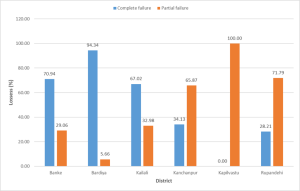
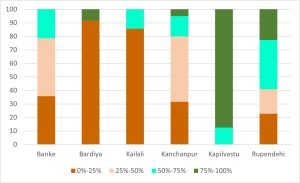
From chemical fertiliser shortages to lack of irrigation, farmers in Nepal have been facing a multitude of human-induced problems every year. The most urgent concern is the climate crisis.
Erratic weather patterns, untimely and uneven rainfall and rapidly rising temperatures have got farmers by the scruff of their necks.
For the farmers, such dramatic climate change manifests in the form of floods, droughts and landslides, directly hitting their agriculture-dependent livelihoods. For the nation as a whole, the climate crisis worsens food insecurity.
The tales of the climate crisis are petrifying. However, not all hope is lost.
Interventions such as climate resilient seeds that are tolerant to extreme climatic stresses like drought, flooding or submersion have been discovered and implemented in phases, according to scientists, to help sustain agricultural productivity.
“Due to the increasing climate change impacts, farmers are facing challenges to produce traditional seeds used during normal situations,” says AbduRahman Beshir Issa, seed systems lead at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Centre, South Asia Office.
“In Nepal, farmers are witnessing both drought stress and excess moisture during the summer cropping season. In the spring season, high temperatures, coupled with drought stress, make it difficult for normal seeds or varieties to grow.”
With an increasing number of mouths to feed, and more pronounced effects of climate change yet to present themselves, climate-resilient seeds can help sustain Nepal’s agricultural productivity, according to crop development experts.
“Climate resilient seeds are crucial for food security. In addition, these crops are nutritionally important,” said Prakash Acharya, a senior crop development officer at the Seed Quality Control Centre. “With changing climate, not all crops and seeds can endure even two-three days of drought or submergence or extreme heat.”
Approximately 3 million hectares of land is cultivated in Nepal, which is 21 percent of the total land area. Rice, maize and wheat constitute more than 80 percent of cereal acreage and production.
The overall cereal yield in Nepal is 2.6 tonnes per hectare, which is far lower than the regional and global average of 4.1 tonnes per hectare, indicating an overall low productivity.
Paddy constitutes the highest production, commanding a 20.8 percent share in the agriculture gross domestic product (AGDP).
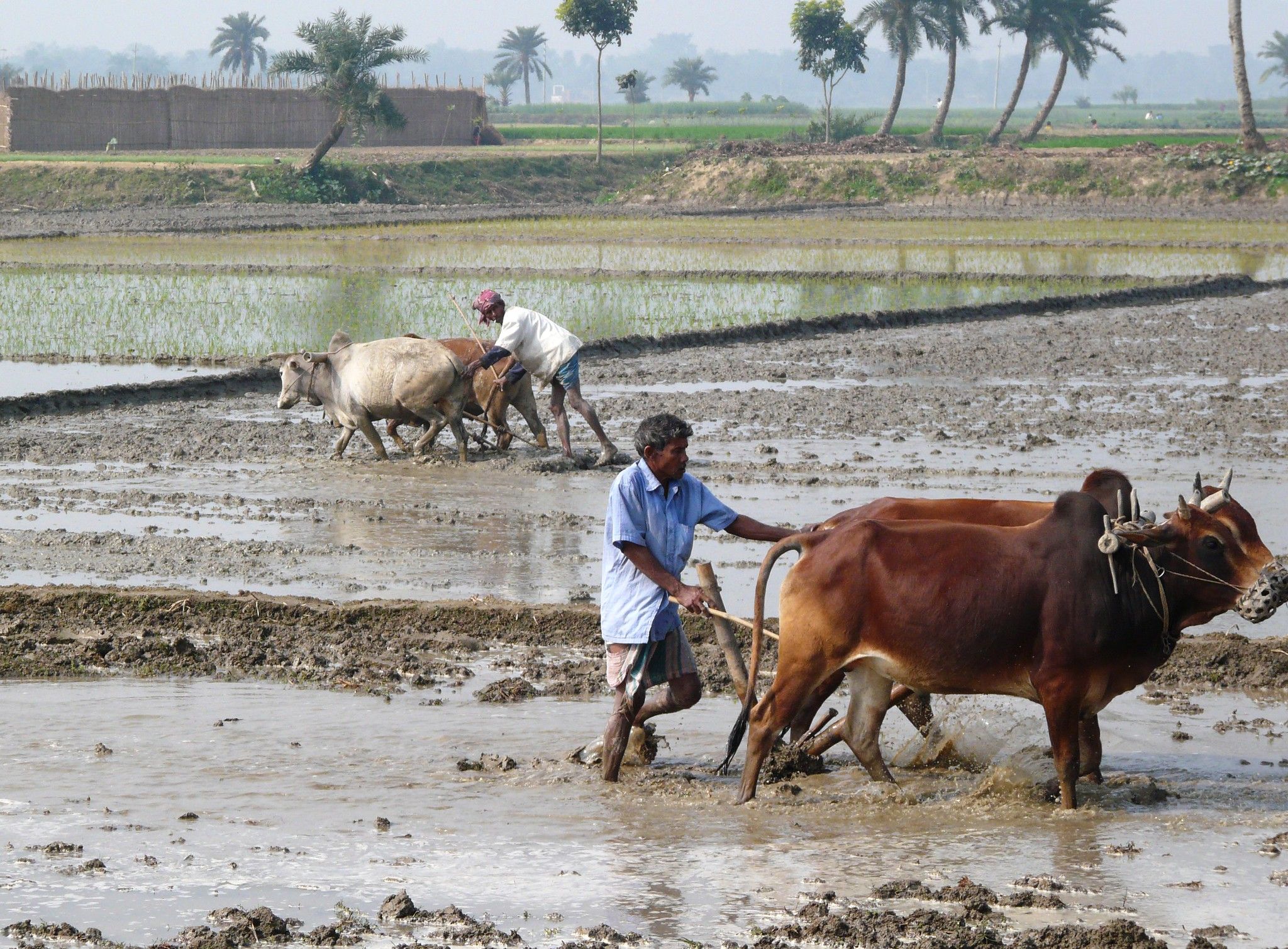
Nepal’s economic wellbeing is intimately linked with the monsoon. Water from the skies is the lifeblood of Nepal’s Rs4.85 trillion economy which is farm-dependent, as nearly two-thirds of the farmlands are rain-fed.
A large part of the country gets nearly 80 percent of its annual rainfall during the four months—June to September.
The production of food grains, mainly rice, depends on the amount and distribution of monsoon rainfall over the country. The monsoon rains also replenish ground water and reservoirs critical for drinking and power generation.
Analysing data from the past 33 years of minimum and maximum temperatures and rainfall, scientists predict drought to be the most important limiting factor for crop production, including paddy.
As paddy is sensitive to drought due to its high water requirement, scientists say there is a need for promoting “climate change-ready rice” that can tolerate drought for up to months.
For instance, research in Nawalparasi in the central Tarai found that the existing paddy varieties would not sustain the yield potential of the present level after 2020.
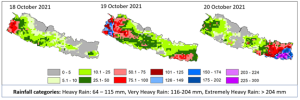
In October 2021, unusual weather patterns led to a torrential downpour lasting three days, causing massive loss of agricultural harvests and physical infrastructure across many parts of Nepal.
In 2020, in East Rukum, continuous rainfall from January to September decreased maize yield. The drought that followed then destroyed the wheat crop. Right after, the heavy rains also wiped out potatoes and maize.
Climate projections further suggest changes in precipitation during the monsoon period (with variations from 14 percent to 40 percent), as well as the increased likelihood of heavy precipitation events.
Experts are concerned that such unpredictable changes in weather patterns will lead to a decline in agricultural productivity, further worsening food insecurity in the region.
“We aren’t food secure right now as well. And with climate change, it is only getting worse. In the long run, the condition of food security in Nepal will be alarming,” says Yamuna Ghale, agriculture and food security policy analyst who is also research director at the Nepal Centre for Contemporary Research.
Around 65 percent of Nepal’s population depends on agriculture for its livelihood, which accounts for 25 percent of the GDP.
With the increasing population and declining agricultural productivity, experts say that Nepal could sooner or later face food insecurity.
“Everyone has the right to food. But the current situation indicates that a food shortage is looming,” said Ghale, who is also an expert at the Food Security Coordination Committee under the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development. “We have to focus on climate-smart alternatives now, beginning with climate-resilient seeds.”
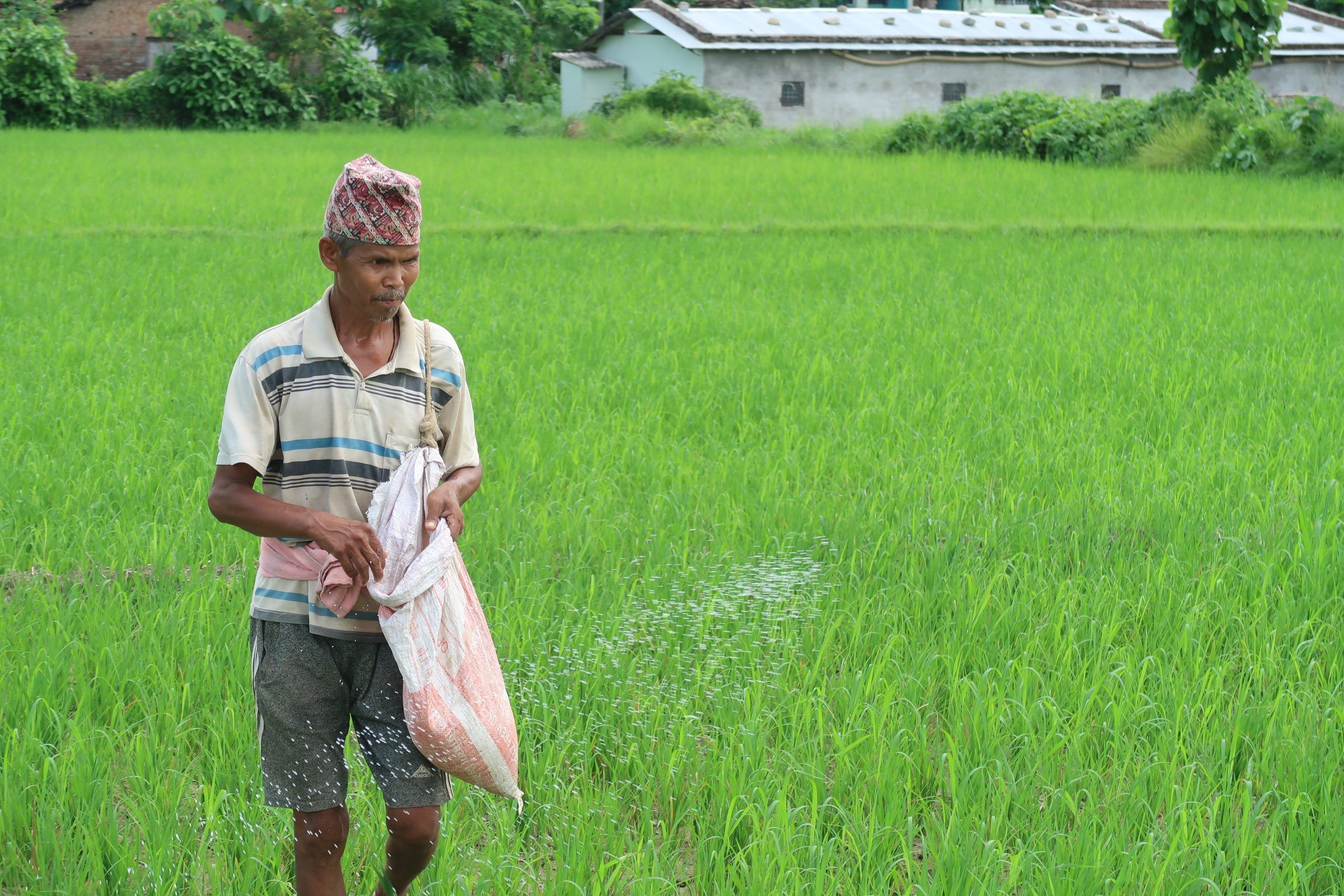
Climate-resilient seeds can withstand extreme conditions brought about by climate change. For example, drought-tolerant seeds can sustain periods of dry conditions, and submergence-tolerant seeds can withstand flood stress.
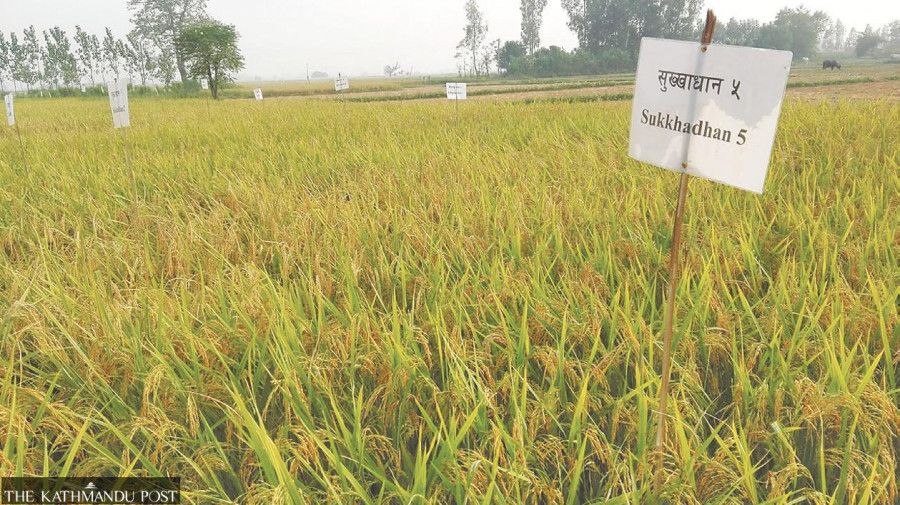
For example, improved varieties like Sukkhaa Dhan 4, Sukkhaa Dhan 5 and Sukkhaa Dhan 6 have an average yield of 4-4.5 tonnes per hectare, and under good irrigation conditions, the output can go up to 5.5 tonnes per hectare on an average.
Sukkhaa 6 has the ability to re-grow even two weeks after submergence.
Swarna Sub-1, Sambha Mansuli Sub-1, Cherang Sub-1, Gangasagar-1, and Gangasagar-2 are submergence-tolerant paddy varieties.
Rice varieties like Bahuguni-1 and Bahuguni-2 are both drought and submergence tolerant.
Similarly, maize varieties that are drought tolerant, such as Deuti, Manakamana-5 and Manakamana-6 are also available. Rampur hybrid-10 and Rampur hybrid-12 are heat-tolerant varieties.
Seto Kaguno is a promising variety of foxtail millet that is drought-tolerant and extremely climate-resilient.
Paddy varieties which possess the “Sub1A” gene remain dormant during submergence, and conserve energy until the floodwaters recede. Paddy plants with the “Sub1A” gene can survive more than two weeks of complete submergence. The plant recovers well from drought by growing new shoots.
“A character is incorporated into existing rice varieties to make them stress-tolerant or climate-resilient. This makes them fare better than traditional crops,” said Acharya.
“In very recent years, because of climate change, we have begun researching drought- and submergence-tolerant seeds,” said Acharya.
These climate-smart varieties, which can survive under stress and retain desirable grain qualities, can create positive impacts on the lives of farmers, scientists say.
Since 1966, Nepal has released and registered 144 varieties of paddy seeds, according to the Agriculture Ministry.
Scientists say that a majority of these stress-tolerant varieties do not demand excess fertilisers or tillage methods.
The Nepal Agriculture Research Council (NARC) is spearheading various projects for producing and popularising drought- and submergence-tolerant seeds.
“Under USAID’s support, Nepal Seed and Fertiliser Project, paddy seeds which are drought and submergence tolerant are being produced and marketed in Nepal in partnership with the government and the private seed companies,” Issa said in an email.
The National Maize Research Programme of NARC has released heat stress-tolerant maize hybrids that can survive at high temperatures compared to traditional varieties.
Likewise, under the National Grain Legumes Research Programme of NARC, field testing of waterlogging-tolerant lentil varieties is being done to come up with varieties that can withstand excess moisture from unusual winter rains during the lentil growing season, according to Issa.
Despite the availability of stress-tolerant seeds, farmers are not much aware of the new varieties and are hesitant to adopt such seeds easily.
Due to lack of awareness, farmers hardly adopt new varieties and they prefer traditional varieties. Local governments too have failed to create awareness.
According to experts, Sukhaa Dhan 3, Samba Mansuli Sub-1 and Cherang Sub-1 are popular among farmers in the Tarai and mid-hills.
However, varieties like Bahuguni-2 have been rejected by farmers because “Nepali consumers prefer non-sticky, fluffy rice as opposed to sticky varieties,” experts say.
Despite being both drought and submergence tolerant, such varieties are not adopted by farmers.
“Farmers are enthusiastic about using new ways and techniques of farming, but local governments have completely ignored investing in agriculture,” said Ujjal Acharya, freelance researcher on climate change and environment economics.
“They have been more focused on building infrastructure, roads, bridges, temples and so on. Food security, climate resilient agriculture, organic farming—all do not fall within the priorities of local governments,” he said.
However, scientists acknowledge that climate resilient crop varieties are only a part of the solution of the bigger climate-resilient agricultural system.
“It is extremely important to develop climate-resilient crop varieties that can withstand extreme weather conditions, but seeds are just one part among the various solutions,” says Issa.
This piece by Aakriti Ghimire, was originally posted on The Kathmandu Post.