Collaborating to accelerate genetic gains in maize and wheat
Stakeholders in the Accelerating Genetic Gains in Maize and Wheat for Improved Livelihoods (AGG) project have pledged to strengthen efforts to deliver desirable stress tolerant, nutritious and high-yielding maize and wheat varieties to smallholder farmers in a much shorter time. The alliance, comprising funders, national agricultural research systems (NARS), private seed companies, non-governmental organizations, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and, for the maize component the International Institute for Tropical Agriculture (IITA), made these assurances during virtual events held in July and August 2020, marking the inception of the 5-year AGG project.
The initiative seeks to fast-track the development of higher-yielding, climate resilient, demand-driven, gender-responsive and nutritious seed varieties for maize and wheat, two of the world’s most important staple crops. The project is funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO), the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), and the Foundation for Food and Agriculture Research (FFAR).
Tackling current and emerging threats
Jeff Rosichan, scientific program director of the Foundation for Food and Agricultural Research (FFAR), acknowledged the significant and ambitious aim of the project in tackling the challenges facing maize and wheat currently and in the future. “We are seeing the emergence of new pests and pathogens and viral diseases like never before. A lot of the work of this project is going to help us to tackle such challenges and to be better prepared to tackle emerging threats,” he said.
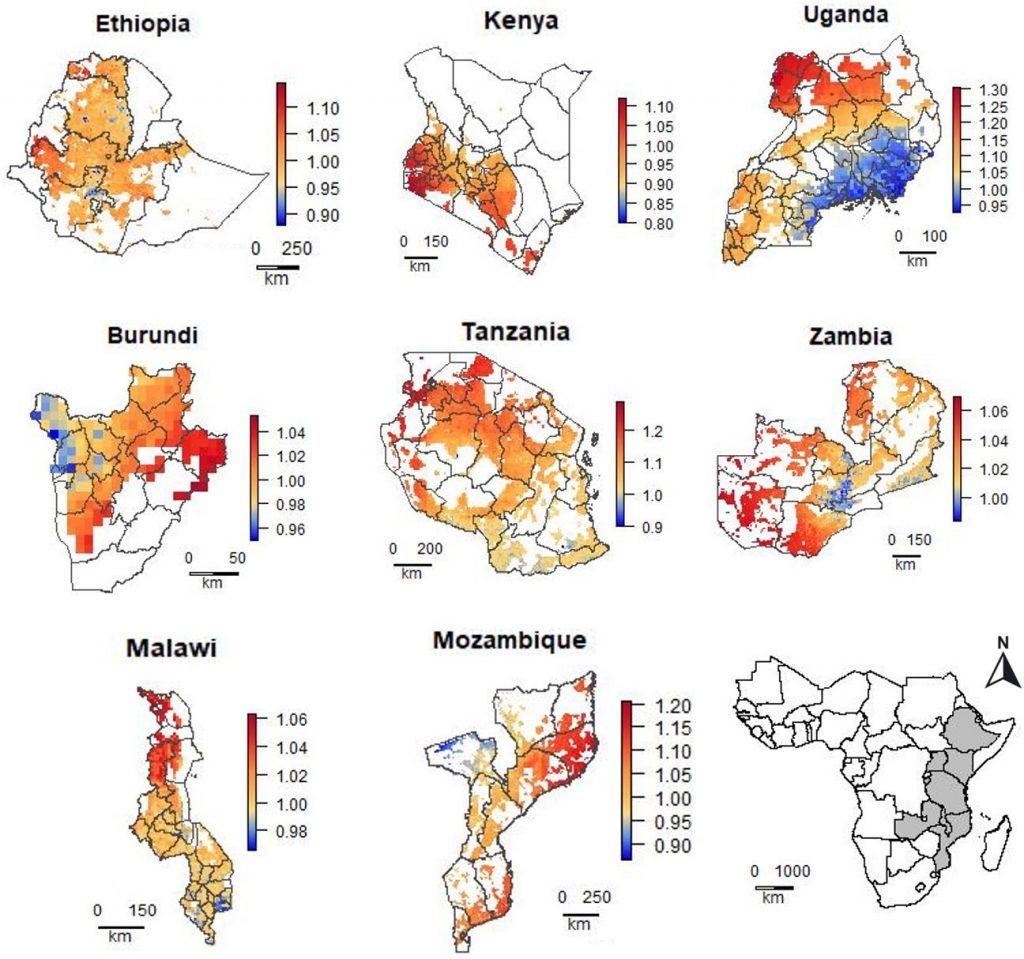
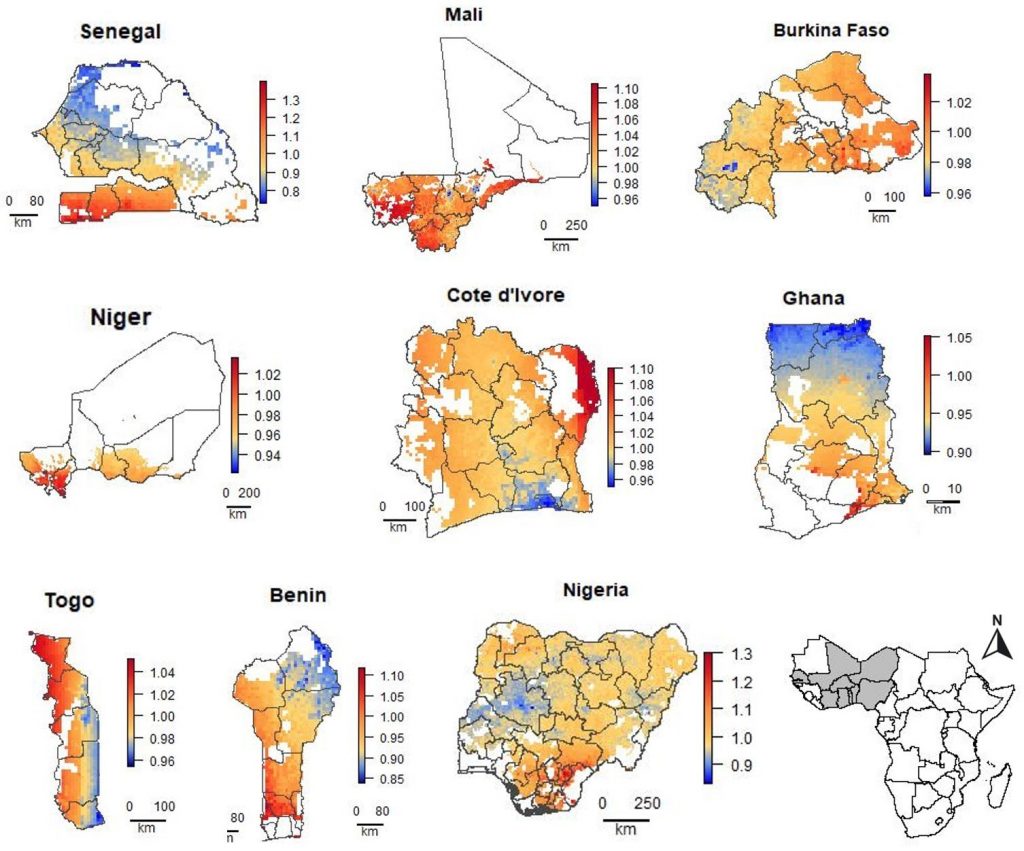
AGG builds on gains made in previous initiatives including Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA), Improved Maize for African Soils (IMAS), Water Efficient Maize for Africa (WEMA), Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) and Delivering Genetic Gain in Wheat (DGGW), with support from partners in 17 target countries in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) and South Asia.
Hailu Wordofa, agricultural technology specialist at the USAID Bureau for Resilience and Food Security, underscored his expectation for CIMMYT’s global breeding program to use optimal breeding approaches and develop strong collaborative relationships with NARS partners, “from the development of product profiles to breeding, field trials and line advancement.”
Similarly, Gary Atlin, senior program officer at the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation lauded the move toward stronger partnerships and greater emphasis on the CIMMYT and IITA breeding programs. “The technical capacity of partners has increased through the years. It is prudent to ensure that national partnerships continue. It is always a challenging environment, this time multiplied by the COVID-19 crisis, but through this collaboration, there is a greater scope to strengthen such partnerships even more,” he said.

Symbiotic partnerships with great impact
“From the NARS perspective, we are committed to doing our part as primary partners to deliver the right seed to the farmers,” said Godfrey Asea, director of the National Crops Resources Research Institute at the National Agriculture Research Organization (NARO), Uganda. “We see an opportunity to review and to use a lot of previous historical data, both in-country and regionally and to continue making improved decisions. We also reiterate our commitment and support to continuously make improvement plans in our breeding programs.”
Martin Kropff, director general of CIMMYT, recognized the tremendous impact arising from the longstanding cooperation between CIMMYT’s maize and wheat programs and national programs in countries where CIMMYT works. “A wheat study in Ethiopia showed that 90% of all the wheat grown in the country is CIMMYT-related, while an impact study for the maize program shows that 50% of the maize varieties in Africa are CIMMYT-derived. We are very proud of that – not for ourselves but for the people that we work for, the hundreds of millions of poor people and smallholder farmers who really rely on wheat and maize for their living and for their incomes,” he said.
Founder and Chief Executive Officer of East Africa-based Western Seed Company Saleem Esmail expressed optimism at the opportunities the project offers to improve livelihoods of beneficiaries. “I believe we can do this by sharing experiences and by leveraging on the impacts that this project is going to bring, from new technologies to new science approaches, particularly those that help save costs of seed production.”
He, however, observed that while the target of fast-tracking varietal turnover was great, it was a tough call, too, “because farmers are very risk averse and to change their habits requires a great deal of effort.”
On his part, director of Crop Research at the Oromia Agricultural Research Institute (OARI) in Ethiopia Tesfaye Letta revealed that from collaborative research work undertaken with CIMMYT, the institute has had access to better-quality varieties especially for wheat (bread and durum). These have helped millions of farmers to improve their productivity even as Ethiopia aims for wheat self-sufficiency by expanding wheat production under irrigation.
“We expect more support, from identifying wheat germplasm suitable for irrigation, developing disease resistant varieties and multiplying a sufficient quantity of early generation seed, to applying appropriate agronomic practices for yield improvement and organizing exposure field visits for farmers and experts,” he said.
Challenges and opportunities in a time of crisis
Alan Tollervey, head of agriculture research at Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO) and the UK representative to the CGIAR System Council, emphasized the need for continued investment in agricultural research to build a resilient food system that can cope with the demands and pressures of the coming decades. This way, organizations such as CIMMYT and its partners can adequately deliver products that are relevant not only to the immediate demands of poor farmers in developing countries – and the global demand for food generally – but also to address foreseen threats.
“We are at a time of intense pressure on budgets, and that is when projects are most successful, most relevant to the objectives of any organization, and most able to demonstrate a track record of delivery. CIMMYT has a long track history of being able to respond to rapidly emerging threats,” he said.
Felister Makini, the deputy director general for crops at the Kenya Agricultural Research Organization (KALRO) lauded the fact that AGG not only brings together maize and wheat breeding and optimization tools and technologies, but also considers gender and socioeconomic insights, “which will be crucial to our envisioned strategy to achieve socioeconomic change.”
Zambia Agriculture Research Organization (ZARI) maize breeder Mwansa Kabamba noted that the inclusion of extension workers will help to get buy-in from farmers especially as far as helping with adoption of the improved varieties is concerned.
In its lifecycle, the AGG project aims to reduce the breeding cycles for both maize and wheat from 5-7 years currently to 3-4 years. By 2024, at least 150,000 metric tons of certified maize seed is expected to be produced, adopted by 10 million households, planted on 6 million hectares and benefit 64 million people. It also seeks to serve over 30 million households engaged in wheat farming the target countries.
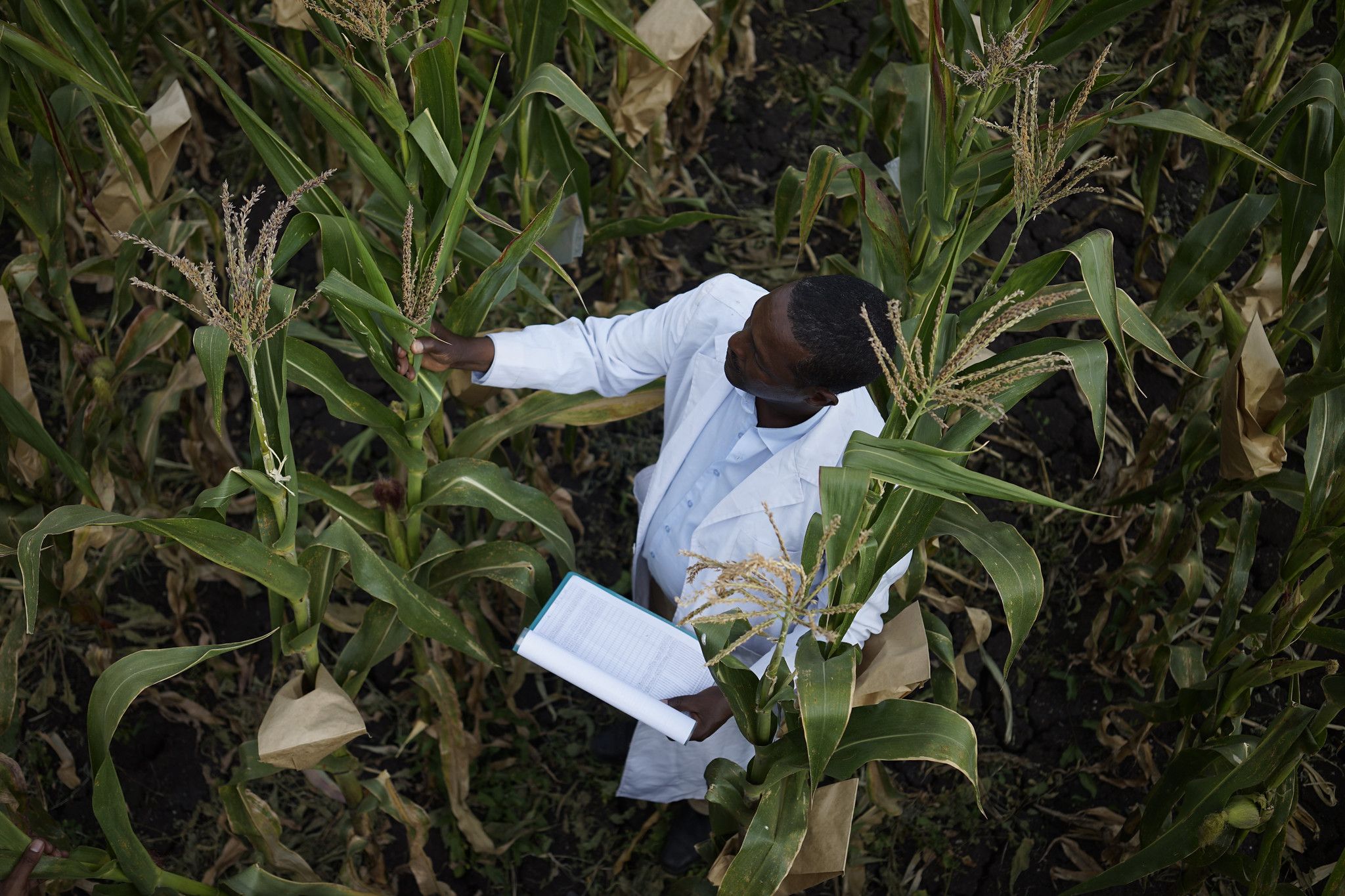
Cover photo: CIMMYT researcher Demewoz Negera at the Ambo Research Center in Ethiopia. (Photo: Peter Lowe/CIMMYT)