Young CIMMYT scientist receives 2022 Japan Award for global research to combat wheat aphids

International science to save wheat — a crucial food grain for 2.5 billion of the world’s poor — from a rising tide of insect pests known as aphids was lauded on November 22 with the 2022 Japan International Award for Young Agricultural Researchers (the Japan Award).
The 2022 Japan Award recognized novel breeding approaches to identify and select for genetic resistance in wheat to two species of aphids that cause wheat grain losses reaching 20% and whose rapid spread is propelled by rising temperatures.
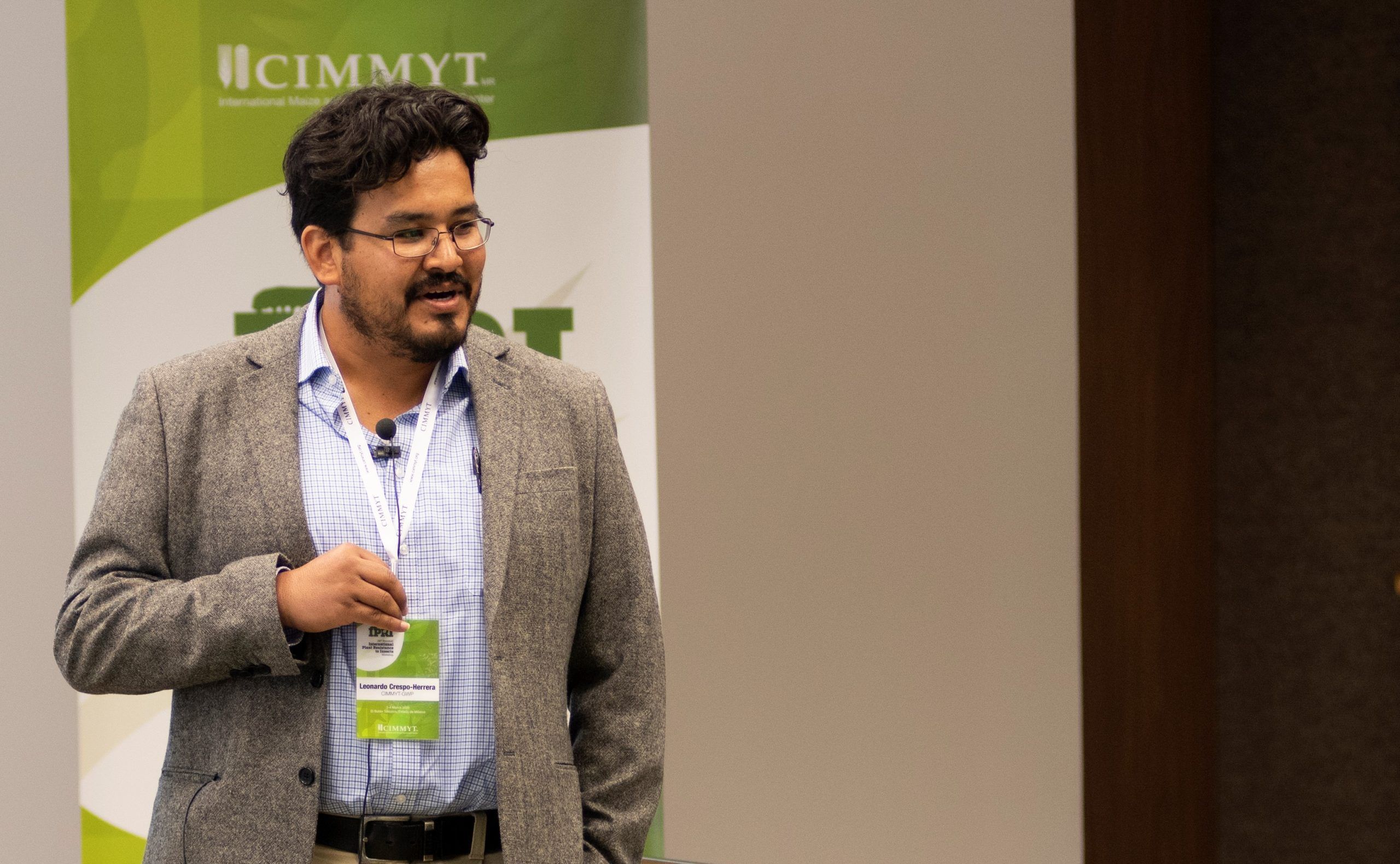
Aphid resistant wheat can contribute to more sustainable food production, protecting farmers’ harvests and profits, while reducing the need to use costly and harmful insecticides, said Leonardo Crespo-Herrera, bread wheat improvement specialist for the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and one of the three 2022 Japan Award recipients.
“In addition to genetic yield potential, CIMMYT wheat breeding focuses on yield stability, disease resistance, and nutritional and end-use quality,” Crespo-Herrera explained. “Adding another target trait — aphid resistance — makes wheat breeding much more challenging.”
Efficient and effective field testing to confirm the genetics
Crespo-Herrera and his CIMMYT colleagues managed to identify and characterize genome segments responsible for aphid resistance in wheat and its near relatives, as well as running innovative field tests for a set of elite wheat breeding lines that were predicted to carry that resistance.
“With the aphid species called the greenbug, its feeding causes yellowing and necrotic spots on wheat, so we could actually measure and score wheat plants in plots that we deliberately infested with the aphids, keeping the resistant lines and throwing out the susceptible ones,” said Crespo-Herrera.
For the other species, the bird cherry-oat aphid, the only visible feeding damage is when the plants become stunted and die, so Crespo-Herrera and colleagues instead measured biomass loss and reduced growth in 1,000 artificially infested wheat lines, identifying a number of lines that had low scores for those measurements. Given that the lines tested came from a set that had already shown resistance to the greenbug, some of the successful lines feature resistance to both aphid species.
For the bird cherry-oat aphid, in two years of additional field tests, Crespo-Herrera and his team found that aphid populations were lower in plots sown with resistant wheat lines. “The experiments included remote sensing measurements that identified certain spectral signatures correlated with aphid populations; this may help us to assess resistance in future field trials.”
The researchers also found that a cutting-edge approach known as “genomic prediction” provided good estimations regarding promising, aphid-resistant wheat breeding lines.
Motivating young researchers in research and development
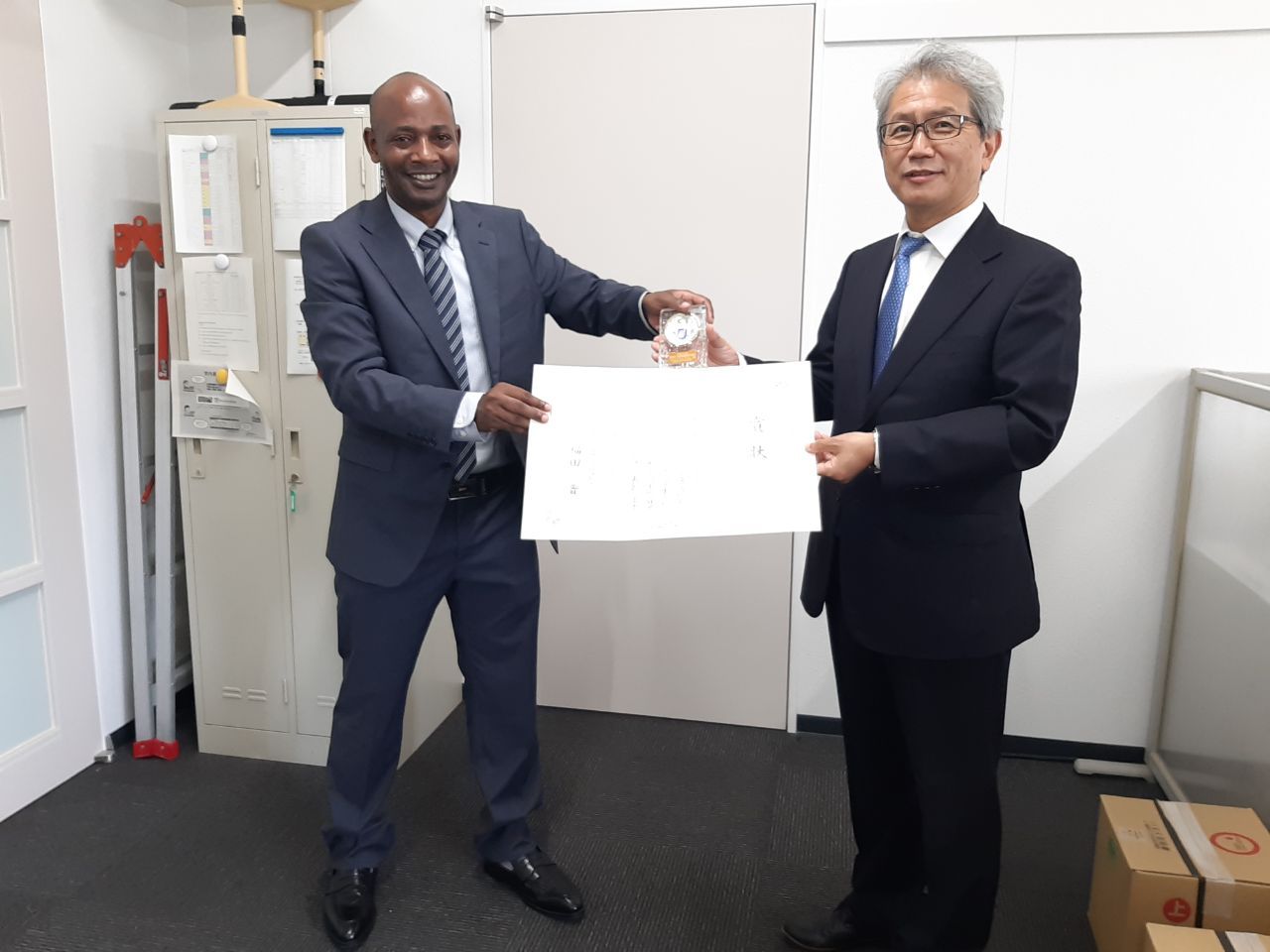
Established in 2007, the Japan Award is an annual prize organized by the Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Research Council (AFFRC) of Japan’s Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) and supported by the Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences (JIRCAS). Awardees receive a $5,000 cash prize.
In an excerpt of an official note regarding Crespo-Herrera’s research, those agencies said “…This study has been highly evaluated for developing (wheat) lines that have been distributed worldwide for use in wheat breeding, and the methods of this study have been applied to develop varieties with resistance mechanisms against various kinds of insects, not only aphids.”
Crespo-Herrera thanked JIRCAS and MAFF for the award. “I feel honored to have been selected.”