Improved Maize for African Soils (IMAS)
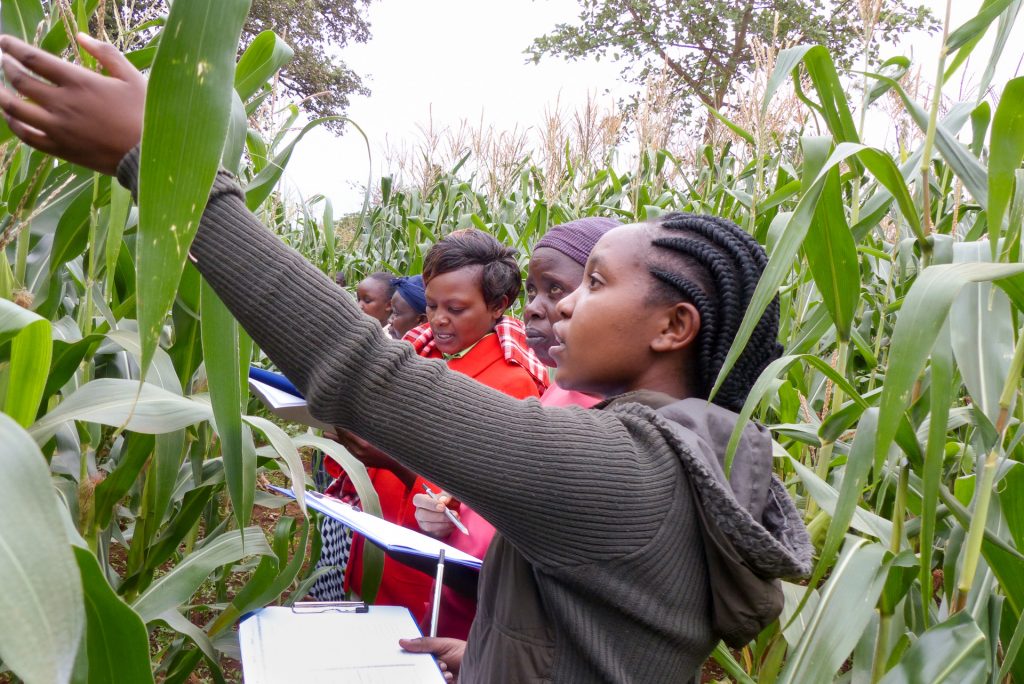
African maize farmers must deal with drought, weeds, and pests, but their problems start with degraded, nutrient-starved soils and their inability to purchase enough nitrogen fertilizer. Maize yields of smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa are a fraction of those in the developed world, due mainly to the region’s poor soils and farmers’ limited access to fertilizer or improved maize seed. On average, such farmers apply only 9 kilograms of fertilizer per hectare of cropland. Of that small amount, often less than half is captured by the crop; the rest is leached deep into the soil where plants cannot recover it or otherwise lost.
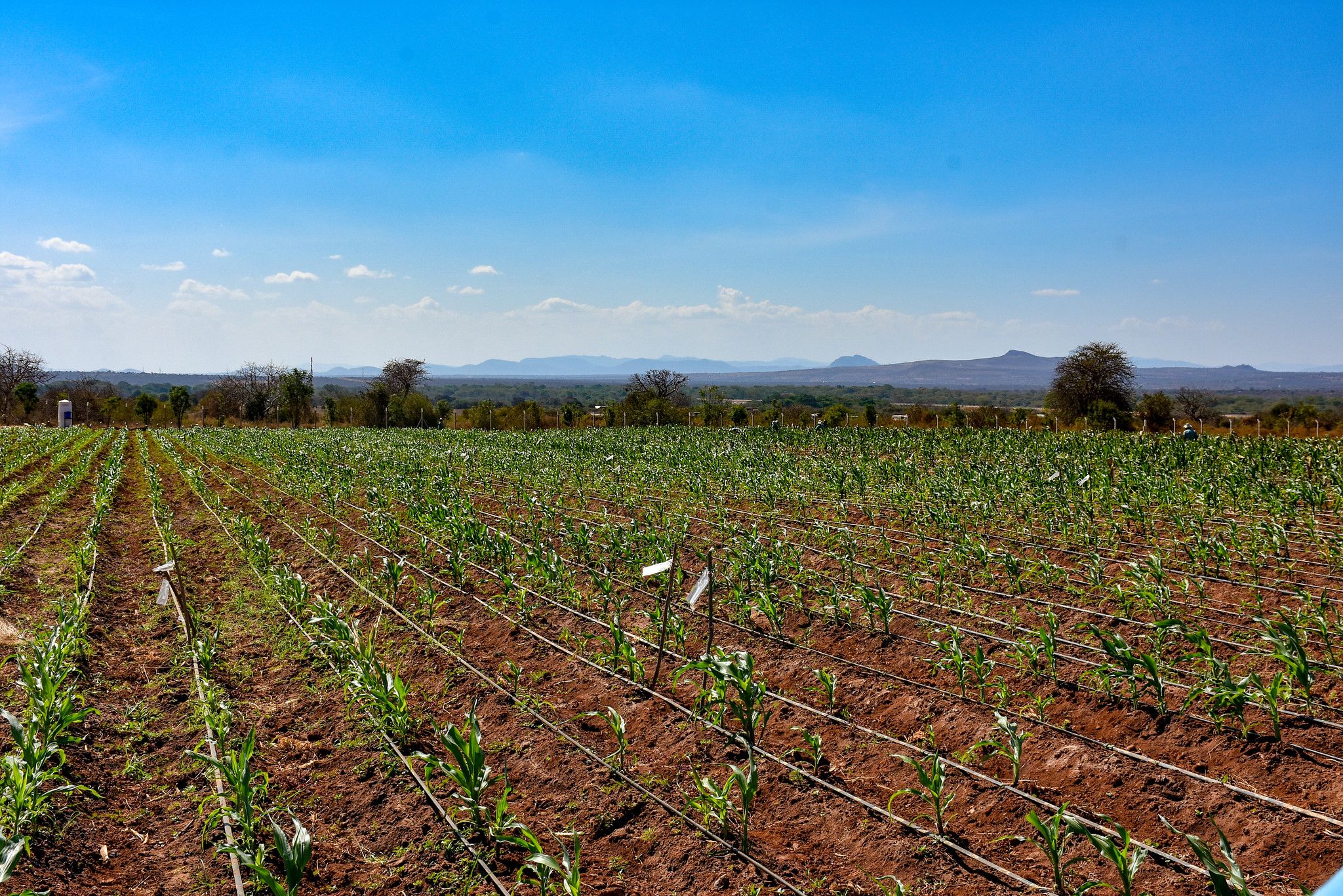
The Improved Maize for African Soils Project (IMAS) develops maize varieties that are better at capturing the small amount of fertilizer that African farmers can afford, and that use the nitrogen they take up more efficiently to produce grain. Project participants will use cutting-edge biotechnology tools such as molecular markers—DNA “signposts” for traits of interest—and transgenic approaches to develop varieties that ultimately yield 30 to 50 percent more than currently available varieties, with the same amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied or when grown on poorer soils.
The varieties developed will be made available royalty-free to seed companies that sell to the region’s smallholder farmers, meaning that the seed will become available to farmers at the same cost as other types of improved maize seed.
In four years or less, African farmers should have access to IMAS varieties developed using conventional breeding that offer a 20 percent yield advantage over current varieties. Improved varieties developed using DNA marker techniques are expected to be introduced within seven to nine years, and those containing transgenic traits are expected to be available in approximately 10 years, pending product performance and regulatory approvals by national regulatory and scientific authorities, according to the established laws and regulatory procedures in each country.
IMAS is being led by CIMMYT and funded with $19.5 million in grants from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the U.S. Agency for International Development. The project’s other partners — DuPont-Pioneer, Kenya Agricultural Livestock and Research Organization and the Agricultural Research Council of South Africa — are also providing significant in-kind contributions including staff, infrastructure, seed, traits, technology, training, and know-how.
The second phase of IMAS continues to be implemented through the Seed Production Technology for Africa (SPTA) project.
OBJECTIVES
- Conventional and marker assisted breeding to develop hybrids and OPVs with improved nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) adapted to southern and eastern Africa
- Identification and deployment of native trait alleles to enhance yield under low nitrogen conditions through association mapping and Quantitative Trait Loci mapping
- Development of transgenic maize varieties adapted to southern and eastern Africa with increased yield under severe nitrogen limitation
- Managing NUE varieties for sustainability in African maize cropping systems
- Project stewardship, public awareness and capacity building
- NUE variety registration, release and dissemination in southern and eastern Africa