 ACIAR’s Dr. John Dixon and Dr. Daniel Rodriguez of the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation, with farmers from Melkassa, Ethiopia ACIAR’s Dr. John Dixon and Dr. Daniel Rodriguez of the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation, with farmers from Melkassa, Ethiopia |
 A maize – legume farm in Tanzania A maize – legume farm in Tanzania |
 Government extension officer Frank Swai, Tanzania Government extension officer Frank Swai, Tanzania |
 Farmer and single mother of four Felista Mateo, Tanzania Farmer and single mother of four Felista Mateo, Tanzania |
 CIMMYT’s Dr. Fred Kanampiu, Tanzania CIMMYT’s Dr. Fred Kanampiu, Tanzania |
By Judie-Lynn Rabar and
Dr. Gio Braidotti
East African farmers are spearheading a research drive to intensify crop production of their most important staple foods. The farmers’ experiments with conservation agriculture and variety selection are part of a broader, 5-country push to stave off a looming food and soil-health crisis.
Kilima Tembo is a secondary school in the Karatu district in Tanzania’s rural highlands. Here, near the Ngorongoro Crater and Tarangira National Park, agriculture is king and food security rests squarely on grains grown in the region’s maize–legume intercropping system.
So important is farming to the community that the school has an agriculture teacher and the school head, Ms Odilia Basso, has allowed the Selian Agricultural Research Institute (SARI) to use school grounds to run field trials as part of a 5-country initiative to overhaul the maize and legumes supply chain—from farm to market.
That means breaking with a long-standing cycle of lifting production simply by bringing more land under the plough. The ecological consequences of that approach are catching up with farmers and their environment, but agricultural science is providing more sustainable alternatives to improve food security.
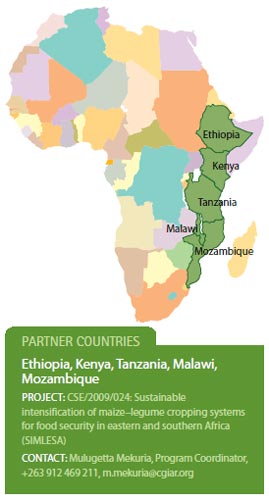
The research-based strategy is called SIMLESA—sustainable intensification of maize–legume cropping systems for food security in eastern and southern Africa. Launched in March 2010, the project is supported by the Australian Government through ACIAR.
Ambitious aims
A major objective is to introduce conservation agriculture techniques and more resilient varieties to increase the productivity and resilience of this vital cropping system. SIMLESA is aiming not only to increase yields by 30% from the 2009 average but also to reduce, by the same factor, risk from yield variability between seasons.
The Kilima Tembo Secondary School will help achieve these goals. The school is hosting the so-called ‘Mother Trial’—a long-term SARI field trial of conservation agriculture. This farming practice involves conserving ground cover between harvests to preserve soil moisture and, over a number of years, radically improve soil health and fertility.
Unlike 11 other farmer-led field sites established by SARI (the so-called ‘Baby Trials’), the Mother Trial is managed directly by the institute’s scientists, landing the school’s students with front-row seats on research and development activities designed to sustain a farming revolution.
Mr. Bashir Makoko, an agronomist working on the SIMLESA project, says students have the opportunity to learn about the project and its significance to the community at an open day with scientists and extension workers from SARI.
The socioeconomist running the trial, Mr. Frank Mbando, is encouraging student participation. He has arranged for data to be collected in ways that allow students to interact with technical staff. “Direct involvement in the project will equip the students with the information they need as potential farmers,” he says.
Household and regional impacts
Supporting these activities are partnerships that link farmers with a suite of national resources—extension officers, research centres and agricultural ministries—and international research centres.
Coordinating these linkages is Dr. Mulugetta Mekuria, from the South African regional office of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT). Also involved is the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT).
Dr. Mekuria says SIMLESA was designed to have impacts at both the household and regional level.
“The aim is to ensure food security through agricultural research, stronger economic institutions, partnerships, and capacity building,” he says. “We want to increase food security and incomes while driving economic development through improved productivity from more resilient and sustainable maize-based farming systems.”
To implement the program, Dr. Mekuria is using the ‘3-I Approach’, a research for development (R4D) strategy designed to enhance smallholder prosperity based on the principles of integration, innovation, and impact. “SIMLESA activities will focus on integrated cropping systems, the use of innovation platforms to test and promote promising practices, and ensuring positive and measurable impacts on food security, sustainability and farm household incomes.”
ACIAR is funding SIMLESA with $20 million in financial support. The centre has enlisted Australian expertise through Dr. Daniel Rodriguez, of the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation, and Professor John Howieson from the Institute for Crop and Plant Sciences at Murdoch University in Perth.
Positive experience
Ms. Felista Mateo, a 37-year-old farmer from Kilima Tembo village is already benefitting from participating in SIMLESA.
A single mother of four, Ms. Mateo supports her family with produce from her land, mainly maize and pigeon pea. Any surpluses, though small, are stored in granaries and either used domestically or sold to middlemen.
Following advice from government extension officer Mr. Frank Swai, she achieved yield gains that her neighbours are now attempting to duplicate. As her harvest increases, she plans to build a larger granary to store her surplus and sell more grain as a cash crop.
Traditionally, farmers have had no way of tracking the market and the middlemen who buy their produce have exercised control over prices. However, Ms. Mateo owns a mobile phone and since the inception of SIMLESA and its support network, she can now call an extension officer and check market prices. The result is greater bargaining power for the villagers when the middlemen come calling.
Averting food insecurity
More than 200 million people living in extreme poverty in the partner countries stand to benefit from SIMLESA.
Currently, the region is barely self-sufficient in grain, importing 10% of its needs—one quarter in the form of emergency food aid.
Maize is the main staple and legumes —primarily groundnut, pigeon pea and chickpea— are an important source of protein. Instead of a more prosperous future, however, the region is facing growth in demand for maize and legumes in the next 10 years. It is that trend towards food insecurity that SIMLESA is attempting to avert.
But it is not just on-farm practices that are targeted for innovation. Urban grain prices have remained stubbornly high following the global food crisis of 2007–08. But higher prices for consumers have not translated into higher prices for farmers. This has weakened incentives for farmers to increase food crop production, a state of affairs that SIMLESA is attempting to change.
CIMMYT’s Dr. Fred Kanampiu says that the SIMLESA project is aiming to achieve a ‘whole-chain’ impact. “Despite the multiple efforts underway with the researchers, the final focus should not be lost,” he says. “It is the farmer who is to be the end beneficiary of the research. The farmers’ lives should be improved, their pockets well-lined and their families well catered for.”
Of all the crops produced by farmers such as Ms. Mateo, it is pigeon pea that has an important role to play as a cash crop. Farmers are fond of this legume because it yields two harvests a year and there is a good export market to India. Pigeon pea retails up to TZS150,000 (about US$100) per 100 kilogram bag. On average, one acre (0.405 hectares) of land yields 300–400 kg of pigeon pea. Typically, 95% of the crop is sold.
In Karatu district some 15% of farmers live on less than a dollar a day. Mr. Makoko says the major obstacles to lifting their profitability are high inputs costs, low produce prices, lack of markets, and prolonged drought. By introducing pigeon pea or similar crops, and integrating the ‘whole-chain’ approach, these obstacles can be reduced or overcome.

Socioeconomist Frank Mbando, Tanzania. |

Senior agronomist Tuaeli Mmbaga, Tanzania.
The way forward will include training farmers to provide them with further education on how to manage their land.”
–Tuaeli Mmbaga
|
Better varieties
While the main research thrust is on conservation agriculture, CIMMY T and ICRISAT are participating in accelerated breeding and performance trials that aim to introduce farmers to maize and legume varieties that yield well in good years and are resilient enough in the bad seasons to help reduce farmers’ risks.
Mr. Mbando is tracking impacts associated with the new varieties and says the farmers’ response to the studies has been positive.
“They suggested that breeders take into account farmers’ criteria when making selections, so a participatory approach will be used to evaluate varieties,” he says. “So far, farmers have indicated early maturity, pest and disease tolerance, high yields and marketability as the preferred traits. Variety registration and production will then also be stepped up to make the seed available in sufficient quantities.”
Partnership approach
Mbulu district, located about 50 kilometres from Karatu, is the next community targeted for SIMLESA activities in Tanzania, to start after the current crop has been harvested. At the SIMLESA inception meeting, farmers agreed to leave post-harvest residue on the ground in preparation for the trials. Field activities in the Eastern Zone districts of Gairo and Mvomero are expected to begin in the next growing season.
Ms. Tuaeli Mmbaga, the senior agronomist on this project, says that with support from extension officers, farmers will assess the technology both pre-harvest and post-harvest.
“The way forward will include training farmers to provide them with further education on how to manage their land,” she says. “This will include an Innovation Learning Platform in partnership with farm produce stockists, community leaders, and other stakeholders to ensure that more people become involved with the project.”
Crop modeling scientist Dr. Daniel Rodriguez, who leads the Queensland component of ACIAR’s SIMLESA program, is convinced that research to reduce food shortages in eastern and southern Africa could have many benefits for farmers, including in his native Queensland.
“Our scientists will be working to improve the resilience and profitability of African farms, providing access to better seeds and fertilisers to raise the productivity of local maize–legume farming systems,” Dr. Rodriguez says. “Together we may be able to help solve one of the greatest challenges for the developed world—eliminating hunger and poverty in Africa—while at the same time boosting legume production here in Australia.”
Building agricultural research capacity
ACIAR’s Dr. John Dixon says the emphasis of Australia’s direct involvement is on building capacity within the African agricultural research system.
“Conservation agriculture amounts to a substantial shift in farming practices for the region,” Dr. Dixon says. “But it stands to provide so many advantages—not just greater water-use efficiency and soil health but also opportunities to break disease cycles and improve livestock nutrition.”
These are long-term efforts that need to be adapted to many agro-climatically diverse locations, Dr. Dixon says. “So it is vital that the African agricultural research system is built up so that it can take lead responsibility for implementing innovation into the future.”
 The CIMMYT team, accompanied by Nginamau and Faceira, had a second meeting with Prata Junior on 22 June 2012. Thanking him for the warm welcome and willingness to support DTMA work in Angola, Abate pointed out the need for favorable policies on variety release and the involvement of the private sector in developing a sustainable seed production and delivery system. Discussions during the meeting also emphasized the need for the agriculture ministry to set targets for increasing the maize yield within the next five years. Abate reiterated CIMMYT’s willingness to offer technical support towards achieving the government’s goal of accelerated maize production. Prata Junior welcomed the suggestions and asked for immediate support in capacity building. He also emphasized the need for the capacity to produce basic seed within Angola and pointed out that the country is importing an additional 20,000 tons seed for the coming season. Prata Junior said the introduction of early-maturing hybrids would be highly appreciated in light of recurrent droughts in the country. He also pledged to follow up with the MOARDF for the large-scale dissemination of DTMA varieties.
The CIMMYT team, accompanied by Nginamau and Faceira, had a second meeting with Prata Junior on 22 June 2012. Thanking him for the warm welcome and willingness to support DTMA work in Angola, Abate pointed out the need for favorable policies on variety release and the involvement of the private sector in developing a sustainable seed production and delivery system. Discussions during the meeting also emphasized the need for the agriculture ministry to set targets for increasing the maize yield within the next five years. Abate reiterated CIMMYT’s willingness to offer technical support towards achieving the government’s goal of accelerated maize production. Prata Junior welcomed the suggestions and asked for immediate support in capacity building. He also emphasized the need for the capacity to produce basic seed within Angola and pointed out that the country is importing an additional 20,000 tons seed for the coming season. Prata Junior said the introduction of early-maturing hybrids would be highly appreciated in light of recurrent droughts in the country. He also pledged to follow up with the MOARDF for the large-scale dissemination of DTMA varieties.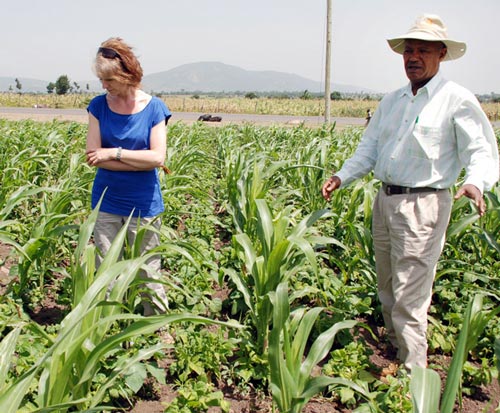 While highlighting that the work she was doing was still ongoing, Diana pointed out key strengths of the DTMA project from her assessment. “DTMA and all project personnel recognize the need to do this because it is generally acknowledged that approximately 70 percent of agricultural labor in sub-Saharan countries is provided by women,” says Diana. “Since women also play a central role in the welfare of household members and the community, understanding how drought tolerant technologies affect them is crucial to defining the impact of DTMA on poor farmers. Amongst many of the research counterparts, both public and private, there is recognition of the significance of women in agricultural systems,” she observes.
While highlighting that the work she was doing was still ongoing, Diana pointed out key strengths of the DTMA project from her assessment. “DTMA and all project personnel recognize the need to do this because it is generally acknowledged that approximately 70 percent of agricultural labor in sub-Saharan countries is provided by women,” says Diana. “Since women also play a central role in the welfare of household members and the community, understanding how drought tolerant technologies affect them is crucial to defining the impact of DTMA on poor farmers. Amongst many of the research counterparts, both public and private, there is recognition of the significance of women in agricultural systems,” she observes. South Sudan, Africa’s newest country, is set to benefit from the project “Sustainable Intensification of Maize-Legume Cropping Systems in Eastern and Southern Africa” (
South Sudan, Africa’s newest country, is set to benefit from the project “Sustainable Intensification of Maize-Legume Cropping Systems in Eastern and Southern Africa” ( “ACIAR has availed initial funding for spillover activities,” said Mekuria. “The idea is to ensure that SIMLESA research results are quickly scaled out to countries like South Sudan and improve food security there.”
“ACIAR has availed initial funding for spillover activities,” said Mekuria. “The idea is to ensure that SIMLESA research results are quickly scaled out to countries like South Sudan and improve food security there.”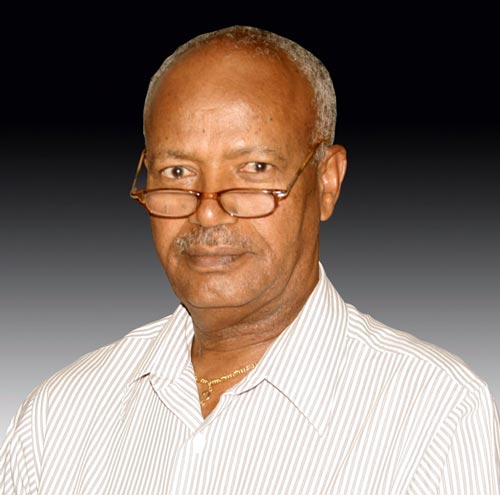 A citizen of Ethiopia, Tsedeke Abate joined CIMMYT Global Maize Program on 08 May 2012, and has taken over responsibilities from Wilfred Mwangi as the project leader of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) project. Abate will be based in Nairobi, Kenya. He obtained his BS and MS degrees in agriculture from the University of Florida, USA, and his PhD in biological sciences from Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada.
A citizen of Ethiopia, Tsedeke Abate joined CIMMYT Global Maize Program on 08 May 2012, and has taken over responsibilities from Wilfred Mwangi as the project leader of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) project. Abate will be based in Nairobi, Kenya. He obtained his BS and MS degrees in agriculture from the University of Florida, USA, and his PhD in biological sciences from Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada. The Regional Planning Meeting for phase III of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) project was held in Kumasi, Ghana, during the week of 16-19 April 2012. The objectives of this meeting were to (i) review and document progress on DTMA project activities conducted in West Africa in 2011, (ii) present, critically review, and approve project proposals submitted for funding by partner countries Benin Republic, Ghana, Mali, and Nigeria under phase III, and develop work plans for the 2012 cropping season. The regional meetings have proved instrumental in planning and monitoring of DTMA project activities and building the requisite partnerships for successful implementation of the project.
The Regional Planning Meeting for phase III of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) project was held in Kumasi, Ghana, during the week of 16-19 April 2012. The objectives of this meeting were to (i) review and document progress on DTMA project activities conducted in West Africa in 2011, (ii) present, critically review, and approve project proposals submitted for funding by partner countries Benin Republic, Ghana, Mali, and Nigeria under phase III, and develop work plans for the 2012 cropping season. The regional meetings have proved instrumental in planning and monitoring of DTMA project activities and building the requisite partnerships for successful implementation of the project. ACIAR’s Dr. John Dixon and Dr. Daniel Rodriguez of the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation, with farmers from Melkassa, Ethiopia
ACIAR’s Dr. John Dixon and Dr. Daniel Rodriguez of the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation, with farmers from Melkassa, Ethiopia





 “The climate is changing, rainfall is decreasing and the weather is now dictating which varieties farmers grow and in turn which varieties seed companies produce,” says Dellings Phiri, general manager of Seed Co. Malawi, a leading southern African seed company.
“The climate is changing, rainfall is decreasing and the weather is now dictating which varieties farmers grow and in turn which varieties seed companies produce,” says Dellings Phiri, general manager of Seed Co. Malawi, a leading southern African seed company. As the price of wheat goes up, countries such as the Republic of Mauritius are feeling the pinch. A former British colony off the coast of Madagascar, it imports most of its wheat from France and Australia. But with help from CIMMYT, the island has started trials to grow its own wheat—and results to date look promising.
As the price of wheat goes up, countries such as the Republic of Mauritius are feeling the pinch. A former British colony off the coast of Madagascar, it imports most of its wheat from France and Australia. But with help from CIMMYT, the island has started trials to grow its own wheat—and results to date look promising.
 In the 2006-07 cropping season, 82 registered maize seed companies produced the bulk of just over 100,000 tons of improved maize seed that were marketed in the major maize producing countries of eastern and southern Africa (excluding South Africa) — enough to sow 35% of the maize land in those countries.
In the 2006-07 cropping season, 82 registered maize seed companies produced the bulk of just over 100,000 tons of improved maize seed that were marketed in the major maize producing countries of eastern and southern Africa (excluding South Africa) — enough to sow 35% of the maize land in those countries.
 CIMMYT is adapting an advanced technology—the doubled haploid approach—to develop inbred lines of tropical maize for sub-Saharan Africa. It promises to reduce costs and speed the arrival of better-adapted maize for resource-poor farmers in the world’s toughest environments.
CIMMYT is adapting an advanced technology—the doubled haploid approach—to develop inbred lines of tropical maize for sub-Saharan Africa. It promises to reduce costs and speed the arrival of better-adapted maize for resource-poor farmers in the world’s toughest environments.
 During the week of 15-20 April 2012, 36 maize technicians participated in a training session in Lusaka, Zambia. The participants were selected from seven seed companies in Zambia, national agricultural research organizations, and NGOs involved in agricultural research and extension in the eastern province of Zambia. The objective of the course was to update maize technical staff on implementing on-station and on-farm trials, seed production, and the use of secondary traits in selecting superior genotypes under low nitrogen, heat and drought trials, and it combined both lectures and field work.
During the week of 15-20 April 2012, 36 maize technicians participated in a training session in Lusaka, Zambia. The participants were selected from seven seed companies in Zambia, national agricultural research organizations, and NGOs involved in agricultural research and extension in the eastern province of Zambia. The objective of the course was to update maize technical staff on implementing on-station and on-farm trials, seed production, and the use of secondary traits in selecting superior genotypes under low nitrogen, heat and drought trials, and it combined both lectures and field work.