An entrepreneur’s journey in aquaculture: Fueled by partnership, innovation, and resilience

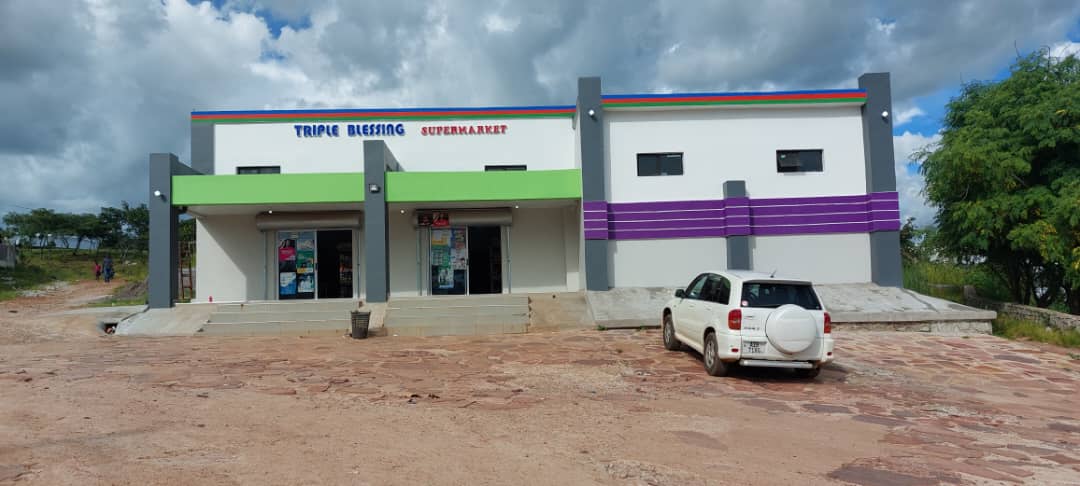
Cosmas Chachi, a 46-year-old businessman, owns Triple Blessing Supermarket in Zambia’s Luwingu District. In 2000, Cosmas identified an opportunity to address the growing demand for fresh fish in his community and started selling the product in his local area. Like many rural entrepreneurs, Cosmas faced initial challenges such as unreliable supply chains, insufficient cold storage, and limited access to financing, all of which prevented him from meeting the rising demand from local customers. Undeterred, Cosmas embarked on a transformative journey into aquaculture.
The turning point for Cosmas occurred in April 2023 when he participated in a training program on integrated aquaculture under the aegis of the Southern Africa Accelerated Innovation Delivery Initiative (AID-I) Rapid Delivery Hub, led by CIMMYT. The training implemented by the International Water Management Institute (IWMI), one of the key implementing partners of the project, emphasized sustainable intensification and equipped Cosmas with advanced skills in sustainable feed management, water quality control, efficient harvesting methods, and business management, among other areas.

“The training equipped me with expert knowledge in aquaculture management and skills to design and operate efficient fishponds,” Cosmas said.
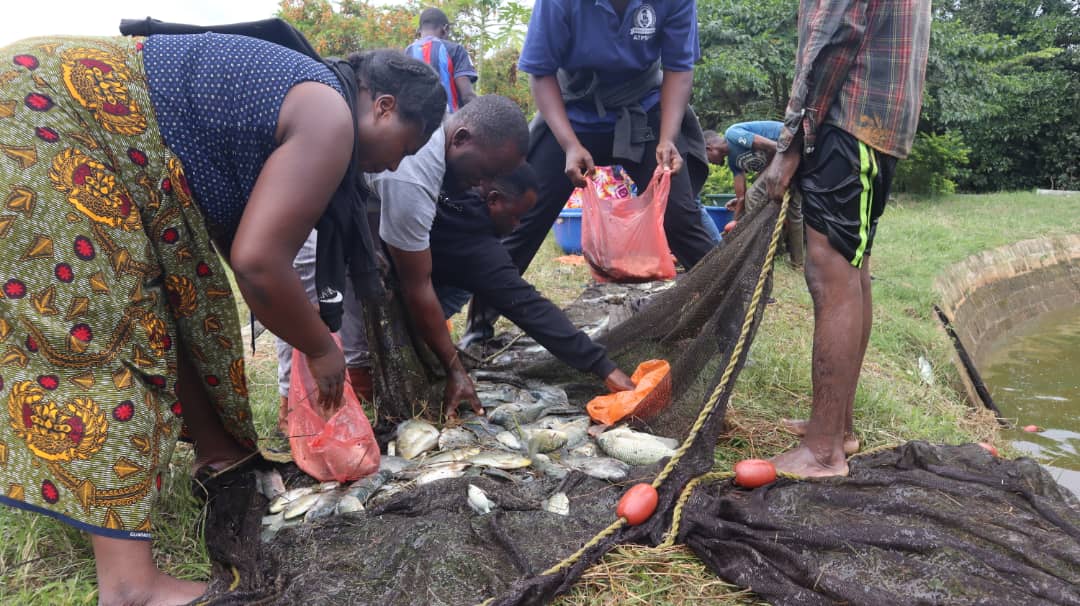
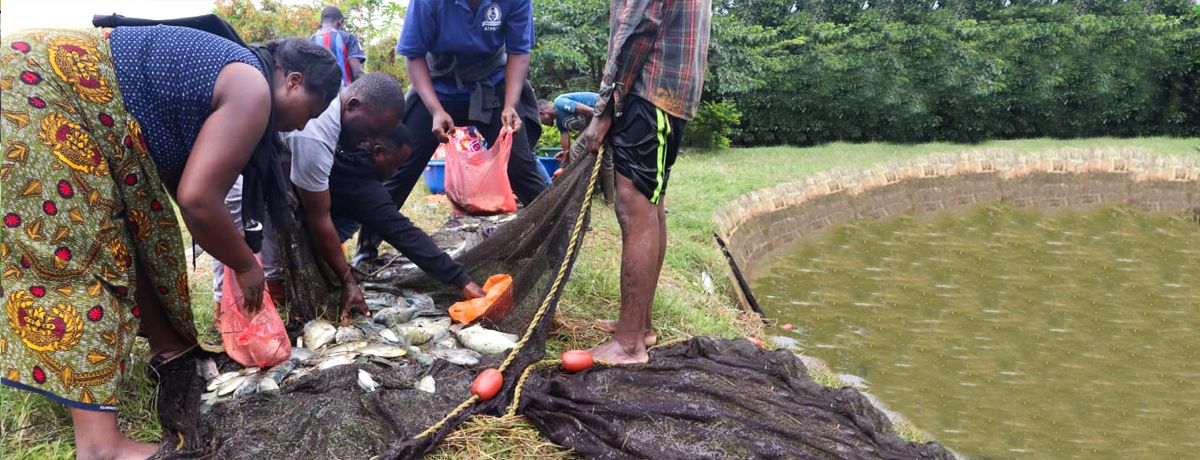
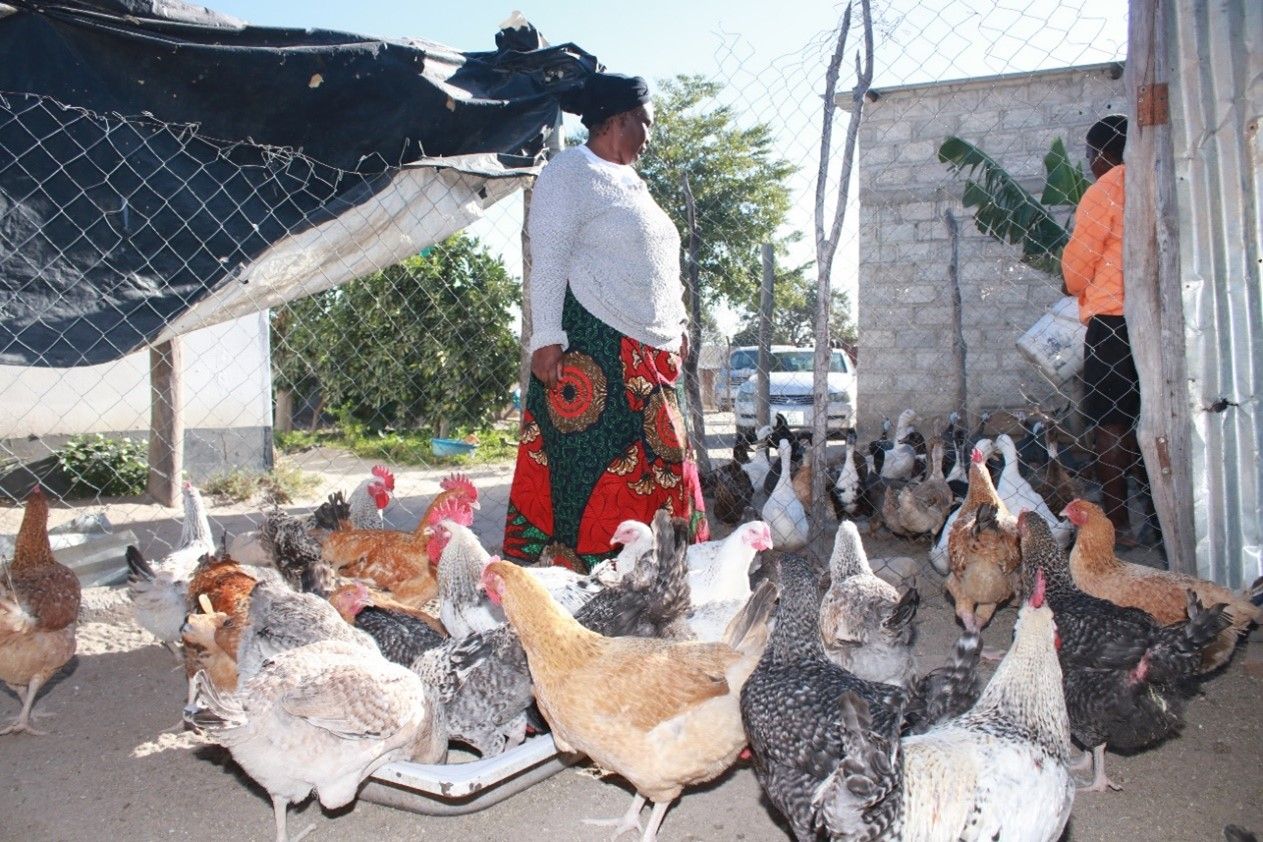
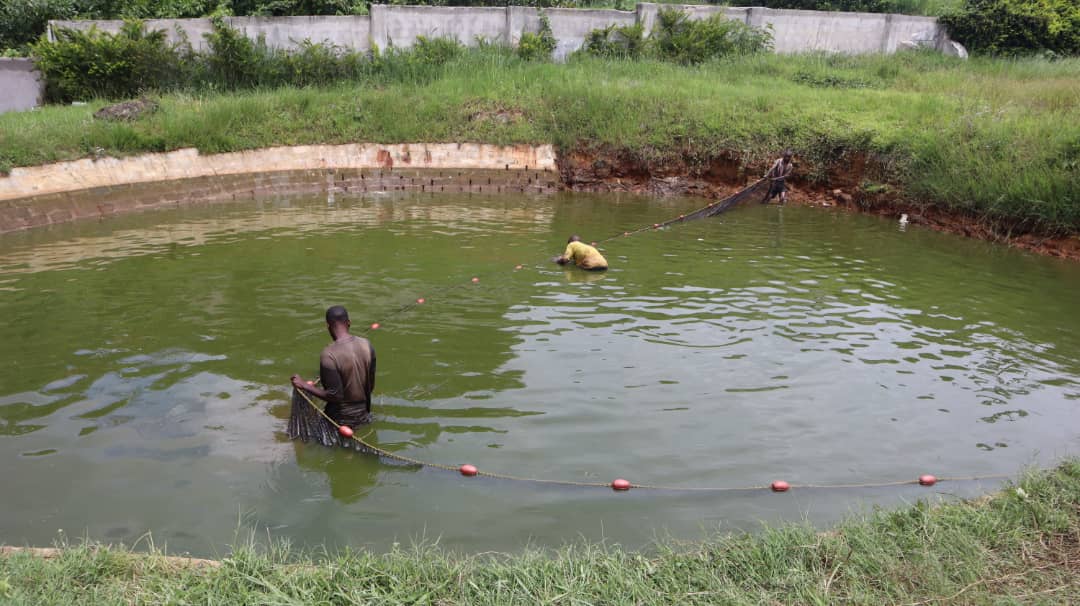
With his new-found expertise, Cosmas upgraded three of his existing fishponds and built six more, each measuring 13×15 meters. To meet customer demand, he introduced a strategic stocking system, staggering the placement of 1,000 fingerlings across his nine ponds. This innovation ensured consistent fish supply even during Zambia’s annual fish ban. “By stocking and harvesting my ponds, I can maintain a steady supply even during the national fish ban when local supply decreases because some other farmers who supply my supermarket depend on fish from natural water bodies,” Cosmas shared.
Creating livelihoods and building resilience
Cosmas’ aquaculture enterprise has become an economic engine in his community, employing 25 permanent workers, primarily local youth, and offering seasonal jobs to 12 more. For Emmanuel Makumba, a shop attendant at Triple Blessing supermarket for the last eight years, the opportunity has been life changing. “The job at the supermarket helped me relocate from my village, build my own house, and send my children to a private school,” said Emmanuel.
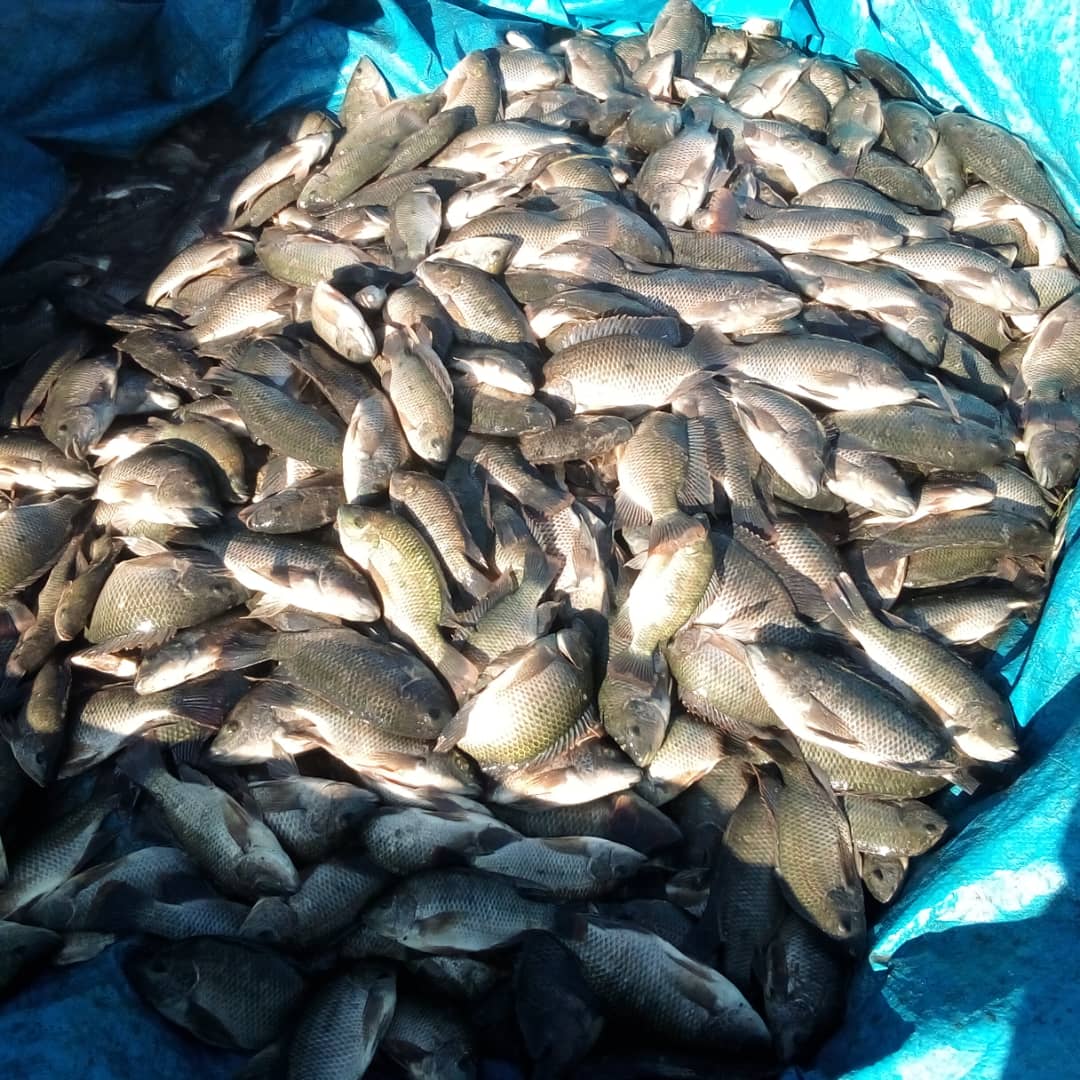
In June 2024, his business received a significant boost with the installation of a 15-ton cold storage facility, funded by IWMI through the AID-I project. The upgrade significantly reduced post-harvest losses and enhanced Cosmas’ fish storage capacity. It ensures a steady supply for his business and the farmers he supports, strengthening the local aquaculture value chain.
“In the past, we could only purchase 50 to 100 kilograms (kg) of fish at a time, selling it at US$ 2.50 per kg,” Cosmas shared. With the new cold storage facility, Cosmas can now buy and store up to 700 kg of fish per harvest without the risk of spoilage. The effort not only secures a reliable supply for his business but also creates a dependable market for local consumers, fostering growth and sustainability in the region’s aquaculture sector.
A ripple effect of progress: Expanding aquaculture for community impact
Today, Cosmas’ success goes beyond his supermarket. He owns a thriving restaurant, offering customers a unique dining experience with fresh fish from his ponds. “The training I received during the AID-I workshops helped me transform my passion for aquaculture into a successful business. Now, in addition to the supermarket, I own a popular restaurant and outdoor fishponds, offering customers a unique dining experience,” he said.

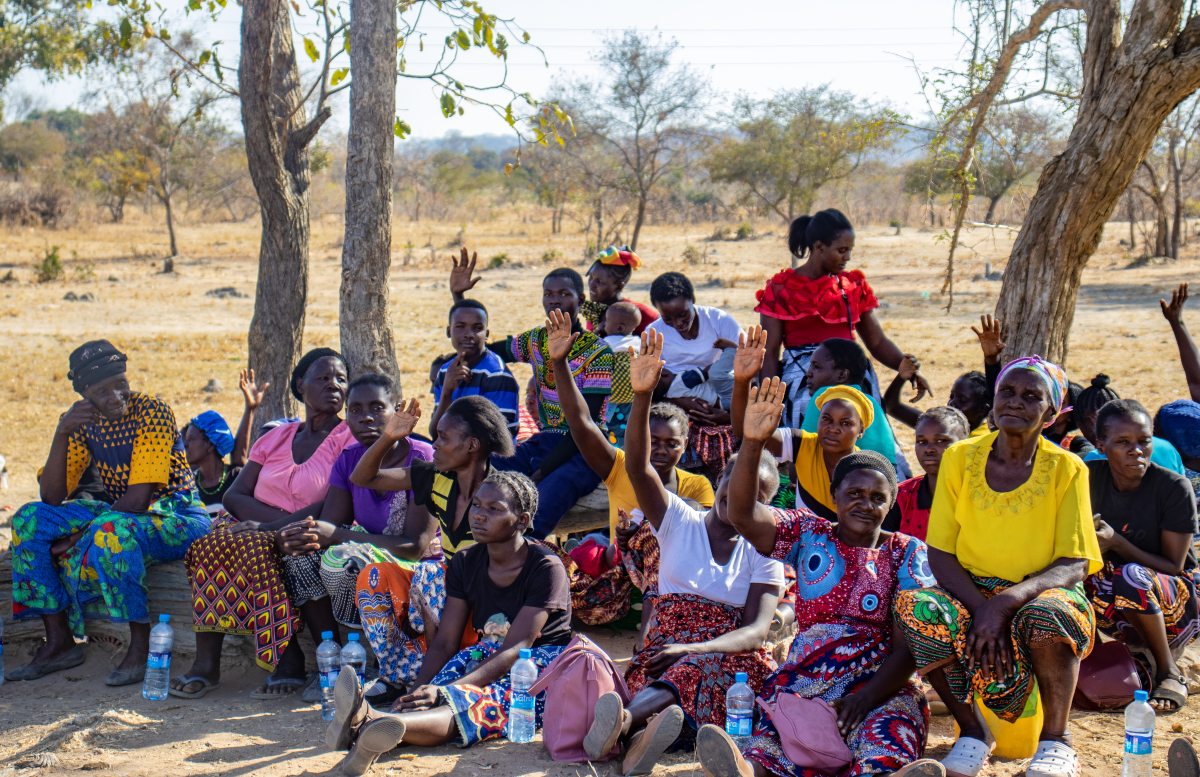
Building on his business success, Cosmas has further expanded his impact by transforming his fishponds into practical classrooms, offering free, hands-on training to aspiring fish farmers. Over the past year, he has trained 50 farmers in sustainable aquaculture best practices.
As more farmers in Luwingu adopt these practices, local food security improves, and income streams diversify. Cosmas’ leadership is stabilizing the community’s food supply and improving diets with nutrient-rich fish. This aligns with AID-I’s broader goal to promote sustainable and scalable agricultural models.
By September 2024, the AID-I project, through IWMI’s efforts, had supported 297 fish farmers with training, market linkages, and tools for success across Northern and Luapula Provinces: creating a ripple effect of progress and also addressing Zambia’s fish supply and demand gap. The project empowers communities to adopt innovative and sustainable aquaculture practices, driving growth in fish production and ensuring a more reliable supply to meet the needs of a growing population. As fish is a critical source of protein and essential nutrients, fostering a sustainable aquaculture sector is vital for supporting Zambia’s food security and nutritional goals.
Cosmas’ journey exemplifies the power of partnerships, innovation, and resilience in driving community progress. It underscores the potential for a robust aquaculture sector in Zambia, where challenges spur solutions and success benefit entire communities. Through AID-I’s comprehensive interventions, Cosmas’ story of transformation offers a vision for sustainable development in rural Zambia, led by innovation and community empowerment.