Work to develop high yielding Striga tolerant maize seed is bearing fruit
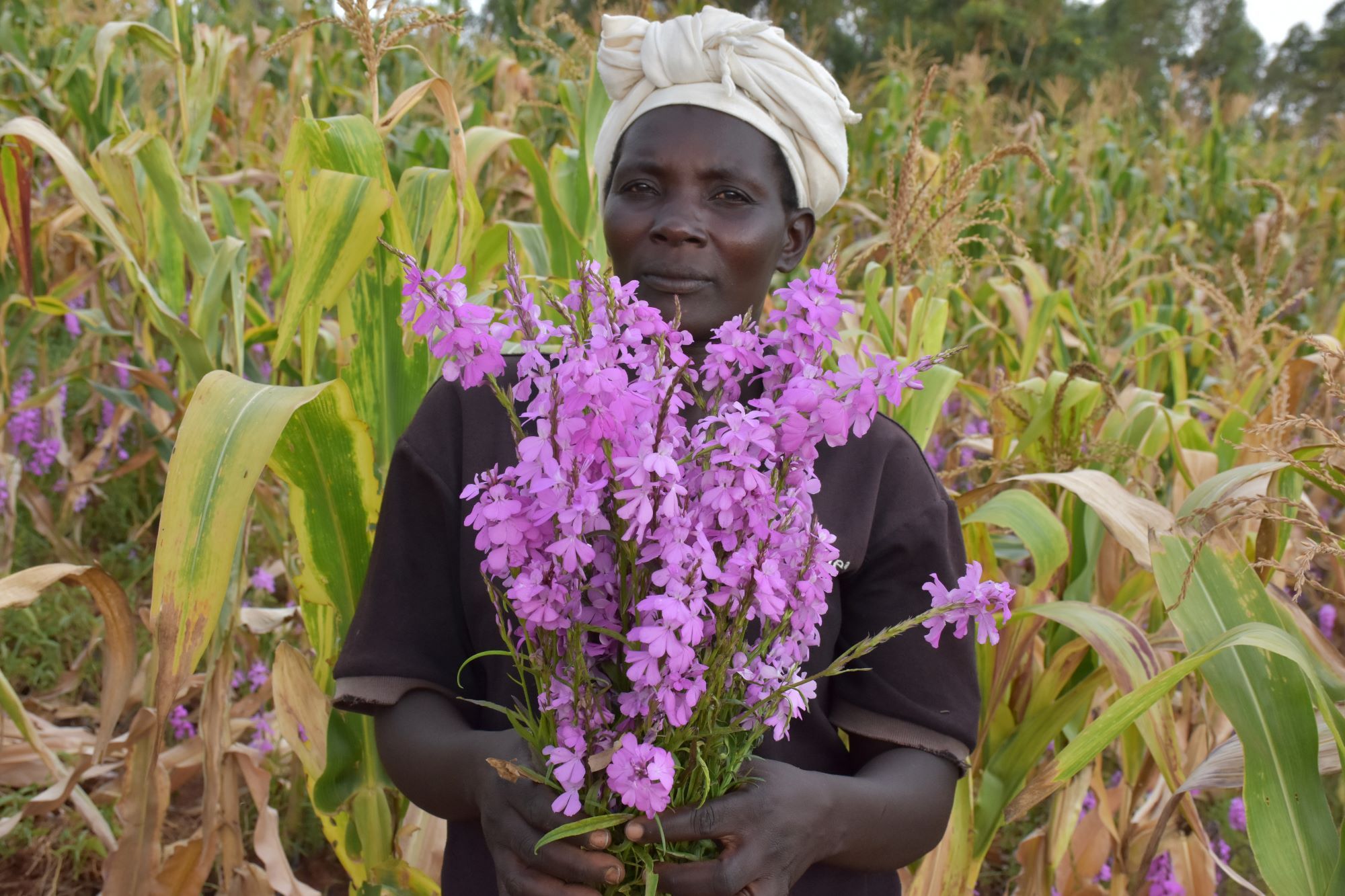
Striga, an invasive parasitic weed with purple-colored flowers, looks striking and harmless. But, beyond that mark of beauty, is a nutrient-sucking monster that stunts crops such as maize and sorghum, leaving affected farmers counting losses.
Witchweed thrives in poor soils with low rainfall conditions. It is prevalent in farming systems with poor crop management practices and in communities where farmers use minimal or no fertilizer. Once maize begins germinating in Striga-prevalent soil, it stimulates Striga seeds to germinate. Striga then attaches to the roots of the host plant, sapping nutrients from the plant, leading to stunting. The potential yield loss can reach up to 100%. Some farmers attempt to uproot it once they notice it germinating alongside their maize plantation, but this is often too late because damage is done as soon as the parasite attaches to the maize roots. When mature, the weed deposits tens of thousands of tiny seeds into the soil. This makes it very difficult for farmers to get rid of it.
To tackle this challenge, farmers need to apply inorganic fertilizer, which is not always affordable, or animal manure to enrich the soil before planting. They are also advised by researchers and extensionists to practice crop rotation or intercropping with legumes such as beans, soybean or groundnuts that restrict Striga’s germination. In the Assessment of Management Options on Striga Infestation and Maize Grain Yield in Kenya, for example, researchers recommend that Striga control measures include a combination of herbicide-resistant or maize varieties with native genetic resistance intercropped with legumes.
Nevertheless, while a few control measures have been moderately successful, the problem still persists, especially in western Kenya, eastern Uganda and lake zone of Tanzania, where farmers have frequently voiced their frustrations at the ubiquity of this invasive weed.
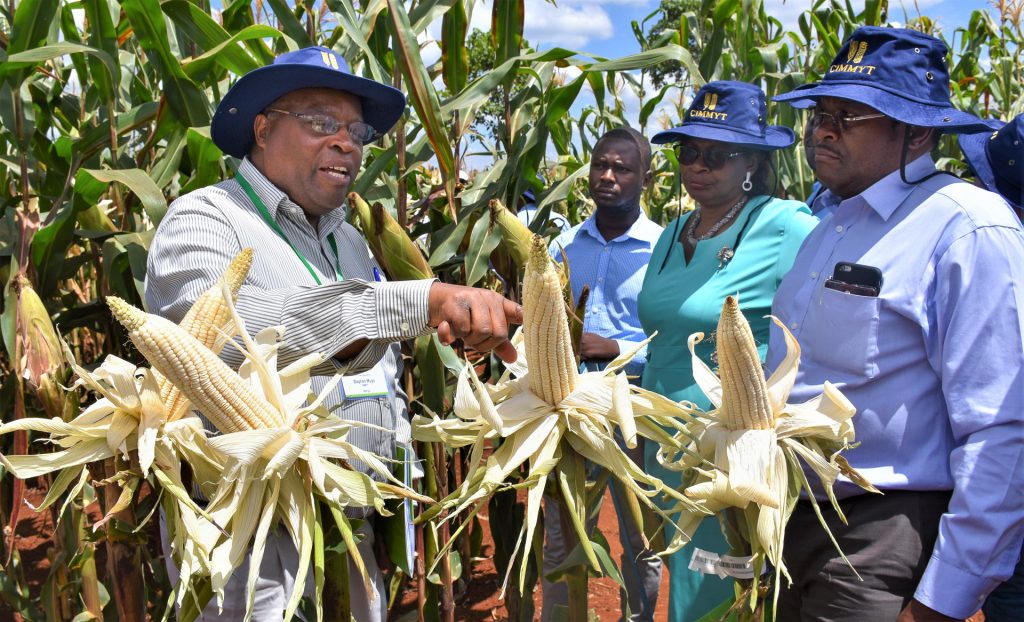
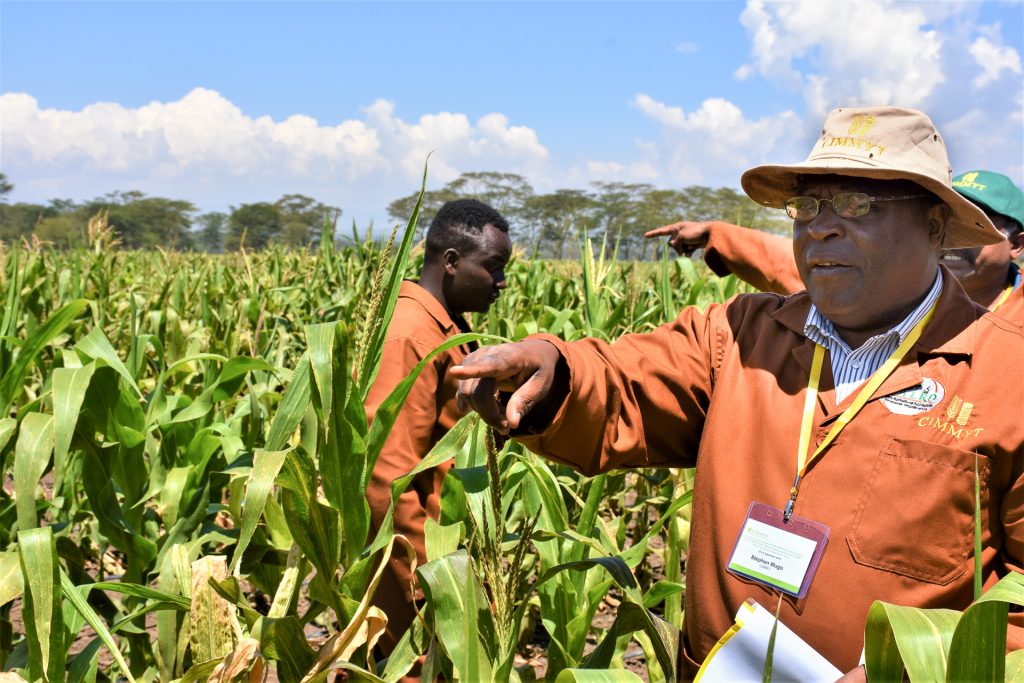
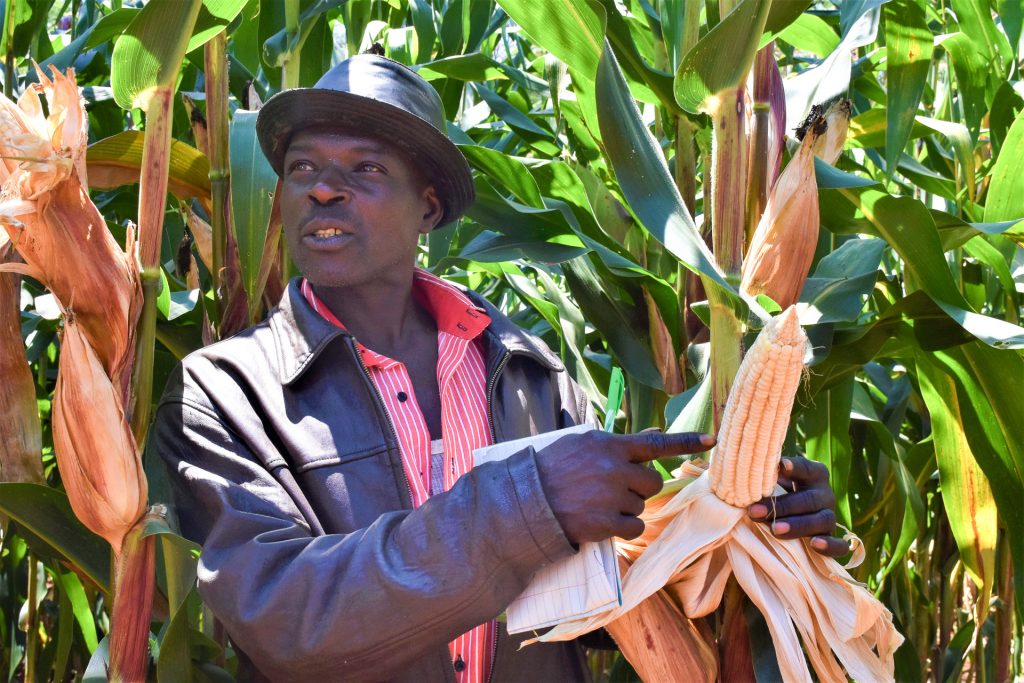
“While crop rotation with crops such as soybean or beans may break the cycle of Striga, its seed can stay in the soil and remain viable for up to 10 years,” says Dan Makumbi, a maize breeder with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), who is leading research efforts against the witchweed.
A blow to optimal yield potential
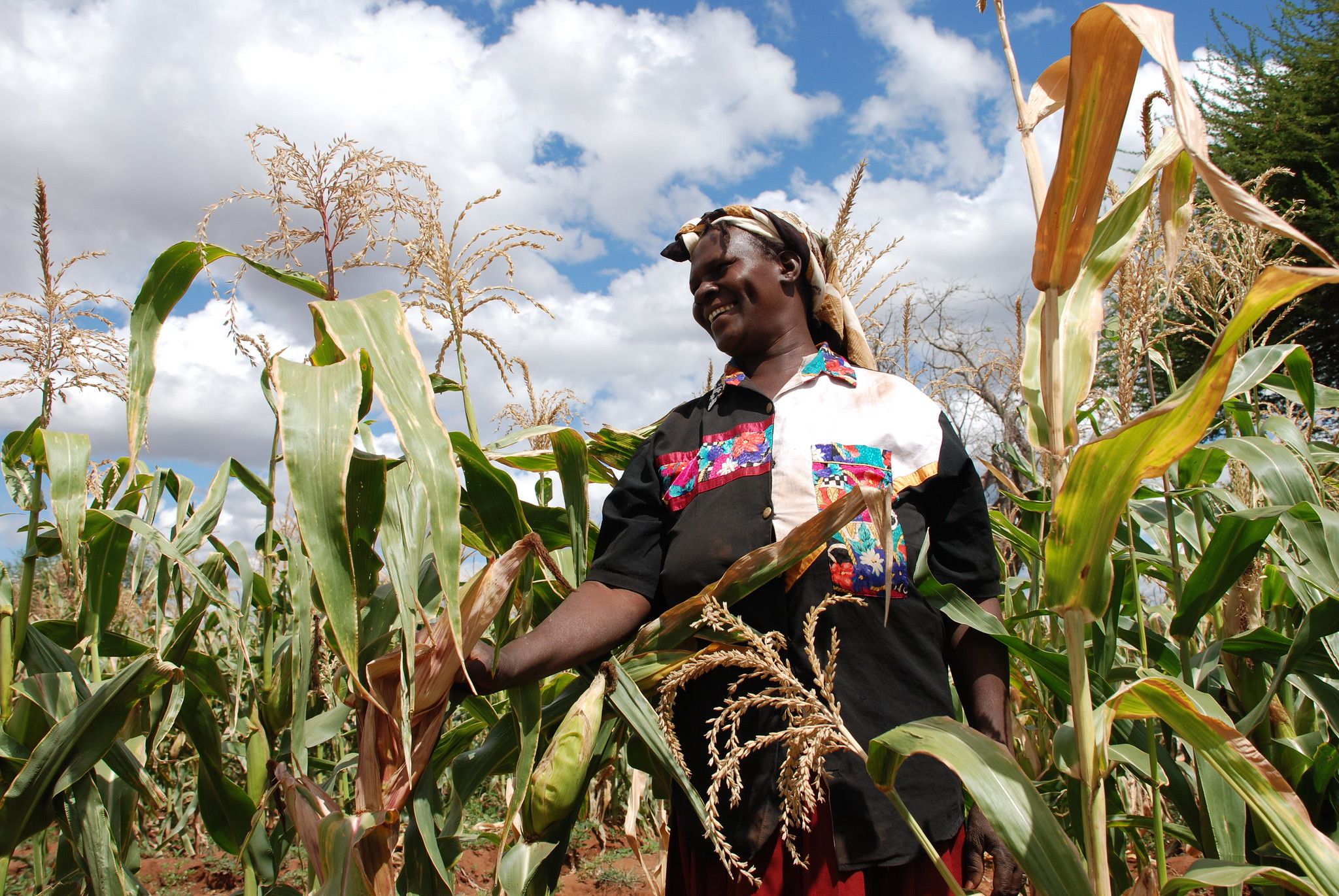
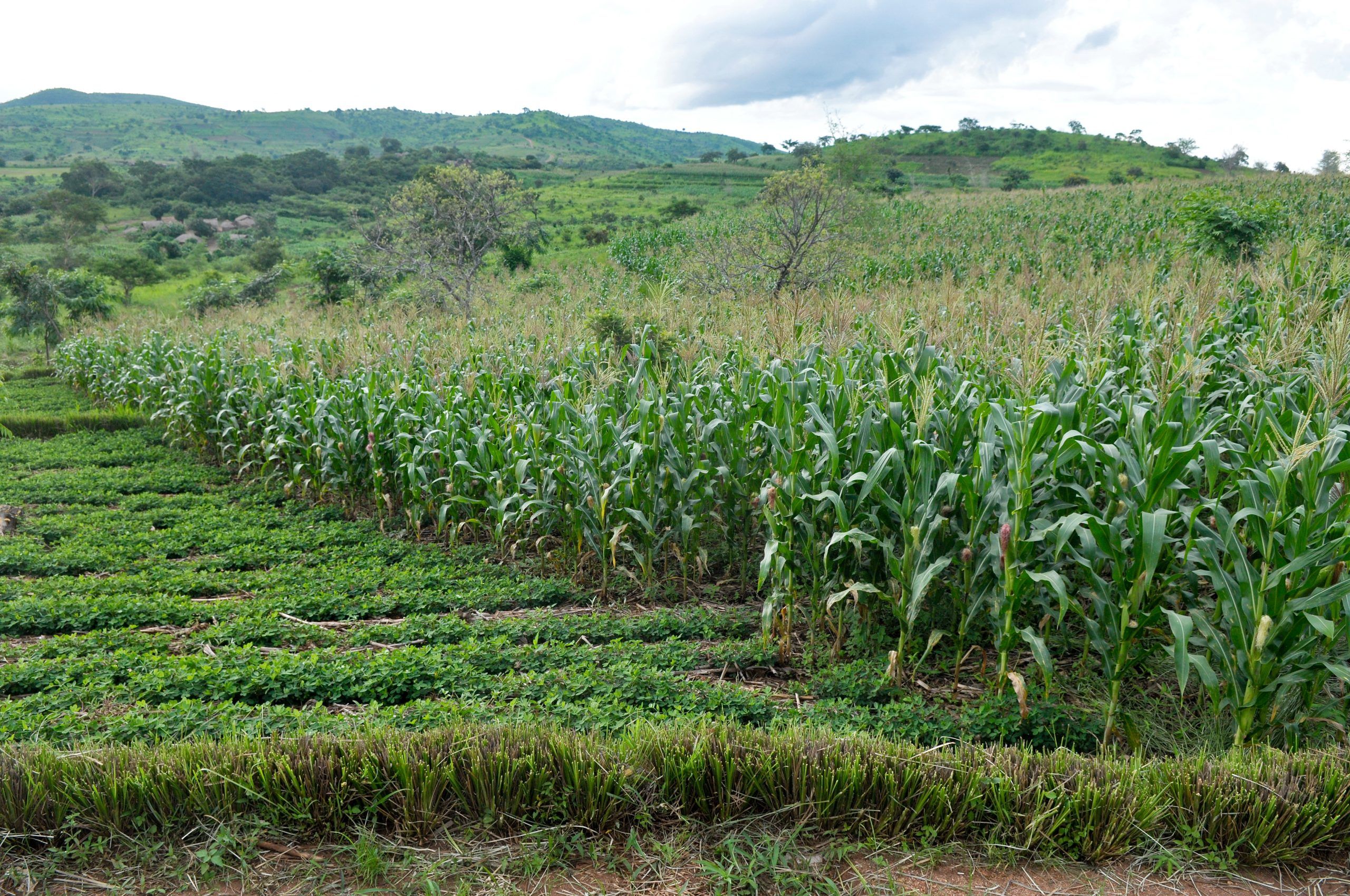
Maize is a staple crop that is predominantly cultivated by smallholder farmers in western Kenya and the lake region. It is an important source of food security and livelihoods of millions of people in the region, but constraints such as Striga prevent farmers from obtaining the crop’s ideal potential.
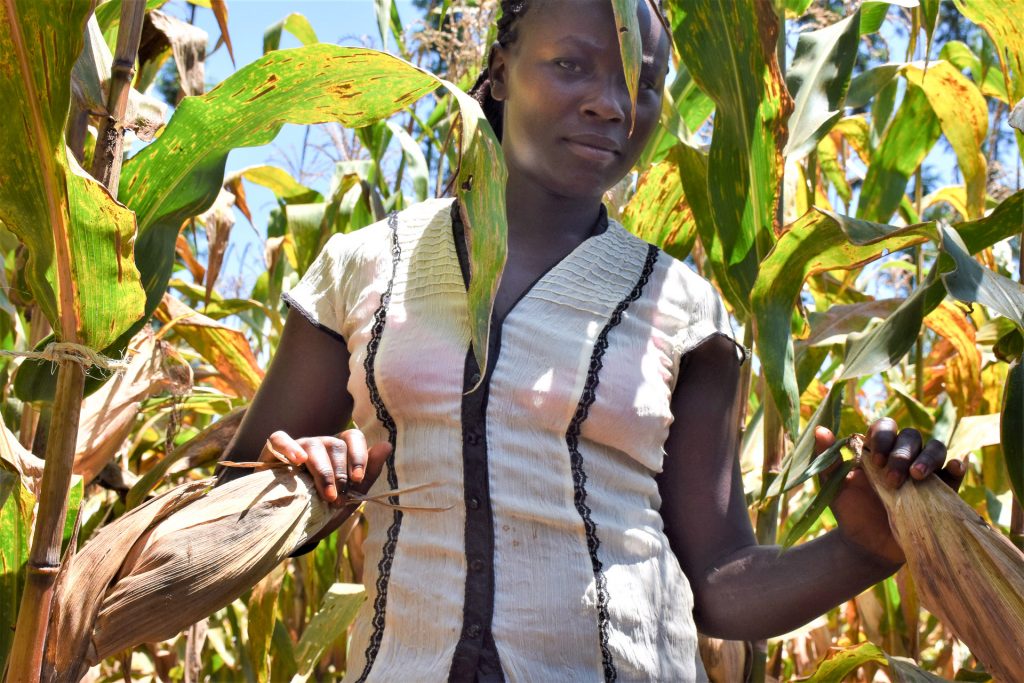
“The yield loss would have been adequate to cover my family’s food requirements for a year,” Naliaka said. “From two farming seasons, I could harvest a sufficient quantity of maize and sell some surplus to pay my children’s school fees. With the Striga menace, all that is but a dream.”
Just like Naliaka, Norah Kayugi, a 40-year-old widowed mother of six children from Siaya County in Kenya, has seen her maize production fall to less than 8 bags of 90kgs per acre. In normal circumstances, they would obtain at least 16 bags of maize per acre. The significant yield loss sets back many affected households in a big way, as they experience food shortage only a few months after harvest. Some divert their reduced incomes for food purchases, possibly leaving other priorities such as health and education of their children unattended.
Kayugi, who has been a farmer since 1997, now takes on casual jobs to supplement her farming in order to support her family, being the sole breadwinner following her husband’s demise years ago. “I plant vegetables, beans and maize to sustain my family. My one-acre farm yields about 10 bags of 90ks each. But I know for sure that were it not for this weed, the yield potential could reach 30 bags of 90kgs each per acre.”

Standing up to multiple farming stresses
These smallholders, like their counterparts elsewhere in sub-Saharan Africa, already face other farming challenges, including climate change-induced droughts, pests such as the fall armyworm, diseases like maize lethal necrosis (MLN), and declining soil fertility, among others. While CIMMYT has registered breakthroughs in developing maize varieties that tolerate such stresses, on-going efforts against Striga are also taking shape, challenges notwithstanding.
The development and deployment of the imazapyr-resistant (IR) maize has been one such instance of effective Striga control. With this method, herbicide-resistant maize seeds are coated with herbicide. The seed germinates and absorbs some of the herbicide used to coat it. The germinating maize stimulates Striga to germinate and as it attaches to the maize root, it is killed before it can cause any damage. Despite its effectiveness, sustaining this technology presented a major challenge to seed companies.
“It was costly for seed companies, as they needed to establish and sustain the operation of separate seed treatment units dedicated to production of the herbicide-coated maize seed. Once you establish a line to dress the seed with the chemical, you cannot use it to treat any other seeds as the chemical will destroy them,” said Makumbi.
Seed companies — like NASECO in Uganda, Kenya Seed Company in Kenya, Western Seed Company and FreshCo in Kenya, and Meru Agro in Tanzania — obtained financial and technical support from a partnership initiative coordinated by African Agricultural Technology Foundation (AATF) and backed by CIMMYT to scale commercialisation of StrigAwayTM maize in East Africa. The initiative was funded by USAID’s Feed the Future Partnering for Innovation program through Fintrac and it supported the seed companies to establish seed treatment facilities to handle herbicide resistant maize. This allowed each of the companies to have a fully dedicated facility for herbicide resistant maize seed processing. “Right now, herbicide resistant maize hybrid seed is available on the market in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda,” Makumbi said.

Native hope
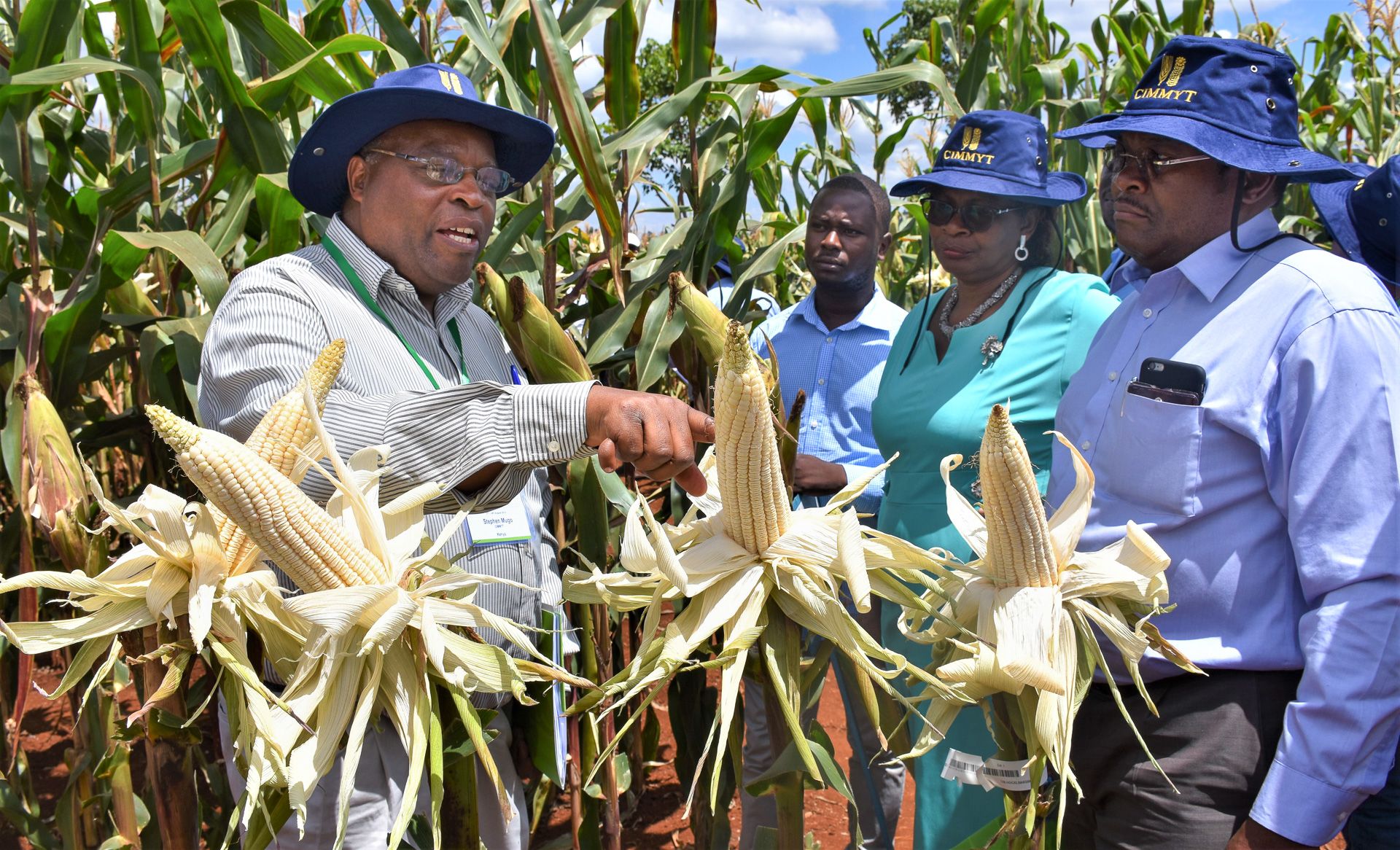
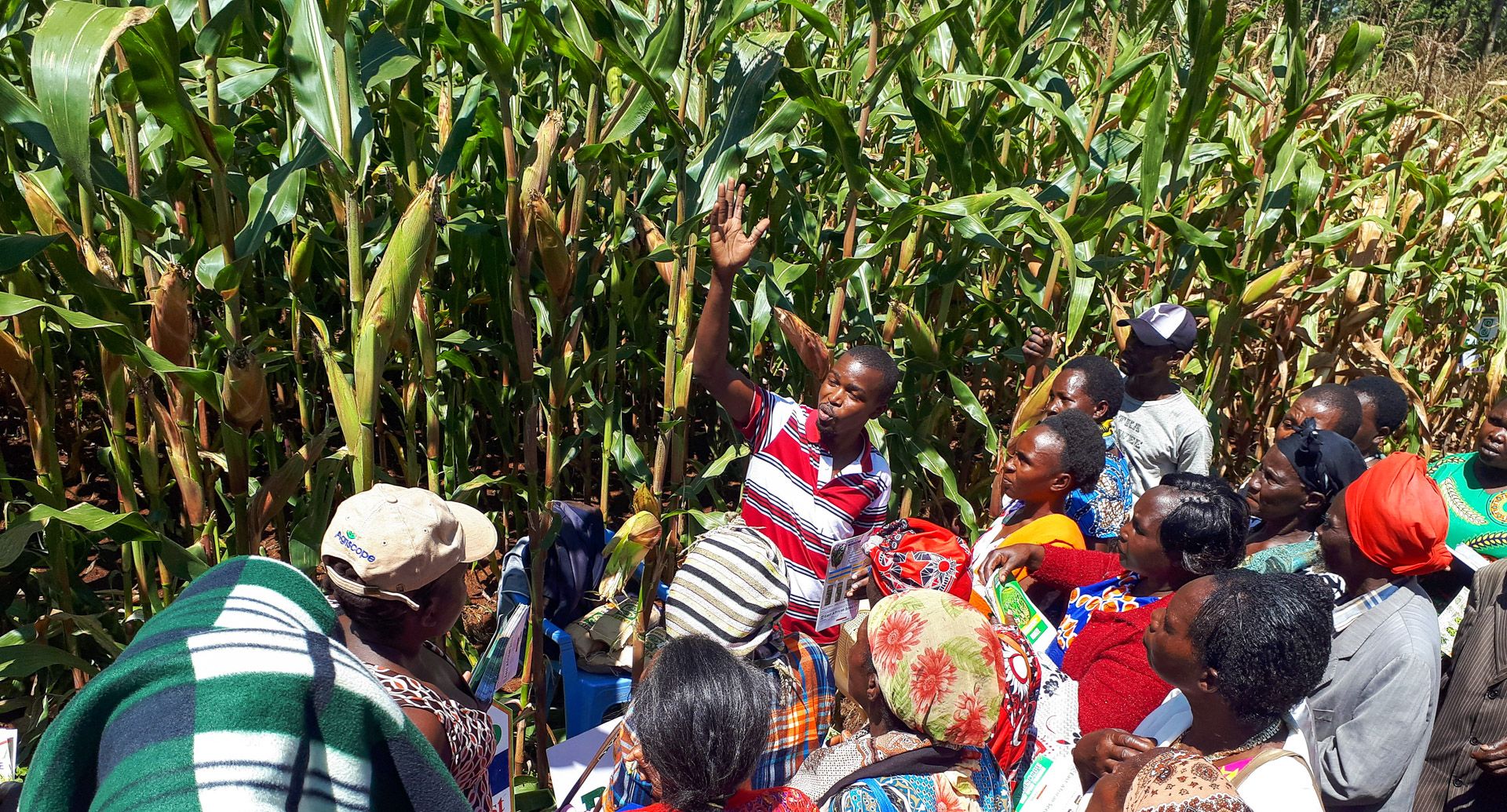
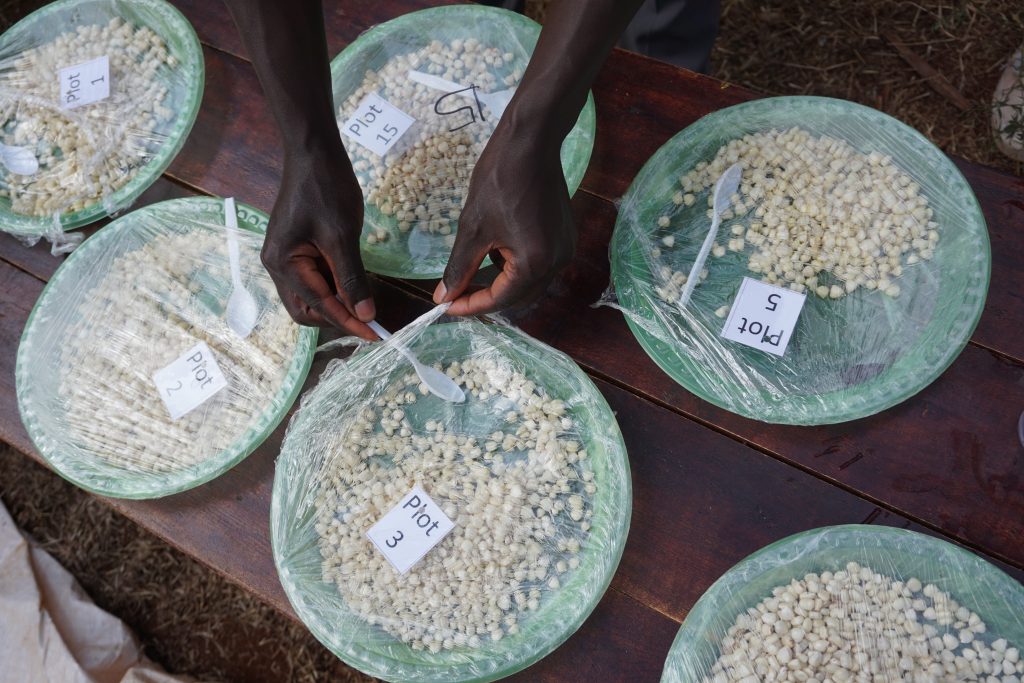
In the past few years, Makumbi and his team, in collaboration with the International Institute for Tropical Agriculture (IITA) and the Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO), have redirected their efforts towards breeding for native genetic resistance to Striga. This means developing seeds which are naturally resistant to Striga, reducing the need for herbicides. The early indication is that there are several parental lines showing potential to tolerate or resist Striga, and these are being used to develop hybrids. The hybrids, which offer multiple benefits for farmers, are under wide scale testing in Kenya.
“In our tests, we are not only looking at Striga resistance alone but also other important traits such as good yield under optimal conditions, drought stress and low soil fertility, resistance to major foliar diseases including gray leaf spot, Turcicum leaf blight, maize streak virus and ear rots,” Makumbi noted.
As these breeding efforts continue, there is light at the end of the tunnel. The hope of farmers taking back full control of their maize farms from Striga’s “bewitching ways” in the near future remains alive.