Ricardo Curiel
Responsible for assisting the Director General with internal and external communications about CIMMYT’s impact, main accomplishments and news relevant to stakeholders.
CIMMYT has several offices in the Americas, including global headquarters in Mexico and a regional office in Colombia. Activities are supported by an additional 140 hectares of stations in diverse agro-ecological zones of Mexico. CIMMYT’s genebank in Mexico stores 27,000 maize and 170,000 wheat seed collections – key to preserving the crop genetic diversity of the region. CIMMYT projects range from developing nutritionally enhanced maize to mapping regional climate change hot spots in Central America. The comprehensive MasAgro project aims to increase wheat production in Mexico by 9 million tons and maize production by 350,000 tons by 2030. CIMMYT promotes regional collaboration and facilitates capacity building for scientists, researchers and technicians.
Responsible for assisting the Director General with internal and external communications about CIMMYT’s impact, main accomplishments and news relevant to stakeholders.
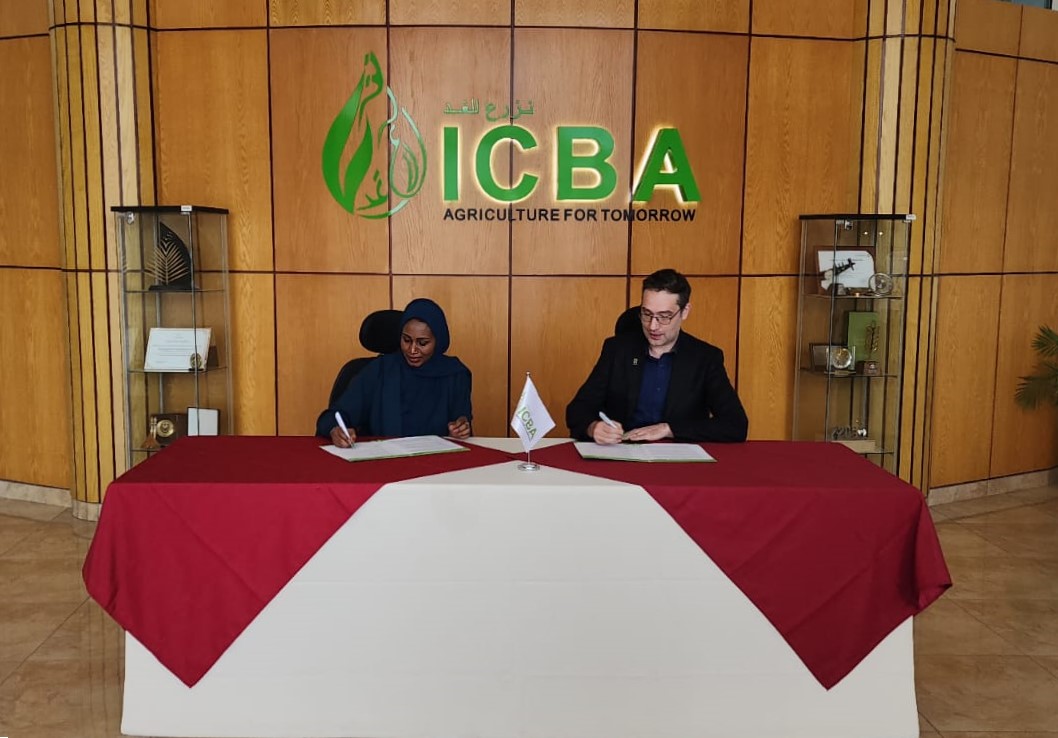

Dubai/Mexico City, 10 January 2024 – An award-winning not-for-profit agricultural research center recognized for its work on sustainable agriculture in the Middle East and North Africa is joining forces with the global organization whose breeding research has contributed to half the maize and wheat varieties grown in low- and middle-income countries.
The International Center for Biosaline Agriculture (ICBA) and CIMMYT have signed an agreement to jointly advance the ecological and sustainable intensification of cereal and legume cropping systems in semi-arid and dryland areas.
“Farmers in such settings confront enormous risks and variable conditions and often struggle to eke out a livelihood, but they still comprise a critical part of the global food system and their importance and challenges are mounting under climate change,” said Bram Govaerts, director general of CIMMYT. “ICBA brings enormously valuable expertise and partnerships to efforts that will help them.”
The specifics of the two centers’ joint work are yet to be defined but will cover soil health, salinity management approaches, crop productivity and breeding, gender-transformative capacity development, and finding markets for underutilized crops, among other vital topics.
Established in 1999 and headquartered in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), ICBA conducts research and development to increase agricultural productivity, improve food security and nutrition, and enhance the livelihoods of rural farming communities in marginal areas. The center has extensive experience in developing solutions to the problems of salinity, water scarcity and drought, and maintains one of the world’s largest collections of germplasm of drought-, heat- and salt-tolerant plant species.
“We are excited about the synergies our partnership with CIMMYT will create. It will focus on a range of areas, but the priority will be given to developing breeding and cropping system innovations to improve farmers’ food security and nutrition, while enhancing water security and environmental sustainability, and creating jobs and livelihoods in different parts of the world,” said Tarifa Alzaabi, director general of ICBA.
Based in Mexico but with projects in over 80 countries and offices throughout Africa, Asia and Latin America, CIMMYT operates a global seed distribution network that provides 80% of the world’s breeding lines for maize and wheat, including many that offer superior yields and resilience in dry conditions and in the presence of crop diseases and pests.
The center is also conducting breeding and seed system development for dryland crops such as sorghum, millet, groundnut, cowpea, and beans, known for their climate resilience and importance as foods and sources of income for smallholder farm households and their communities.
With global and local partners, CIMMYT is also refining and spreading a suite of resource-conserving, climate-smart innovations for highly diverse maize- and wheat-based cropping systems, including more precise and efficient use of water and fertilizer, as well as conservation agriculture, which blends reduced or zero-tillage, use of crop residues or mulches as soil covers, and more diverse intercrops and rotations.
As part of the new agreement, the centers will also explore research collaborations with universities and research institutions in the UAE to develop and test maize varieties that are suitable for the UAE’s climate and soil conditions, as well as organizing training programs and workshops for farmers, extension workers, and other stakeholders in the UAE to build their capacity in maize production and management.
About ICBA
The International Center for Biosaline Agriculture (ICBA) is a unique applied agricultural research center in the world with a focus on marginal areas where an estimated 1.7 billion people live. It identifies, tests, and introduces resource-efficient, climate-smart crops and technologies that are best suited to different regions affected by salinity, water scarcity, and drought. Through its work, ICBA helps to improve food security and livelihoods for some of the poorest rural communities around the world.
About CIMMYT
CIMMYT is a cutting edge, non-profit, international organization dedicated to solving tomorrow’s problems today. It is entrusted with fostering improved quantity, quality, and dependability of production systems and basic cereals such as maize, wheat, triticale, sorghum, millets, and associated crops through applied agricultural science, particularly in the Global South, through building strong partnerships. This combination enhances the livelihood trajectories and resilience of millions of resource-poor farmers, while working towards a more productive, inclusive, and resilient agrifood system within planetary boundaries. CIMMYT is a core CGIAR Research Center, a global research partnership for a food-secure future, dedicated to reducing poverty, enhancing food and nutrition security and improving natural resources.
For more information or interviews:
CIMMYT
Sarah Fernandes
Head of Communications
s.fernandes@cgiar.org
ICBA
Abdumutalib Begmuratov
Head of Knowledge Management and Communications
a.begmuratov@biosaline.org.ae
As part of her fact-finding mission across CGIAR Research Centers, Ismahane Elouafi, CGIAR’s executive managing director, returned to CIMMYT headquarters in Texcoco, Mexico, where she studied as a Ph.D. student twenty years ago. Through meetings with CIMMYT staff from 21-24 December 2023, Elouafi learned how CIMMYT’s 2030 Strategy of more investment in developing food systems and climate-smart agriculture will contribute to CGIAR’s 2030 vision of a food and nutrition secure future.
“CIMMYT was pleased to host Ismahane,” said Bram Govaerts, CIMMYT director general. “Our ultimate mission is to transform agrifood systems. The only way we will reach our goal of food and nutrition security is by working globally and collaboratively across the value chain.”
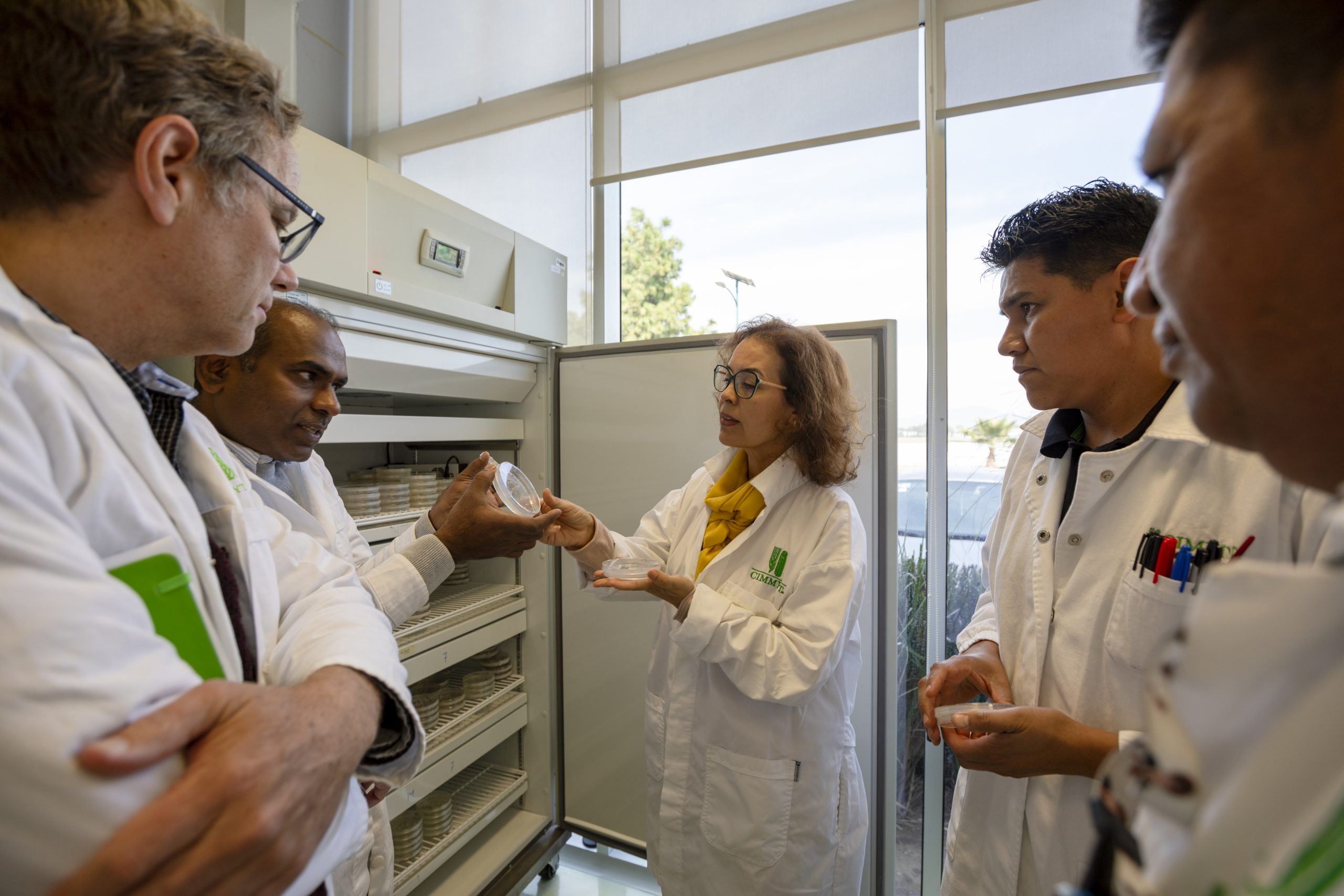

At CIMMYT’s museum and gene bank, Elouafi met with researchers to discuss the latest discoveries in genetic innovation, biodiversity conservation, and crop breeding. Elouafi and Kevin Pixley, director of the Dryland Crops program, visited the biosafety laboratory and glasshouses where gene editing on pearl millet and ground nut represent cutting-edge work with dryland crops. Elouafi also saw gene editing for resistance to maize lethal necrosis, which is already in field validation with Kenyan partners from the Kenya Agricultural & Livestock Research Organization (KALRO).
Global Wheat and Dryland Crops presented CIMMYT’s 2050 vision for wheat in Africa and near-term goals of advancing partnerships from phenotyping platforms to the International Wheat Improvement Network (IWIN). Seed experts from the Seed Health Unit shared progress on the productivity and nutrition findings of key cereals for healthy and balanced diets.
Elouafi also visited conservation trial plots with Jelle Van Loon, associate director of the Sustainable Agrifood Systems (SAS) program, who briefed Elouafi on cropping systems diversity related to maize, wheat, and beans, and showcased a variety of innovative farming technologies. At the trial plots, Elouafi met with Guillermo Bretón, a farmer, to talk about CIMMYT’s efforts to expand the MasAgro program into Central America aiming to address the region’s growing food insecurity contributing to migration.
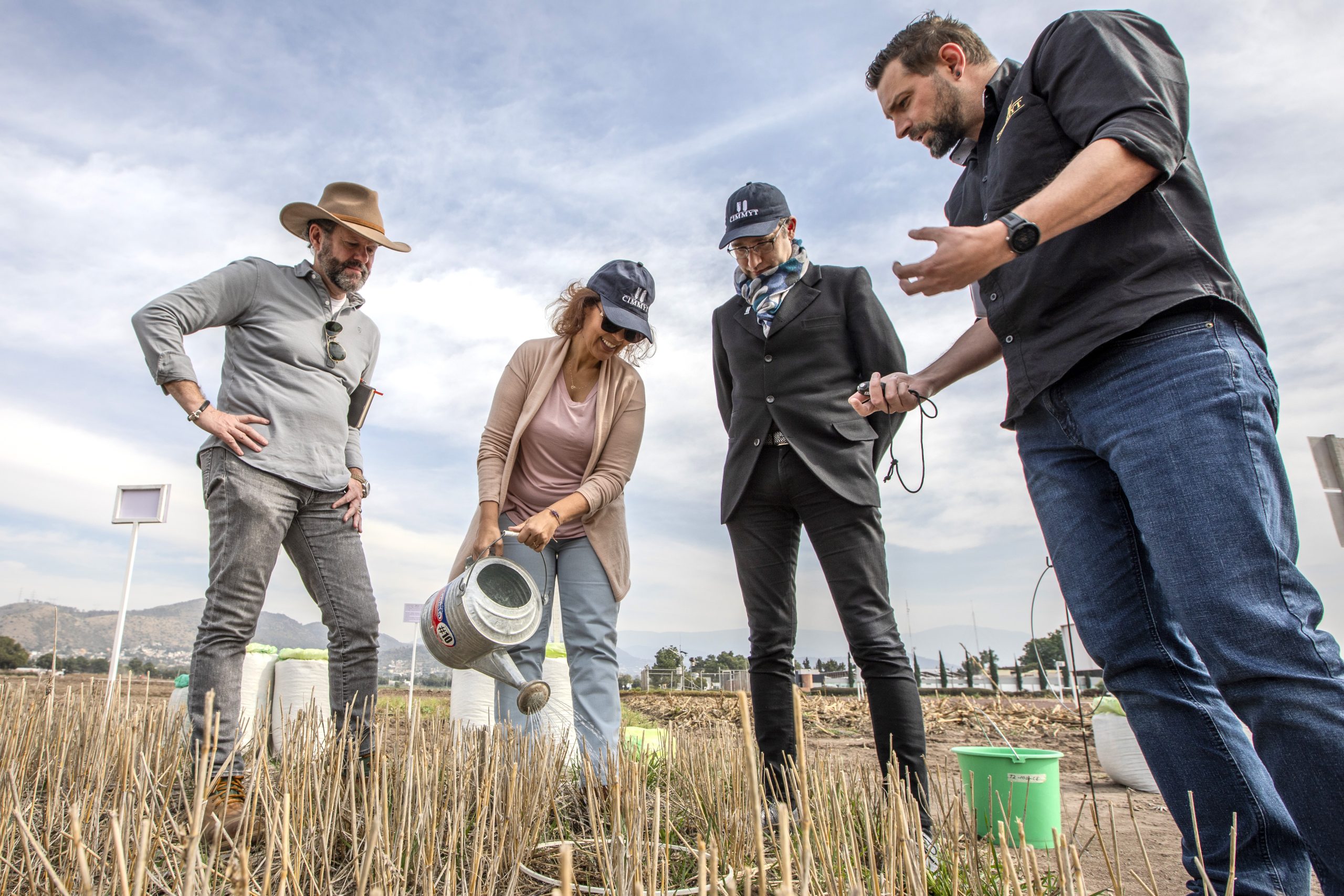

The value of genetic resources as sources of novel diversity was discussed with Elouafi during a visit to field screenhouses, where she saw wide crosses work for biological nitrification inhibition (BNI) in wheat, gene bank accessions of triticale—a cross between wheat and rye—for use in searching for new sources of resistance to wheat blast, and the ex-situ clonal collection of tripsacum, a wild relative of maize.
“CIMMYT’s 2030 Strategy adopts a systems approach to food science, which I strongly support. Through the development of mechanization and post-harvest management, increased focus on seed systems and health, and most importantly, cooperation with partners to ensure that improved crop varieties are adopted by smallholders, I am confident that this approach will only strengthen CIMMYT’s historical strength of research and innovation for food and nutrition security and contribute to achieving CGIAR’s 2030 mission,” said Elouafi.
Kevin Kabunda, chief of party for the Southern Africa Accelerated Innovation Delivery Initiative (AID-I) MasAgro Africa Rapid Delivery Hub (AID-I) and Sieglinde Snapp, director of the SAS program, presented key milestones achieved in southern and eastern Africa on expanded seed systems, market access, and mechanization technologies. Snapp also highlighted important CIMMYT-led initiatives like the CGIAR Plant Health Initiative and the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA) which have had a positive impact on smallholders in part because of partnerships with government agencies and other CGIAR Research Centers.
Elouafi and Govaerts visited the ancient city of Teotihuacán to learn about the cultural significance of maize to the history and agricultural practices of the Americas. She received a guided tour by chef Carlos Cedillo, operational director of La Gruta, a local restaurant dedicated to understanding and promoting the production and consumption of native maize varieties in the Valley of Mexico. CIMMYT has collaborated with La Gruta through capacity building initiatives by CIMMYT specialists for technicians and farmers.
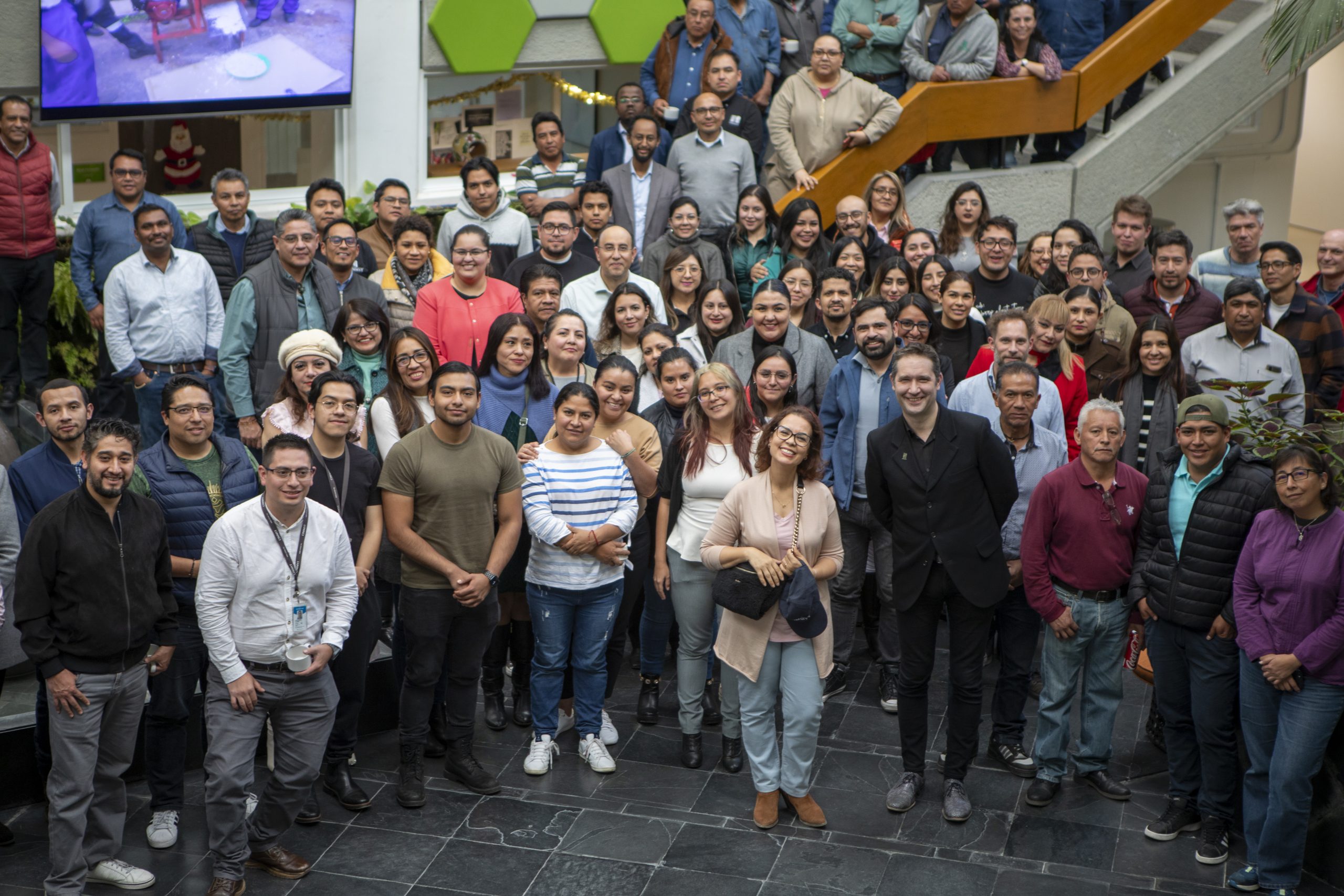

Elouafi joined CIMMYT staff in a meet and greet session on 21 December, where staff expressed the strides being made by CIMMYT’s leadership team to foster a more inclusive workplace. “This moment of coming together with the staff that make CIMMYT a great place to work and who position the Center as a significant actor in agricultural development will be a highlight of my visit,” said Elouafi.
CIMMYT stands out for its role in agricultural innovation, demonstrated through the dedicated research of visiting Chinese scholar Wang Hui. Her tenure at CIMMYT underscores the center’s pivotal role in driving agricultural advancements through international partnerships, significantly contributing to global food security and scientific development.
Read the full story.
Harnessing Change was the theme of the 2023 Borlaug Dialogue, an annual summit of international thought leaders, development specialists, researchers, farmers, and practitioners, designed to promote global food systems transformation and food security, and is organized by the World Food Prize Foundation.
This iteration of the Borlaug Dialogue, held in Des Moines, Iowa, October 24-26, 2023, was the site of the inauguration of a collaboration between CIMMYT and the Gorongosa Restoration Project to improve climate resilience, food security and nutrition in Mozambique’s Gorongosa National Park.
“These kinds of collaborations exemplify what the Borlaug Dialogue is all about,” said CIMMYT Director General Bram Govaerts. “The annual event and the work of the World Food Prize Foundation year-round is dedicated to bringing people and organizations together to work better and smarter. CIMMYT is proud to be a part of it.”
CGIAR Centers based in the Americas host discussion on Latin America’s food security challenges and opportunities
CIMMYT, the International Potato Center (CIP), the Alliance of Bioversity International and the International Center for Tropical Agriculture, and International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) co-organized the side event Maximizing Latin America and the Caribbean’s Contributions to Global Agriculture and Biodiversity Solutions at Dialogue.
Govaerts moderated the panel discussion and the Q&A session that followed with members of the audience.
Panelists, including Elsa Murano, director of the Norman E. Borlaug Institute for International Agriculture & Development, Rob Bertram, chief scientist for the Bureau for Resilience and Food Security at the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), and María (pilu) Giraudo, honorary president of Argentina’s No Till Farmers Association, shared views on Latin America’s role in global agriculture from academic, development and farming offer academic insights, international cooperation recommendations and farmer perspectives.
CIMMYT and USAID co-host panel focused on AID-I’s impact at the Borlaug Dialogue
CIMMYT and USAID hosted an event at the Dialogue organized by the World Food Prize Foundation on October 25 focused on the Southern Africa Accelerated Innovation Delivery Initiative (AID-I).
The discussion labelled, Harnessing Innovation to Rapidly Respond to Crises, aimed to present AID-I’s innovative approach to addressing systemic weaknesses in agriculture by accelerating the market-based delivery of improved seeds, fertilizers, and critical information to farmers.

Dina Esposito, USAID’s Global Food Crisis coordinator and assistant to the Administrator for the Bureau for Resilience, Environment and Food Security, described how AID-I is “turning crisis into opportunity” by improving farmers’ resilience and profitability.
“We joined CIMMYT and went to Zambia, and the partnership was a glimmer in our eyes,” said Esposito, referring to a recent visit to a model farm with AID-I partners.
Reporting progress in Zambia, Malawi and Tanzania, Kevin Kabunda, CIMMYT’S AID-I chief of party in southern Africa, noted that the private sector had produced 13,000 tons of maize in the first year.
“The extended or increased potential for every farmer who uses fall armyworm-tolerant varieties translates to US$100 dollars,” said Kabunda who estimated AID-I reached 1.3 million farmers in its first year generating an aggregated value of at least US$65 million dollars.
In addition, Mtieyedou (Abdou) Konlambigue, AID-I chief of party in the Great Lakes Region, pointed out that the project has given access to new bean varieties and fertilizer recommendations to over 500,000 farmers in Rwanda, Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Farmers take the stage
Two champion farmers, María (pilu) Giraudo and Guillermo Bretón joined CIMMYT’s Director General, Bram Govaerts, and CGIAR Board Chair, Lindiwe Majele Sibanda, during a main stage session of the Borlaug Dialogue organized by the World Food Prize Foundation on Tuesday, October 24.
The event, MasAgro Taking it to the Farmer, reported on progress achieved and milestones reached by one of CIMMYT’s flagship projects, Crops for Mexico (MasAgro), which began 14 years ago and earned Govaerts the 2014 Norman E. Borlaug Award for Field Research and Application endowed by The Rockefeller Foundation.
Giraudo, an Argentinian farmer who co-founded the Rural Women Network and serves as honorary president of Argentina’s no till farmer association Aapersid, said that the best way to acknowledge MasAgro’s work is to seize the opportunity to offer women farmers the possibility of having full access to science and technology.
Bretón, a farmer from Mexico’s state of Tlaxcala, described MasAgro as a disruptive way of understanding agriculture. “Investing in our soils is better than investing in a one-cycle crop,” he said.
CGIAR Board Chair Lindiwe Majele Sibanda was enthusiastic about the project’s trajectory and proud of its evolution into CIMMYT’s ongoing efforts, including adapting MasAgro to southern Africa.
Sibanda expressed her excitement about MasAgro-inspired activities in Africa and praised the diversified seed systems that today include dryland crops sold in smaller seed bags by young entrepreneurs who are taking up businesses in villages without having to go to urban centers.
Govaerts moderated the event and thanked Dina Esposito, and U.S. Special Envoy for Global Food Security, Cary Fowler, for facilitating the establishment of MasAgro programs in southern Africa.
On October 4, 2023, CIMMYT continued its online seminar series — Catalysts of Change: Women Leaders in Science. The event featured a talk by Esther Ngumbi, an entomologist and academic at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
A riverside farm
Born into a small, rural community on the Kenyan coast, Esther Ngumbi grew up farming alongside her family. “I enjoyed the process of growing crops because I knew at the end of the season, we would have extra food for ourselves,” she explained. By the age of seven she decided she wanted to go it alone, and her father provided a small strip of land by the river, where she took to growing vegetables.
“Every morning I would sit there and just enjoy looking at this thriving cabbage patch I had,” she says. “And then one day the rains came. It rained for three days, the field flooded, and by the time the water receded I had lost my cabbages. The joy that had built was gone.”
“But this heartbreak continued,” she added. “Halfway through the season I would watch all our hard work go to waste.” Along came insects, drought, or flooding—all the stresses associated with climate change—and for her family it would mean no food. Ngumbi soon realized that this was not limited to her family’s farm: her neighbors, community, county, and country were all impacted by these challenges, leading to widespread food insecurity.
Feeding curiosity
“As a girl I was very curious,” said Ngumbi. “How do these insect pests find our crops? And when they find them, why aren’t our crops resilient enough to overcome these stresses? Little did I know that this curiosity would lead me into what my career is today: an entomologist.”
“But growing up in a rural village there were no role models; there were no scientists. There were no people I could look up to and be inspired to know that you could make a career out of entomology or that you could be a woman in science.”
Despite initially considering a career in accountancy, Ngumbi ended up studying for a BSc in biochemistry and zoology at Kenyatta University, where she immediately fell in love with practical research. “Stepping into the lab was such an exciting day for me,” she recalled. “I had so many questions, and I remember not wanting to leave because I wanted to answer all the questions I had grown up with.”
Later, extra-curricular experience at a local research center would feed her interest in entomology. The scientists she ended up working with ran a biological control program to assess how maize is impacted by lepidoptera pests, and the natural biological control agents that could be used to combat these. “How do plants communicate and call for help? Through releasing a chemical. I discovered that there is a wave of communication happening between our food crops and the community of organisms that associate with plants.”
Eager to learn more, Ngumbi went on to pursue an MSc before joining a Ph.D. program at Auburn University in Alabama, USA. “My parents had always told me that education is the gateway out of poverty, and they consistently encouraged me to go to the highest level. I knew I had to go to the top.”
At Auburn she had the opportunity to delve deeper into how plants defend themselves, and her successful research into beneficial soil microbes led to at least three U.S. patents. Following a few post-doctoral positions, she landed a role at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, where she currently works as an assistant professor in the Departments of Entomology and African American Studies.
Bringing others along
Ngumbi credits mentorship with getting her to where she is today. “At Kenyatta University my teachers saw a spark in me; I was curious and wanted to find answers. Mentors introduced me to scientists the International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology (ICIPE), so I could carry out experiments beyond what we were doing as part of my course.”
She recalled walking across the stage during her Ph.D. graduation ceremony, a key moment of reflection. “It was real that there were very few women like me in science. That I was only one of the many women I had grown up with that was privileged to have a PhD. And I wanted not to be the only person,” she said. “I wanted to make sure that I would leave open the same door I had walked through. That I would do my best to bring other women along.”
“I would step up to be a mentor. Step up to encourage other women. Step up to encourage other children from rural communities to say: you can do it, you can dream, you can follow your passions, you can be a scientist.”
With this in mind, Ngumbi ensures she collaborates with others in all areas of her research, incorporating young researchers into her labs and working directly with farmers. “I’m committed to ensuring that farmers who work so hard — especially smallholders — can grow crops and see all their hard work pay off.”
“I will continue to follow this journey of finding solutions to feed our growing planet, but I know that I cannot do it alone. We need all of us,” she added. “We still have very few women scientists — UNESCO estimates around 30% — and I hope that by the time I’m done with my career that number changes. But it’s going to depend on all of us.”
Ngumbi’s talk was followed by a Question and Answer led by Olivia Odiyo, a CIMMYT research associate based in Nairobi. The full discussion can be viewed online here. Spanish and French-language audio is also available.
Jared Crain, a research assistant professor of plant pathology, collaborates with CIMMYT on wheat genomics. Leading the Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Applied Wheat Genomics at K-State, Crain and his team annually analyze DNA from 19,000 plants.
Read the full story.
During his visit to the CIMMYT, Governor Little initiated conversations between the center, the University of Idaho College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and various Idaho commodity groups. These discussions aim to explore potential collaborations in wheat breeding, sustainability initiatives, and the advancement of bean seed development.
Read the full story.
In a collaborative effort to tackle global food challenges, Melinda Yerka, an associate professor in the Department of Agriculture, Veterinary & Rangeland Sciences and her team are partnering with sorghum breeders at the CIMMYT. Together, they’re extending the reach of sorghum varieties to developing nations.
Read the full story.
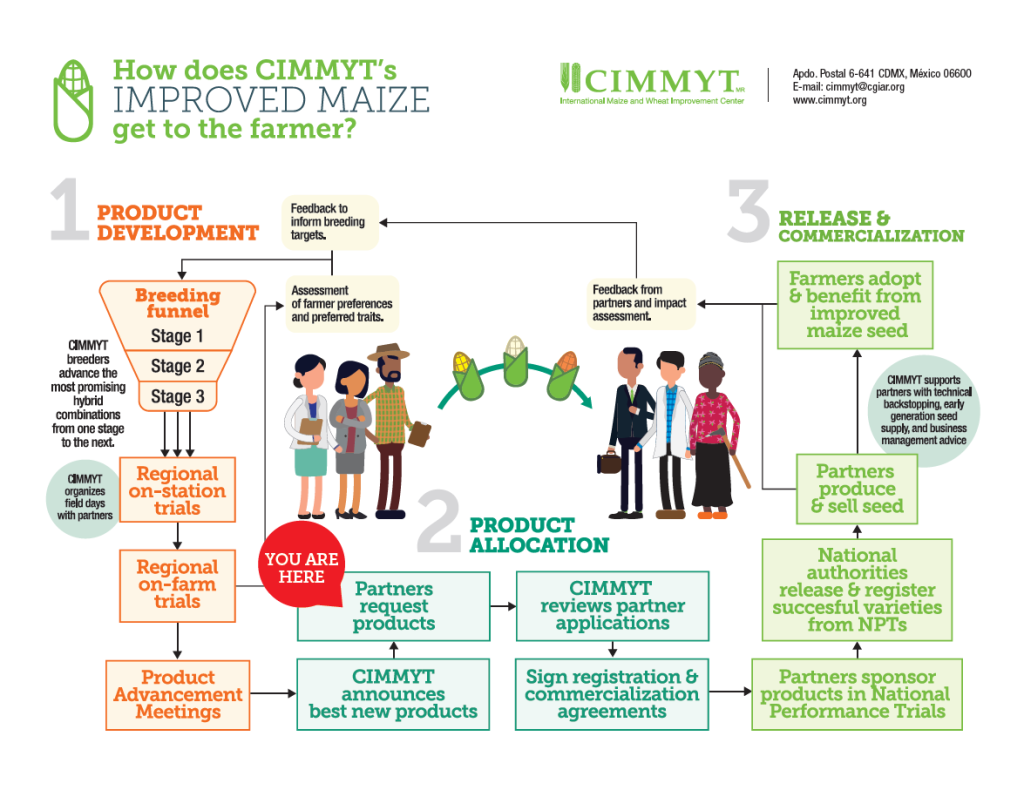
CIMMYT is happy to announce five new, improved tropical and subtropical maize hybrids that are now available for uptake by public and private sector partners, especially those interested in marketing or disseminating hybrid maize seed across Latin America and similar agro-ecologies in other regions. NARES and seed companies are hereby invited to apply for licenses to pursue national release, scale-up seed production, and deliver these maize hybrids to farming communities.
| Newly available CIMMYT hybrids | Key traits | Target Agro-ecology |
| CIM21LAPP1A-12 | Intermediate maturing, white, high yielding, and resistant to TSC, MLB, and Ear rots | Lowland tropics |
| CIM21LAPP1C-10 | Intermediate maturing, yellow, high yielding, and resistant to TSC, MLB and Ear rots | |
| CIM21LAPP2A-4 | Intermediate-maturing, white, high-yielding, FSR, GLS, and Ear rots. | Mid-altitudes/
Spring-Summer season |
| CIM21LAPP2A-8 | ||
| CIM20LAPP2B-12 | Intermediate-maturing, yellow, high-yielding, resistant to GLS, and Ear rots. |
The newly available CIMMYT maize hybrids were identified through rigorous, years-long trialing and a stage-gate advancement process which culminated in the 03-22LTHTWM4M, 04-22LTHTYM4M, 01-22MASTCHSTW and 02-22MASTCHSTY Stage 5 Trials. The products were found to meet the stringent performance and farmer acceptance criteria for CIMMYT’s breeding pipelines that are designed to generate products tailored in particular for smallholder farmers in stress-prone agroecologies of Latin America.
| Performance data | Download the CIMMYT LATAM Maize Regional (Stage 4) and On-Farm (Stage 5) Trials: Results of the 2020 -2021 and 2022 Seasons and Product Announcement from Dataverse. |
| How to apply | Visit CIMMYT’s maize product allocation page for details |
| Application deadline | The deadline to submit applications to be considered during the first round of allocations is December 1st, 2023. Applications received after that deadline will be considered during subsequent rounds of product allocations. |
Applications must be accompanied by a proposed commercialization plan for each product being requested. Applications may be submitted online via the CIMMYT Maize Licensing Portal and will be reviewed in accordance with CIMMYT’s Principles and Procedures for Acquisition and use of CIMMYT maize hybrids and OPVs for commercialization. Specific questions or issues faced with regard to the application process may be addressed to GMP-CIMMYT@cgiar.org with attention to Debora Escandón, Project Administrator, Global Maize Program, CIMMYT.
Seed the World Group hosted a webinar to find a common ground between public and private breeding programs in North America and some possible paths forward. Fernando Gonzalez, a retired plant breeder from CIMMYT mentioned a noticeable uptick in the involvement of the private sector in breeding programs in Mexico.
Learn more about the primary goals underlying public and private breeding efforts.
Erratic climate patterns, global and regional conflicts, biodiversity degradation, and insufficient funding for agricultural research pose a serious risk to meeting global food production goals by mid-century, according to Cary Fowler, the U.S. special envoy for food security.
The world must produce 50-60% more food by 2050 to nourish a growing population. Yet global crop yields are projected to drop between 3-12% over the same period. Wheat yields in Africa and South Asia, two regions with the fastest growing and youngest populations, are expected to decline by 15% due to global warming. Food systems have also been disrupted by the Russia-Ukraine conflict and the COVID-19 pandemic, raising food and fertilizer prices, and exacerbating regional instability.

Fowler cites inadequate government funding for plant breeding programs as a contributor to an ineffective response to introducing improved climate-adaptable staple crops. “With the state of current affairs, we are on our way to failing to feed the world by century’s end,” said Fowler.
Science and Innovation for a Food and Nutrition Secure World: CIMMYT’s 2030 Strategy
Global peace and development efforts will demand a cross-sector and coordinated response. Through its 2030 Strategy, CIMMYT has laid out a robust series of investments in crop systems innovation, partnership, and sustainable development, to advance more resilient food systems. The 2030 Strategy consolidates CIMMYT’s target areas through three pillars: Discovery, SystemDev, and Inc. These pillars focus on research and innovation, systems approach, and strong partnerships and advocacy efforts with the private and government sectors to address an emerging food crisis.
“Our 2030 Strategy places research, innovation and partnership at the center of facing the challenges of the 21st century to solve tomorrow’s problems today—for greater food security and the prosperity of smallholder farmers. As we implement work plans, CIMMYT is proud of the achievements it has seen through projects in sub-Saharan Africa, our contribution to influential policy reports, and continued praise for our agri-development initiatives in Latin America. All these feats will help us deliver on and expand our efforts to reach our 2030 vision,” said Bram Govaerts, CIMMYT director general.
CIMMYT remains prominent in developing sustainable solutions for farmers and policy actors
CIMMYT has achieved important progress in Eastern and Southern Africa. Projects such as the Southern Africa Accelerated Innovation Delivery Initiative (AID-I) Rapid Delivery Hub have brought together regional seed partners, government agencies, and CGIAR Research Centers, to reduce fertilizer prices, boost resilience to drought and pests, and facilitate market access for smallholders.
In the recent SPG Coalition report, CIMMYT featured prominently as a leading organization in climate-smart agriculture, nutrient-use efficiency, and pest and fertilizer management. This report informs researchers, non-governmental organizations and private sector partners in agrifood and climate policy development.

MasAgro, a research-for-development initiative, has received praise by international organizations and governments as an exemplary program for sustainable development in Latin America. Over 500,000 farmers in Mexico have adopted hardy maize or wheat varieties and resource-conserving agricultural practices. To maximize on the experience of MasAgro, CIMMYT has partnered with a CGIAR initiative: AgriLAC Resiliente. This initiative aims to bolster the competitiveness and sustainability of agrifood systems to respond to forced migrations in Central and South America which are worsened by regional food insecurity and conflict.
Science and innovation powered by partnership can deliver a food secure world
Climate change undoubtedly threatens global peace and agrifood systems. With over 130 countries depending on food imports, today’s hyper-connected world demands collaborative partnership across all sectors to build up shockproof food systems. Through a grassroots approach to research and innovation, the CIMMYT 2030 Strategy is built upon decades of applied science which has impacted communities around the world, to continue influencing policy, pioneering innovations, and advocating for the development of a food secure future.
Latin America is a particularly rich source of neglected crops, which have been replaced by a small number of modern varieties that have come to dominate global commodity markets. However, CIMMYT has utilized various methodologies and developed new initiatives to highlight the value of neglected crops and create market opportunities for smallholders.
What are the crucial practices, to help enhance the contribution to local communities and the preservation of their cultural heritage?
Read the full story.
In plant breeding, efforts to increase the rate of genetic gains and enhance crop resilience to the effects of climate change are often limited by the inaccessibility and costs of phenotyping methods. The recent rapid development of sensors, image-processing technology and data analysis has provided new opportunities for multiple scales phenotyping methods and systems. Among these, satellite imagery may represent one of the best ways to remotely monitor trials and nurseries planted in multiple locations, while standardizing protocols and reducing costs.
This is because relevant data collected as part of crop phenotyping can be generated from satellite images. For instance, the sensors onboard the SkySat satellite constellation of Planet Labs have four spectral bands—blue, green, red, and infrared—which can be used to calculate the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), which is a measure of vegetation and its greenness, and various canopy traits like ground cover, leaf area index and chlorosis. It can also be used to monitor plot establishment and phenological parameters.
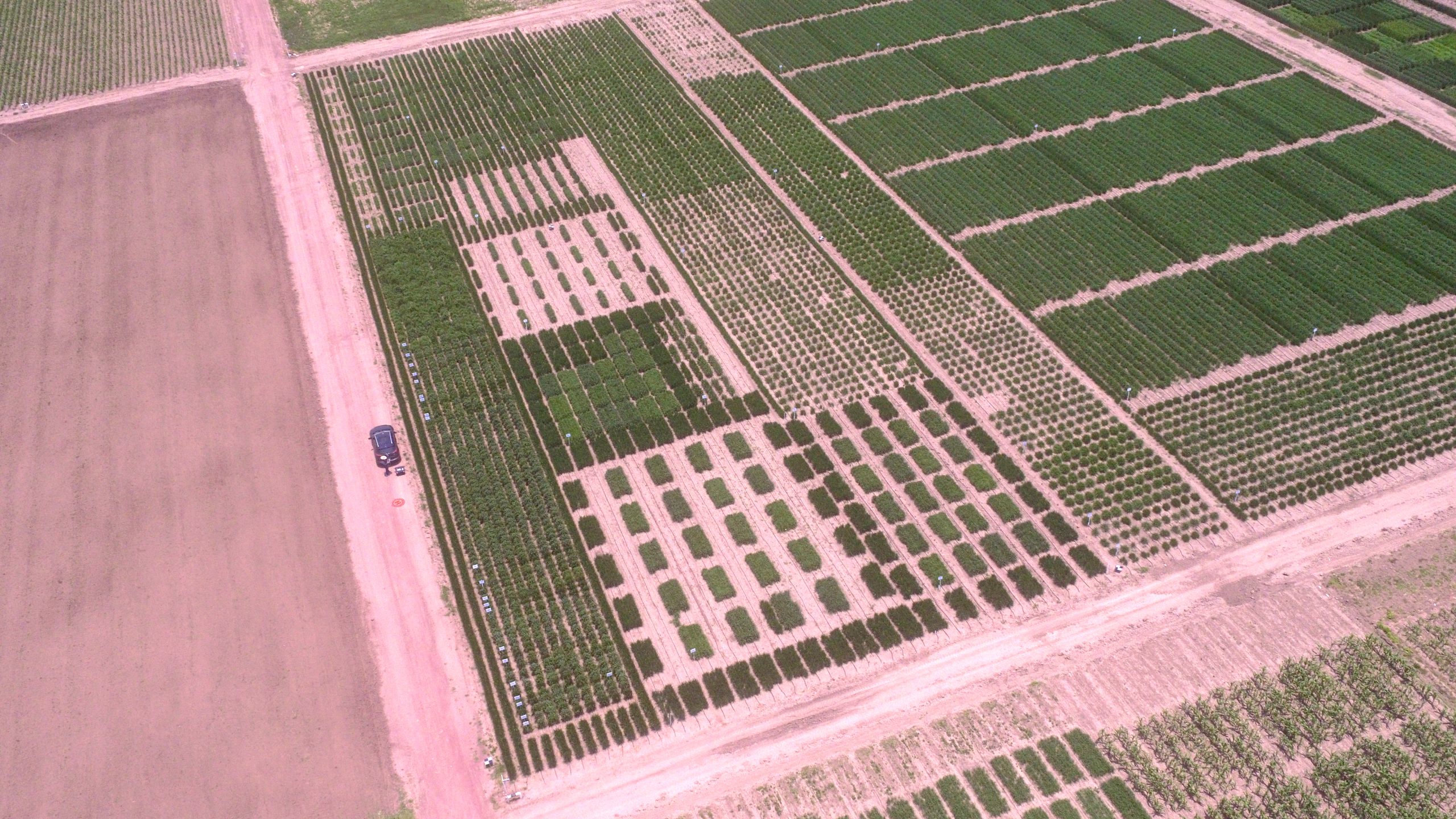

The use of satellite-based phenotyping in breeding trials has typically been restricted by low resolution, high cost and long intervals between fly-overs. However, the advent of a new generation of high-resolution satellites—such as the SkySat constellation—now offers multispectral images at a 0.5m resolution with close to daily acquisition attempts on any place on Earth. This could be a game changer in terms of the scale at which yield trials can be conducted, enabling more precise variety placement and thereby increasing genetic diversity across farmer’s fields and reducing the probability of disease epidemics. It could also revolutionize the capacity for research in realistic field conditions, since traits can be measured throughout the cycle in a highly standardized way, over multiple sites at low cost. For example, an image which covers 25 km2 can monitor an entire research station at a cost of about US$300.
To test the suitability of this technology, a team of researchers from CIMMYT set out to evaluate the reliability of SkySat NDVI estimates for maize and wheat breeding plots of different sizes and spacing, as well as testing its capacity for detecting seasonal changes and genotypic differences.
Both their initial findings, recently published in Frontiers in Plant Science, and more recently acquired data, show that the SkySat satellites can be used to monitor plots commonly used in wheat and maize nurseries. While wheat yield plots usually are 1.2m wide, maize plots tend to consist of at least two rows, resulting in a width of 1.5m. Plot length ranges from 2-4m. The authors also discuss on other factors to be considered when extracting and interpreting satellite data from yield trials, such as plot spacing.
Through the successful collection of six satellite images in Central Mexico during the rainy season and parallel monitoring of a maize trial in Zimbabwe, the researchers demonstrate the flexibility of this tool. Beyond the improvement of spatial resolution, the researchers suggest that the next challenge will be the development and fine-tuning of operational procedures that ensure high quality, standardized data, allowing them to harness the benefits of the modern breeding triangle, which calls for the integration of phenomics, enviromics and genomics, to accelerate breeding gains.
Read the full study: Satellite imagery for high-throughput phenotyping in breeding plots
This research was supported by the Foundation for Food and Agriculture Research, the CGIAR Research Program on Maize, the CGIAR Research Program on Wheat, and the One CGIAR Initiatives on Digital Innovation, F2R-CWANA, and Accelerated Breeding.
Scientists from CIMMYT, founded in Mexico in 1966, have pursued decades of participatory research with Mexico’s smallholder maize farmers to improve their local varieties for traits like yield and insect resistance, while preserving their special grain quality, as well as testing and promoting zero-tillage and other resource-conserving farming practices.

Smallholder farm operations account for more than 80% of all farms worldwide and produce roughly 35% of the world’s food, according to FAO census data and follow-up studies.
An estimated two-thirds of the Mexico’s farmers are smallholders, typically working challenging agroecologies scattered across the country’s mountainous terrain and applying generations-old subsistence practices to grow low-yielding local maize varieties.
Ancient milpa multicropping systems can lift up the present and future
The milpa intercrop — in which maize is grown together with beans, squash, or other vegetable crops — has a millennial history in the Americas and can furnish a vital supply of food and nutrients for marginalized, resource-poor communities.
One hectare of a milpa comprising maize, common beans, and potatoes can provide the annual carbohydrate needs of more than 13 adults, enough protein for nearly 10 adults, and adequate supplies of many vitamins and minerals, according to a CIMMYT-led study in the western highlands of Guatemala, an isolated and impoverished region, reported in Nature Scientific Reports in 2021.
But milpas are typically grown on much smaller areas than a hectare, so households cannot depend on this intercrop alone to satisfy their needs. A solution? Customized milpas that merge farmers’ age-old wisdom and practices with science-based innovation.
An example is planting fruit trees — guava, avocado, mango, peaches, or lime among others — among milpa crops in lines perpendicular to hill slopes. The practice was tested and promoted in the Los Tuxtlas region of the state of Veracruz by Mexico’s National Institute of Forestry, Agriculture, and Livestock Research (INIFAP) and the Colegio de Postgraduados (ColPos) and has been refined by farmers in other areas through CIMMYT-led innovation networks.

In Los Tuxtlas the practice provided added income and nutrition, dramatically reduced erosion, improved land and water-use efficiency by around 50%, and boosted soil health and fertility.
In the state of Puebla and other parts of South and southwestern Mexico, milpa-fruit tree intercrops have worked well on steep hillsides. In the state of Oaxaca, for example, versions of the practice have notably improved farming by indigenous communities in the Mixe and Mazateca regions, supported by outreach of the Mexican Agency for the Sustainable Development of Hillsides (AMDSL), a partner in a CIMMYT research hub in the region.
Research by AMDSL and CIMMYT on smallholder plots in two Oaxaca municipalities where farmers have been combining milpas with peach and avocado production and conservation agriculture practices for more than a decade found that cropping diversification, together with use of zero tillage and keeping crop residues on the soil rather than removing or burning them, raised total yearly crop outputs by as much as 1.7 tons per hectare and reduced farmers’ risk of catastrophic crop losses due to droughts or other climate extremes.
Blue maize pleases diners and delivers profits
Farmers’ local maize varieties yield less than hybrids but are still grown because they provide ideal grain quality for traditional foods, as well as marketable stalks and leaves to feed farm animals and maize husks for wrapping tamales, to name a few products.
Building on longstanding partnerships with INIFAP and the Autonomous University of Chapingo (UACh) to improve local varieties and preserve maize genetic diversity in Mexico, CIMMYT breeders have recently developed improved blue maize hybrids and open-pollinated varieties.
Sought by restauranteurs worldwide for its flavor and beauty, blue maize grain normally comes from native varieties grown by smallholder farmers on small plots with low yields and variable quality.
The new CIMMYT varieties are derived from traditional Guatemalan, Mexican, and Peruvian landraces and feature higher yields, more consistent grain quality, and enhanced resistance to common maize diseases, offering smallholders and other Mexican farmers a profitable product for the country’s booming restaurant industry and for export chains.

Parental inbred lines of the new hybrids have been distributed to private and public partners, who are developing their own hybrids and OPVs in Mexico. CIMMYT continues to test the new hybrids under various farming systems to ensure they produce stable yields when grown in farmers’ fields.
Data driven extension
Using cutting-edge data systems, CIMMYT has leveraged information from nearly 200,000 plots representing more than 26,000 hectares across diverse agroecologies to offer Mexican farmers — including smallholders — site-specific recommendations that make their farming systems more productive, resilient, and sustainable. The initiative was supported by MasAgro, an integrated development partnership of Mexico and CIMMYT during 2010-21 and funded by Mexico’s Secretariat of Agriculture and Rural Development (SADER).