funder_partner: International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
Smallholder Mexican farmers adopt resource-conserving innovations: slowly and in bits
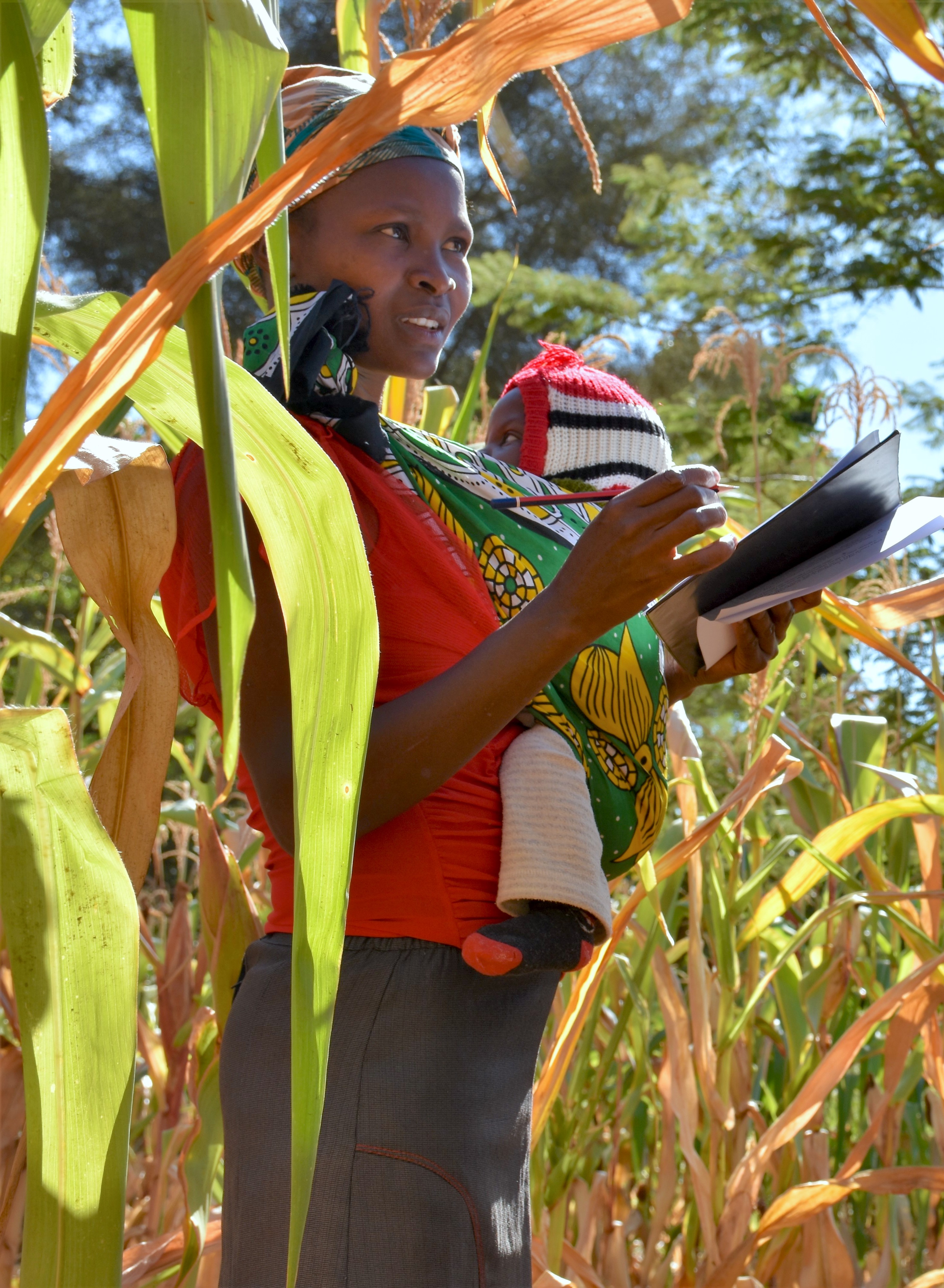
Small-scale farmers in Mexico often adopt conservation agriculture innovations gradually and piecemeal, to fit their diverse agroecological and socioeconomic contexts and risk appetites, according to studies and the on-farm experience of CIMMYT.
Research and extension efforts need to consider this in work with smallholders, said Santiago Lopez-Ridaura, a CIMMYT specialist in agricultural systems and climate change adaptation.
“Farmer practices typically involve heavy tillage before seeding, growing maize as a monocrop, and removing crop residues after harvest for use as forage,” explained Lopez-Ridaura. “Full-on conservation agriculture (CA) is a radical shift, requiring farmers to reduce or eliminate tillage, keep a permanent cover of crop residues on the soil, and diversify the crops they grow. It can support more intense yet environmentally friendly farming, reducing erosion, improving soil fertility and water filtration, boosting crop yields, and saving farmers money. However, it also requires purchasing or contracting specialized sowing implements and fencing fields or agreeing with neighbors to keep livestock from eating all the residues, to name just a few changes.”

Lopez-Ridaura and colleagues published a 2021 analysis involving farmers who grew maize and sorghum and keep a few livestock on small landholdings (less than 4 hectares), with limited mechanization and irrigation, in the state of Guanajuato, Central Mexico.
They found that scenarios involving hybrid maize plus a legume crop with zero-tillage or keeping a residue mulch on the soil provided an average net profit of some US $1,600 (MXP 29,000) per year, in addition to ecological benefits, added forage, and more stable output under climate stress.
“Using a modeling framework from Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) that combines bioeconomic simulation, risk analysis, adoption theory, and impact assessment, we not only confirmed the worth of conservation agriculture but found that disaggregating CA into smaller component packages and including a more productive crop and variety were likely to increase farmers’ adoption, in riskier settings.”
Advancing more sustainable farming in Mexico
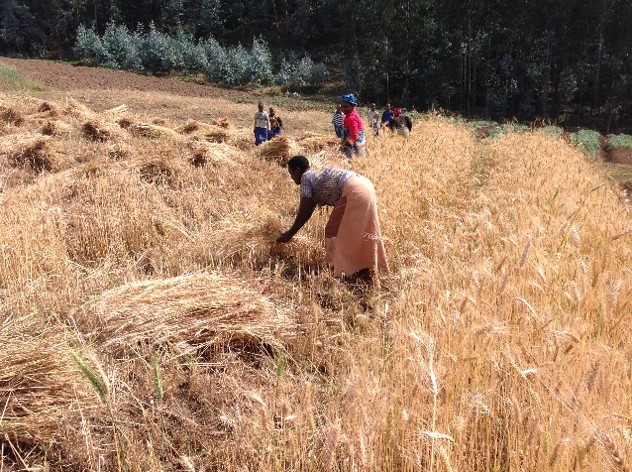
Conservation agriculture can generate substantial economic and environmental benefits under marginal conditions, particularly by enhancing climate change resilience, increasing soil organic matter, and retaining soil moisture. In Central Mexico dryland maize yields rose by 38-48%, after 10 years of implementing CA.
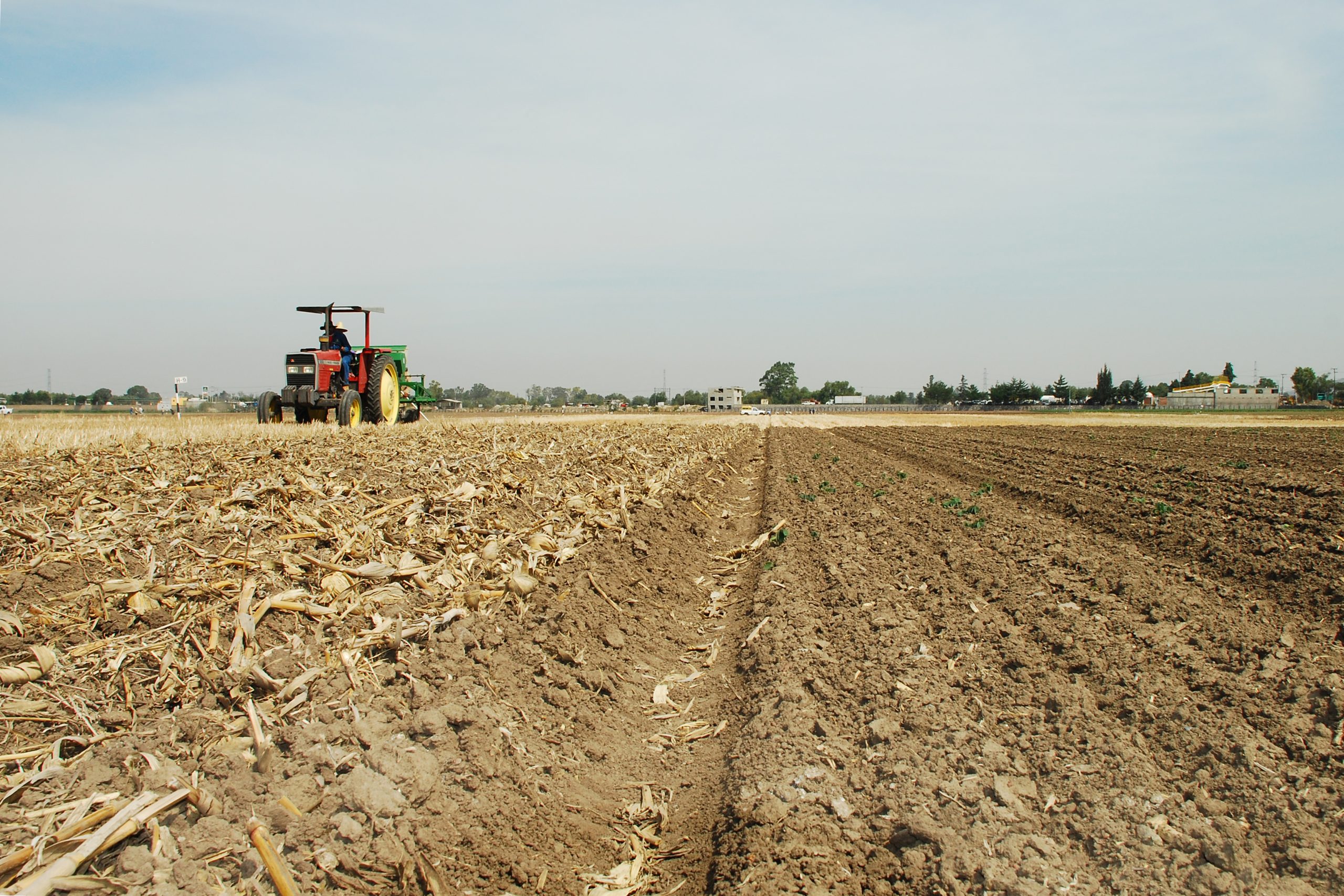

CIMMYT has studied and promoted zero-tillage for maize and other resource-conserving practices in Mexico for more than three decades, but efforts to spread sustainable farming and use of improved maize and wheat varieties redoubled thanks to MasAgro, a research initiative led by the Center and supported by the government of Mexico during 2010-21. Testimonials such abound of Mexican smallholder farmers who have adopted and benefited from CA practices through CIMMYT and national partners’ efforts in MasAgro and other initiatives.
- Looking to lower his farm costs without losing output, wheat and oil crop farmer Alfonso Romo of Valle de Mayo, state of Sonora, began practicing CA in 2010. “We’ve learned a lot and this year (2022) we obtained the same yields as we used to get through conventional practices but, following more sustainable farming methods, with a 30 and even 40% savings in fertilizer.”
- With CA practices he adopted in 2018 through MasAgro, maize farmer Rafael Jacobo of Salvatierra, state of Guanajuato, obtained a good crop despite the late dispersal of irrigation water. Seeing his success and that of other nearby farmers, neighbor Jorge Luis Rosillo began using CA techniques and has noticed yearly improvements in his soil and yields. “I did everything the technicians recommended: keeping the residues on the soil and renewing only the sowing line on soil beds…. There are lots of advantages but above all the (cost) savings in land preparation.”

- Farmers in the Milpa Sustentable project in the Yucatán Peninsula have improved maize yields using locally adapted CA methods, in collaboration with the Autonomous University of Yucatán. Former project participant Viridiana Sei said she particularly liked the respectful knowledge sharing between farmers and project technicians.
- CA practices have allowed more than 320 women farmers in the Mixteca Region of the state of Oaxaca to provide more and better forage for the farm animals they depend on, despite drought conditions, through the Crop and Livestock Conservation Agriculture (CLCA) project supported by the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD). According to farmer María Martínez Cruz, “… it hasn’t rained much and everything’s dry, but our verdant oat crop is allowing us to keep our farm animals fed.”
- With CLCA support and facing Mexico’s increasingly fickle rainy season, farmer Mario Guzmán Manuel of San Francisco Chindúa village in Oaxaca began using CA and says he’ll never go back to the old practices. “We used to do as many as two harrow plowings to break up the soil, but if we leave the residues from the previous crop, they hold in the soil moisture more effectively. People hang onto the old ways, preferring to burn crop residues, but we should understand that this practice only deprives the soil of its capacity to produce.”
SP Poonia
SP Poonia is a Lead Researcher with CIMMYT’s Global Wheat Program and Sustainable Agrifood Systems (SAS) program in India.
Through his work, he aims to feed nutritionally rich and safe food globally through best collective efforts for enhancing farming systems’ productivity with efficient resource use and the adoption of conservation agriculture-based preferred technologies at grassroot level.
Conservation agriculture practices revive saline and sodic soils
In arid and semi-arid regions, soil salinity and sodicity pose challenges to global food security and environmental sustainability. Globally, around 932 million hectares are affected by salinization and alkalinization. Due to growing populations, anthropogenic activities and climate change, the prominence of salt stress in soil is rising both in irrigated and dryland systems.
Scientists from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) employed long-term conservation agriculture practices in different agri-food systems to determine the reclamation potential of sodic soil after continuous cultivation for nine years, with the experiment’s results now published.
Using different conservation agriculture techniques on areas cultivating combinations of maize, wheat, rice and mungbean, the study used soil samples to identify declines in salinity and sodicity after four and nine years of harvesting.
Evidence demonstrates that this approach is a viable route for reducing soil sodicity and improving soil carbon pools. The research also shows that the conservation agriculture-based rice-wheat-mungbean system had more reclamation potential than other studied systems, and therefore could improve soil organic carbon and increase productive crop cultivation.
Read the full publication: Long-term conservation agriculture helps in the reclamation of sodic soils in major agri-food systems
Cover photo: Comparison of crop performance under conservation agriculture and conventional tillage in a sodic soil at Karnal, Haryana, India. (Credit: HS Jat/ICAR-CSSRI)
La Agricultura de Conservación, una oportunidad para afrontar los retos presentes y futuros de la agricultura
At the 8th World Congress on Conservation Agriculture (8WCCA), Martin Kropff, Director General of CIMMYT, argued that “agriculture cannot take a toll on the environment”, praising conservation agriculture for its contribution to building resilience to drought.
Critical reflections on COVID-19
The COVID-19 global health crisis has disrupted food and agricultural systems around the world, affecting food production, supply chains, trade and markets, as well as people’s livelihoods and nutrition. Following an initial assessment in May 2020, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) joined the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and other CGIAR centers to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on Bangladesh’s agri-food system.
The report shares critical reflections and lessons learned, as well as providing detailed quantitative and qualitative information on all disruption pathways and possible recovery strategies.
According to the research team, the major visible impact was the decline of food demand due to the disruption of value chain actors in the food market and income shortages, especially among low- and daily wage-earning populations. This reduced demand lead in turn to reduced prices for agricultural goods, particularly perishable food items like vegetables, livestock and fish products.
Additionally, constraints on the movement of labor led to a disruption in agricultural services, including machinery and extension services, while domestic and international trade disruptions created input shortages and lead to price volatilities which increased production costs. This increase, coupled with reductions in production and output prices, essentially wiped farmer profits.
Building back a better food system
The latest report was launched at the same time as the CGIAR COVID-19 Hub in Bangladesh, which aims to build local resilience to the effects of the pandemic and support government-led recovery initiatives. At a panel discussion presenting the results of the assessment, researchers emphasized the importance of social safety net mechanisms and food demand creation, as well as the need for strong monitoring of food systems to ensure continued availability and affordability, and early detection of any critical issues.
The discussion centered on the need for public access to trustworthy information in order to raise awareness and instill confidence in the food they consume. One key recommendation which emerged is facilitating the digitalization of farming, which looks to re-connect farmers and consumers and build the food system back better. The accelerated development of digital platforms connecting farmers to markets with contactless delivery systems can ensure the safer flow of inputs and outputs while generating a higher share of consumer money for farmers. There is also a need to explore green growth strategies for reducing food waste — the creation and distribution of improved food storage systems, for instance — and circular nutrient initiatives to better utilize food waste as feed and bio manure.
Read the full report “Second rapid assessment of food and nutrition security in the context of COVID-19 in Bangladesh, May – July 2020”
Breaking Ground: Jordan Chamberlin avidly explores the changing landscapes of Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is undergoing important transformations, including climate change, population growth, urbanization and migration flows, and growth in digital technologies. What can we say about the likely development trajectories that African rural economies are on, and the implications for poor farming households? These are central questions for Jordan Chamberlin, an economist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) in Kenya.
Chamberlin’s desk is covered with screens teeming with numbers, complex mathematical equations, lines of code and aerial views of African landscapes. He combines traditional microeconomic analysis with geospatial modelling skills to study some of the ways in which rural transformations are occurring. In this era of big data, he examines the wealth of spatial and socioeconomic datasets to explore the relationships between drivers of change and smallholder welfare, sometimes revealing surprising insights on how rural communities in Africa are evolving.
“Are commercial farms good or bad for neighboring smallholder farmers? Which households can benefit from the rapidly evolving rural land markets in Africa? What drives migration between rural areas? These are some examples of the complex but increasingly important questions that inform how we understand the evolution of agri-food systems in developing countries,” Chamberlin explains. “Fortunately, we also increasingly have access to new data that helps us explore these issues.”
In addition to household survey datasets — the bread and butter of applied social scientists — today’s researchers are also able to draw on an ever-expanding set of geospatial data that helps us to better contextualize the decisions smallholder farmers make.
He cites current work, which seeks to understand input adoption behaviors through better measurement of the biophysical and marketing contexts in which small farms operate. “Evidence suggests that low use rates of inorganic fertilizer by smallholders is due in part to poor expected returns on such investments,” he explains, “which are the result of site-specific agronomic responses, rainfall uncertainty, variation in input-output price ratios, and other factors.”
We are increasingly able to control for such factors explicitly: one of Chamberlin’s recent papers shows the importance of soil organic carbon for location-specific economic returns to fertilizer investments in Tanzania. “After all, farmers do not care about yields for yields’ sake — they make agronomic investments on the basis of how those investments affect their economic welfare.”
Better data and models may help to explain why farmers sometimes do not adopt technologies that we generally think of as profitable. A related strand of his research seeks to better model the spatial distribution of rural market prices.

A spatial economist’s journey on Earth
Ever since his experience as a Peace Corps volunteer in Paraguay, where he worked as a beekeeping specialist, Chamberlin knew he wanted to spend his professional life working with smallholder farmers. He wanted to better understand how rural development takes place, and how policies and investments can help rural households to improve their welfare.
In pursuit of these interests, his academic journey took him from anthropology to quantitative geography, before leading him to agricultural economics. “While my fundamental interest in rural development has not changed, the analytical tools I have preferred have evolved over the years, and my training reflects that evolution,” he says.
Along with his research interests, he has always been passionate about working with institutions within the countries where his research has focused. While working with the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) in Ethiopia, he helped establish a policy-oriented GIS lab at the Ethiopian Development Research Institute (EDRI). Years later, as part of his work with Michigan State University, he served as director of capacity building at the Indaba Agricultural Policy Research Institute (IAPRI), a not-for-profit Zambian research organization. He continues to serve as an external advisor on PhD committees, and considers mentorship a key part of his professional commitments.
He joined CIMMYT at the Ethiopia office in 2015 as spatial economist, part of the foresight and ex ante group of the Socioeconomics program.
As part of his research portfolio, he explores the role of new technologies, data sources and extension methods in the scaling of production technologies. Under the Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale in Africa (TAMASA) project, one area he has been working on is how we may better design location-specific agronomic advisory tools. Working with the Nutrient Expert tool, developed by the African Plant Nutrition Institute (APNI), he and his research team have conducted randomized control trials in Ethiopia and Nigeria to evaluate the impacts of such decision-support tools on farmer investments and productivity outcomes. They found that such tools appear to contribute to productivity gains, although tool design matters — for example, Nigerian farmers were more likely to take up site-specific agronomic recommendations when such information was accompanied by information about uncertainty of financial returns.

Creative rethinking
While Chamberlin’s research portfolio is diverse, one commonality is the drive to use new data and tools to better guide how development resources are allocated.
“Given the scarcity of resources available to governments and their partners, it is important to have sound empirical foundations for the allocation of these resources. Within CIMMYT, I see my role as part of a multidisciplinary team whose goal is to generate such empirical guidance,” he says.
This research also contributes to better design of agricultural development policies.
“Even though many of the research topics that my team addresses are not traditional areas of emphasis within CIMMYT’s socioeconomic work, I hope that we are demonstrating the value of broad thinking about development questions, which are of fundamental importance to one of our core constituencies: the small farmers of the region’s maize and wheat-based farming systems.”
Equal and climate-smart
Sixteen years of consistent learning and practice of climate-smart agriculture, led by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), are paying off for Luganu Mwangonde. Together with her husband Kenson, she has established herself as a successful smallholder farmer in Malawi’s Balaka district. She enjoys the multiple benefits of high yields from diverse crops, surplus to sell at the markets and improved soil quality.
“I started practicing the farming that does not demand too much labor back in 2004,” she explains at her 2.5-acre farm. “Over the years the process has become easier, because I have a full understanding of the benefits of techniques introduced through the project.”
In Malawi’s family farms, women often carry the burden of land preparation and weeding in the fields while juggling household responsibilities, contributing to widen gender differences already prevalent in the community.
Mwangonde observes that learning climate-smart techniques — such as minimum tillage, mulching and planting on flat land surfaces — has given her an advantage over other farmers practicing conventional agriculture.
Better off
At the beginning, like other farmers in the area, Mwangonde thought conservation agriculture and climate-smart techniques required a lot of work, or even hiring extra labor. As she tried this new approach, however, weed pressure in her plot decreased gradually, with the help of mulching and other techniques, and the labor required to maintain the fields reduced significantly. This allowed her to have extra time to add value to her products and sell them on the markets — and to rest.
The best gain for her is knowing that her family always has enough to eat. “I have enough grain to last until the next harvest,” she says. “My husband and I can provide for our seven children and four grandchildren.” During the 2018/19 season, Mwangonde’s family harvested six bags of maize, two bags of pigeon pea and four bags of groundnuts. The surplus from the harvest is reserved for later, when prices are more competitive.
“I am an equal partner in the farming activities. That means I can make decisions about how we work on our plot, distribute crops and apply everything that I have learnt about conservation agriculture,” Mwangonde explains. She has participated in CIMMYT activities where she could share her experiences on climate-smart agriculture with other women. As a lead farmer, she notes, she can confidently inspire the next generation of smallholders because of the empowering knowledge she has acquired.
Out of the 3,538 smallholder farmers from Balaka, Machinga and Zomba districts, up to 2,218 are women smallholder farmers who have successfully adopted climate-smart technologies.
Mwangonde is one of the beneficiaries of the Africa Research in Sustainable Intensification for the Next Generation (Africa RISING) project. She also benefitted from the support of the German Development Agency (GIZ), the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), Total Land Care (TLC) and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).

Pulses, cobs and a healthy soil prove the success of a rural innovator
Mary Twaya is an exemplary farmer in Lemu, a rural drought-prone community in southern Malawi, near Lake Malombe. On her one-hectare farm she grows cotton, maize, and legumes like groundnut and cowpea, which she just picked from her fields. Since agriculture is Twaya’s sole livelihood, it is important for her to get good harvests, so she can support her three children and her elderly mother. She is the only breadwinner since her husband left to sell coffee in the city and never returned.
Agriculture is critically important to the economy and social fabric of Malawi, one of the poorest countries in the World. Up to 84% of Malawian households own or cultivate land. Yet, gender disparities mean that farmland managed by women are on average 25% less productive than men. Constraints include limited access to inputs and opportunities for capacity building in farming.
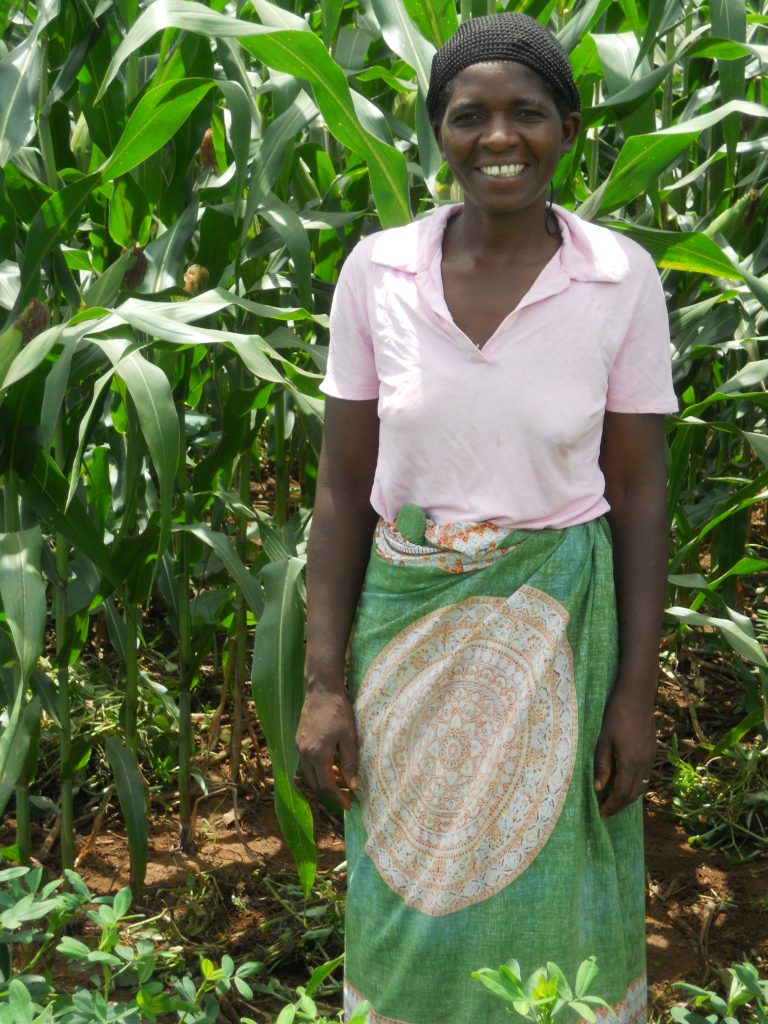

Climate change may worsen this gender gap. Research from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) shows that there are multidimensional benefits for women farmers to switch to climate-smart agriculture practices, such as planting drought-tolerant maize varieties and conservation agriculture with no tillage, soil cover and crop diversification.
Twaya was part of a CIMMYT project that brought climate-smart agriculture practices to smallholder farmers in Malawi, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
She was enthusiastic about adopting climate-smart agriculture practices and conservation agriculture strategies in her plot. “I have always considered myself an active farmer, and when my husband left, I continued in the project around 2007 as part of the six lead ‘mother farmers’ with about 30 more ‘baby farmers’ learning through our field trials,” Twaya explained.
“We worked in Lemu since 2007 with Patrick Stanford, a very active and dedicated extension officer who introduced conservation agriculture to the village,” said CIMMYT agronomist Christian Thierfelder. “Farmers highlighted declining yields. The Lemu community was keen to transform their farming system, from conventional ridge tillage to more sustainable and climate-adapted cropping systems.” This was an ideal breeding ground for new ideas and the development of climate-smart solutions, according to Thierfelder.
Mulching, spacing and legume diversification
Showing her demonstration plot, which covers a third of her farm, Twaya highlights some of the climate-smart practices she adopted.
“Mulching was an entirely new concept to me. I noticed that it helps with moisture retention allowing my crops to survive for longer during the periods of dry spells. Compared to the crops without mulching, one could easily tell the difference in the health of the crop.”
“Thanks to mulching and no tillage, a beneficial soil structure is developed over time that enables more sustained water infiltration into the soil’’, explained Thierfelder. “Another advantage of mulching is that it controls the presence of weeds because the mulch smothers weeds unlike in conventional systems where the soil is bare.”
Research shows that conservation agriculture practices like mulching, combined with direct seeding and improved weed control practices, can reduce an average of 25-45 labor days per hectare for women and children in manual farming systems in eastern Zambia and Malawi. This time could be used more productively at the market, at home or in other income-generating activities.

After 12 years of practicing conservation agriculture, Twaya confirms that she does not spend too much time in the field because she just uproots the weeds with no need for using a hoe. This makes the weeding task less laborious and allows her to spend her time on other chores such as fetching water, washing laundry or cleaning her homestead. “I have time to also go to the village banking and loan savings club to meet with others”.
Adopting optimum plant density, instead of throwing in three seeds in each planting hole was another transformational change. The “Sasakawa spacing” — where maize seeds are planted 25 centimeters apart in rows spaced every 75 centimeters — saves seed and boosts yields, as each plant receives adequate fertilizer, light and water without competing with the other seeds. This practice was introduced in Malawi in the year 2000 by Sasakawa Global.
Twaya pays more attention to the benefits of planting nitrogen-fixing crops alongside her maize, as she learned that “through crop rotation, legumes like pigeon pea improve the nutrition of my soil.” In the past she threw pigeon pea seeds loosely over her maize field and let it grow without any order, but now she practices a “double-up legume system,” where groundnut and pigeon pea are cropped at the same time. Pigeon peas develop slowly, so they can grow for three months without competition after groundnut is harvested. This system was introduced by the Africa RISING project, funded by USAID.

A mother farmer shows the way
Switching to climate-smart agriculture requires a long-term commitment and knowledge. Some farmers may resist to the changes because they initially find it new and tedious but, like Twaya observed, “it may be because they have not given themselves enough time to see the long-term benefits of some of these practices.”
With all these innovations — introduced in her farm over the years with the support of CIMMYT and the Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Water Development of Malawi — Twaya reaped important economic and social benefits.
When Twaya rotates maize and pigeon pea, the maize stalks are healthy and the cobs are big, giving her higher yields. Passing-by neighbors will often exclaim ‘‘Is this your maize?’’ because they can tell it looks much more vigorous and healthier than what they see in other fields.
For the last season, Twaya harvested 15 bags of 50kg of maize from her demo plot, the equivalent of five tons per hectare. In addition to her pigeon pea and groundnut crops, she was able to feed her family well and earned enough to renovate her family home this year.
This new way of managing her fields has gained Twaya more respect and has improved her status in the community.

African leaders rely on science and technology to improve food security
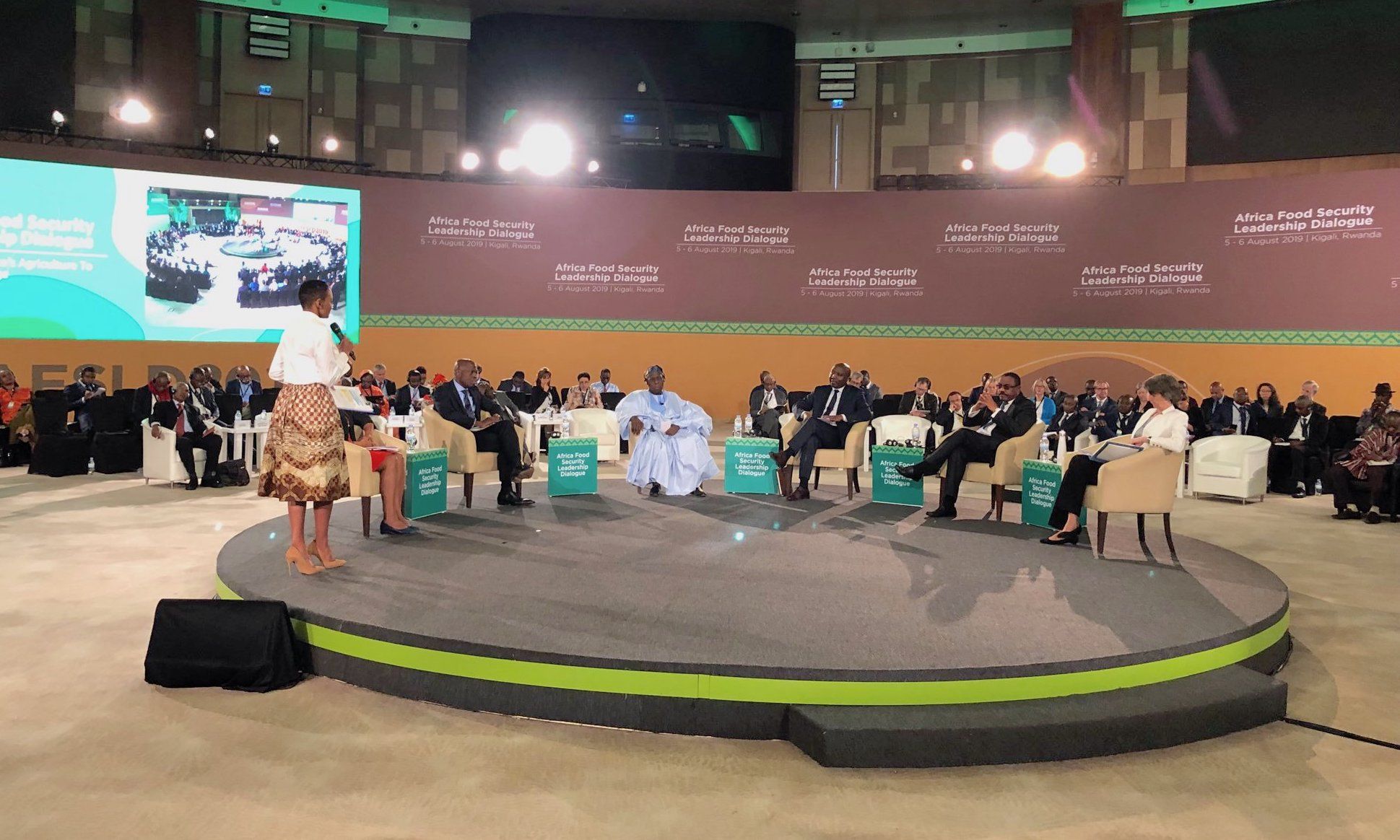
Rural areas in Africa are facing unprecedented challenges. From high levels of rural-urban migration to the need to maintain crop production and food security under the added stress of climate change, rural areas need investment and support. The recent Africa Food Security Leadership Dialogue brought together key regional actors to discuss the current situation as well as ways to catalyze actions and financing to help address Africa’s worsening food security crisis under climate change.
Heads of state, ministers of agriculture and finance, heads of international institutions and regional economic commissions, Nobel laureates, and eminent scientists took part in the dialogue in Kigali, Rwanda, on August 5 and 6, 2019.
This high-level meeting was convened by core partners including the African Union Commission (AUC), the African Development Bank (AfDB), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), and the World Bank.
The Director General of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), Martin Kropff, participated in a session entitled “Leveraging science to end hunger by 2025”, where he discussed the challenges to adapt Africa’s wheat sector to climate change, and what CIMMYT is doing to help. Demand for wheat is growing faster than any other commodity, and sub-Saharan Africa has tremendous potential to increase wheat production. People in Africa consume nearly 47 million tons of wheat a year. However, more than 80% of that — 39 million tons— is imported and used for human consumption, costing the countries billions of dollars. Kropff discussed the great strides CIMMYT has made in supporting wheat production on the continent despite biological challenges such as Ug99, a dangerous strain of wheat rust native to east Africa.
“The potential for wheat production in Africa is tremendous; existing varieties already realize very high yields but poor agronomic practices often result in low yields,” Kropff said. “The challenges we have to tackle together are as much in reshaping policies in favor of wheat and develop the wheat market and surrounding infrastructure. Africa’s environment is friendly for wheat production, but it needs the right supporting policies to develop a sustainable wheat market.”
Kropff highlighted Ethiopia’s case. “Ethiopia has decided to become self-sufficient in wheat by 2025. CIMMYT is already talking to the government and working with the national system to assure the best varieties and technologies will be used. We are ready to do this with every single African nation that is interested in producing quality wheat.”

Climate change is also posing dire threats to maize, a key staple crop in sub-Saharan Africa.
We talked to Cosmos Magorokosho, CIMMYT researcher and project leader of the Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) project, who attended the dialogue, on what CIMMYT can do to better support farmers in Africa’s rural communities.
How can projects such as Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa contribute to protecting food security in Africa in the face of climate change?
Stress-tolerant maize varieties can contribute by cushioning farmers against total crop failures in case of drought and heat stress, among other stresses during the growing season. In addition, stress-tolerant varieties can also yield well under good growing conditions, therefore benefiting farmers both during difficult growing seasons as well as those seasons when conditions are favorable for maize growth.
What can be done to support rural areas and smallholder farmers in Africa to improve food security?
Rural areas and smallholder farmers need support with climate resilient crop varieties, supporting agronomic practices, environment conserving farming practices, labor and drudgery- reducing farm operations, access to affordable finance, and rewarding markets for their produce.
What role can international research organizations such as CIMMYT play in this?
International agricultural research can unlock the potential of small holder farmers through the generation of new appropriate technologies, testing and helping farmers adopt those technologies, refining and fine tuning of new technologies, as well as scaling up and out of farmer-demanded technologies. International agriculture research can influence policy across and within borders, political divide, religion, ecologies, and diversity of farmers.
What would it take for CIMMYT to effectively move science from the lab and package it into solutions that can be disseminated and adopted by majority of small family farms in Africa?
CIMMYT should keep and broaden its engagement with farmers, policy makers, and continue with capacity enhancement of partners to reach scale and bring new cutting-edge smallholder-farmer appropriate technologies to farmers’ fields in the shortest possible timeframe.
Exploring young Africans’ role and engagement in the rural economy

How do young rural Africans engage in the rural economy? How important is farming relative to non-farm activities for the income of young rural Africans? What social, spatial and policy factors explain different patterns of engagement? These questions are at the heart of an interdisciplinary research project, funded by the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), that seeks to provide stronger evidence for policy and for the growing number of programs in Africa that want to “invest in youth.”
One component of the Challenges and Opportunities for Rural Youth Employment in Sub-Saharan Africa project, led by the Institute of Development Studies (IDS), draws on data from the World Bank’s Living Standard Measurement Study – Integrated Surveys on Agriculture (LSMS-ISA) to develop a more detailed picture of young people’s economic activities. These surveys, covering eight countries in sub-Saharan Africa, were conducted at regular intervals and in most cases followed the same households and individuals through time. While the LSMS-ISA are not specialized youth surveys and therefore may not cover all facets of youth livelihoods and wellbeing in detail, they provide valuable knowledge about the evolving patterns of social and economic characteristics of rural African youth and their households.
“LSMS-ISA data are open access, aiming to help national governments and academics analyze the linkages between poverty and agricultural productivity in developing countries,” said Sydney Gourlay, Survey Specialist in the Development Data Group of the World Bank. She explained that LSMS-ISA datasets cover rural and urban livelihoods — including asset ownership, education, farm and non-farm incomes — and contain detailed information on farming practices and productivity. “LSMS-ISA data have untapped potential for valuable youth analyses that could lead to evidence-based youth policy reform,” Gourlay said.
To stimulate greater use of LSMS-ISA data for research on these issues, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), IDS, and the LSMS team of the World Bank organized a workshop for young African social scientists, hosted by CIMMYT in Nairobi from February 4 to February 8, 2019.
Early-career social scientists from Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, Uganda, and Zimbabwe explored the potential of LSMS-ISA data, identified research issues, and developed strategies to create new analyses. The workshop was also a chance to uncover potential areas for increased data collection on youth, as part of the LSMS team’s IFAD-funded initiative “Improving Data on Women and Youth.”
What does that data point represent?
The workshop stressed the importance of getting to know the data before analyzing them. As explained by World Bank senior economist Talip Kilic in The Crowd and the Cloud, “Every data point has a human story.” It is important to decipher what the data points represent and the limits within which they can be interpreted. For instance, the definition of youth differs by country, so comparative studies across countries must harmonize data from different sources.
“Because LSMS-ISA survey locations are georeferenced, it is possible to integrate spatial information from multiple sources and gain new insights about patterns of interest, as well as the drivers associated with such patterns,” said Jordan Chamberlin, spatial economics expert at CIMMYT. “For example, in all countries we’ve examined, the degree of non-farm economic engagement is strongly associated with distance from urban centers.”
Chamberlin noted that georeferencing also has limitations. For instance, to ensure privacy, LSMS-ISA coordinates for households are randomly offset by as much as 5 km. Nonetheless, diverse geospatial data from the datasets — distance to the nearest tarmac road or population density, among other information — may be integrated via the location coordinates.

One key variable to assess farm productivity is harvested area. The LSMS team’s research has revealed high, systematic discrepancies between farmers’ self-assessments of area, GPS measurements, and compass and rope, which is considered the most accurate method. Methodological validation data from Ethiopia, Nigeria, and Tanzania show that on average farmers overestimate the area of plots smaller than 200 m2 by more than 370 percent and underestimate the size of plots larger than 2 hectares by 13 percent, relative to compass and rope measurements. Such errors can skew yield analyses and the accuracy of assessments of national agricultural research programs’ impact.
Several workshop participants expressed interest in using the LSMS dataset for studies on migration, given that it contains information about this variable. In the case of internal migrants — that is, persons who have moved to another area in the same country — LSMS enumerators will find and interview them and these migrants will continue to be included in future rounds of the panel survey. In Malawi, for example, about 93 percent of individuals were tracked between the 2010/11 and the 2013 Integrated Household Surveys. Plot characteristics — such as type of soil, input use, and crop production — include information on the person who manages the plot, allowing for identification and analysis of male and female managed plots.
Following the training, the participants have better articulated their research ideas on youth. Prospective youth studies from the group include how land productivity affects youth opportunities and whether migration induces greater involvement of women in agriculture or raises the cost of rural labor. Better studies will generate more accurate knowledge to help design more effective youth policies.
Smallholder wheat production can cut Africa’s costly grain imports
International scientists are working with regional and national partners in sub-Saharan Africa to catalyze local wheat farming and help meet the rapidly rising regional demand for this crop.
The specialists are focusing on smallholder farmers in Rwanda and Zambia, offering them technical and institutional support, better links to markets, and the sharing of successful practices across regions and borders, as part of the project “Enhancing smallholder wheat productivity through sustainable intensification of wheat-based farming systems in Rwanda and Zambia.”
“Work started in 2016 and has included varietal selection, seed multiplication, and sharing of high-yielding, locally adapted, disease-resistant wheat varieties,” said Moti Jaleta, a socioeconomist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) who leads the project. “Our knowledge and successes in smallholder wheat production and marketing will also be applicable in Madagascar, Mozambique, and Tanzania.”

Maize is by far the number-one food crop in sub-Saharan Africa but wheat consumption is increasing fast, driven in part by rapid urbanization and life-style changes. The region annually imports more than 15 million tons of wheat grain, worth some US$ 3.6 billion at current prices. Only Ethiopia, Kenya, and South Africa grow significant amounts of wheat and they are still net importers of the grain.
“Growing more wheat where it makes sense to do so can help safeguard food security for people who prefer wheat and reduce dependence on risky wheat grain markets,” Jaleta explained. “We’re working in areas where there’s biophysical potential for the crop in rain-fed farming, to increase domestic wheat production and productivity through use of improved varieties and cropping practices.”
In addition to the above, participants are supporting the region’s wheat production in diverse ways:
- Recommendations to fine-tune smallholder wheat value chains and better serve diverse farmers.
- Testing of yield-enhancing farming practices, such as bed-and-furrow systems that facilitate efficient sowing and better weed control.
- Testing and promotion of small-scale mechanization, such as power tillers, to save labor and improve sowing and crop establishment.
- Exploring use of hand-held light sensors to precisely calibrate nitrogen fertilizer dosages throughout the cropping season.
Innocent Habarurema, wheat breeder in the Rwanda Agriculture and Animal Resources Development Board (RAB), cited recent successes in the release of improved, disease resistant wheat varieties, as well as engaging smallholder farmers in seed multiplication and marketing to improve their access to quality seed of those varieties.
“The main challenge in wheat production is the short window of time between wheat seasons, which doesn’t allow complete drying of harvested plants for proper threshing,” Habarurema explained. “Suitable machinery to dry and thresh the wheat would remove the drudgery of hand threshing and improve the quality of the grain, so that it fetches better prices in markets.”

Critical wheat diseases in Zambia include spot blotch, a leaf disease caused by the fungus Cochliobolus sativus, and head blight caused by Fusarium spp., which can leave carcinogenic toxins in the grain, according to Batiseba Tembo, wheat breeder at the Zambian Agricultural Research Institute (ZARI).
“Developing and disseminating varieties resistant to these diseases is a priority in the wheat breeding program at Mt. Makulu Agricultural Research Center,” said Tembo. “We’re also promoting appropriate mechanization for smallholder farmers, to improve wheat production and reduce the enormous drudgery of preparing the soil with hand hoes.”
Participants in the project, which runs to 2020, met at Musanze, in Rwanda’s Northern Province, during February 5-7 to review progress and plan remaining activities, which include more widespread sharing of seed, improved practices, and other useful outcomes.
“There was interest in trying smallholder winter wheat production under irrigation in Zambia to reduce the disease effects normally experienced in rainfed cropping,” said Jaleta, adding that the costs and benefits of irrigation, which is rarely used in the region, need to be assessed.
Project participants may also include in selection trials wheat varieties that have been bred to contain enhanced grain levels of zinc, a key micronutrient missing in the diets of many rural Africa households.
“The project will also push for the fast-track release and seed multiplication of the best varieties, to get them into farmers’ hands as quickly as possible,” Jaleta said.
In addition to CIMMYT, RAB, and ZARI, implementing partners include the Center for Coordination of Agricultural Research and Development for Southern Africa (CCARDESA). Generous funding for the work comes from the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) and the CGIAR Research Program on Wheat.
Scaling to new heights in agriculture
How to scale? This question frequently comes up as projects look to expand and replicate results. In order to sustain enduring impacts for projects after their lifetime, agricultural programs are turning to scaling strategies. These strategies look beyond the numbers that are reached within a project and include sustainability and transformation beyond the project context. Methods and tools exist that help anticipate realistic and responsible scaling pathways.
The Scaling team at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), led by Lennart Woltering, drives the initiative to incorporate scaling principles into existing and developing projects to maximize impact.
Maria Boa recently joined the team as Scaling Coordinator. Last year Boa and Woltering participated in regional meetings on scaling in Morocco, Tunisia and Vietnam, which highlighted the need for better dissemination of information on how to approach scaling, in addition to its benefits.

According to Boa, one of the key messages highlighted throughout these events was that in order for scaling to take hold and be integrated into projects, “…there needs to be a shift in mindset to accept that change is complex and that most projects only address a fraction of the problem.” This is essential in using scaling to effectively support long-term results.
At a workshop in Tunisia organized by ICARDA, IFAD and CIMMYT in November 2018, many participants expressed interest in scaling strategy tools, but were puzzled on how to integrate them into their specific projects. Many determined that they were stuck developing scaling strategies in an outdated framework, or one that strictly focused on using technological innovations. One participant admitted that she was skeptical of scaling perspectives because many did not lie in her field of expertise.
The November 2018 CCAFS SEA Conference on Scaling in Vietnam provided a platform for the sharing and learning of experiences in the scaling world. Some of the key messages from the event included the importance of scaling agricultural innovations taking place in complex systems of agricultural transformation, and the necessity of joint cooperation from all involved stakeholders and their openness to taking on challenges as a way to support sustainable system change.
According to Boa, scaling is a process that heavily relies on strategic collaboration for lasting impact. “Projects often don’t take into account how they’re a part of a larger chain of potential change,” she says.
Already recognized as a sustainable leader within scaling, CIMMYT is looking to strengthen scaling efforts in order to foster a more enduring impact within CIMMYT projects and beyond.

Currently, the Scaling team at CIMMYT is conducting research on the “science of scaling” as it continues to function as a “help desk,” providing support integrating scaling principles in proposals and projects. Its primary role is to consider a project’s scaling needs and guide the development of an informed strategy to leverage efforts and resources. Boa hopes that by integrating responsible scaling approaches early on, projects can better balance the trade-offs associated with change.
Success in scaling is measured by a project’s enduring impact. However, stakeholders need more experience and capacity to see programs through to their end and be willing to monitor them beyond that lifespan. CIMMYT is developing and collecting the tools to support stakeholders with these specific capacities.
Developing a scaling strategy can also bring additional benefits: a discussion about scaling opens the door for raising awareness and fostering actions among different stakeholders towards system change and sustainable impact.
Farmer in Malawi defines true project success

LIWONDE, Malawi (CIMMYT) — Esnath Shaibu, a smallholder farmer from Matandika, southern Malawi was a host farmer with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) for seven years who helped the organization conduct research trials on sustainable agriculture intensification with support from the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
Shaibu’s farm in Matandika, like most other farms in this area, is small and restricted to less than one hectare (ha) per household. Matandika is highly affected by the effects of climate change and a growing population is putting more pressure on dwindling land resources. Farmers have experienced more droughts in recent years which has affected food and nutritional security. Investment into soil conservation and maintaining soil fertility has therefore become critical.
A good proportion of Shaibu’s livelihood is generated from the land of his .3 ha research plot, which evaluates conservation agriculture (CA) systems in the environments and circumstances of Matandika.
The fields in Matandika are on hillsides and need to be seeded with as little disturbance as possible to avoid soil erosion and run-off. Farmers have also understood the value of crop residues and integrate legumes as intercrops in their fields to intensify their farming systems and increase diversification. Optimal plant spacing, early planting and precision application of fertilizers have been other good agriculture practices that farmers perfected in this area.
During the trials, Shaibu practiced a direct seeded CA method, intercropping maize and pigeonpea, and compared the results with conventional tillage practices just planting maize. Yields from Shaibu’s plots were increasingly stable under the CA system, as they proved to be more resilient against in-season dry-spells, drought and unevenly disturbed rainfalls which often fell at great intensity.
Shaibu graduated from the CA program in 2014, but continued to implement the same principles and practices on his own without CIMMYT’s interference or support.
When questioned about his rationale during a field visit in 2017, Shaibu said “we saw something good in it,” and his healthy looking crop spoke for itself.
Shibu’s case demonstrates that technology adoption is only successful if we as development practitioners work ourselves out of a job. He is a true adopter who has continued investing his own resources to produce a good maize crop on a significant proportion of his land by applying CA principles at highest standards. Shaibu has also converted other fields he owns to CA and continues to be an influential advocate in the community for the benefits of CA.











