Unlocking genetic innovations through collaborative pathways
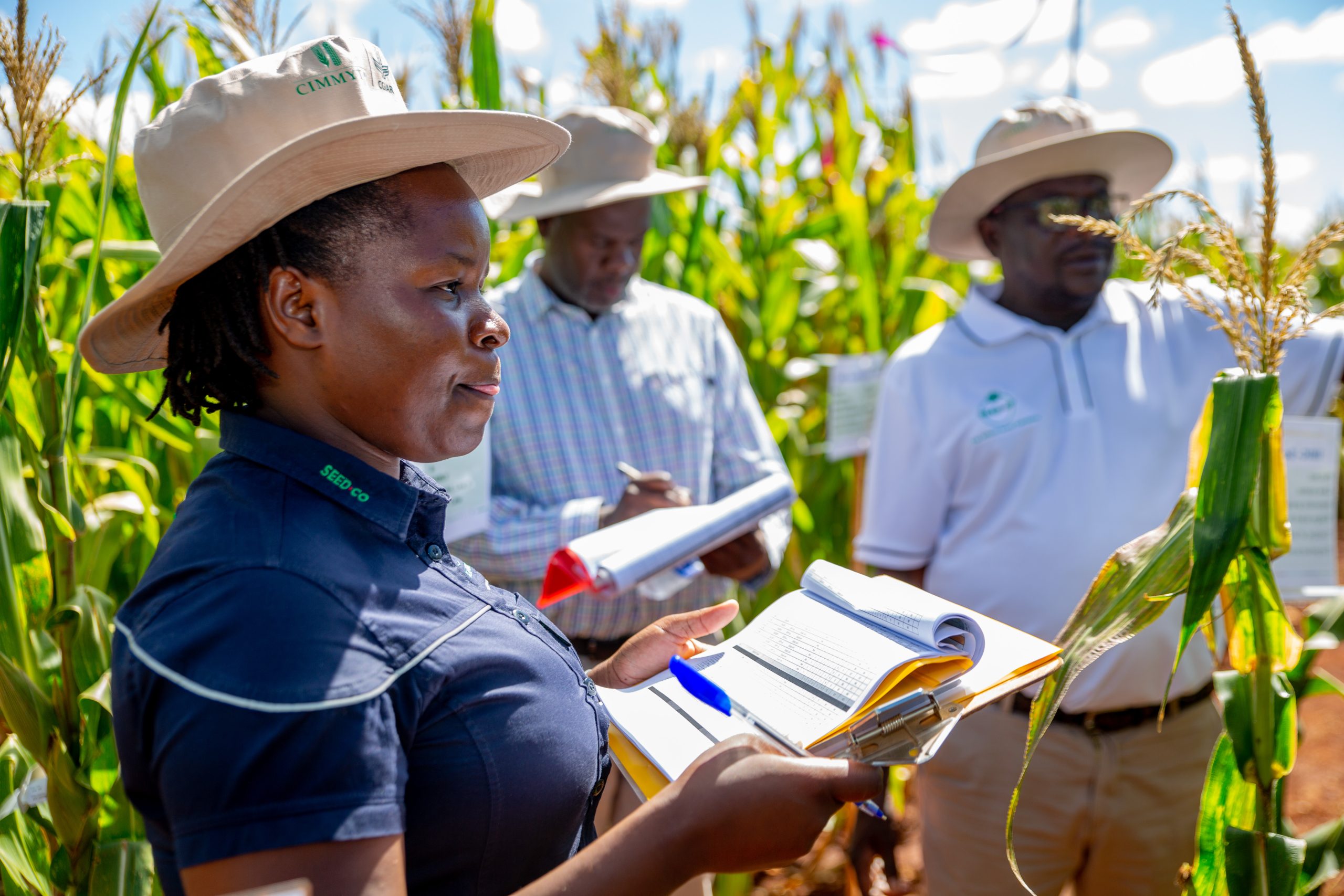

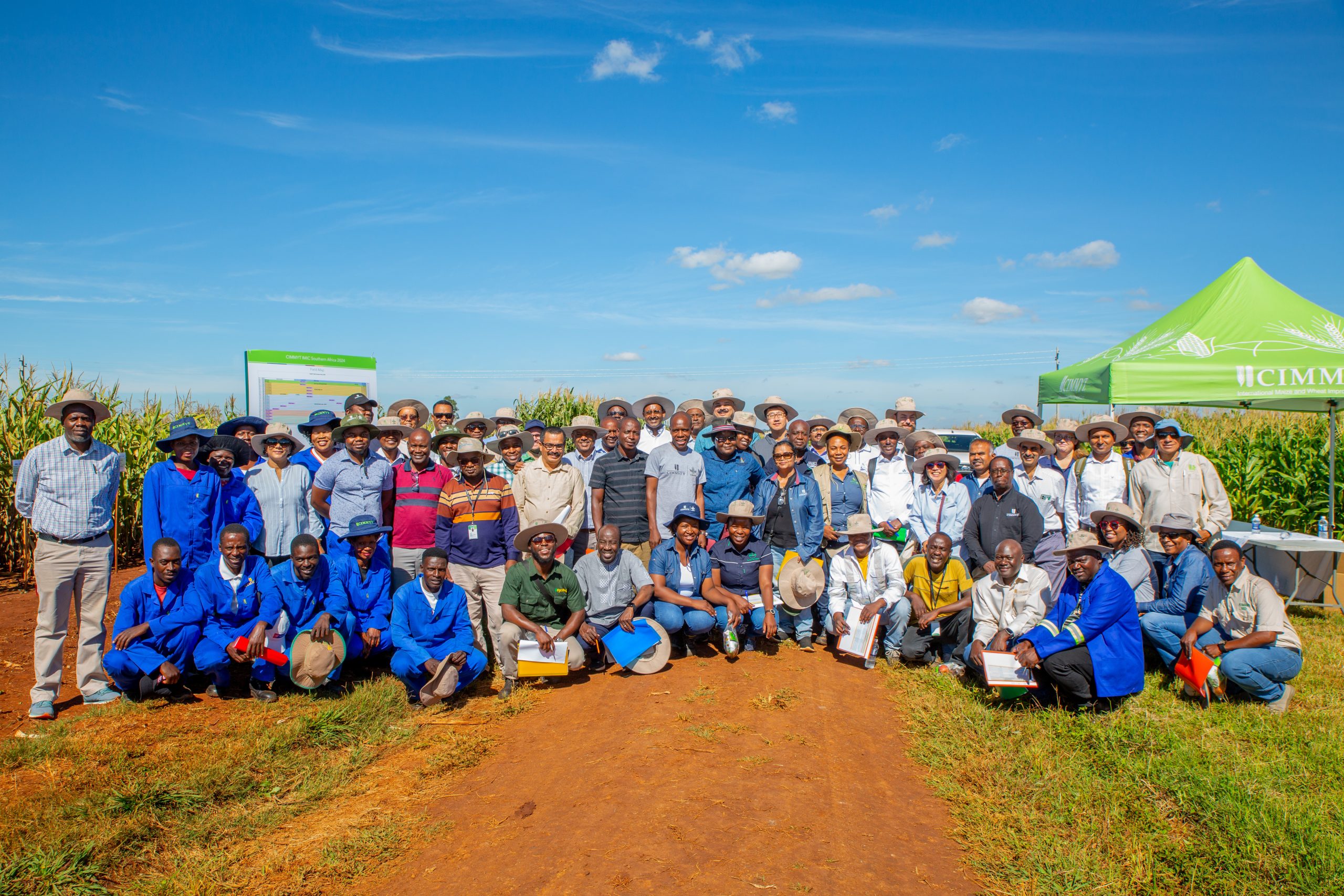
The International Maize Improvement Consortium for Africa (IMIC-Africa) held its Southern Africa field day on 25 March 2024 at Harare, Zimbabwe. IMIC-Africa, launched by CIMMYT in 2018, is a public-private partnership designed to strengthen maize breeding programs of partner institutions in Africa. As part of this initiative, CIMMYT organizes annual field days which bring together representatives from seed companies and national agricultural research system (NARS) partners across Zimbabwe and Kenya.
At the heart of the IMIC-Africa field day lies a vibrant showcase of genetically diverse materials developed from various maize breeding pipelines of CIMMYT in Southern Africa. Such events serve as a catalyst to drive innovations in maize breeding programs, deliver solutions to stakeholders, and enable seed companies and NARS partners to make informed selections tailored to local contexts.
“It is an important forum to have organized discussions with partners, and redesign—where possible—our breeding approaches to deliver targeted products to stakeholders,” said Director of CIMMYT’s Global Maize Program, One CGIAR Global Maize Breeding Lead, and One CGIAR Plant Health Initiative Lead, B.M. Prasanna. “The main stakeholders here are our partners, including seed companies and public sector national programs, through whom we reach out to farming communities.”
The significance of these field days cannot be overstated. It allows the partners to have a critical look at the breeding materials on display and undertake selections of maize lines relevant to their breeding programs. In addition, the IMIC-Africa field days enable CIMMYT team to have structured dialogues with diverse stakeholders and to review and refine breeding (line and product development) strategies and approaches.
“It is key to bridge the gap between the national programs and private sector players. This platform allows us to stay ahead in terms of research, and innovative breakthroughs in the seed sector,” added Kabamba Mwansa, principal agriculture research officer, ZARI, Zambia and Southern Africa Breeding, and seed systems network coordinator.
Highlights from the Harare field day
With an impressive array of 737 CIMMYT maize lines on display, partners at the Harare field day gained insights about the performance of different materials. The materials span early-, intermediate-, and late- maturity groups to nutritious maize breeding pipelines. This comprehensive showcase enabled seed companies and NARS partners to make informed selections, tailored to their local contexts. The material on display ranged from early generation (one or two years of testing data) to advanced generation (more than three years of testing) coming from the Southern Africa breeding pipelines targeting multiple market segments.
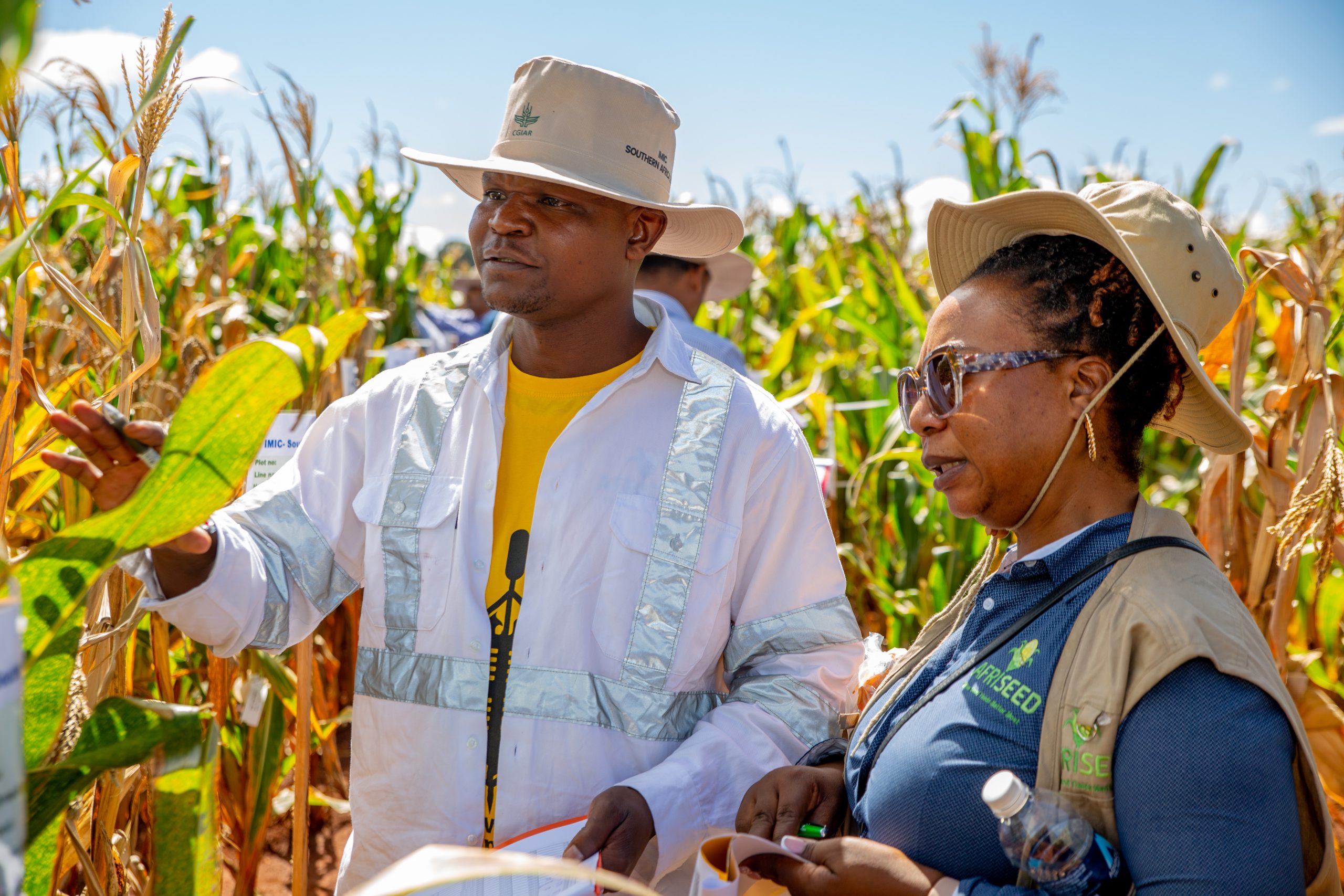

One of the strategic priorities of CIMMYT’s maize breeding program in Africa is improving the nutritional quality of maize. This is exemplified by the development of provitamin A-enriched maize (PVA). On display were 169 lines originating from the PVA-enriched maize breeding pipeline. The efforts underscore CIMMYT’s commitment to address regional nutritional needs through targeted breeding initiatives.
Felix Jumbe, a partner from Peacock Seeds in Malawi reflected on the importance of the IMIC-Africa partnership. “We have been part of IMIC-Africa since its inception, and we continue to appreciate the different climate-resilient lines emerging from CIMMYT maize breeding programs in Africa. Last year, we sold out of our seed as people continue to appreciate the need for resilient maize varieties. The drought-tolerant (DT) maize lines from the consortium have been a huge selling point as most farmers are happy with it,” he said.
The field day not only showcased cutting-edge breeding innovations but also offered a historical perspective by tracing the trajectory of the most popular lines taken up under IMIC-Africa from 2019 to 2023. This served as a crucial reference point for partners, enabling them to assess the performance of newly displayed lines against established benchmarks. Furthermore, partners considered the presence of trait donors as invaluable in improving resistance to key biotic stresses or tolerance to certain abiotic stresses prevalent in Africa.

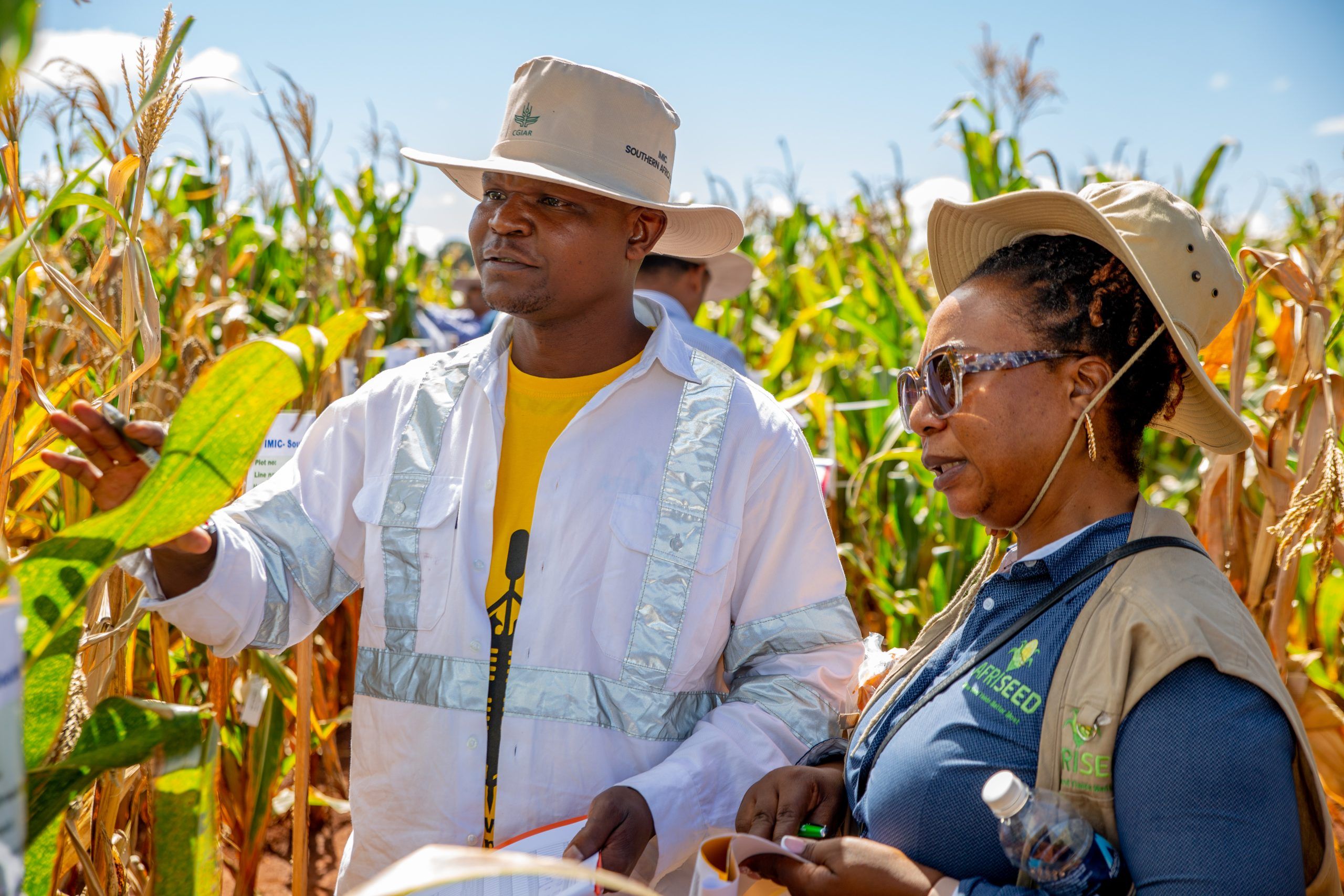
CIMMYT partnership continues to add value
In the face of escalating environmental pressures, including climate change and pest infestations such as the fall armyworm (FAW), CIMMYT breeders have been working tirelessly to develop resilient varieties capable of withstanding these challenges. Partners such as SeedCo have embraced these robust varieties. For breeder Tariro Kusada, it is her second year of attending the IMIC- Africa field day. “We continue to see value in getting breeding materials through IMIC. The vigor from the lines on display is outstanding as compared to last year. We hope the vigor translates to yield.”
Danny Mfula from Synergy Zambia reinforced the value of the partnership. “It is always good to tap into CIMMYT’s germplasm to supplement what we have. We are glad that more FAW-tolerant hybrids are coming on board. We want to leverage on these developments as farmers have gone through a lot of challenges to control FAW,” he said.
As the harvest stage approaches, partners can select their material by assessing the performance of the lines from flowering to grain filling stages. Each plot’s harvest provides invaluable insights, guiding partners in their selections. Partners are also given the opportunity to view the improved maize lines from CIMMYT through a virtual gallery of ears from each plot, ensuring informed decision-making. By fostering dialogue, facilitating partnerships, and highlighting genetic innovations, the field days catalyze progress towards a more sustainable and resilient future for African agriculture.




















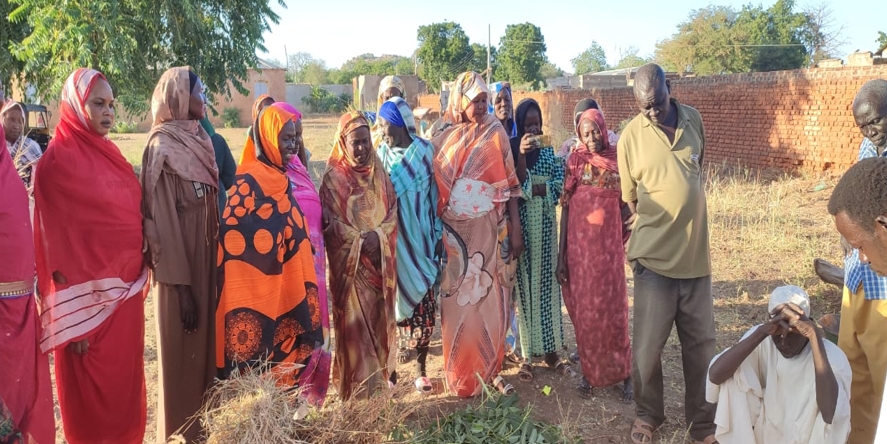
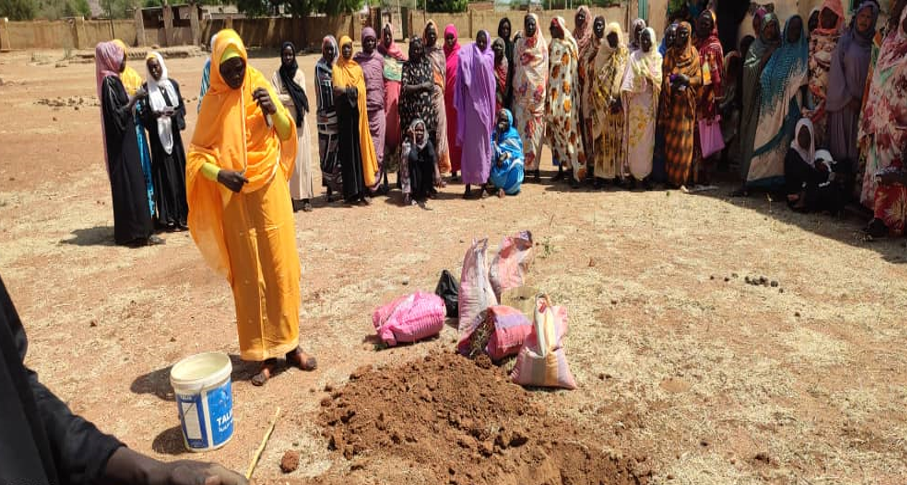
 This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that
This terrible season of global conflict just hit a particularly grim milestone in Sudan with the one-year anniversary of the violent civil war last month. One consequence of the conflict is that 






