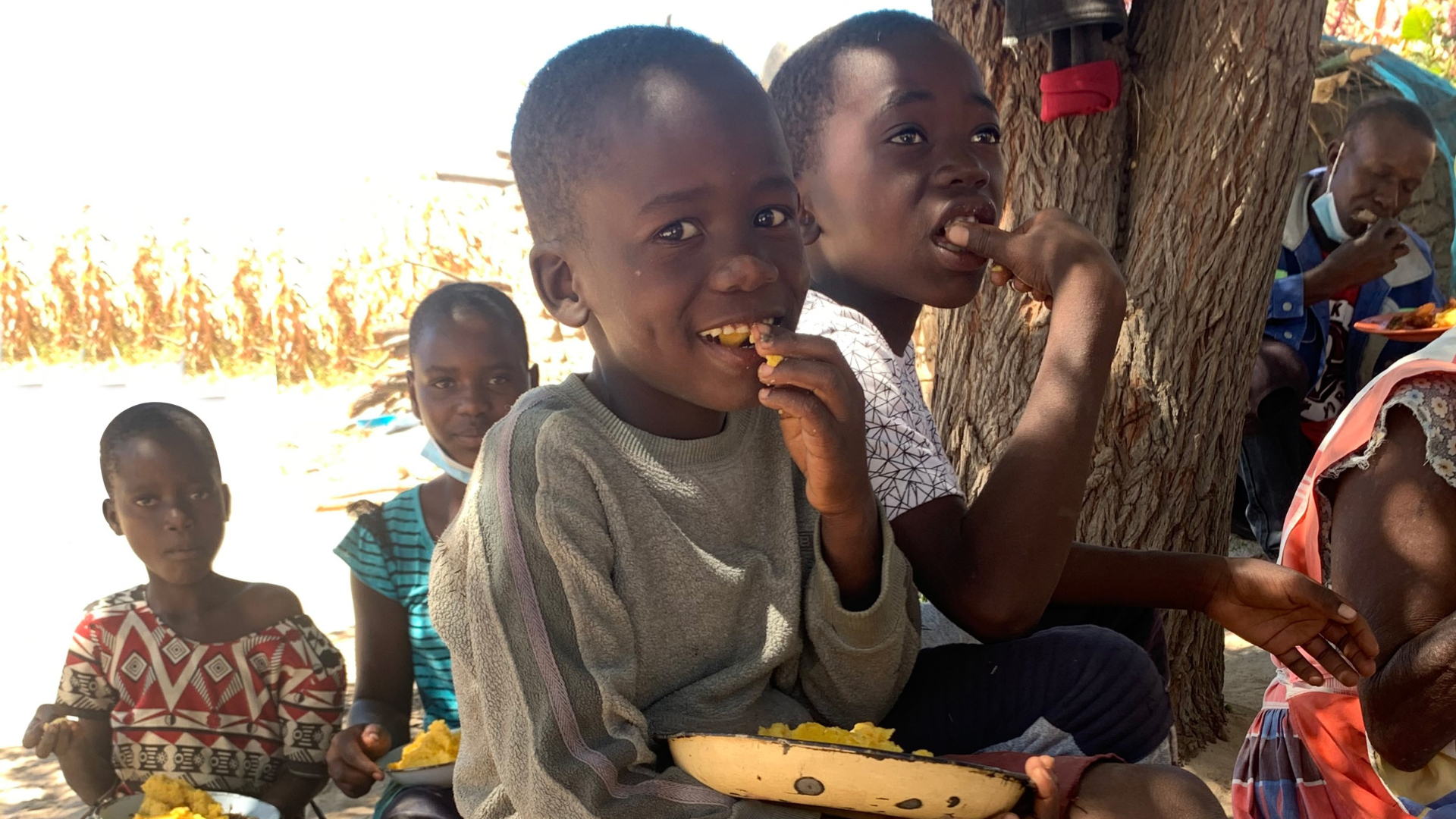
Climate Change and Child Malnutrition in Zimbabwe: Evidence to Action will generate evidence to understand the effects of climate change on child malnutrition in rural Zimbabwe. The overarching hypothesis is that climate change and related weather events indirectly increase child malnutrition by increasing food insecurity and decreasing dietary diversity.
This project will use a multisectoral approach to evidence generation and co-creation of community and policy action that incorporates village, district, provincial and national participation. The project aims to generate evidence linking climate change to malnutrition and co-develop mitigation strategies with communities that directly address the link between climate change and malnutrition.
The project has four activities:
- Examine the relationship between climate change in rural Zimbabwe and patterns of malnutrition utilizing environmental data (rainfall, temperature) and national Zimbabwe survey data (livelihoods, climate change mitigation strategies, dietary diversity and child malnutrition).
- Explore community understanding of the relationships between climate change and malnutrition with a mixed methods approach in two districts (survey and community-led workshops).
- Co-develop and refine climate-smart strategies that address the effects of climate change on malnutrition with agricultural and health cadres.
- Develop a communication plan with policymakers to disseminate findings about the relationship between climate change to child malnutrition.
Objectives:
- Use environmental data and national-level survey data on climate change and shocks related to climate change and examine associations with nutritional outcomes including food security, dietary diversity and child malnutrition.
- Conduct household surveys to understand how agricultural and child feeding practices change under climate variability.
- Conduct community workshops using community walks and River of Life Methodology to understand community perspectives on the relationship between climate change and child malnutrition.
- Co-develop and refine climate-smart strategies that communities can implement to directly address the relationship between climate change and malnutrition.
- Pilot implementation of strategies in two sites utilizing community health and agricultural extension workers.
- Share results with policy makers to contextualize malnutrition in the context of climate change policy.

Atubandike (“Let’s Chat”)
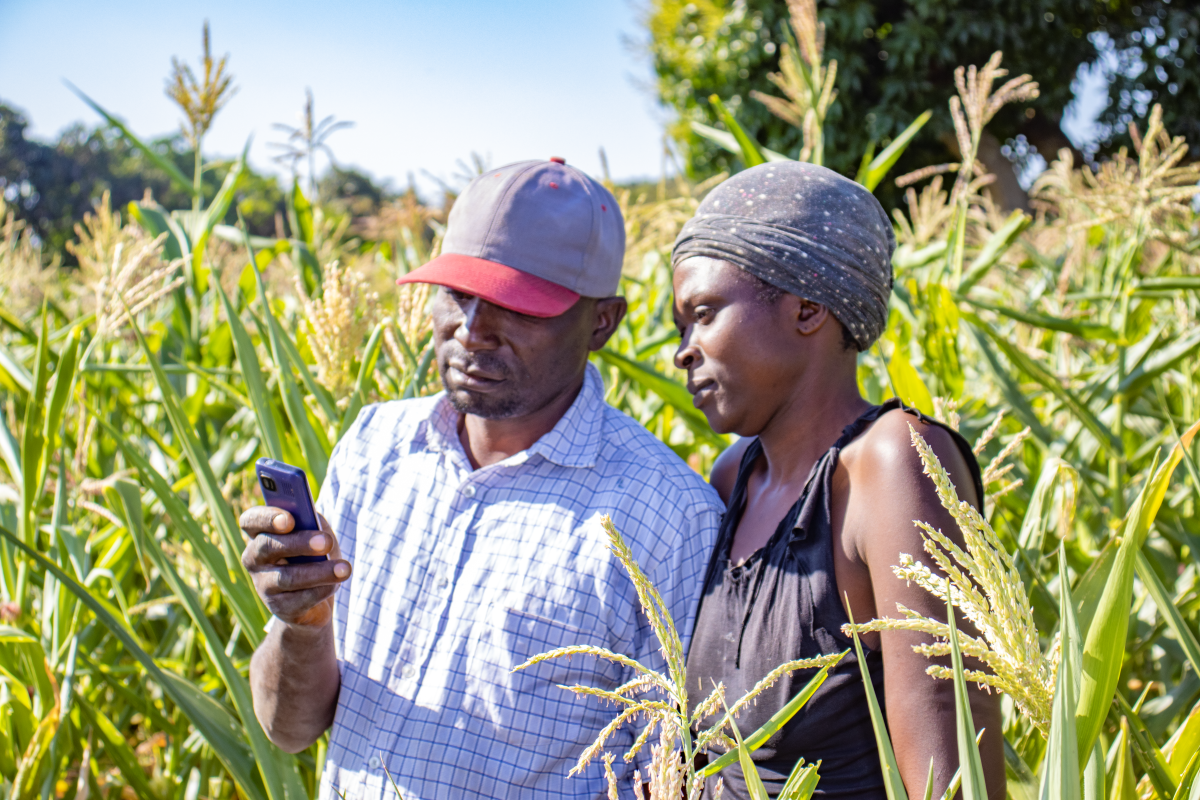
Atubandike (“Let’s Chat”) is a phygital platform co-developed by CIMMYT, Viamo, and farmers to transform agricultural information channels in Zambia’s Eastern and Southern Provinces. Through the toll-free 667 platform, 4,000 farmers – more than 50% of whom are women – access an interactive voice response (IVR) menu powered by a Viamo Database (see infographic). The platform delivers timely and engaging pre-recorded messages on climate-smart agriculture (CSA); enables farmers to ask questions, which informs content for the platform’s biweekly “talk shows” (like radio shows but on a mobile phone); and provides a space for them to share their stories as “peer farmer experiences” on the platform.
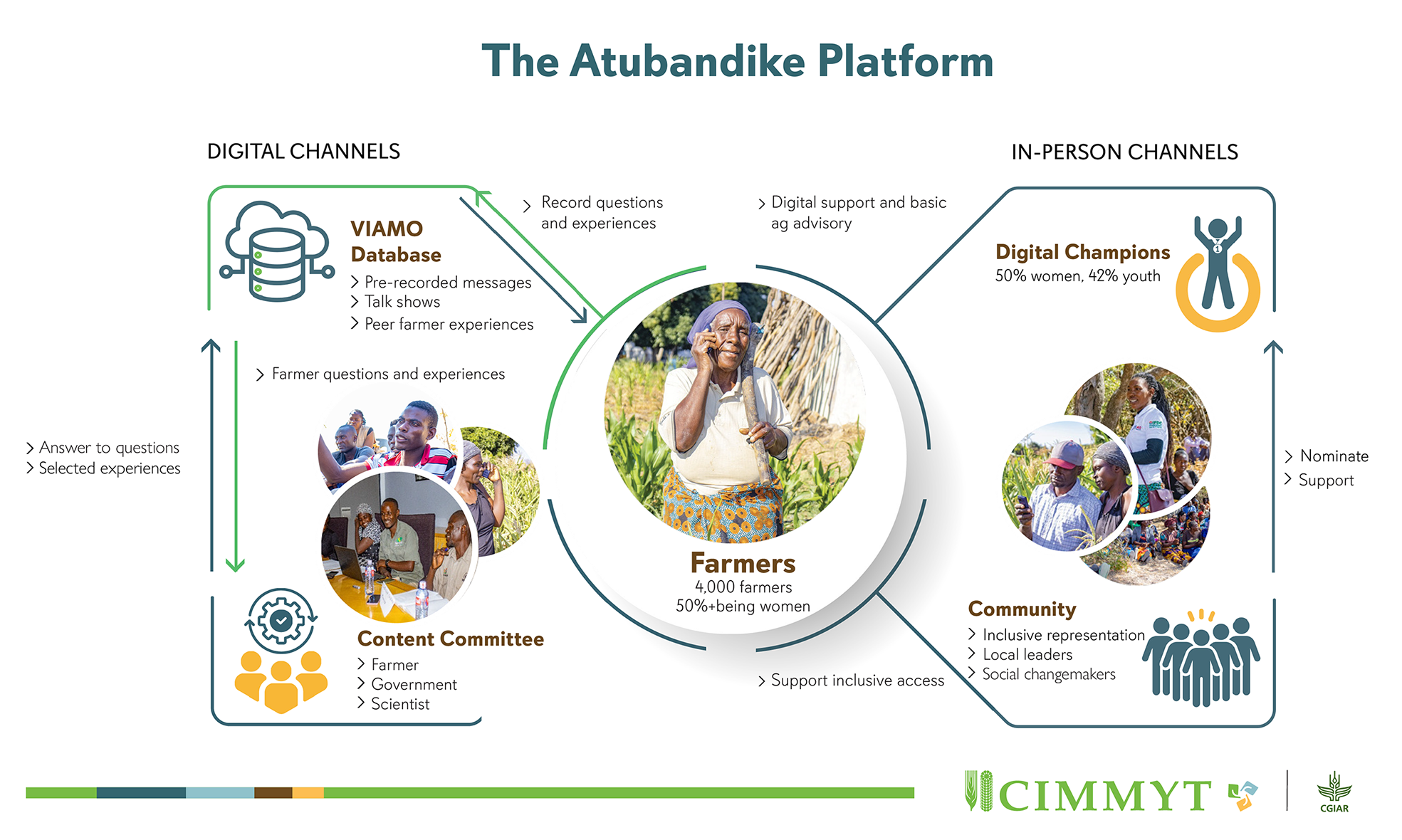
Atubandike’s model involves farmers as co-creators, not merely recipients, of advisory content. Their contributions are curated by a content committee – with farmer, government, and scientist representation – before being published on the 667 platform. Village-based digital champions (50% women, 42% youth aged 18-29) play a crucial role in supporting farmers’ digital skills and promoting trust in digital advisory; they also act as intermediaries between farmers and CIMMYT to address time-sensitive farming questions immediately.
The Atubandike initiative mobilizes local communities to take collective action in challenging social norms that underpin digital access divides. Through community-driven efforts, digital champions are nominated and social changemakers selected to promote inclusive access to the platform.
Together, we are advancing awareness and uptake of CSA practices to boost agricultural productivity and climate change adaptation, using on-the-ground insights to continuously refine Atubandike’s services and ensure every farmer, across the spectrum of demographic groups, thrives in today’s dynamic agricultural landscape.
Listen to Atubandike’s Talk Show:

Intercropping
The Intercropping project aims to identify options for smallholder farmers to sustainably intensify wide-row crop production through the addition of short-duration, high-value intercrop species and to help farmers increase their productivity, profitability and nutrition security while mitigating against climate change.
The focus is on intensification of wide-row planted crops: dry (rabi) season maize in Bangladesh, eastern India (Bihar and West Bengal states) and Bhutan, and sugarcane in central north India (Uttar Pradesh state). The primary focus is to sustainably improve cropping system productivity, however, the effects of wide-row, additive intercropping at the smallholder farm level will be considered, including potential food and nutrition benefits for the household.
There are many potential benefits of wide-row, additive intercropping, beyond increased cropping system productivity and profitability: water-, labor- and energy-use efficiencies; improved nutrition and food security for rural households; empowerment for women; and (over the longer term) increased soil health.
Little research has been conducted to date into wide-row, additive intercropping (as distinct from traditional replacement intercropping) in South Asian agroecologies. To successfully and sustainably integrate wide-row, additive intercropping into farmers’ cropping systems a range of challenges must be resolved, including optimal agronomic management and crop geometry, household- and farm-scale implications, and potential off-farm bottlenecks.
This project aims to identify practical methods to overcome these challenges for farming households in Bangladesh, Bhutan and India. Focusing on existing wide-row field crop production systems, the project aims to enable farmers to increase their cropping system productivity sustainably and in a manner that requires relatively few additional inputs.
Project activities and expected outcomes:
- Evaluating farming households’ initial perspectives on wide-row, additive intercropping.
- Conducting on station replicated field trials into wide-row, additive intercropping, focusing on those aspects of agronomic research difficult or unethical to undertake on farms.
- Conducting on farm replicated field trials into wide-row, additive intercropping.
- Determining how wide-row, additive intercropping could empower women. Quantify the long-term benefits, risks and trade-offs of wide-row, additive intercropping.
- Describing key value/supply chains for wide-row, additive intercropping. Determine pathways to scale research to maximize impact.
- Quantifying changes in household dry season nutrition for households representative of key typologies in each agroecological zone.
CropSustaiN BNI Wheat Mission
The Novo Nordisk Foundation and CIMMYT have launched the 4-year CropSustaiN initiative to determine the global potential of wheat that is significantly better at using nitrogen, thanks to Biological Nitrification Inhibition (BNI)—and to accelerate breeding and farmer access to BNI wheat varieties.
With a budget of US$ 21 million, CropSustaiN addresses the pressing challenges of nitrogen pollution and inefficient fertilizer use, which contribute to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and ecological degradation. Currently, no other seed or agronomic practice-based solution matches BNI crops’ mitigation impact potential. Growing BNI crops can complement other climate mitigation measures.
The challenge
Agriculture is at the heart of both food and nutrition security and environmental sustainability. The sector contributes ca. 10-12% of global GHG emissions, including 80% of the highly potent nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. Fertilizer use contributes to such N losses, because plants take up about 50%, the remainder being lost. Wheat is the world’s largest ‘crop’ consumer of nitrogen-based fertilizer—a relatively nitrogen-inefficient cereal—at the same time providing affordable calories to billions of resource-poor people and ca. 20% of globally consumed protein. CropSustaiN targets this nexus of productivity and planetary boundary impact by verifying and thus de-risking the needed breeding, agronomic, and social innovations.
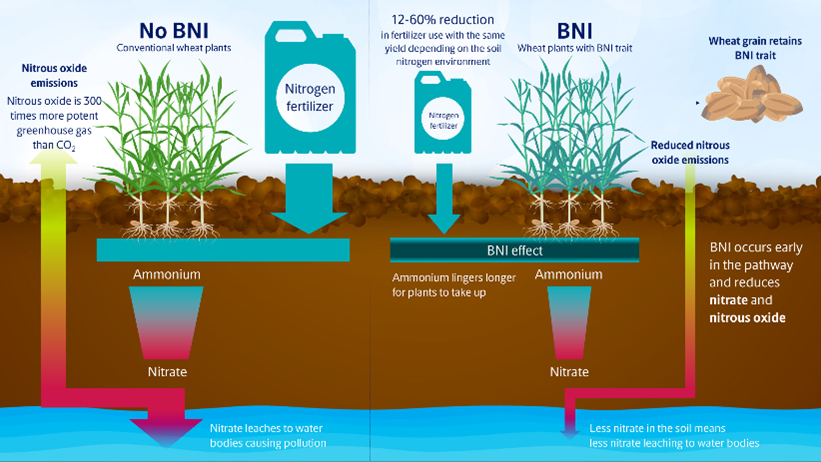
A solution: BNI-wheat
BNI is a natural ability of certain plant species to release metabolites from their roots into the soil. They influence the nitrogen-transforming activity of nitrifying bacteria, slowing down the conversion of ammonium to nitrate in the soil. This preserves soil ammonium levels for a longer time, providing plants with a more sustained source of available nitrogen and making them more nitrogen-use efficient (nitrogen plant use efficiency). As a result, BNI helps reduce the release of N2O gas emissions and nitrate leaching to the surrounding ecosystem.
A research breakthrough in 2021, led by the Japan International Research Center of Agricultural Sciences (JIRCAS) in collaboration with CIMMYT, demonstrated that the BNI trait can be transferred from a wheat wild relative to a modern wheat variety by conventional breeding. BNI wheat can be made available to farmers worldwide.
Growing BNI wheat could reduce nitrogen fertilizer usage by 15-20%, depending on regional farming conditions, without sacrificing yield or quality.
Incorporating BNI into additional crops would reduce usage further. Farmers can get the same yield with less external inputs.
Other BNI-crops
CropSustaiN will work on spring and winter wheats. Rice, maize, barley, and sorghum also have BNI potential. CropSustaiN will build the knowledge base and share with scientists working on other crops and agronomic approaches.
Objectives and outcomes
This high risk, high reward mission aims to:
- Verify the global, on-farm potential of BNI-wheat through field trial research and breeding.
- Build the partnerships and pathways to meet farmer demand for BNI-wheat seeds.
- Work with stakeholders on policy change that enables BNI crops production and markets
Success will be measured by determining nitrogen pollution reduction levels under different soil nitrogen environments and management conditions on research stations, documenting crop performance and safety, breeding for BNI spring and winter wheats for a wide range of geographies, and gauging farmer needs, interest, and future demand.

A collaborative effort
CIMMYT is the lead implementer of Novo Nordisk Foundation’s mission funding. CropSustaiN’s interdisciplinary, intersectoral, systems approach relies on building partnerships and knowledge-sharing within and outside this research initiative. 45+ partners are engaged in CropSustaiN.
The potential GHG emissions reduction from deploying BNI-wheat is estimated to be 0.016-0.19 gigatonnes of CO2-equivalent emissions per year, reducing 0.4-6% of total global N2O emissions annually, plus a lowering of nitrate pollution.
Impact on climate change mitigation and Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
The assumption is that BNI wheat is grown in all major wheat-growing areas and that farmers will practice a behavioral shift towards lower fertilizer use and higher fertilizer use efficiency. That could lead to ca. a reduction of 17 megatons per year globally. This can help nations achieve their NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
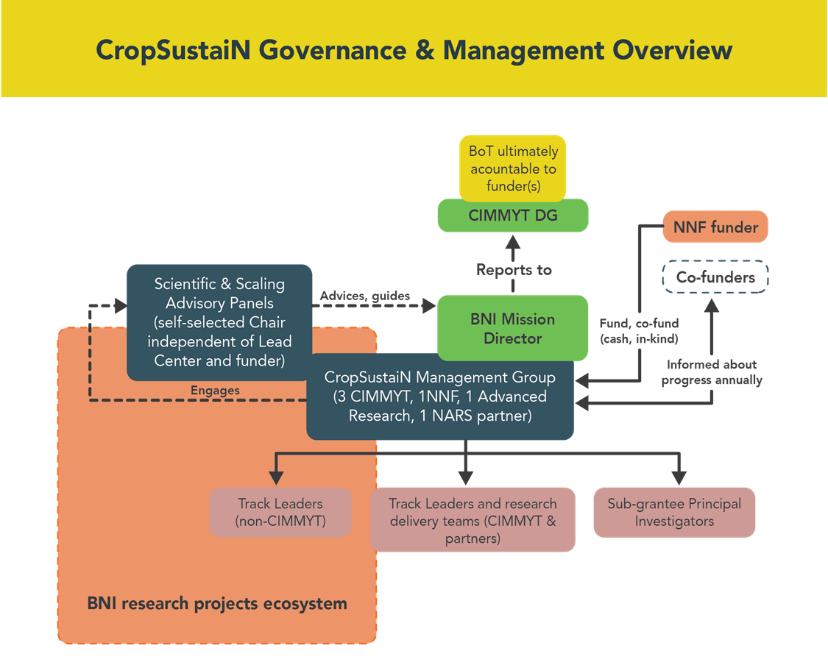
International public goods, governance, and management
CIMMYT and the Foundation are committed to open access and the dissemination of seeds, research data, and results as international public goods. The governance and management model reinforces a commitment to equitable global access to CropSustaiN outputs, emphasized in partnership agreements and management of intellectual property.
Invitation to join the mission
The CropSustaiN initiative is a bold step towards agricultural transformation. You are invited to become a partner. You can contribute to the mission with advice, by sharing methods, research data and results, or becoming a co-founder.
Please contact CropSustaiN Mission Director, Victor Kommerell, at v.kommerell@cgiar.org or Novo Nordisk Foundation’s Senior Scientific Manager, Jeremy A. Daniel, at jad@novo.dk.
Additional reference material
- BNI International Consortium (Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, JIRCAS)
- Nitrification inhibitors: biological and synthetic (German Environment Agency, Umweltbundesamt)
- CropSustaiN: new innovative crops to reduce the nitrogen footprint form agriculture
- Annual Technical Report 2024. CropSustaiN: A new paradigm to reduce the nitrogen footprint from agriculture
- BNI-Wheat Future: towards reducing global nitrogen use in wheat
- CIMMYT Publications Repository
VACS Crop Improvement Coalition
The main objective of VACS is to boost agricultural productivity and nutrition by developing diverse, climate-resilient crop varieties and building healthy soils.
Strategic objectives:
- CIMMYT is an efficient, innovative, and inclusive partner contributing to agrifood systems transformation.
- Food and nutrition security in the global south is ensured within planetary boundaries.
- Smallholder farmers and their livelihood trajectories are resilient and significantly improved.
- Agrifood systems are rendered more inclusive, efficient, productive, sustainable and climate resilient.
- Global community takes informed, coordinated, and consolidated measures to systematically overcome agrifood system disruptions, the impacts of the climate crisis, and structural inequalities.
The project aims to align with the Sustainable Development Goals: Contributing to SDG 2 – Zero Hunger; SDG 3 – Good Health and Well-Being for People; SDG 13 – Climate Action; SDG 15 – Life on Land; SGD 17 – Partnerships for the Goals.
Zambuko Livelihoods Initiative
Persistent vulnerability to frequent climate-related shocks, exacerbated by the effects of climate change poses a continual threat to the capacity of communities to secure an adequate and nutritious food supply throughout the year. The R4 Rural Resilience Initiative, led by the World Food Programme (WFP), aims to enable vulnerable, smallholder farmers to increase their food security, income, and resilience by managing climate-related risks. Expanding on the success of R4, WFP launched the Zambuko Livelihoods Initiative, a comprehensive program supported by United States Agency for International Development (USAID). This initiative strategically concentrates on fostering social cohesion within communities, advancing crop and livestock production, and facilitating improved access to financial resources.
In a collaborative endeavor, CIMMYT is leading the implementation of the climate-smart agriculture and mechanization components of the Zambuko program, with a specific focus on Masvingo Rural (Ward 15) and Mwenezi (Ward 6) in Zimbabwe. Focused on mitigating the impact of climatic shocks and stresses, the initiative aims to empower local farmers, improve agricultural practices, and foster sustainable livelihoods. This collaborative effort represents a crucial step towards building resilience in the face of climate challenges, offering a holistic approach to enhancing the adaptive capacity of vulnerable communities.
Key objectives
The overall objective is to diversify and strengthen climate-resilient livelihoods, while mitigating household vulnerability to recurring shocks, such as droughts and floods.
CIMMYT oversees interlinked goals which are –
- Viable conservation agriculture (CA) and mechanization options are tested and expanded in rural farming communities.
- Seed and fodder options are tested and available for wider use by smallholders.
- Increased smallholder farmer knowledge and capacity to implement climate-smart agriculture interventions to build resilience.
Livestock Production Systems in Zimbabwe (LIPS-Zim)
The livestock sub-sector is one of the most important arms of the agricultural sector, contributing to the livelihoods of 70% of Zimbabwe’s rural population. Sustainable livestock production depends on the maintenance of healthy and productive animals which requires paying particular attention to the problems of both endemic and introduced animal diseases and zoonotic. Climate relevant livestock production practices such as fodder management and conservation, water harvesting, and manure management have been identified as solutions to increasing livestock productivity.
The Livestock Production Systems in Zimbabwe (LIPS-Zim) project, funded by the European Union (EU) focuses on increasing agricultural productivity in Zimbabwe’s semi-arid, agro-ecological regions IV and V. Led by the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) and in partnership with CIMMYT, the French Agricultural Research Center for International Development (Cirad) and the University of Zimbabwe (UZ), LIPS-Zim is working in 10 districts of Zimbabwe, i.e. Matabeleland South Province (Beitbridge and Gwanda districts), the parched Matabeleland North Province (Binga, Hwange and Nkayi districts), Midlands (Gokwe North district), Masvingo (Chiredzi and Zaka districts), Manicaland (Buhera district) and Mashonaland East (Mutoko district). LIPS-Zim is conducting research that seeks to increase livestock feed productivity and well as reducing diseases and mortality of livestock.
Main objectives
Core to the project is to increase the adoption of climate-relevant innovations (e.g feeding) in livestock-based production systems and improve the surveillance and control of livestock diseases. CIMMYT’s main thrust in this project is based on the recognition that at least 50% of the arable land area in semi-arid region IV and V of Zimbabwe is still put to maize despite extension recommendations for farmers to grow the more resilient small grains in those regions. Given the above, and to address their food and feed needs, farmers in those regions need drought-tolerant and nutritious maize varieties that are resilient in those dry environments. CIMMYT’s work is thus focusing on testing the feed value of these nutritious and drought tolerant maize varieties when intercropped with various legumes such as mucuna, cowpea, lab-lab and pigeonpea. CIMMYT is also testing the later, along with climate smart production techniques such as conservation agriculture and water harvesting practices.
Understanding and Enhancing Adoption of Conservation Agriculture in Smallholder Farming Systems of southern Africa (ACASA)
Conservation agriculture (CA) has increasingly been promoted in southern Africa to address low agricultural productivity, food insecurity, and land degradation. Despite significant experimental evidence on the agronomic and economic benefits and the large scaling-up investments by donors and national governments, the adoption rates of CA practices among smallholder farmers are low and slow.
With funding from the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (NORAD) and implemented by the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) and CIMMYT, ACASA strives to understand “why previous efforts and investments to scale CA technologies and practices in southern Africa have not led to widespread adoption.” It is a three-year project implemented in Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, where CA is part of national policy.
Since 2021, the project has undertaken extensive surveys aimed to understand incentives, drivers, and barriers of CA adoption across the three countries (Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe) typifying much of the southern Africa smallholder systems. The aim of the project is to consolidate the lessons learned so far and provide a pathway to scaling and foster the next generation of social, crop, agronomic and climate research; to mainstream CA enabled by fundamental paradigm shifts in farming practices, markets, and social institutions for sustainable intensification of smallholder farming systems of southern Africa.
Project objectives include –
- Understanding the contexts of smallholder farmer in southern Africa to identify the drivers and barriers preventing adoption of CA practices, including biophysical, socio-economic, institutional and policy constraints
- Identifying labor-efficient mechanization options for smallholder farmers
- Identifying opportunities and tools for better targeting of appropriate CA practices and options across heterogenous agroecologies and farm types, and
- Identifying approaches and strategies for inclusive scaling of CA practices (policy, institutional and value chain entry points and pathways to promote and scale CA)
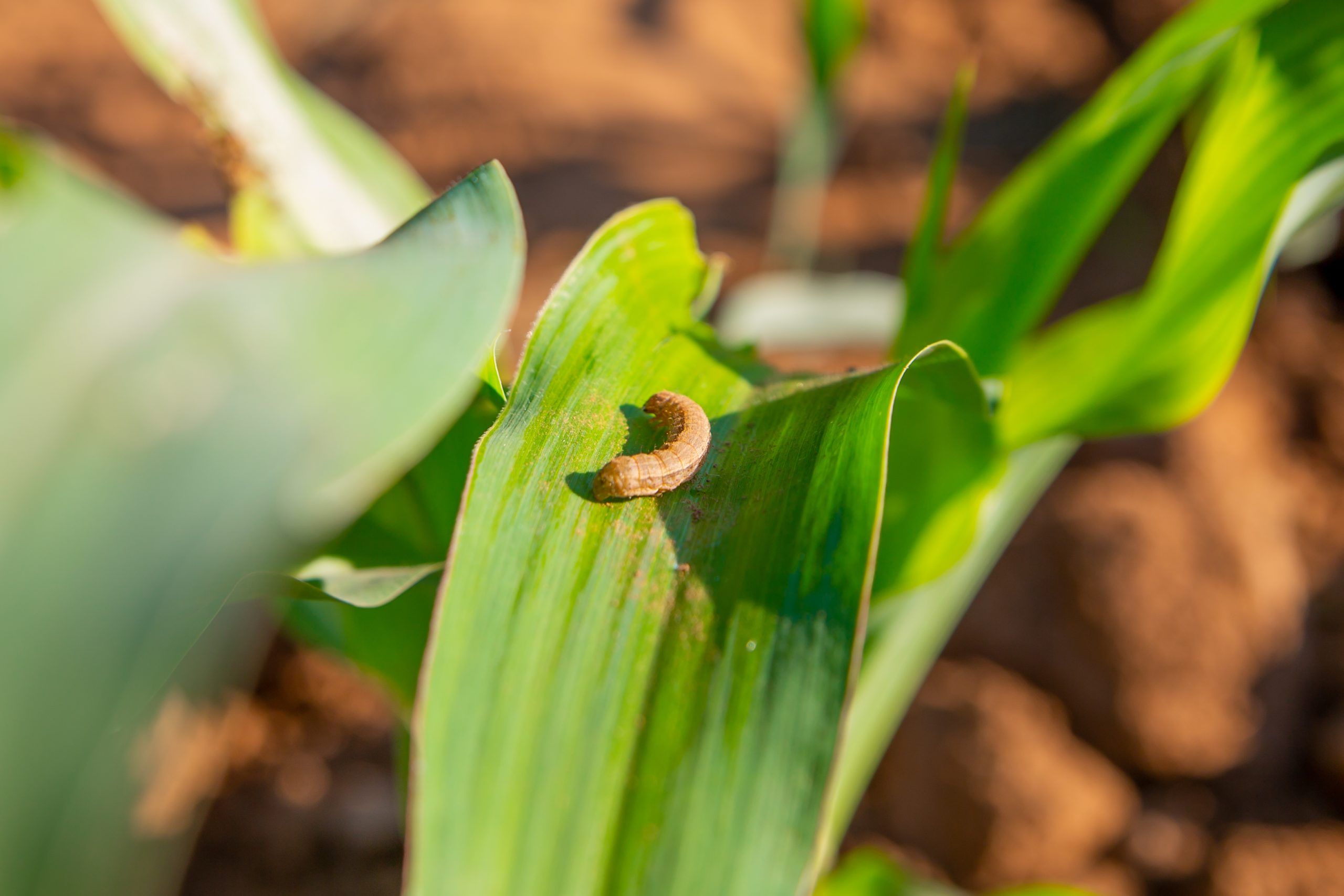
Evaluating Agro-ecological Management Options for Fall Armyworm in Zimbabwe
Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda J.E. Smith) has emerged as a major threat to farming communities across Africa, including Zimbabwe. This destructive pest feeds on a wide range of crops, including maize, posing a significant challenge to food security. To combat this pest, the project “Evaluating Agro-ecological Management Options for Fall Armyworm in Zimbabwe” was initiated in October 2018 with support from USAID. It aims to address research gaps on fall armyworm management and cultural control in sustainable agriculture systems.
The project has implemented research trials in ten (10) districts across Zimbabwe, with work reaching close to 9,000 beneficiaries in target areas being exposed and applying new control practices that reduce the damage of FAW without heavily relying on chemical pesticides. This has been supported by a strong focus on agronomy trainings, field days, documentation, education through technical videos, knowledge sharing, and developing farmer manuals. In addition, the project supports Farmer Field Schools involving all relevant players in the farming communities to mainstream cultural practices in fall armyworm management.
Key objectives
The overall objective is to explore climate-adapted push pull systems and low-cost cultural control options for smallholder farmers in Zimbabwe. This project focused on research trials in Murehwa (Mashonaland East) and Mhondoro Ngezi (Mashonaland West), where the proof of concept was developed. After the inception phase it expanded to establishing demonstration sites and Farmer Field Schools in the Manicaland province, conducting trainings with farmers, and promoting knowledge sharing with Agritex officers and engaging with all relevant players in the target localities. Through continuous research and collaborative efforts, this project aims to develop sustainable and eco-friendly strategies to manage all armyworm infestations.
CGIAR Initiative on Diversification in East and Southern Africa
East and Southern Africa is a climate hotspot, with more than US$45 billion in agricultural production at risk from higher temperatures, shorter growing seasons and more extreme droughts and floods. Maize, a staple crop covering up to 75% of cropland in parts of the region, is particularly vulnerable and is projected to face yield declines of 15%, among other climate impacts if no adaptation measures are taken. Many of the affected areas already have serious levels of hunger and malnutrition, with the highest burden experienced by women and youth from marginalized and vulnerable communities. If these systems are sustainably diversified, they can contribute to stabilizing regional and global agrifood systems.
The next decade will be critical for strengthening food, land and water systems in East and Southern Africa. The agribusiness ecosystem for both regions has been identified as a critical engine for agricultural and economic development, climate change adaptation and gender and youth empowerment. Investment in innovation, capabilities and supportive environments will be essential for driving sustainable growth.
Objective
This Initiative aims to support climate-resilient agriculture and livelihoods in 12 countries in East and Southern Africa by helping millions of smallholders intensify, diversify and reduce the risks in maize-based farming through improved extension services, small and medium enterprise development, supporting governance frameworks and increased investment with a gender and social inclusion lens.
Activities
This objective will be achieved through:
- Diversifying and sustainably intensifying production by assessing needs and options for the introduction of crops, livestock, mechanization and irrigation, applying innovations in value chains and building capacity while scaling to larger farming communities.
- Reducing risk and digitalizing value chains by co-designing and delivering “Innovation Package” bundles of digital agro-advisory systems and research management products — including mobile apps, TV programs and social media — to build resilience and improve productivity.
- Supporting and accelerating value chain business enablers in maize mixed systems by using CGIAR’s expertise and partner network to unlock access to funding, investment and tailored technical assistance.
- Promoting the governing and enabling of multifunctional landscapes for sustainable diversification and intensification with a focus on strengthening the evidence base for decision-makers.
- Empowering and engaging women and youth in agribusiness ecosystems by mapping challenges and opportunities to address gender and social inequality and applying inclusive and coordinated interventions for transformative change.
- Scaling innovations and coordinating CGIAR and partner activities in the region through a scaling hub that uses the “scaling readiness” approach to inform, activate and bring to scale innovations that respond to regional or country demand.
Resilience Building through agroecological intensification in Zimbabwe (RAIZ)
Zimbabwe’s agricultural sector is predominantly subsistence-oriented, with maize as the main staple crop and limited use of external inputs. To promote sustainable and climate-smart agriculture, Zimbabwe has developed a 10-year framework (2018-2028) that emphasizes the adoption of climate-smart agriculture (CSA). However, the adoption of CSA practices remains limited in the country. Agroecological practices (AE) and the systemic perspective embedded in agroecological approaches hold great potential to address climate change and enhance agricultural sustainable intensification in Zimbabwe. RAIZ was conceived as the research component of the “Team Europe Initiative” (TEI) on “Climate-Smart Agriculture for Resilience Building”, formulated by the European Union (EU) delegation in Zimbabwe together with its member states.
Led by the French Agricultural Research Centre for International Development (CIRAD), in partnership with CIMMYT and the University of Zimbabwe, with funding from the European Union, RAIZ operates along a gradient of declining rainfall from Murewa in Natural Region II to Mutoko in Natural Region IV. Both districts are in the Mashonaland East province. Under RAIZ, CIMMYT leads Work Package 3 which involves ‘developing the capacity of extension and advisory services on agroecological approaches’ is actively involved in research and development activities, including the creation of training materials and the establishment of on-farm trials. In efforts to address challenges associated with low soil fertility on Zimbabwe’s granitic sandy soils. CIMMYT scientists working on RAIZ are testing the contribution of organic fertilizers and conservation agriculture in building up soil organic carbon and bringing back soil life to these mostly dead soils. These efforts aim to support farmers in adopting sustainable and climate-smart agricultural practices, ultimately contributing to the long-term resilience and prosperity of Zimbabwe’s agricultural sector.
Key objectives
The overall objective is to support government in the development and implementation of scientifically tested agroecological approaches which will enhance agricultural production and resilience to climate change in Zimbabwe.
In addition, the project focuses on protecting the environment and reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It will provide scientific evidence and experience for the design of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) at the plot, farm, and landscape levels, contextualized for mixed crop–livestock farms under sub-humid to semi-arid environments.
Sustainable Intensification of Smallholder Farming Systems in Zambia (SIFAZ)
Sustainable Intensification of Smallholder Farming Systems in Zambia (SIFAZ) is driven by the need to address systemic productivity and sustainability challenges in Zambian smallholder farming systems. This project is implemented in a research-for-development approach where applied research is conducted alongside scaling-up of sustainable and climate-smart crop production and land management practices within selected pilot areas in the three agro-ecological zones (AEZ) of Zambia.
SIFAZ strives to test, promote and enhance the uptake of sustainable intensification practices (SIPs) including mechanization among smallholder farmers while fostering market linkages and creating an enabling environment for sustainable agriculture growth. Such efforts will contribute to the government’s development priorities, which are framed by the Vision 2030 (Republic of Zambia, 2006) of “a prosperous middle-income nation by 2030” including an efficient, competitive, sustainable and export-led agriculture sector that assures food security and increased income.
The SIFAZ project cycles I and II are being implemented by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) in partnership with CIMMYT and the Ministry of Agriculture (MOA) in Zambia, with funding from the European Union (EU) for a period of seven years (2019-2026). Under the SIFAZ project, CIMMYT is leading the implementation of adaptive research and is currently working on establishing on-station and on-farm and field testing in and around three research centers in the southern, eastern and northern provinces of Zambia; the research approach includes co-development of on-farm trials using mother and baby trials; mechanization and socio-economics research.
To achieve this, SIFAZ supports three closely interlinked outputs:
- Sustainable intensification practices (SIPs) co-developed with farmers and made available for scaling up.
- Farmers trained, mentored and capacitated to use SIPs, better manage farmer enterprises and engage value chain actors.
- Enabling institutional and policy environment for scaling and adoption of SIPs by smallholder farmers established.
Feed the Future Mechanization and Extension Activity
In 2015, the General Assembly of the African Union committed to retiring the hand hoe to museums and pushing for sustainable agricultural mechanization on the African continent.
Today, approximately 75-82% of smallholder farmers in eastern and southern Africa rely on human or animal draft power for primary tillage operations. Mechanization helps to reduce drudgery, increases productivity, and contributes to food security and increased livelihoods.
What is Feed the Future Mechanization and Extension Activity?
The Feed the Future Mechanization and Extension Activity, funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), aims to improve smallholder farmers’ access to farm power and machinery to enhance their land and labor productivity.
This is achieved through three integrated components that stimulate demand for scale-appropriate machinery.
Components:
- Identification of demand-driven smallholder farm machinery and building capacity of manufacturing companies to produce, repair, and import machinery for smallholder agricultural production systems.
- Building the capacity of local service providers to purchase, operate, and maintain farm machinery to provide mechanized services to small-scale agricultural value chain actors.
- Coordinate and collaborate with other FTF activities to build the capacity of interested local service providers.
What are the objectives?
- Assess and build the capacity of smallholder machinery manufacturers and suppliers to manufacture demand-driven farm machinery.
- Enhance land and labor productivity and income through the establishment of mechanization service provision to small scale agricultural value chain actors.
- Promote the use of the machinery through demonstrations and other demand creation activities, and inclusive training of rural women and youth in post-harvest processing of agricultural produce to generate increased income.
- Coordinate and collaborate with other mechanization and Feed the Future activities to build capacity of the interested service providers to be agricultural extension agents to their customers during the cropping season.
- Support service providers, manufacturers, and distributors to access credit to acquire machinery or mechanized services.
The project sites are located in Zimbabwe’s Manicaland and Masvingo provinces with project presence implemented across 10 districts.
The Mechanization and Extension Activity will directly benefit 150 service providers who in turn will reach up to 22,500 women and men smallholder farmers through provision of mechanized services. In addition, the mechanization activity will identify and build the capacity of 30 rural mechanics and 30 technicians drawn from local farm machinery manufacturing companies and/or small and medium enterprises.















