funder_partner: Turkish Department of Agricultural Economics and Project Management (TAGEM)
CropSustaiN BNI Wheat Mission
The Novo Nordisk Foundation and CIMMYT have launched the 4-year CropSustaiN initiative to determine the global potential of wheat that is significantly better at using nitrogen, thanks to Biological Nitrification Inhibition (BNI)—and to accelerate breeding and farmer access to BNI wheat varieties.
With a budget of US$ 21 million, CropSustaiN addresses the pressing challenges of nitrogen pollution and inefficient fertilizer use, which contribute to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and ecological degradation. Currently, no other seed or agronomic practice-based solution matches BNI crops’ mitigation impact potential. Growing BNI crops can complement other climate mitigation measures.
The challenge
Agriculture is at the heart of both food and nutrition security and environmental sustainability. The sector contributes ca. 10-12% of global GHG emissions, including 80% of the highly potent nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. Fertilizer use contributes to such N losses, because plants take up about 50%, the remainder being lost. Wheat is the world’s largest ‘crop’ consumer of nitrogen-based fertilizer—a relatively nitrogen-inefficient cereal—at the same time providing affordable calories to billions of resource-poor people and ca. 20% of globally consumed protein. CropSustaiN targets this nexus of productivity and planetary boundary impact by verifying and thus de-risking the needed breeding, agronomic, and social innovations.
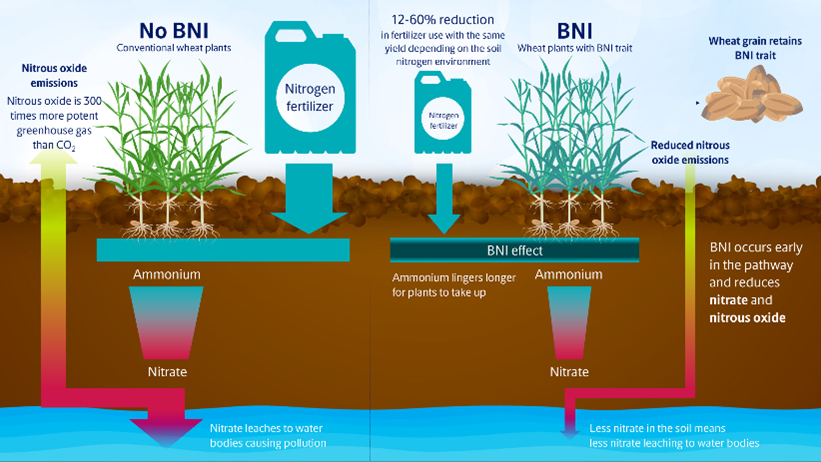
A solution: BNI-wheat
BNI is a natural ability of certain plant species to release metabolites from their roots into the soil. They influence the nitrogen-transforming activity of nitrifying bacteria, slowing down the conversion of ammonium to nitrate in the soil. This preserves soil ammonium levels for a longer time, providing plants with a more sustained source of available nitrogen and making them more nitrogen-use efficient (nitrogen plant use efficiency). As a result, BNI helps reduce the release of N2O gas emissions and nitrate leaching to the surrounding ecosystem.
A research breakthrough in 2021, led by the Japan International Research Center of Agricultural Sciences (JIRCAS) in collaboration with CIMMYT, demonstrated that the BNI trait can be transferred from a wheat wild relative to a modern wheat variety by conventional breeding. BNI wheat can be made available to farmers worldwide.
Growing BNI wheat could reduce nitrogen fertilizer usage by 15-20%, depending on regional farming conditions, without sacrificing yield or quality.
Incorporating BNI into additional crops would reduce usage further. Farmers can get the same yield with less external inputs.
Other BNI-crops
CropSustaiN will work on spring and winter wheats. Rice, maize, barley, and sorghum also have BNI potential. CropSustaiN will build the knowledge base and share with scientists working on other crops and agronomic approaches.
Objectives and outcomes
This high risk, high reward mission aims to:
- Verify the global, on-farm potential of BNI-wheat through field trial research and breeding.
- Build the partnerships and pathways to meet farmer demand for BNI-wheat seeds.
- Work with stakeholders on policy change that enables BNI crops production and markets
Success will be measured by determining nitrogen pollution reduction levels under different soil nitrogen environments and management conditions on research stations, documenting crop performance and safety, breeding for BNI spring and winter wheats for a wide range of geographies, and gauging farmer needs, interest, and future demand.

A collaborative effort
CIMMYT is the lead implementer of Novo Nordisk Foundation’s mission funding. CropSustaiN’s interdisciplinary, intersectoral, systems approach relies on building partnerships and knowledge-sharing within and outside this research initiative. 45+ partners are engaged in CropSustaiN.
The potential GHG emissions reduction from deploying BNI-wheat is estimated to be 0.016-0.19 gigatonnes of CO2-equivalent emissions per year, reducing 0.4-6% of total global N2O emissions annually, plus a lowering of nitrate pollution.
Impact on climate change mitigation and Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
The assumption is that BNI wheat is grown in all major wheat-growing areas and that farmers will practice a behavioral shift towards lower fertilizer use and higher fertilizer use efficiency. That could lead to ca. a reduction of 17 megatons per year globally. This can help nations achieve their NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
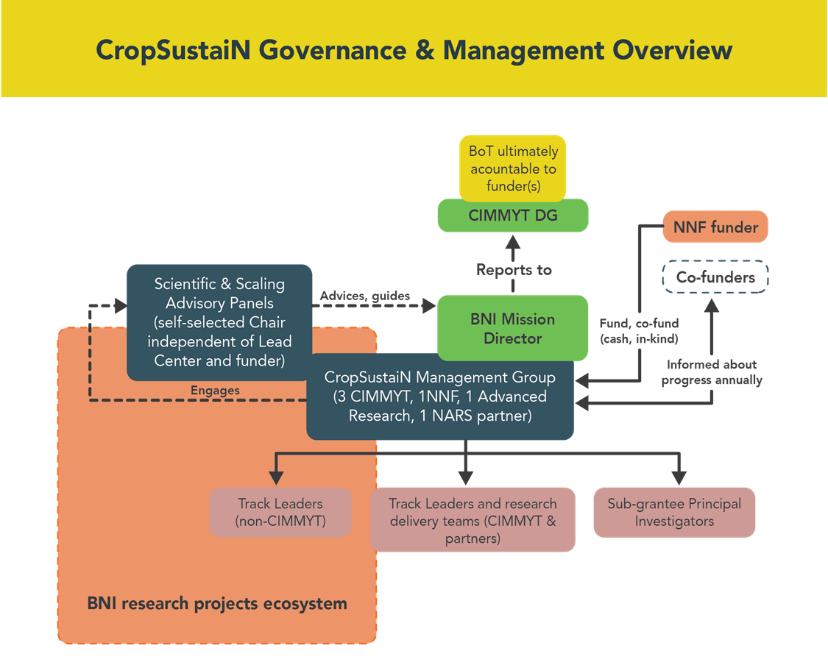
International public goods, governance, and management
CIMMYT and the Foundation are committed to open access and the dissemination of seeds, research data, and results as international public goods. The governance and management model reinforces a commitment to equitable global access to CropSustaiN outputs, emphasized in partnership agreements and management of intellectual property.
Invitation to join the mission
The CropSustaiN initiative is a bold step towards agricultural transformation. You are invited to become a partner. You can contribute to the mission with advice, by sharing methods, research data and results, or becoming a co-founder.
Please contact CropSustaiN Mission Director, Victor Kommerell, at v.kommerell@cgiar.org or Novo Nordisk Foundation’s Senior Scientific Manager, Jeremy A. Daniel, at jad@novo.dk.
Additional reference material
- BNI International Consortium (Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, JIRCAS)
- Nitrification inhibitors: biological and synthetic (German Environment Agency, Umweltbundesamt)
- CropSustaiN: new innovative crops to reduce the nitrogen footprint form agriculture
- Annual Technical Report 2024. CropSustaiN: A new paradigm to reduce the nitrogen footprint from agriculture
- BNI-Wheat Future: towards reducing global nitrogen use in wheat
- CIMMYT Publications Repository
CIMMYT scientists deliver training to improve agriculture in Uzbekistan
Scientists from the Research Institute of Plant Genetic Resources in Uzbekistan (RIPGR) attended training on gene bank management and genetic resources, coordinated by CIMMYT-Türkiye on 13-20 April 2024. Hosted at the Turkish Department of Agricultural Economics and Project Management (TAGEM), the training is supported by the World Bank Group, which is helping Uzbekistan to modernize the country’s agriculture. With one of the highest levels of wheat consumption in Central Asia, the modernization project aims to increase Uzbekistan’s wheat yield and meet demand for the crop.
The course included lectures on status and activity of the Turkish Seed Germplasm Bank (TSGB), policy instruments and international perspectives on plant genetic resources, herbarium techniques, biotechnology studies, and genetic resources. Uzbek scientists also became acquainted with scientific laboratories, visiting the field station in İkizce Gölbaşı and learned about the breeding, pathology, and agronomy activities at the station as well as the collaboration activities between CGIAR Research Centers and TAGEM.
Country-wide expertise
In addition to sessions at CIMMYT’s office in Türkiye, participants also visited the National Gene Bank in Ankara and the National Gene Bank of Izmir.
At the latter location, experts delivered sessions on a range of topics, such as the Plant Diversity and Genetic Resources Program of Türkiye; in vitro and cryopreservation techniques; the conservation, data recording, and documentation of plant genetic resources; conservation and utilization of vegetable genetic resources; conservation studies on mushroom genetic resources; studies on wheat genetic resources and wheat breeding at the international winter wheat breeding program; regional collaboration to combat wheat rust disease in Central and West Asia and North Africa (CWANA); and international winter wheat breeding strategies.
In addition to the seminar sessions, the participants also visited several locations to familiarize themselves with scientific processes in field and laboratory conditions. They visited the field gene banks, guided by Fatih Çağir, who provided brief information about the fruit genetic resources activities of Türkiye. They also visited the plant collection activities and herbarium techniques laboratory, the National Gene Bank, Herbarium, Fungarium & Seed Physiology Laboratory of the Plant Genetics Resources Department & Plant Tissue Center, and the Regional Cereal Rust Research Center.
The importance of the training course for Uzbek scientists is to study the system of rational use, conservation, and management of plant genetic resources of Türkiye and to introduce new innovative knowledge in Uzbekistan. It also consists of discussing aspects related to bilateral cooperation and sustainable development in the field of plant genetic resources as well gene bank management.
The delegation from Uzbekistan, on behalf of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Uzbekistan, and the director of the Research Institute of Plant Genetic Resources, Zafarjon Mashrapovich Ziyaev, expressed their deep gratitude to the organizers and departments for this training course.



