Transformative research provides pathways for including gender and socially marginalized groups
Intention, collaboration and commitment are critical to bridging the research and practice gap. Gender development practitioners and researchers from CGIAR centers, universities, national agricultural research and extension systems (NARES), civil society, and donor representatives this week shared insights from their research and work at the gender conference in New Delhi, India.
The discussion and exchange promises to create collaborations and opportunities devoted to improving the conditions and agency of women, youth and Indigenous communities in the Global South. “Transformative research can lead to meaningful impact,” said Angela Meentzen, senior gender researcher at CIMMYT. “We have been looking forward to this conference because coming together as researchers, scientists and development practitioners, we can discuss and share insights from each other’s practices and experiences from the field.”

Leading researchers and scientists from CIMMYT Asia and Africa presented their research and enriched the gender discussions at the conference. Meentzen said that CIMMYT is proud to support gender research that contributes meaningfully to transformative change and impact.
Below are highlights of four research poster presentations by our researchers (of the six presented by CIMMYT) at the conference:
Scientist Vijayalaxmi Khed examined how women manage excess workload (working inside and outside the house), a clear trade-off between productive and leisure time without change in domestic responsibilities. Due to domestic workload, she found that women’s time away from farms does not translate into leisure. Another important finding was that women with more agency had less time for leisure, unlike for men.
In her poster presentation, she concluded that rural women’s nexus of time poverty and decision-making has “clear implications for the development and diffusion of laborsaving technologies in agriculture.”
Working on the same study with Khed, Vijesh Krishna explored the relationship between women’s involvement in agricultural activities and decision-making. His presentation, ‘Farm managers or unpaid laborers?’, from the study covering 347 wheat-farming households across two years, concludes that “despite playing a crucial role in wheat farming in central India, most women lacked the ability to influence decisions.”
Gender-intentional maize breeding for better adoption and productivity in sub-Saharan Africa
Michael Euler, agriculture and resource economist, in his poster presentation explained how an on-farm trial to improve gender-intentional breeding and varietal adoption in maize was designed by CIMMYT breeders and researchers.
The study hypothesized that gender dynamics in household labor allocation and decision-making in maize systems influence trait preferences and farmers’ adoption of varieties. So, researchers conducted on-farm trials and household surveys with individual women and men household members to capture differences in their trait preferences in maize cultivation—production systems, seed demand and seed access—with 800 smallholder farmers in Zimbabwe and Kenya.
Euler emphasized the influence of socioeconomic and agroecological factors, including biotic–abiotic stress, in the household decisions on maize varietal adoption.
He concluded that the study results will help “guide the product development of regional maize breeding programs and strengthen communities’ adaptation to the changing environmental conditions for maize cultivation.”
Adoption of a weeding technology may lead to labor displacement of marginalized women laborers
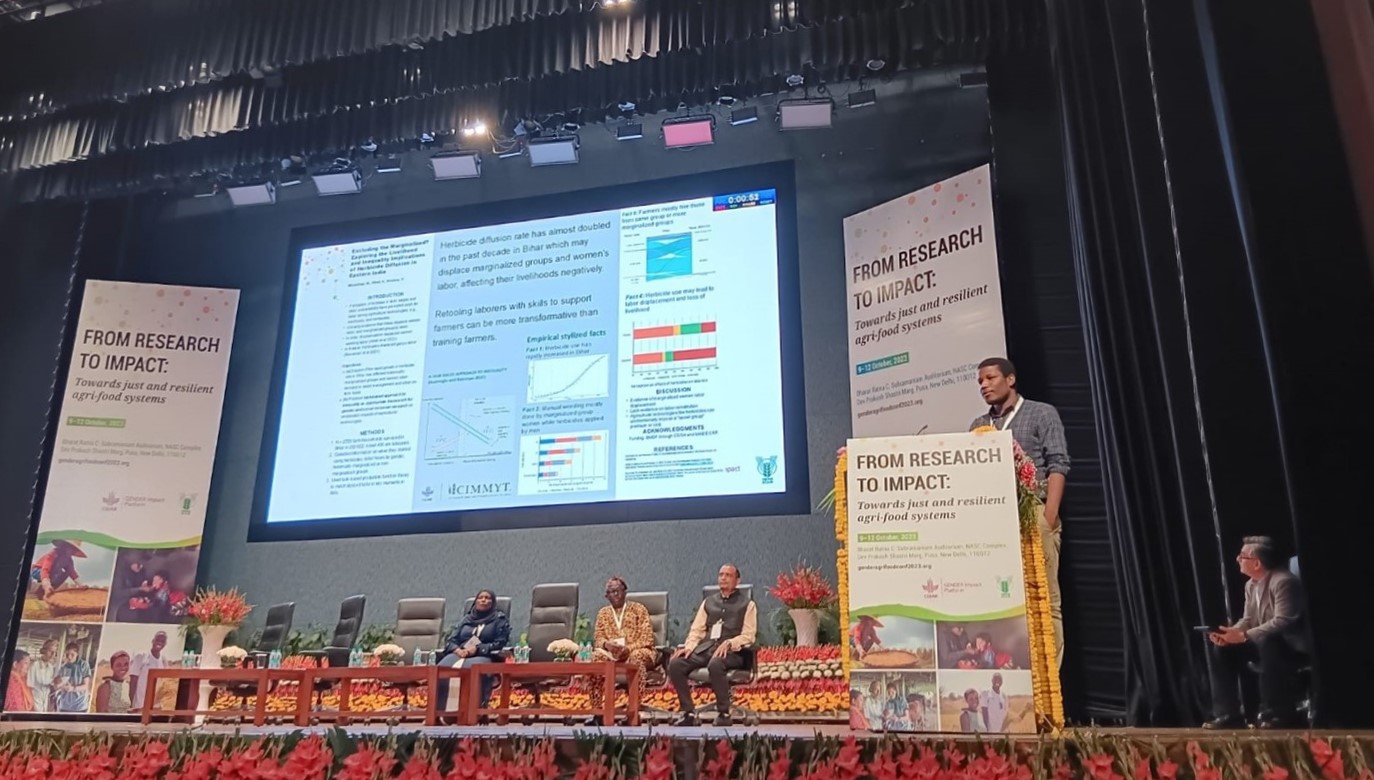
Presenting a poster for the same session as Euler, Maxwell Mkondiwa—in a study coauthored with colleagues Khed and Krishna—highlighted how rapid diffusion of a laborsaving technology like herbicides could exclude the marginalized further. The study occurred in India’s state of Bihar, looking at nonfarming rural poor, primarily women, from socially marginalized groups.
From data on chemical weeding, the study analyzed the technology’s impact on inequality— highlighting how marginalized women laborers who work on manual weeding are then replaced by men who apply herbicides.
He stressed that not enough research is devoted to understanding whether farmer adoption of laborsaving technologies worsens economic inequalities or reinstates labor into better tasks. “We hope the evidence we generated will help researchers and policymakers develop relevant actions toward more inclusive innovations, and support laborers with new skills for the transitions,” said Mkondiwa.

Women exhibit limited technical knowledge and experience social benefits differently in male-headed households of CASI technology adoption
Emma Karki, in her poster, explained that there is limited knowledge of the impact of technology adoption on women in a male-headed household in South Asia—with decision powers generally resting with male household members. The research tried to understand the gendered differences in the evaluation of technology adoption in male-headed households using conservation agriculture-based sustainable intensification (CASI) technology as a case study.
The study focused on identifying the commonalities and differences in the experiences and evaluation of CASI technology. Results indicated that “despite technology adoption, women had limited mechanistic understanding compared to men, with similar limitations on women’s time use and capacity development,” said Karki.
For future CASI promotion, Karki concluded: “Reducing information gaps and incorporating technological preferences of women needs prioritizing, including creating opportunities for them to access knowledge and engage both men and women in critical discussions surrounding gender norms.”
Similarly, Moti Jaleta’s research presentation highlighted the challenges of mechanization adoption for smallholder farmers in Ethiopia, primarily women. “Intentional research, whether in gender or social development, helps identify problems and opportunities for change,” endorsed Jaleta.
Meaningful research helps achieve gender and social inclusion goals
The ‘From Research to Impact: CGIAR GENDER Impact Platform and ICAR Conference 2023’, between October 9-12, 2023, in New Delhi, gathered researchers from 68 countries. In her inaugural address at the conference’s opening, the President of India Smt. Draupadi Murmu affirmed, “For ecologically sustainable, ethically desirable, economically affordable and socially justifiable production, we need research which can enable conditions to reach these goals.”
At the end of the four-day conference—with 60 research presentations and six plenary sessions—the organizers and participants reflected on their resolve ‘From Research To Impact,’ and the promise to recognize and collectively address the gender and social inequities in agrifood systems development.