Enhancing maize seed and feed security
Maize is the second most important cereal in Laos after rice, driven primarily by the demand for animal feed in neighboring countries such as China, Thailand, and Vietnam. Laos has an export-oriented maize sector, with most of the country’s production destined for these markets. The sector reached its peak in 2016, when production levels hit 6 metric tons per hectare across an area of 0.26 million hectares.
Over 90% of Laos’s maize production relies on rain-fed agriculture, with maize grain and stover serving as the primary source of feed for smallholder farmers who depend on mixed crop and livestock farming systems for their livelihoods. However, between 2016 and 2022, total maize area and production declined significantly, contracting by 64% and 70%, respectively. Several factors contributed to this decline, including volatile market prices, competition from cassava and other crops, rising production costs, and yield losses due to pests, diseases, and soil nutrient degradation because of monocropping.
Additionally, Laos relies on imported hybrid maize seed, primarily from Thailand and Vietnam, which creates a dependence on external suppliers and exposes farmers to price fluctuations. Recognizing the importance of improving maize productivity and sustainability, the Laotian government is taking steps to enhance local capacity for seed production and ensure access to affordable high-quality feed.
Enhancing local hybrid maize seed production
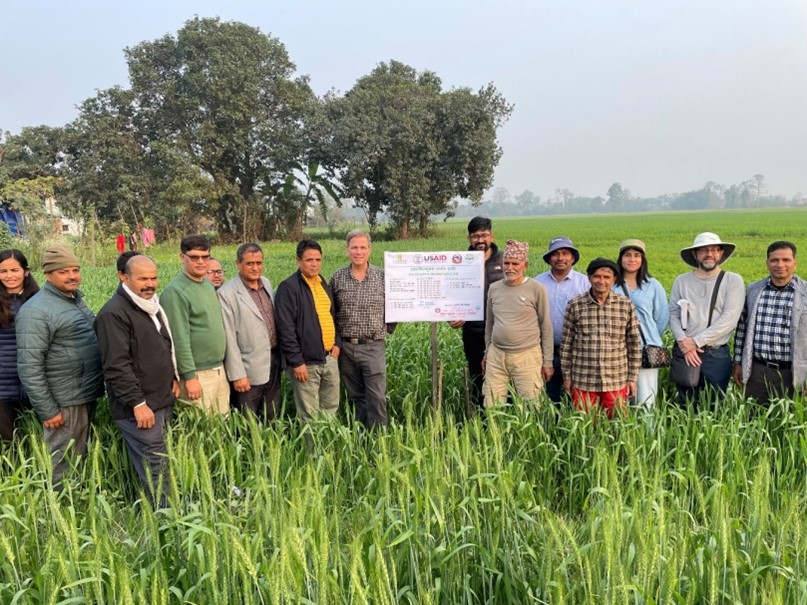
Recognizing the importance of enhancing the availability and accessibility of quality maize seed and feed, CIMMYT and Laos’s National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) have initiated the evaluation of high-yielding maize hybrids for both grain and stover quality. In 2023, 12 yellow-kernel maize hybrids developed by the CIMMYT-Asia breeding program underwent evaluation in Laos. The same set of hybrids is undergoing evaluation in 2024 to identify stable and suitable germplasm. According to Siviengkhek Phommalath, director of the rice and cash crop research center at NAFRI, the 2023 evaluation provided promising results, with at least two hybrids performing better or on par with widely grown commercial ones in Laos. These hybrids exhibit high productivity, particularly in terms of grain and stover quality. However, further validation is planned for 2024, with the introduction of additional testing sites to assess performance across various environments.
Following thorough evaluations across multiple years and environments, the most suitable dual-purpose maize hybrids will be allocated to NAFRI by CIMMYT along with their parental lines, to kickstart local seed production. However, the capacity of national partners needs to be strengthened to initiate local hybrid maize seed production effectively, and this necessitates the integration and coordination of efforts among all stakeholders in the seed and feed value chains in Laos.
Capacity building across seed and feed value chains
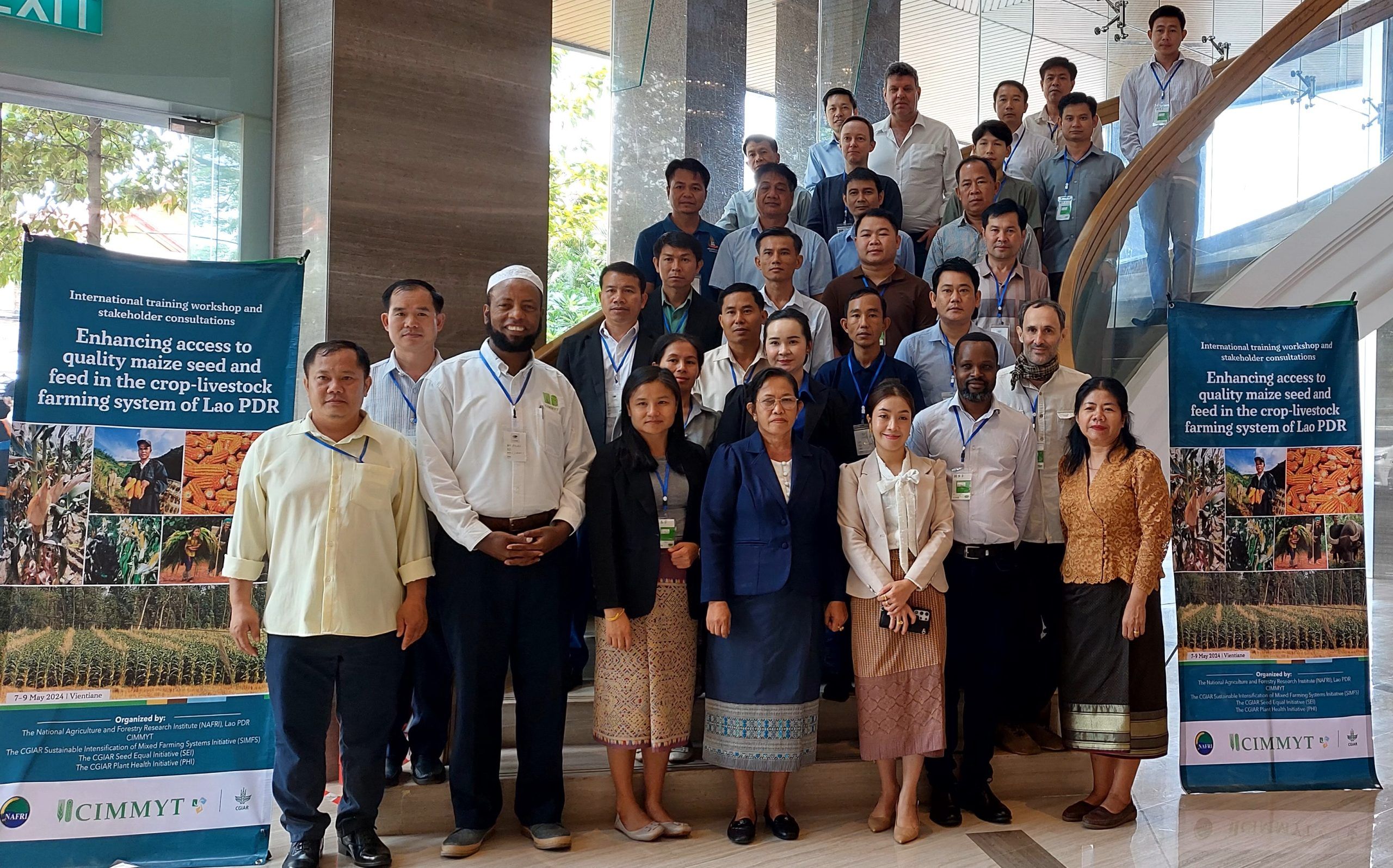
In response to the need for capacity building in local hybrid seed production and ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality seed and feed to Laotian smallholder farmers, NAFRI has collaborated with CIMMYT under the CGIAR Sustainable Intensification of Mixed Farming Systems (SIMFS), Seed Equal, and Plant Health Initiatives to organize an international training workshop on enhancing access to quality maize seed and feed in the crop-livestock farming system of Lao PDR, which took place from May 7-9, 2024.
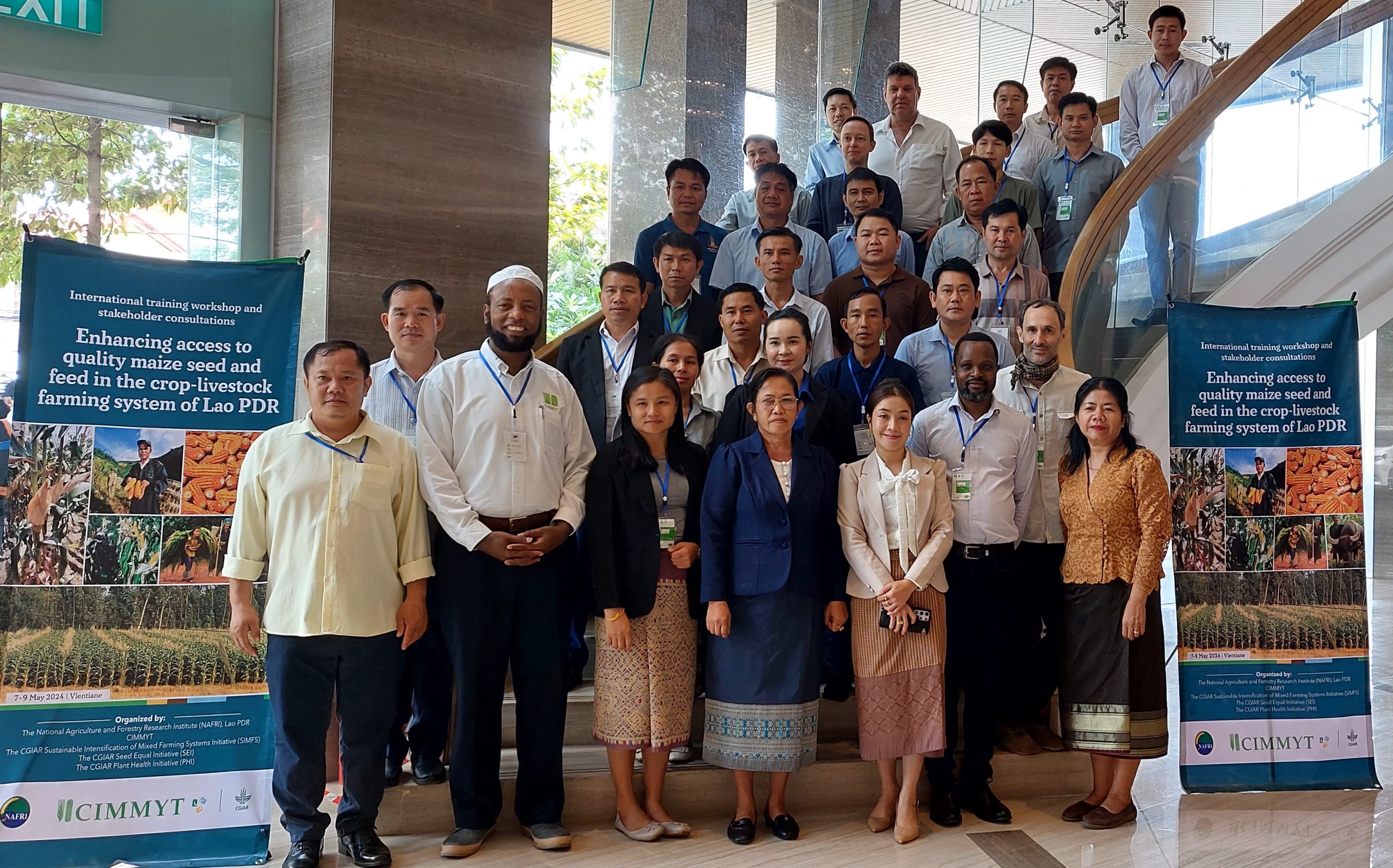

The three-day interactive workshop, held in Vientiane, brought together 28 specialists from various organizations, including NAFRI, Souphanou Vong University, the Upland Agriculture Research Center (UARC), Provincial Agriculture and Forestry Offices (PAFO), as well as maize seed importers and grain traders from different provinces within the country.
The first day was dedicated to understanding the challenges and opportunities of the maize seed value chain. Participants were divided into three groups based on their practical backgrounds and invited to discuss challenges, stakeholder roles, and develop actionable recommendations for better coordination across value chains. This multi-stakeholder platform aimed to comprehend the challenges and opportunities of the crop-livestock farming nexus and integrate them into a more sustainable and productive system. It also served as a forum to promote synergistic partnerships among value-chain actors in enhancing local access to good quality seed and feed. The following days focused on various essential components of quality hybrid seed production, including understanding product profiles and market segments, realizing the economics of hybrid maize seed production, seed quality assurance, management of maize pests and diseases, and enhancing maize stover quality.
A collaborative approach
Workshop participants highlighted the challenges they face in acquiring maize seeds from external sources, citing inconsistent delivery times and limited availability of preferred varieties as factors that posed significant operational constraints. “The development of a competitive domestic maize seed system would ensure timely seed supply for farmers and save resources for the nation,” said Maisong Yodnuanchan, an agripreneur from Xiangkhouang province. His concerns resonated with fellow agripreneurs Bounmy Si and Teuang Sophapmixay, from Oudomxay and Hua Phan provinces, respectively, who both acknowledged the challenges associated with the current reliance on imported seeds and the potential benefits of a sustainable, locally produced seed supply.

The training workshop offered valuable insights into addressing these concerns, providing a comprehensive overview of effective seed system development and the technical aspects of seed production applicable to a wide range of crops beyond maize. “This is the first ever training I received in my career and the knowledge gained will be directly applicable to my research activities at the UARC,” said researcher Malay Soukkhy. Recognizing the unique context of Laos compared to most of its neighboring countries with more established seed systems, AbduRahman Beshir, CIMMYT’s seed systems specialist for Asia and the lead trainer and facilitator for the workshop, emphasized the need for a collaborative approach to develop a custom solution for Laos. The workshop itself exemplified this collaborative spirit, incorporating a variety of engaging formats such as group discussions, lectures, assignments, and participant presentations. Subject matter specialists from CIMMYT offices in Nepal, India, and Kenya, as well as experts from Alliance Bioversity-CIAT and ILRI offices in Asia, shared valuable experiences applicable to Laos’s seed and feed systems.
Cementing partnerships
While addressing the participants, Timothy J. Krupnik, regional director for CIMMYT’s Sustainable Agrifood Systems Program in Asia, opened the workshop by acknowledging the invaluable support of NAFRI for organizing the event and collaborating under the CGIAR mixed farming initiative. He highlighted the imminent finalization of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between CIMMYT and NAFRI, which will pave the way to further cement partnerships and establish a long term CIMMYT operations in Laos.
NAFRI’s Director General, Chanthakhone Bualaphan, presided over the workshop and emphasized the importance of continued collaboration between CIMMYT and NAFRI. Bualaphan requested CIMMYT’s continued focus on capacity building in Laos, encompassing both human resource development and institutional strengthening. She further highlighted the establishment of a specific target for domestic hybrid maize seed production, aligning with the government’s self-sufficiency goals. To translate plans into action, Bualaphan emphasized the need for future training programs to be more action-oriented and practical. She concluded by reiterating NAFRI’s unwavering support for CIMMYT’s expanded activities in Laos, with the ultimate objective of significantly improving the livelihoods of Laotian farmers. The workshop culminated with the presentation of certificates to participants and the development of a collaborative follow-up plan for deploying well-tailored maize germplasm within the mixed farming system of Laos.
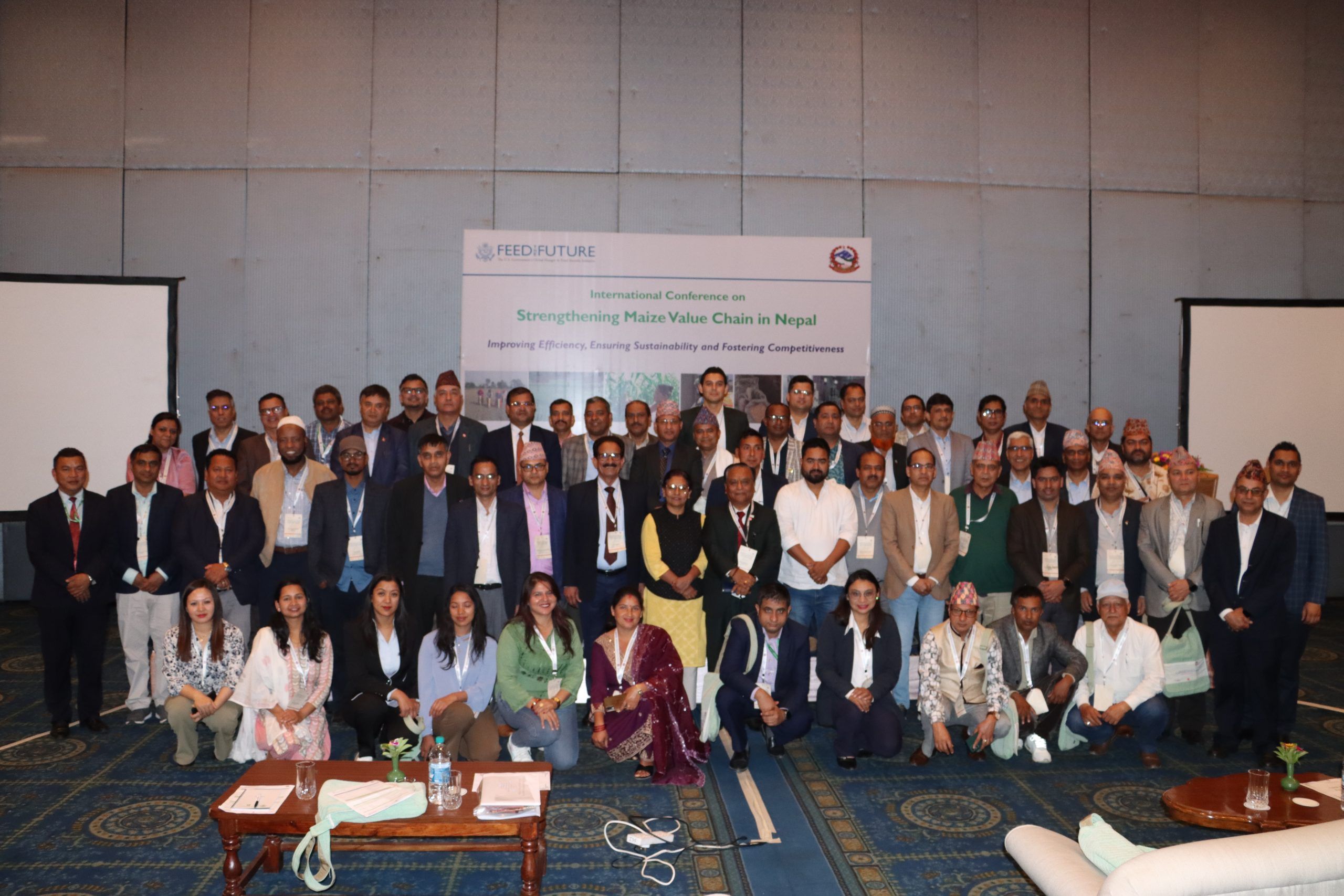
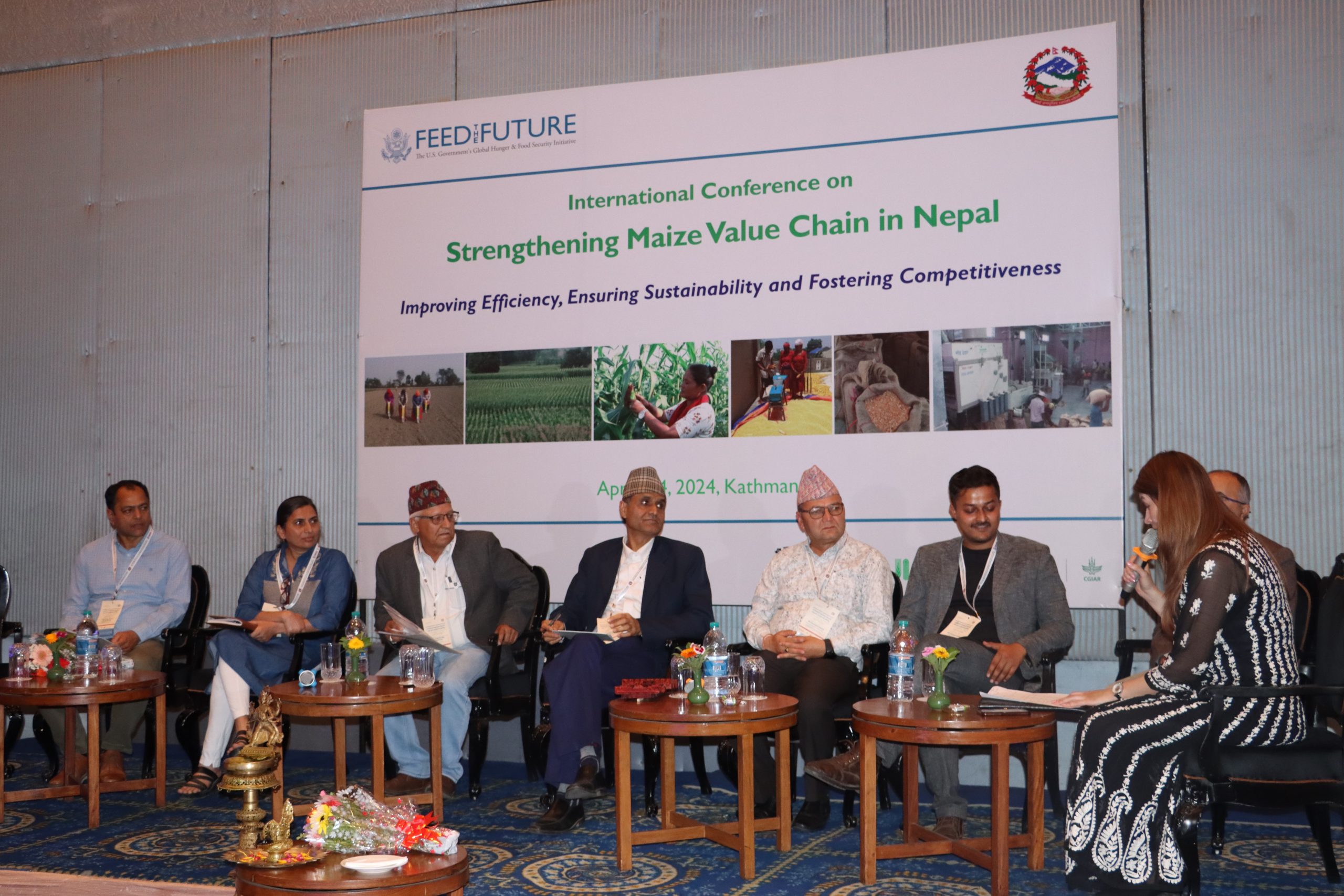





 This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that
This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that