Location: Ethiopia
For more information, contact CIMMYT’s Ethiopia office.
Isaiah Nyagumbo
Isaiah Nyagumbo is a cropping systems agronomist working with CIMMYT’s Sustainable Agrifood Systems (SAS) program. He is passionate about soil and water conservation technologies, and participatory technology development for farmers.
Prior to joining CIMMYT in 2010, he completed a DPhil on seasonal water balance in conservation tillage systems and spent several years working as a lecturer at the University of Zimbabwe.
As part of the SIMLESA team, he has mainly works on developing sustainable and resilient conservation agriculture-based production systems in southern Africa, where he is regional coordinator of agronomy activities.
Improved Maize for African Soils (IMAS)
African maize farmers must deal with drought, weeds, and pests, but their problems start with degraded, nutrient-starved soils and their inability to purchase enough nitrogen fertilizer. Maize yields of smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa are a fraction of those in the developed world, due mainly to the region’s poor soils and farmers’ limited access to fertilizer or improved maize seed. On average, such farmers apply only 9 kilograms of fertilizer per hectare of cropland. Of that small amount, often less than half is captured by the crop; the rest is leached deep into the soil where plants cannot recover it or otherwise lost.
The Improved Maize for African Soils Project (IMAS) develops maize varieties that are better at capturing the small amount of fertilizer that African farmers can afford, and that use the nitrogen they take up more efficiently to produce grain. Project participants will use cutting-edge biotechnology tools such as molecular markers—DNA “signposts” for traits of interest—and transgenic approaches to develop varieties that ultimately yield 30 to 50 percent more than currently available varieties, with the same amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied or when grown on poorer soils.
The varieties developed will be made available royalty-free to seed companies that sell to the region’s smallholder farmers, meaning that the seed will become available to farmers at the same cost as other types of improved maize seed.
In four years or less, African farmers should have access to IMAS varieties developed using conventional breeding that offer a 20 percent yield advantage over current varieties. Improved varieties developed using DNA marker techniques are expected to be introduced within seven to nine years, and those containing transgenic traits are expected to be available in approximately 10 years, pending product performance and regulatory approvals by national regulatory and scientific authorities, according to the established laws and regulatory procedures in each country.
IMAS is being led by CIMMYT and funded with $19.5 million in grants from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the U.S. Agency for International Development. The project’s other partners — DuPont-Pioneer, Kenya Agricultural Livestock and Research Organization and the Agricultural Research Council of South Africa — are also providing significant in-kind contributions including staff, infrastructure, seed, traits, technology, training, and know-how.
The second phase of IMAS continues to be implemented through the Seed Production Technology for Africa (SPTA) project.
OBJECTIVES
- Conventional and marker assisted breeding to develop hybrids and OPVs with improved nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) adapted to southern and eastern Africa
- Identification and deployment of native trait alleles to enhance yield under low nitrogen conditions through association mapping and Quantitative Trait Loci mapping
- Development of transgenic maize varieties adapted to southern and eastern Africa with increased yield under severe nitrogen limitation
- Managing NUE varieties for sustainability in African maize cropping systems
- Project stewardship, public awareness and capacity building
- NUE variety registration, release and dissemination in southern and eastern Africa
Ethiopia Wheat Rust Scaling
Wheat is a traditional crop cultivated by about five million households on 1.6 million hectares in Ethiopia. Despite the country’s huge potential, the average wheat productivity of 2.5 tonnes per hectare is lower than the global average of 3 tonnes per hectare. Stem rust and yellow rust diseases caused by Pucccinia spp. are the major biotic constraints for wheat production in the country and recent recurrent outbreaks have debilitated many wheat varieties in major production areas in Ethiopia.
Projects to accelerate seed multiplication of rust resistant varieties funded by the U.S. Agency for International Development, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and others contributed to the replacement of the widely grown susceptible varieties Kubsa and Galama. However, in 2013–2014, a new Pgt race, identified as TKTTF, unrelated to the highly virulent Ug99 rust disease, which is also present in Ethiopia, caused 100 percent yield losses on bread wheat variety Digalu in some regions.
The Ethiopia Wheat Rust Scaling seed and surveillance project aims to develop, demonstrate and scale up high-yielding wheat varieties with adult plant resistance to prevailing rust pathogens with the following objectives: enhancement of rust surveillance; early warning and phenotyping; fast-track variety testing and pre-release seed multiplication to assure availability of rust resistant improved wheat varieties for distribution in targeted districts; accelerating seed multiplication of durable rust resistant wheat varieties through the formal and informal seed systems; demonstration and scaling up of improved wheat varieties and improving linkages between small scale durum wheat producers and agro-industries with the aim of creating market access to smallholder durum wheat producers.
The project includes conducting wheat rust surveys, training and field days. Farmer cooperative unions are being organized in clusters and women and youth groups will participate in informal seed production. The number of private seed enterprises and women farmers participating in the accelerated informal seed multiplication program will be increased as the project progresses in consultation with stakeholders.
CIMMYT worked with the Durable Rust Resistance in Wheat project to import of 5 tons of stem rust resistant bread wheat variety “Kingbird” and the U.S. Department of Agriculture Cereal Disease Laboratory, the University of Minnesota and Washington State University in phenotyping and genotyping of commercial cultivars and elite materials from the national wheat research program, respectively.
Objectives
- Enhancement of rust surveillance, early warning and phenotyping.
- Fast-track variety testing and pre-release seed multiplication to assure availability of rust resistant improved wheat varieties for distribution in targeted districts.
- Accelerating seed multiplication of durable rust resistant wheat varieties through the formal and informal seed systems.
- Demonstration and scaling up of improved wheat varieties.
- Improving linkages between small scale durum wheat producers and agro-industries with the aim of creating market access to smallholder durum wheat producers in 10 districts.
Farm Mechanization and Conservation Agriculture for Sustainable Intensification (FACASI)
Agricultural intensification is both a need and an opportunity for countries in sub-Sahara Africa. For intensification to occur sustainably — with minimum negative environmental and social consequences — it is widely recognized that resources must be used with much greater efficiency. Although much emphasis is being placed in current research for development work on increasing the efficiency with which land, water and nutrients are being used, farm power appears as the “forgotten resource.” However, farm power in countries sub-Saharan Africa is declining due to the collapse of most hire tractor schemes, the decline in number of draft animals and the decline in human labor related to rural-urban migration. Another aspect of low farm power is high labor drudgery, which affects women, who generally due the majority of threshing, shelling and transport by head-loadings, disproportionally. Undoubtedly, sustainable intensification in these countries will require an improvement of farm-power balance through increased power supply — via improved access to mechanization — and/or reduced power demand – via energy saving technologies such as conservation agriculture techniques.
The Farm Mechanization and Conservation Agriculture for Sustainable Intensification project examines how best to exploit synergies between small-scale-mechanization and conservation agriculture. The overall goal of the project is to improve farm power balance, reduce labour drudgery, and minimize biomass trade-offs in Eastern and Southern Africa, through accelerated delivery and adoption of two-wheel-tractor-based technologies by smallholders.
This project is now in the second phase, which began on June 1, 2017.
OBJECTIVES
- To evaluate and demonstrate two wheel tractor-based technologies in the four selected sites of Eastern and Southern Africa, using expertise/knowledge/skills/implements from Africa, South Asia and Australia
- To test site-specific market systems to deliver two wheel tractor-based mechanization in the four countries
- To identify improvements in national markets and policies for wide delivery of two wheel tractor-based mechanization
- To create awareness on two wheel tractor-based technologies in the sub-region and share knowledge and information with other regions
Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale in Africa (TAMASA)
Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale in Africa (TAMASA) is a 4-year project seeking to improve productivity and profitability for small-scale maize farmers in Ethiopia, Nigeria and Tanzania.
The overall purpose of TAMASA is to use innovative approaches to transform agronomy that:
- Use available geospatial and other data and analytics to map maize areas, soil constraints, and actual and yields at different scale.
- Work with service providers (i.e. input suppliers, government and private research and extension services, agro-dealers, and others) to identify and co-develop systems and applications that transform this data and information to useable products that support their businesses or programs to reach clients more effectively
- Build capacity in national programs to support and sustain these approaches.
The core products and services of this project include:
- Annual assessments and digital maps of maize growing areas, actual and attainable yields in core research areas or focal areas.
- Decision-support tools for ex-ante spatial analysis, nutrient management, fertilizer formulation and variety selection.
- Open-access databases of agronomic data.
- Increased capacity in national programs and partners through in-country data science and software application training and mentoring.
How the data revolution could help design better agronomic investments
What fertilizer application will give me the best returns? What maize crop variety should I use?
Each farmer faces constraints related to weather uncertainty, soil fertility management challenges, or access to finance and markets. To improve their yields and incomes, African smallholder farmers need agronomic advice adapted to their specific circumstances. The challenge is even greater in sub-Saharan Africa, where agricultural production landscapes are highly diverse. Yet traditional agronomic research was not designed to fit with complex agroecological regions and farming systems. Compounding the problem, research organizations often have limited resources to develop the necessary experiments to generate farm- and site-specific agronomic advice at scale.
“Agronomic research is traditionally not equipped to consider spatial or socio-economic diversity among the millions of farmers it targets,” said Sebastian Palmas, data scientist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) in Nairobi, Kenya.
Palmas presented some of the learnings of the Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale in Africa (TAMASA) project during a science seminar called “A spatial ex ante framework for guiding agronomic investments in sub-Saharan Africa” on March, 4, 2019.
The project, funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, has used data to improve the way agronomic research for development is done. Researchers working on the TAMASA project addressed this challenge by using available geospatial information and other big data resources, along with new data science tools such as machine learning and Microsoft’s AI for Earth. They were able to produce and package information that can help farmers, research institutions and governments take better decisions on what agronomic practices and investments will give them the best returns.
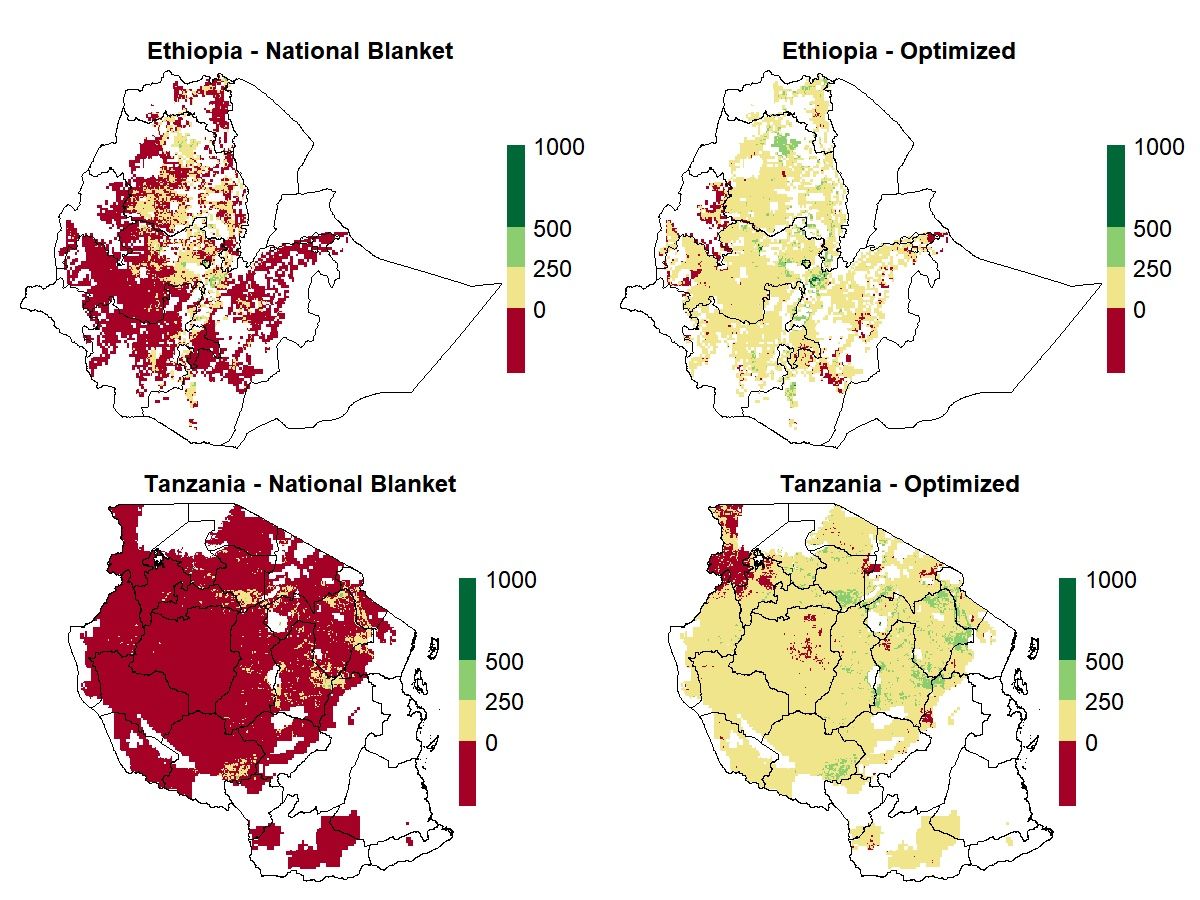
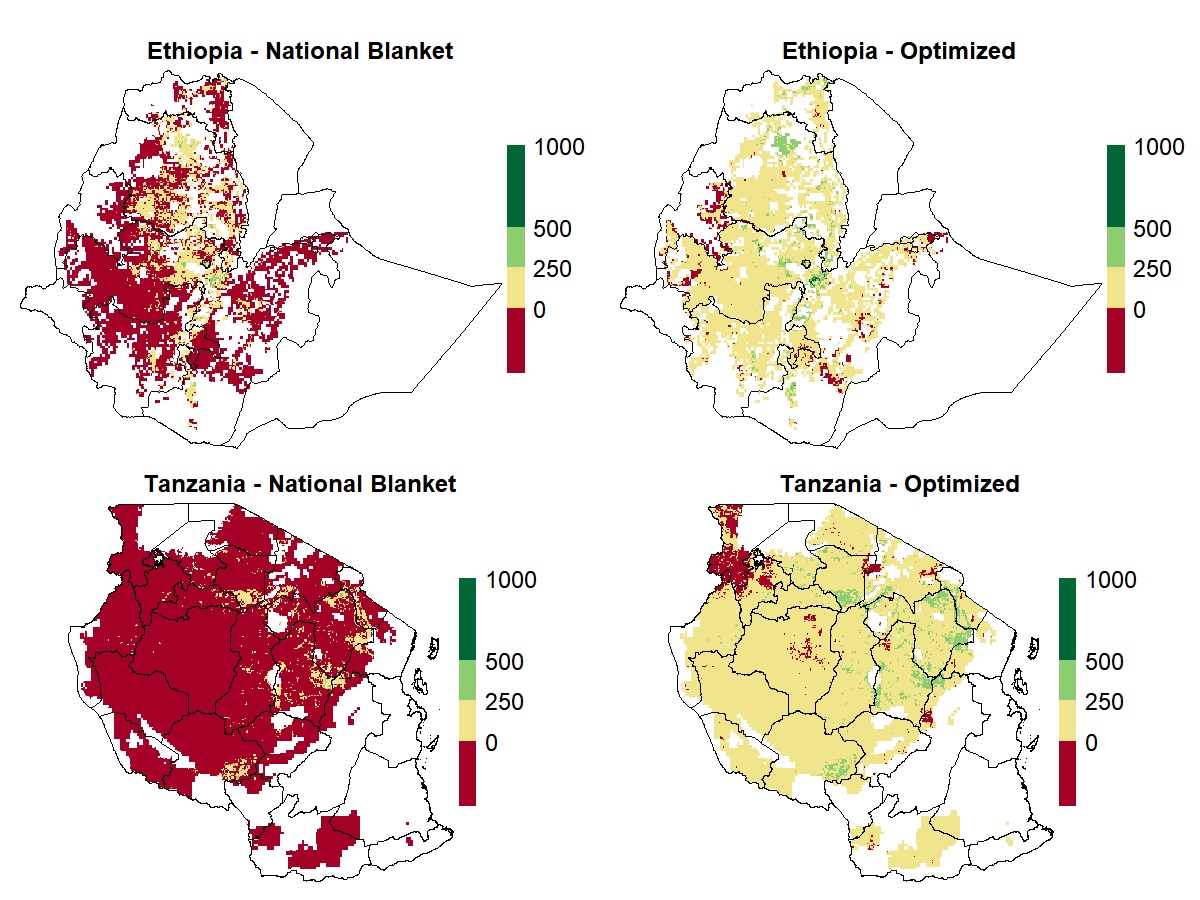
By adapting the Quantitative Evaluation of the Fertility of Tropical Soils (QUEFTS) model to the conditions of small farmers in TAMASA target countries (Ethiopia, Nigeria and Tanzania), using different layers of information, CIMMYT and its partners have developed a versatile geospatial tool for evaluating crop yield responses to fertilizer applications in different areas of a given country. Because calculations integrate spatial variation of fertilizer and grain prices, the tool evaluates the profitability — a key factor influencing farmers’ fertilizer usage — for each location. The project team can generate maps that show, for instance, the estimated agronomic and economic returns to different fertilizer application scenarios.

Making profits grow
These tools could potentially help national fertilizer subsidy programs be more targeted and impactful, like the ambitious Ethiopia’s Fertilizer Blending initiative which distributes up to 250,000 tons of fertilizer annually. Initial calculations showed that, by optimizing diammonium phosphate (DAP) and urea application, the profitability per hectare could improve by 14 percent on average, compared to the current fertilizer recommendations.
Such an approach could generate farm-specific advice at scale and boost farmers’ incomes. It could also provide insights on many different issues, like estimating market demand for a new fertilizer blend, or the estimated quantity of additional fertilizer required to bring about a targeted maize yield increase.
Future extensions of the framework may incorporate varietal differences in nutrient management responses, and thus enable seed companies to use the framework to predict where a new maize hybrid would perform best. Similarly, crop breeders could adapt this ex ante assessment tool to weigh the pros and cons of a specific trait and the potential impact for farmers.
The TAMASA team plans to publish the code and user-friendly interface of this new geospatial assessment tool later this year.
Maize Lethal Necrosis Diagnostics and Prevention of Seed Transmission
This four-year Maize Lethal Necrosis Diagnostics and Prevention of Seed Transmission project will coordinate regional efforts to strengthen response to the rapid emergence and spread of Maize Lethal Necrosis (MLN).
Coordinated by CIMMYT, it will establish a community of practice among national plant protection organizations in eastern Africa for implementing harmonized MLN diagnostic protocols for detecting MLN-causing viruses and enable commercial seed companies to implement necessary standard operational procedures to produce MLN-free clean seed at various points along the maize seed value chain. It will also step-up MLN surveillance and monitoring in Malawi, Zambia and Zimbabwe, three of the major commercial maize seed exporting countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
The MLN project will be implemented in close partnership with the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa, the African Agricultural Technology Foundation, national plant protection organizations and commercial seed companies in eastern Africa. It will also pool expertise from relevant public- and private-sector partners, regional organizations, and seed trade organizations operating in the region.
Partners: The Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa, the African Agricultural Technology Foundation, national plant protection organizations and commercial seed companies in eastern Africa
Nutritious Maize for Ethiopia (NuME)
Nutritious Maize for Ethiopia (NuME) is implemented in collaboration with research institutions, international non-governmental organizations, universities and public and private seed companies in Ethiopia.
Through the development and dissemination of new maize varieties, including quality protein maize (QPM), and the deployment of improved agronomic practices, NuME is helping to reduce food insecurity by strengthening Ethiopia’s capacity to feed itself.
NuME brings QPM to rural maize producers in the Ethiopian maize belt and beyond, where consumers – especially young children and women – are at risk of lysine deficiency. Since 2003, the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research and CIMMYT have made good progress in breeding, resulting in new QPM hybrids and open-pollinated varieties adapted to all major maize-producing agro-ecologies in Ethiopia, including the high-potential mid-altitude and highland zones, as well as adapted to drought-prone zones.
Partners: Ethiopian research institutions, international non-governmental organizations, universities and public and private seed companies
Sustainable Intensification of Maize-Legume Systems for Food Security in Eastern and Southern Africa (SIMLESA)
The Sustainable Intensification of Maize-Legume Systems for Food Security in Eastern and Southern Africa (SIMLESA) program aims to improve maize and legume productivity by 30 percent and to reduce the expected downside yield risk by 30 percent on approximately on approximately 650,000 farm households by 2023. Launched in 2010, the focal countries of program research are Australia, Botswana, Burundi, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
The main thrust of the SIMLESA program is increasing farm-level food security, productivity and incomes through promotion of maize-legume intercropping systems in the context of reduced climate risk and change.
The program has also laid the foundation for developing conservation agriculture based sustainable intensification options, including integration of improved maize and legume varieties identified for their compatibility with CA-based practices; promoting technology adoption by both female and male farmers; capacity building for national agricultural research systems of partner countries; creating enhanced partnerships and collaboration with established innovation platforms for coordinated scaling-out of SIMLESA-generated options and practices.
Funding Institutions: Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR)
Partners: National agricultural systems of Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania, as well as international and local research centers, extension agencies, non-governmental organizations, universities and agribusinesses along the value chain.
Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa Seed Scaling (DTMASS)
The Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa Seed Scaling (DTMASS) project was officially launched in 2014 with the aim to meet demand and improve access to good-quality maize through production and deployment of affordable and improved drought-tolerant, stress-resilient and high-yielding maize varieties for smallholder farmers.
Led by CIMMYT and implemented through in-country public and private partnerships, DTMASS emphasizes scaling up and scaling out of drought tolerant maize seed, and uptake of the same among smallholder farmers. Over its lifespan, the project aims to produce close to 12,000 metric tons of certified seed for use by approximately 400,000 households, or 2.5 million people, in six countries in eastern and southern Africa.
DTMASS target countries (Ethiopia, Kenya, Mozambique, Tanzania, Uganda and Zambia) account for 25 percent, or 252 million, of the people in sub-Saharan Africa, and 41 percent of the maize production areas. DTMASS builds on the progress made by Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa and other complementary CIMMYT maize projects in Africa, including Improved Maize for African Soils and Water Efficient Maize for Africa.
Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA)
The Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) project aims to diminish devastating constraints in maize production across sub-Saharan Africa. The project develops improved maize varieties with resistance and tolerance to drought, low soil fertility, heat, diseases such as Maize Lethal Necrosis and pests affecting maize production areas in the region.
STMA operates in eastern (Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda), southern (Malawi, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe) and West Africa (Benin, Ghana, Mali, Nigeria). These countries account for nearly 72 percent of all maize area in sub-Saharan Africa and include more than 176 million people who depend on maize-based agriculture for their food security and economic well-being. Climate change effects like drought, a lack of access to resources like fertilizer and other stresses increase the risk of crop failure that negatively affects income, food security and nutrition of millions of smallholder farmers and their families.
The project will develop 70 new stress-tolerant varieties using innovative modern breeding technologies, and promote improved stress-tolerant varieties expected to increase maize productivity up to 50 percent. The project aims to produce estimated 54,000 tons of certified seed to put into the hands of more than 5.4 million smallholder farmer households by the end of 2019.
Objectives
- Use innovative breeding tools and techniques applied for increasing the rate of genetic gain in the maize breeding pipeline.
- Increase commercialization of improved multiple-stress-tolerant maize varieties with gender-preferred traits by the sub-Saharan African seed sector.
- Increase seed availability and farmer uptake of stress-tolerant maize varieties in target countries.
- Optimize investment impact through effective project oversight, monitoring, evaluation and communication.
Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA)
The Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa project aims to mitigate drought and other constraints to maize production in sub-Saharan Africa, increasing maize yields by at least one ton per hectare under moderate drought and with a 20 to 30 percent increase over farmers’ current yields, benefiting up to 40 million people in 13 African countries. The project brings together farmers, research institutions, extension specialists, seed producers, farmer community organizations and non-governmental organizations. It is jointly implemented by CIMMYT and the International Institute for Tropical Agriculture, in close collaboration with national agricultural research systems in participating nations. Millions of farmers in the region are already benefiting from the outputs of this partnership, which includes support and training for African seed producers and promoting vibrant, competitive seed markets.
Achievements:
- Between 2007 and 12, participants marketed or otherwise made available 60 drought tolerant hybrids and 57 open-pollinated varieties to smallholder farmers
- In addition to drought tolerance, the new varieties and hybrids also possess such desirable traits as resistance to major diseases
- Engage government officials in policy dialogue to help fast-track varietal releases and fosters competitive seed markets and more
widespread access to quality seed at affordable prices - Help ensure farmers’ access to the best possible products and services, coordinate various capacity-building events and
activities for maize breeders, technicians, seed producers, extension workers, non-government organizations and farmer groups - Provide technical and advisory support to 50 African undergraduate and 28 African graduate students
- Expand smallholder farmers’ use of drought and other stress tolerant maize seed to benefit 30 to 40 million people and provide added grain worth $160-200 million each year in drought-affected areas of sub-Saharan Africa
Principal coordinator
Tsedeke Abate
Ethiopia calls for continued collaboration to increase wheat production and meet nutritional and food security

The Ethiopian wheat sector has seen progress since the early 2000s, more than doubling the average farm yields from 1.13 tons per hectare in 1998/99 to 2.74 tons per hectare in 2017/18. Progressive farmers who plant improved wheat varieties and follow recommended agronomic practices could harvest four to six tons per hectare in high-potential wheat growing areas. However, the production is not keeping up with the growing wheat demand: imports reached over 1.5 million tons last year. The Ethiopian government has announced recently that the country should become wheat self-sufficient over the next four years.
One of the biggest wheat production challenges in Ethiopia has been the stem rust and yellow rust diseases caused by Pucccinia spp, which severely affected popular wheat varieties like Kubsa, Galema and Digalu that wiped out from production.
In response to these losses, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) started an emergency project to multiply and disseminate rust-resistant wheat varieties in the affected regions in 2014, with support from USAID.
The following year, CIMMYT launched the Seed Multiplication and Delivery of High Yielding Rust Resistant Bread and Durum Wheat Varieties to Ethiopian Farmers project. It benefitted people in 54 woredas (districts) of 4 regions: Amhara, Oromia, SNNP and Tigray. CIMMYT collaborated with the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR), regional agricultural research institutes and the regional bureaus of agriculture.
This wheat seed scaling project wrapped up with a closure workshop on March 7, 2019. Organized by CIMMYT and EIAR, it gathered representatives from USAID, policymakers, researchers and other governmental and non-governmental institutions.
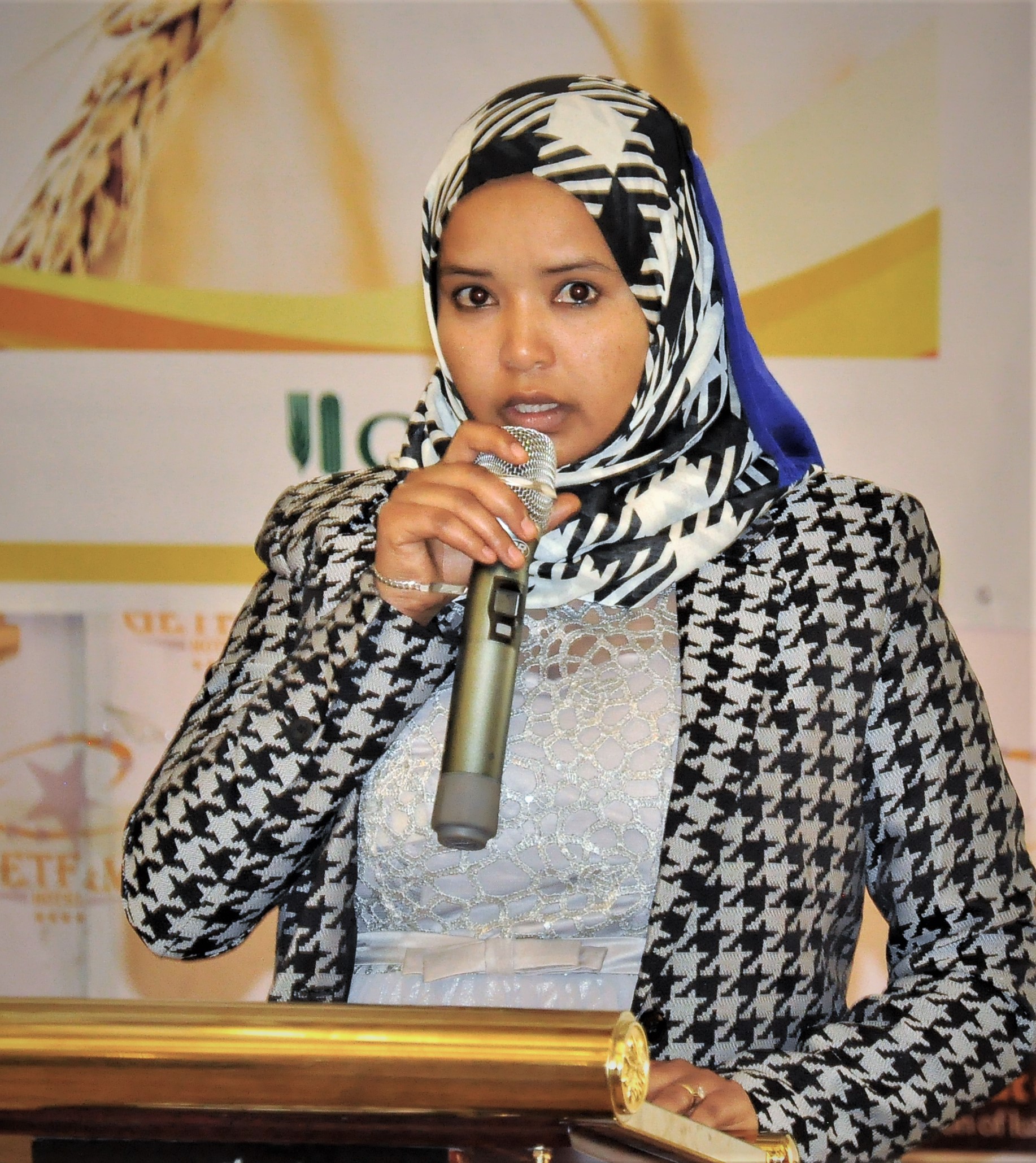

State minister of agriculture Aynalem Nigussie noted that the project boosted farmers’ productivity thanks to better seeds, improved farming practices and increased knowledge to deal with wheat rust diseases. She recognized that the project aligned with national priorities, as the government is devising a new seed policy to address the current challenges of the Ethiopian wheat seed sector.
CIMMYT’s representative in Ethiopia, Bekele Abeyo, highlighted some of the project outcomes. Some of the achievements in the past four years included the release and demonstration of 23 wheat varieties — 18 bread and 5 durum types —, increased access to these improved seeds for 131,132 households and production of 39,750 tons of wheat grain. Extension agents from 54 woredas participated in training in wheat rust management, recommended agronomic packages for the new wheat varieties, and field data collection and management.
Lessons learned
Abeyo explained that the project could reach a high number of farmers thanks to effective teamwork between the various stakeholders, seed support on revolving bases and a decentralized seed production to reach even remote places. Clustering farmers’ plots favored quality seed production.
Participants flagged weak market linkages, particularly for farmers producing durum wheat, , as a bottleneck to address. Workshop participants recommended the establishment of a wheat task force involving the private sector and with continuous support from funders like USAID.
The director general of EIAR, Mandefro Nigusse, said that the issues raised are inputs for further actions, and some will have to be directed to researchers and breeders to come up with additional solutions for the challenges the wheat sector is facing.
Eyasu Abrha, Advisor to the Minister of Agriculture, officially closed the workshop. He noted that the government of Ethiopia is putting effort into ensuring nutritional and food security, and that projects such as this one are important to address critical challenges in the sector. Abrha acknowledged the support of CIMMYT, EIAR and USAID, and called for a continued collaboration with the government of Ethiopia to meet nutritional and food security goals.

Exploring young Africans’ role and engagement in the rural economy

How do young rural Africans engage in the rural economy? How important is farming relative to non-farm activities for the income of young rural Africans? What social, spatial and policy factors explain different patterns of engagement? These questions are at the heart of an interdisciplinary research project, funded by the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), that seeks to provide stronger evidence for policy and for the growing number of programs in Africa that want to “invest in youth.”
One component of the Challenges and Opportunities for Rural Youth Employment in Sub-Saharan Africa project, led by the Institute of Development Studies (IDS), draws on data from the World Bank’s Living Standard Measurement Study – Integrated Surveys on Agriculture (LSMS-ISA) to develop a more detailed picture of young people’s economic activities. These surveys, covering eight countries in sub-Saharan Africa, were conducted at regular intervals and in most cases followed the same households and individuals through time. While the LSMS-ISA are not specialized youth surveys and therefore may not cover all facets of youth livelihoods and wellbeing in detail, they provide valuable knowledge about the evolving patterns of social and economic characteristics of rural African youth and their households.
“LSMS-ISA data are open access, aiming to help national governments and academics analyze the linkages between poverty and agricultural productivity in developing countries,” said Sydney Gourlay, Survey Specialist in the Development Data Group of the World Bank. She explained that LSMS-ISA datasets cover rural and urban livelihoods — including asset ownership, education, farm and non-farm incomes — and contain detailed information on farming practices and productivity. “LSMS-ISA data have untapped potential for valuable youth analyses that could lead to evidence-based youth policy reform,” Gourlay said.
To stimulate greater use of LSMS-ISA data for research on these issues, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), IDS, and the LSMS team of the World Bank organized a workshop for young African social scientists, hosted by CIMMYT in Nairobi from February 4 to February 8, 2019.
Early-career social scientists from Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, Uganda, and Zimbabwe explored the potential of LSMS-ISA data, identified research issues, and developed strategies to create new analyses. The workshop was also a chance to uncover potential areas for increased data collection on youth, as part of the LSMS team’s IFAD-funded initiative “Improving Data on Women and Youth.”
What does that data point represent?
The workshop stressed the importance of getting to know the data before analyzing them. As explained by World Bank senior economist Talip Kilic in The Crowd and the Cloud, “Every data point has a human story.” It is important to decipher what the data points represent and the limits within which they can be interpreted. For instance, the definition of youth differs by country, so comparative studies across countries must harmonize data from different sources.
“Because LSMS-ISA survey locations are georeferenced, it is possible to integrate spatial information from multiple sources and gain new insights about patterns of interest, as well as the drivers associated with such patterns,” said Jordan Chamberlin, spatial economics expert at CIMMYT. “For example, in all countries we’ve examined, the degree of non-farm economic engagement is strongly associated with distance from urban centers.”
Chamberlin noted that georeferencing also has limitations. For instance, to ensure privacy, LSMS-ISA coordinates for households are randomly offset by as much as 5 km. Nonetheless, diverse geospatial data from the datasets — distance to the nearest tarmac road or population density, among other information — may be integrated via the location coordinates.

One key variable to assess farm productivity is harvested area. The LSMS team’s research has revealed high, systematic discrepancies between farmers’ self-assessments of area, GPS measurements, and compass and rope, which is considered the most accurate method. Methodological validation data from Ethiopia, Nigeria, and Tanzania show that on average farmers overestimate the area of plots smaller than 200 m2 by more than 370 percent and underestimate the size of plots larger than 2 hectares by 13 percent, relative to compass and rope measurements. Such errors can skew yield analyses and the accuracy of assessments of national agricultural research programs’ impact.
Several workshop participants expressed interest in using the LSMS dataset for studies on migration, given that it contains information about this variable. In the case of internal migrants — that is, persons who have moved to another area in the same country — LSMS enumerators will find and interview them and these migrants will continue to be included in future rounds of the panel survey. In Malawi, for example, about 93 percent of individuals were tracked between the 2010/11 and the 2013 Integrated Household Surveys. Plot characteristics — such as type of soil, input use, and crop production — include information on the person who manages the plot, allowing for identification and analysis of male and female managed plots.
Following the training, the participants have better articulated their research ideas on youth. Prospective youth studies from the group include how land productivity affects youth opportunities and whether migration induces greater involvement of women in agriculture or raises the cost of rural labor. Better studies will generate more accurate knowledge to help design more effective youth policies.